5G Security Issues Raise Mission Critical Questions & Issues
The type of AKA associated with 5G (via 3GPP- not ITU-R) should ensure that a device and a 5G network can authenticate each other while maintaining a confidential data exchange and keeping the user’s identity and location private. However, the researchers say, in its current state, the AKA could not fulfill those security aims because the requirements it sets forth are not sufficiently precise.
The team of researchers emphasized their belief that the AKA security for 5G would be superior to the AKA used in 3G and 4G network protocols. It still has gaps, though, including one that shows a phone’s presence in the vicinity without disclosing its owner’s identity. Moreover, this vulnerable version of the AKA could result in a person getting wrongfully charged for a third party’s usage of the 5G network.
The published paper about these findings recommends fixes. They include explicitly requiring intended security properties currently missing from the AKA and modifying the key-confirmation component so it offers a provably secure solution. Overall, the researchers say the AKA does not adequately protect privacy from active attackers but admit remedying that problem would not be straightforward.
In an attempt to implement more security in the AKA, the researchers have reached out to 3GPP and hope to engage in a joint effort to improve the protocol before 5G’s widespread rollout. Also, the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security, or ENISA, released a different report warning that identified flaws with signaling protocols on the 2G, 3G and 4G networks could appear in the 5G network.
Ericsson show there could be 3.5 billion Internet of Things units by 2023 — equalling five times the number of connected devices used now. Additionally, the company forecasts that 5G networks will spur the growth of Internet-connected devices.
People became familiar with the security weaknesses of IoT devices when cybercriminals first targeted them with distributed denial of service attacks several years ago.
An insecure 5G network sets the stage for increasingly widespread attacks due to 5G’s high-speed bandwidth, which increases the available attack points. It’s not difficult to imagine a business using IoT sensors within a factory setting and getting shut down due to a DDoS attack.
Chip architecture company Arm is working on a software stack that would let IoT devices run with SIM card chips, thereby making them similar to smartphones with mobile data plans. Then, it would not be necessary to connect IoT devices via Wi-Fi. However, hackers can attack SIM cards and make them unusable. They can also distribute malware through text messages during SIM card attacks.
It’s too soon to say whether hackers will exploit SIM vulnerabilities in IoT devices that may eventually include them, but the possibility is there. In any case, it’s evident that the opportunities 5G offers could spur hackers’ efforts to launch increasingly devastating attacks using methods people already know, as well as wholly new techniques.
“5G doesn’t necessarily changes the risk factors we have today,” said Tom Lally, vice president of sales for data storage and management company, DataSpan, Inc. “But it is going to exponentially increase the threat vectors and opportunities for attackers to exploit.”
“5G is going to enable businesses to connect more and more devices at higher speeds so more data can be consumed at much faster rates,” he says. “Thus, increasing the capacity and data flows in and out of the datacenter. So if you have more devices connected and more traffic flows, then you have more potential vulnerabilities derived from the increase in new vectors.”
“It’s going to become more important than ever to have proper monitoring, be able to identify attacks once inside, and have the capability to respond effectively, to remediate any potential issue,” says Lally. “At the end of the day, you’re still looking for anomalies, you’re just going to have more. So the ability to swiftly identify and respond will be critical to minimizing risk.”
It is both valuable and admirable that researchers endeavored to bring the security concerns mentioned here to light. However, it’s crucial for people to remember that 5G is a pioneering technology. Besides these potential problems, there are inevitable risks not anticipated yet in these early stages.
Conversely, there are unforeseen benefits that are more specific than the advantages so often highlighted in media coverage of the 5G network. For example, some of the inventions people rely on soon might not have been possible to develop on older networks. In order to enjoy all those advantages to the fullest, it’s necessary to continually prioritize 5G network security.
References:
UPDATE:
The real work on 5G security is being done by 3GPP with technical specification (TS) 33.501 Security architecture and procedures for 5G system being the foundation 5G security document. That 3GPP spec was first published in Release 16, but the latest version dated 16 December 2020 is targeted at Release 17. You can see all versions of that spec here.
3GPP’s 5G security architecture is designed to integrate 4G equivalent security. In addition, the reassessment of other security threats such as attacks on radio interfaces, signaling plane, user plane, masquerading, privacy, replay, bidding down, man-in-the-middle and inter-operator security issues have also been taken in to account for 5G and will lead to further security enhancements.
Another important 3GPP Security spec is TS 33.51 Security Assurance Specification (SCAS) for the next generation Node B (gNodeB) network product class, which is part of Release 16. The latest version is dated Sept 25, 2020.
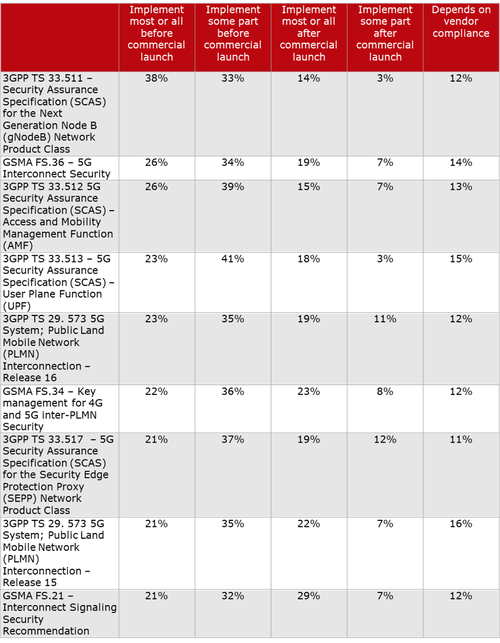
Here’s a chart on 3GPP and GSMA specs on 5G Security, courtesy of Heavy Reading: