Month: April 2023
Safaricom Increases 5G Coverage to 21 Counties in Kenya; Partners with Huawei for 5G Centers in Nairobi
Safaricom, the leading telecommunications company in Kenya, has expanded its 5G coverage to 28 towns across 21 counties in the country. With this expansion, Safaricom’s customers in 5G-covered areas can enjoy faster internet connectivity on the move, in their homes and businesses. Also, Safaricom has introduced 5G data bundles that offer personalized options based on usage to enable the over 400,000 customers using 5G smartphones to browse at ultra-fast speeds of 400 Mbps to 700 Mbps. These customers can get the personalized 5G bundles via Tunukiwa on MySafaricom App, Safaricom.com, and USSD *444# or *544#. Additionally, home and enterprise customers in 5G zones can enjoy the network through 5G Wi-Fi. Customers can visit the website to check available 5G zones or get 5G Wi-Fi.
In a statement, Safaricom said, “As a digital lifestyle enabler, we are excited about a 5G future, which makes it possible to close the digital divide in underserved communities, provide access to critical services such as healthcare or spur economic growth by connecting small businesses to new opportunities. By increasing 5G coverage, we are enhancing Kenya’s best internet network and empowering our customers to start exploring the possibilities of 5G.”
Safaricom became the first service provider in Kenya to launch 5G in October 2022. Since then, its coverage has increased from 11 towns to 28 towns across 21 counties, including Nairobi, Kiambu, Mombasa, Kisumu, Uasin Gishu, Nakuru, Garissa, Kajiado, Kisii, Machakos, Kakamega, Kilifi, Siaya, Kericho, Kwale, Laikipia, Marsabit, Meru, Narok, Nyeri, and Vihiga Counties. To help Kenyans experience how 5G can transform homes and businesses, Safaricom has partnered with Huawei to set up three 5G experience centers in Nairobi. These centers, located in Safaricom’s Village Market, The Hub and Buruburu Shops, contain virtual reality gaming zones, showcase smart capabilities for homes and enterprises, and speed-testing booths.
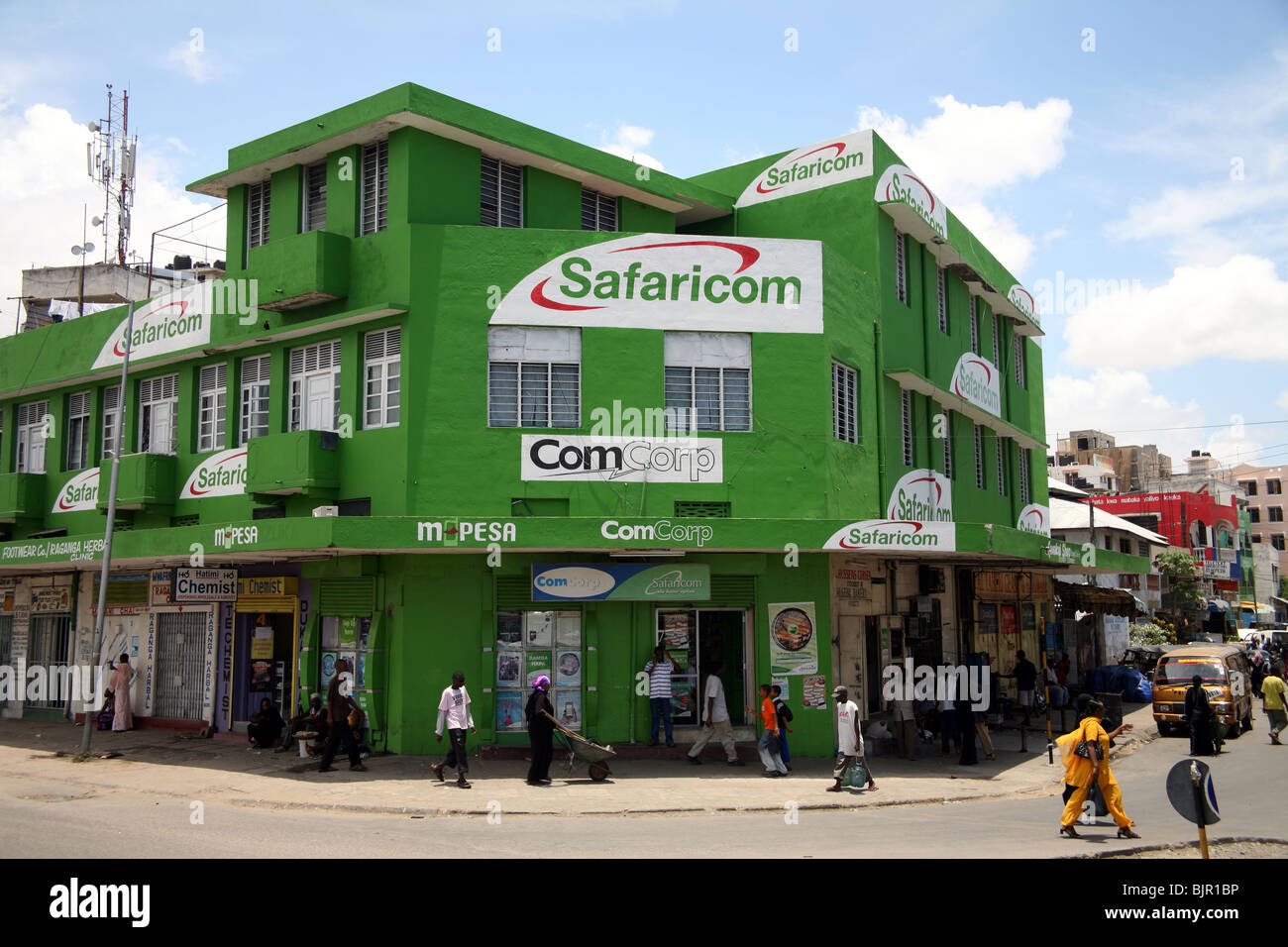

In March, Safaricom announced it had partnered with Huawei to unveil three 5G experiential centers across Nairobi, Kenya. The three 5G centers, located in Safaricom’s Village Market, The Hub and Buruburu Shops, will showcase the superfast speeds and cutting-edge devices that come with 5G connectivity. 5G customers will experience virtual reality gaming zones, showcases of smart-capabilities for homes and enterprises, and speed-testing booths.
“We are excited to unveil these experience centers, which will enable Kenyans to discover the power of 5G firsthand. As a digital lifestyle enabler, we are further enhancing Kenya’s best internet network, and empowering our customers to start exploring the limitless possibilities that 5G provides,” said Peter Ndegwa, CEO, Safaricom PLC.
“As a long-time partner with Safaricom, we are delighted to collaborate on these experience centres. They show how 5G can be transformative in connecting homes and small businesses to drive economic growth and social development, unlocking the digital economy,” said Sheng Kaifu, Deputy CEO, Huawei Kenya.Over the years, Safaricom has consistently invested in its network, with its 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G in aggregate covering 97% of Kenya’s population, while its fibre network has passed more than 450,000 homes and businesses.
References:
6th Digital China Summit: China to expand its 5G network; 6G R&D via the IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group
China will ratchet up resources to advance the construction of its 5G network, expand the application of 5G technology in various fields, and promote the research and development of 6G, officials and experts said at the 6th Digital China Summit, which ended on Friday in Fuzhou, Fujian province.
“China has built the world’s largest 5G network with the most advanced technologies. The number of the country’s 5G base stations had exceeded 2.64 million by the end of March this year,” said Zhao Ce, deputy head of the information and telecommunications development department at the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
Zhao said the ministry will make more efforts to bolster the building of the 5G network in an orderly manner and accelerate its industrial applications, push forward the R&D of 6G, and strengthen international exchange and communication in 5G-related technology, standards and application. 5G wireless technology has been used in 52 of the 97 major economic categories, with large-scale application expanded to mining, ports and electricity, he said. Moreover, China has already established the IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group, a flagship platform in China promoting 6G and international cooperation.
As 5G technology serves as a critical foundation supporting the development of artificial intelligence, big data and cloud computing, heightened efforts should be made to explore application scenarios of 5G and empower the transformation of traditional industries, said Zhang Wang, deputy head of the informatization development bureau of the Cyberspace Administration of China.
China has recently unveiled a plan for the overall layout of the country’s digital development, vowing to make important progress in the construction of a digital China by 2025, with effective interconnectivity in digital infrastructure, a significantly improved digital economy, and major breakthroughs achieved in digital technology innovation.
Cao Ming, president of the wireless product line at Huawei Technologies, said China is taking the lead in 5G development across the globe, and 5G is expected to play a bigger role in bolstering digitalization in a wide range of sectors covering intelligent connected vehicles and intelligent transportation.

6G is the upcoming sixth-generation cellular network technology that is currently in early development. One of the goals of 6G cellular technology is not just to deliver basic content faster to smartphones, like streaming video, but to create a cellular network capable of supporting real-time augmented reality, virtual reality, and a future Internet of Things (IoT) model where small smart devices are a ubiquitous presence in and outside of our homes.
When reading anything about 6G, especially the breathless and hype-laden announcements from telecommunications companies that emphasize how 6G will usher in the metaverse, a fusion of our physical and virtual lives, and so on, you should keep the “early” part of early development in mind.
Currently, there are no established 6G specifications or standards, let alone deployed 6G networks or devices. Even the most basic aspects of 6G development, like which specific frequencies the next generation cellular technology will rely on, are still being ironed out along with technical challenges like energy and heat dissipation demands of advanced 6G devices.
That said, we do have some idea what 6G will look like. Current cellular technology operates in the Megahertz (MHz) and the lower Gigahertz (GHz) frequency ranges. The portion of the radio spectrum under consideration and testing for 6G includes frequencies in the 30-300 Ghz range—also known as millimeter waves (mmWave) or Extremely High Frequency (EHF) radio—and the Terahertz (THz) frequency up to 3000 Ghz. The use of these frequencies will allow for data transmission well beyond the bandwidth capacity of current cellular technology.
In December of 2022, Qualcomm released a 6G development plan with 2030 as a projected rollout date for 6G tech. Ericsson’s 6G messaging echoes the early 2030s timeframe too, as do various interviews with telecom executives.
5G was first introduced in 2019. Four years later, there are still millions of cellular subscribers using 4G, and 5G is yet to have a fully realized coast-to-coast rollout. GSMA’s authoritative 2023 Mobile Economy report, for instance, indicates North American adoption rate of 5G is only 39%, with more than half of cellular subscribers still using 4G. By their projections, the North American 5G adoption rate will be 91% by 2030, meaning by the time 6G potentially arrives, there will still be 4G subscribers out there.
References:
China to introduce early 6G applications by 2025- way in advance of 3GPP specs & ITU-R standards
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
LightCounting: Sales of Optical Transceivers will decline in 2023
|
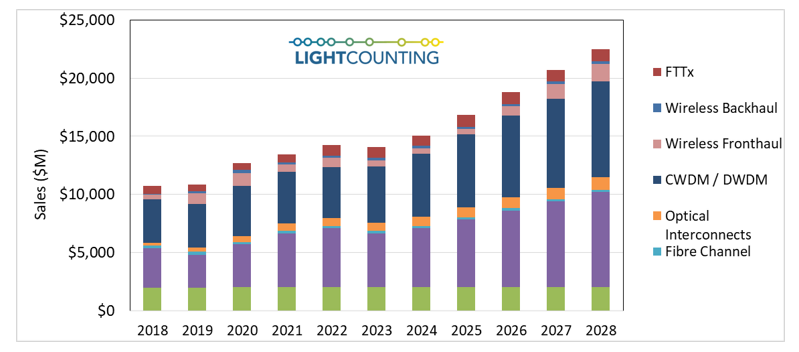
The optical communications industry entered 2020 with very strong momentum. Demand for DWDM, Ethernet, and wireless fronthaul connectivity surged at the end of 2019, and major shifts to work-at-home and school-at-home in 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic created even stronger demand for faster, more ubiquitous, higher reliability networks. While supply chain disruptions continued, the industry was able to largely overcome them, and the market for optical components and modules saw strong growth in 2020-2022, as shown the figure in below.
We believe the optical transceiver market will be down slightly (1% or so) in 2023 due to declines in the sales of Ethernet and wireless fronthaul transceivers of 10% and 30%, respectively, offsetting growth in all other market segments in 2023.
|
 |
|
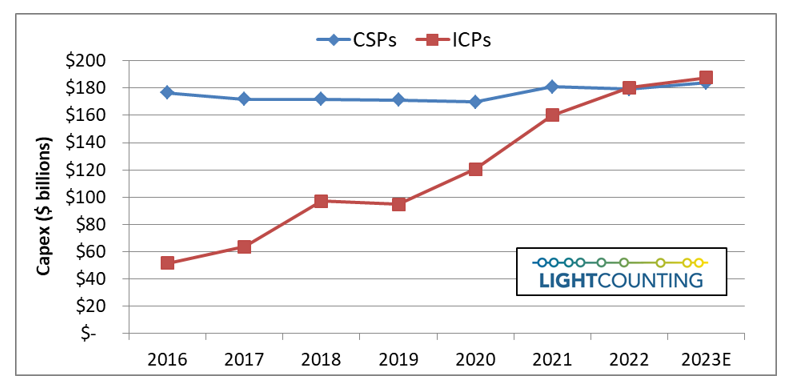
Amazon and other cloud companies plan to moderate their investments in 2023 and beyond, even if there is no economic recession. The Cloud companies benefited from the COVID-19 pandemic, but they were forced to reassess their plans at the end of 2022, as growth slowed. Their capex almost doubled between 2019 and 2022 but future investments will be more conservative. We expect the Top 15 ICP’s capex to be up only 4% in 2023, essentially flat, after several years of double-digit growth. Investments in AI infrastructure will remain a priority.
Telecom service providers plan to reduce their capex in 2023 also but they will continue to upgrade access networks. Connecting business and consumers to the Cloud is a priority now. Their customers are willing to pay more for secure and low-latency broadband services and it is a great opportunity for revenue growth. Telecom service providers plan to digitize their operations and offer Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) to an increasing number of end users, not just a few of their largest customers.
|
 |
|
Despite a slower than expected growth in revenues of the leading Cloud companies, AI infrastructure remains a priority. This new focus will sustain the market for high bandwidth and low latency Ethernet and InfiniBand switches in the next 5 years. We also expect the deployments of optical circuit switches in AI clusters to expand beyond Google’s datacenters.
Other notable forecast changes include increased sales of 50G and 100G fronthaul transceivers in the 2026-2028 timeframe, as we believe they will be needed for early 6G deployments, and increased sales of PON optics as deployments of FTTx are increasing due to government stimulus in the US and elsewhere.
LightCounting’s Market Forecast Report presents our forecast for optical transceivers used in the telecom and datacom sectors, and includes chapters reviewing the health and spending outlook for both CSPs and ICPs, as well as explanations of forecast drivers and assumptions for each of the six product segments covered: Ethernet, WDM, Fronthaul, Backhaul, FTTX, and Optical Interconnects. The accompanying Excel database includes unit and sales forecasts for over 200 product categories.
More information on the report is available at ttps://www.lightcounting.com
|
Omdia Surveys: PON will be a key part of network operator energy reduction strategies
Omdia (owned by Informa) surveys have found a “very high” number of telcos regarded PON as a key part of their energy savings programs. Omdia’s chief analyst Julie Kunstler said PON technology is fiber-asset efficient, easy to upgrade, and highly secure.
Speaking at a Light Reading webinar Thursday, Kunstler said another large cohort of network operator execs said they believed PON would play some role in their energy reduction strategies. “PON is energy efficient and this is definitely gaining attention.” Kunstler said “a very strong movement” by operators was underway toward next gen PON, in particular XGS PON. “But perhaps more importantly, PONs are also supporting other types of customers and applications.” She also noted PON technology was fiber-asset efficient, easy to upgrade, highly secure and allowed operators to choose when to upgrade. But she cautioned that in many telcos PON faced organizational obstacles because of the belief that it was for consumer services only and because of the silos between residential and business.
Anuradha Udunuwara, a senior enterprise solutions architect at Sri Lanka Telecom, said energy costs had become a bigger concern in the past 12 months following sharp hikes in power tariffs. He agreed that PON “definitely has an advantage… it is passive, so there is no energy consumption there.”
Udunuwara described PON as an “architectural option” that could support FTTX deployment. He said it was a myth about PON that it was for FTTH only. “It’s not confined to any of the variations of FTTX.” He expected that in the long run services would converge on to a single access technology.
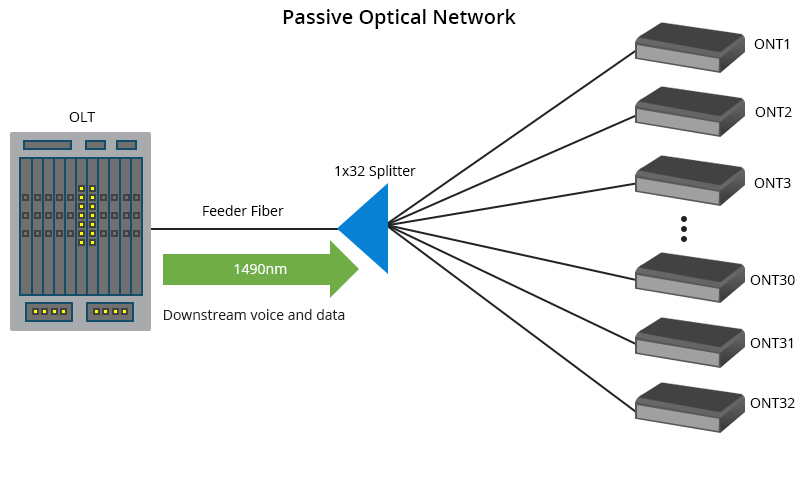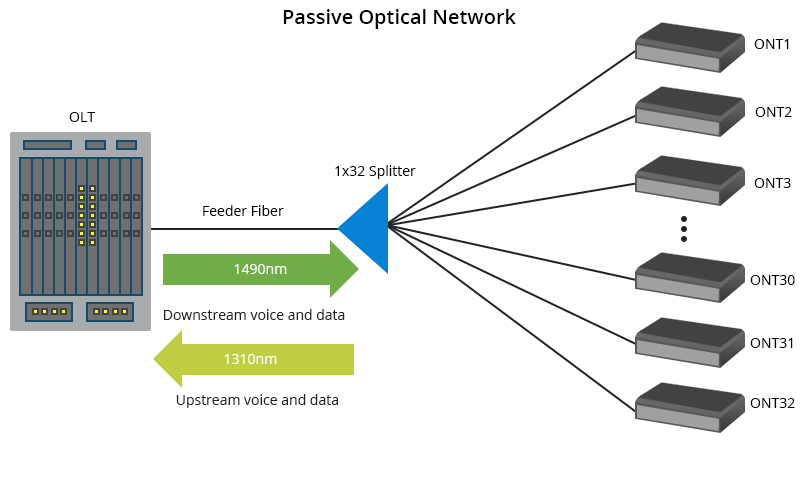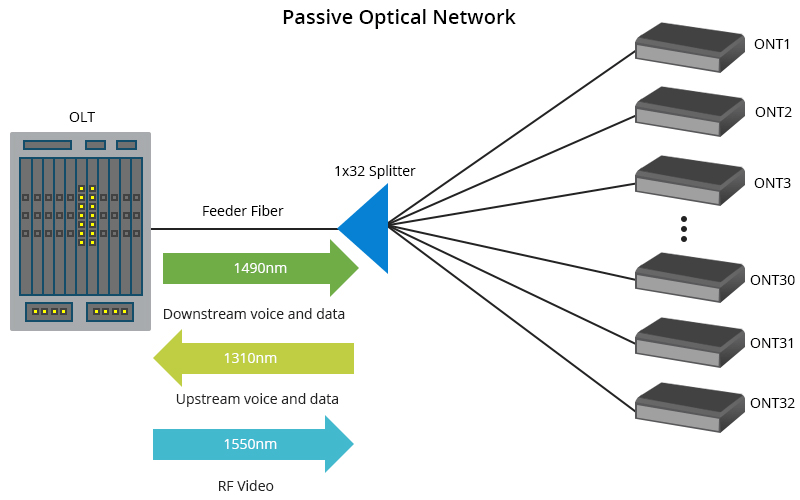
“Oftentimes, sales and marketing teams don’t feel comfortable about PON, simply because they don’t understand it,” Kunstler said. “Many believe its point to multipoint topology is for residential only and that it’s simply best effort and there’s no technical ability to support enterprise services.”
“A lot of education is needed within some operators to explain to the sales and marketing team that PON is not just best effort and that you can actually commit to rates,” she pointed out.
“Not all enterprises need point to point. They don’t all need their own dedicated fiber, and many of them really don’t want to have to pay for dedicated fiber.”
Kunstler said selling business services over PON increased the ROI over that access infrastructure. “With 10G PON, you can easily support one gig symmetrical, two gig symmetrical five gig symmetrical and so forth, and 50 GPON, which will be here within a couple of years, can even support more bandwidth.
By using that optical distribution network for more than just residential, operators were already moving to a converged access approach. “You have more revenues over a single access network. You have a single network to upgrade. You have improved optics and you have improved energy savings.”
References:
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
AT&T to deploy FTTP network based on XGS-PON in Amarillo, TX
ZTE PON ONT obtains EasyMesh R3 certification from WiFi Alliance
Dell’Oro: PONs boost Broadband Access; Total Telecom & Enterprise Network Equipment Markets
AST SpaceMobile completes 1st ever LEO satellite voice call using AT&T spectrum and unmodified Samsung and Apple smartphones
Satellite communications firm AST SpaceMobile, with the help of AT&T, has announced the first two-way audio call using satellites with standard smartphones as the end points. The initial call was placed using AT&T’s cellular network in Midland, Texas, to mobile carrier Rakuten in Japan using AST SpaceMobile’s BlueWalker 3 satellite in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), a breakthrough that could improve global cellular connectivity in remote regions without access to cell towers.
AST SpaceMobile claims this is “the first time anyone has ever achieved a direct voice connection from space to everyday cellular devices.” The phone call was made from an unmodified Samsung Galaxy S22 in Midland, Texas, using mobile spectrum from AT&T and connected to an iPhone used by Japanese tech giant Rakuten. Engineers from AT&T, Rakuten, and UK-based telecommunications company Vodafone assisted with the testing.
The use of satellites could be a significant step toward increasing cellular access not only in the U.S., where large areas of the country struggle with service, but in developing countries too. Typically a mobile phone call requires nearby cell towers to provide service. Many areas across the United States, such as rural communities and national parks, are “dead zones” — yes, just like the eerie early 2000s Verizon commercials warned. The same technology could be a great solution to the same issues in developing countries. Instead, satellites could act as a sort of space-based network of cell towers — with AST SpaceMobile claiming it’s “building the first and only space-based cellular broadband network.”
AT&T aims to use satellites to provide global cellular broadband from 2G to 5G. “Achieving what many once considered impossible, we have reached the most significant milestone to date in our quest to deliver global cellular broadband from space,” Abel Avellan, CEO and chairman of AST SpaceMobile, said in a press release. “While we take a moment to celebrate this tremendous accomplishment, we remain focused on the path ahead and pivotal next steps that get us closer to our goal of transforming the way the world connects.”
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24612767/2022_11_BlueWalker_3_test_satellite_unfolded_3D.original.jpg)
Image Credit: Image: AST SpaceMobile
Margherita Della Valle, Vodafone Group Chief Executive, said: “Today, we have taken another major step in mobile communications. 30 years after Vodafone sent the world’s first text message, we supported AST SpaceMobile in successfully making the first ever direct-to-smartphone test call using satellite communications. This is just the start. As a lead investor in AST SpaceMobile, we will continue to break technological boundaries by connecting many more millions of people across the planet when the service becomes commercially available.”
Mickey Mikitani, Rakuten Chairman & CEO, commented: “It was a unique thrill and honor to have the Rakuten team talk with Abel in a world-first direct-to-satellite experience. Congratulations to AST SpaceMobile and all of its strategic collaborators on this groundbreaking event. As technological advancements like space connectivity become possible with pioneers like AST SpaceMobile, Rakuten will also progress even further along the road to democratizing connectivity for all.”
Chris Sambar, Head of AT&T Network, said: “AT&T’s heritage began with the birth of the telephone 147 years ago and has continued with many other firsts including: trans-continental call, overseas call, call from the moon, and partnering to deliver the only network built with and for America’s first responders. We connect people to greater possibility, and this important milestone with AST SpaceMobile is a big step and we can’t wait to see what’s next in our space-based journey.”
It’s unclear whether satellite access would come at an extra cost. In AT&T’s original AST SpaceMobile partnership annoucement, the company couldn’t say whether existing plans would include satellite coverage. While satellite offerings aren’t available for consumers yet, this successful test brings widespread access one step closer to becoming a reality.

Chairman & CEO Abel Avellan and an AST SpaceMobile engineer completing test calls in Texas
Image Credit: Image: AST SpaceMobile
Other U.S. network operators are also pursuing satellite network mobile phone calls:
Verizon teamed up with Amazon’s Project Kuiper satellite network in 2021 with the intention of connecting underserved communities and industries. Amazon is in the midst of launching its satellites into space, with its FCC license requiring at least half of the 3,236 they plan to deploy to be operational by July 2026.
T-Mobile has partnered with SpaceX, a major competitor of Project Kuiper, with plans to “start getting into testing” its satellite mobile coverage this year. There are currently over 4,000 Starlink satellites in orbit, though some have experienced issues requiring them to be removed from orbit or tested further. T-Mobile has claimed customers should have satellite access through most existing plans and, like AT&T, that existing phones should work with the satellite offerings.
See References below for more global Satellite Internet initiatives.
References:
AT&T realizes huge value from AI; will use full suite of NVIDIA AI offerings
Emergency SOS: Apple iPhones to be able to send/receive texts via Globalstar LEO satellites in November
Musk’s SpaceX and T-Mobile plan to connect mobile phones to LEO satellites in 2023
China’s GalaxySpace launches 6 satellites to test LEO internet constellation
European Union plan for LEO satellite internet system
Keysight and partners make UK’s first 100 Gbps “6G” Sub-THz connection
Highlights:
- Data link made at speeds greater than 100 Gbps at a frequency of 300 GHz using both 32 and 64 quadrature amplitude modulation
- Achievement enabled by Keysight’s 6G sub-THz testbed platform
Keysight Technologies, Inc, in collaboration with National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and the University of Surrey, has made the first 6G connection at speeds greater than 100 gigabits per second (Gbps) over sub-terahertz (THz) frequencies in the U.K.
Future 6G use cases, such as augmented reality and autonomous vehicles, will require data throughput speeds from 100 Gbps to 1 terabit per second (Tbps). To achieve the extreme data speeds and low latencies required by these revolutionary use cases, the use of sub-THz frequencies is being explored. However, operations in sub-THz frequency bands introduce signal integrity and path loss challenges that can negatively impact performance.
Keysight, NPL, and the University of Surrey established the first sub-THz high throughput 6G testbed in the U.K. to address these challenges. Funded by the U.K. government for 6G research, NPL and Surrey scientists are using the testbed to study and characterize sub-THz signal performance to generate new techniques for optimizing data paths and calibration methodologies.
Located at NPL, this new 6G testbed achieved the U.K.’s first high-speed sub-THz data link. The demonstration was made at a frequency of 300 GHz using both 32 and 64 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). Built on Keysight’s 6G Sub-Terahertz R&D Testbed, the testbed uses the M8194A Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) combined with Virginia Diodes Inc. (VDI) upconverters / downconverters to generate the signal and Keysight’s UXR0704A Infiniium multichannel high-performance 70 GHz oscilloscope to analyze the signal.
Keysight, NPL, and the University of Surrey will demonstrate the new 6G testbed at the Spring 2023 6G Symposium at the University of Surrey, April 24-26.
Irshaad Fatadin, Principal Scientist, National Physical Laboratory, said: “6G is a key focus for NPL and we are using our scientific and measurement capabilities to tackle the challenges of this new technology. Our partnership with Keysight will be a critical success factor in our 6G research work.”
Mosaab Abughalib, Senior Research Director and General Manager for Keysight’s Network Emulation Group, said: “Through this partnership we are bringing Keysight solutions and experts together with scientists from NPL and the University of Surrey to unlock the true potential of 6G.”
Resources:
- White paper: 6G: Going beyond 100Gbps to 1 Tbps
- Keysight 6G Sub-Terahertz R&D Testbed
- M8194A Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG)
- UXR0704A Infiniium UXR-Series Oscilloscope
About Keysight in 6G:
Keysight creates the runway that enables researchers to launch evolutionary and revolutionary technology platform solutions based on 5G-Advanced and 6G technologies. A cohesive set of design and development building blocks across multiple interconnected technology domains enables innovators to spark new insights. Keysight plays a pivotal role in bringing to life 6G use cases that have the potential to transform society, enhance human interactions, enable enterprises to achieve greater efficiencies, and accelerate life-changing innovations.
About Keysight Technologies:
At Keysight (NYSE: KEYS), we inspire and empower innovators to bring world-changing technologies to life. As an S&P 500 company, we’re delivering market-leading design, emulation, and test solutions to help engineers develop and deploy faster, with less risk, throughout the entire product lifecycle. We’re a global innovation partner enabling customers in communications, industrial automation, aerospace and defense, automotive, semiconductor, and general electronics markets to accelerate innovation to connect and secure the world.
Learn more at Keysight Newsroom and www.keysight.com.
References:
Enable-6G: Yet another 6G R&D effort spearheaded by Telefónica de España
China to introduce early 6G applications by 2025- way in advance of 3GPP specs & ITU-R standards
India unveils Bharat 6G vision document, launches 6G research and development testbed
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
Juniper Research: 5G to Account for 80% of Operator Revenue by 2027; 6G Requires Innovative Technologies
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
Enable-6G: Yet another 6G R&D effort spearheaded by Telefónica de España
Telefónica de España has initiated yet another 6G R&D project, named Enable-6G, that aims to tackle the user privacy protection and energy-efficiency challenges associated with future generation wireless networks. In a statement, the Spanish telco announced the launch of the Enable-6G project, which is funded by the European Union’s economic recovery plan NextGenerationEU as well as Spain’s Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transformation.
The initiative is led by the IMDEA Networks Institute (an innovation and development centre in Spain) and includes involvement from tech giant NEC and BluSpecs (a Spanish digital transformation consultant). It is designed to address “the challenges that will be faced by future 6G networks, such as increased connectivity, higher performance demands, and advanced object and environment detection and communication,” the company noted.
One of the main objectives is to ensure advanced privacy protections are built into the architecture, as precise mapping and sensing, data privacy and security have become major concerns, and has also become a major benefit for new use cases. Another strategic objective is the design and implementation of software-defined networks that can operationalise optimized edge-to-cloud processing to facilitate time-critical and geo-distributed network orchestration (e.g., via the application of control-task algorithms). The ENABLE-6G project represents a major step forward in the new technologies into 6G to improve wireless communications, provide environmental sensing and significantly reduce the energy footprint per device to avoid a large overall increase in network power consumption. We are excited about the potential impact of this project and look forward to collaborating with our partners to bring it to fruition.
Telefónica is one of the leading private R&D centers in Spain, aiming to explore and develop new technologies and solutions that can improve the company’s existing products and services, as well as identify and create new business opportunities in the telecommunications and technology sectors. One of the big companies joining this project is NEC Corporation, with a great capacity has a strong commitment to research and development and invests heavily in new technologies and innovative solutions. ENABLE-6G counts on the excellent IMDEA Networks scientists, one of the best innovation and development centres in Spain, with a variety of experts from all over the world. Finally, this project will count on the consultancy of BluSpecs, facilitating the digital transformation of private and public organisations through the application of knowledge, data, and methodologies in the field of strategy, implementation of new technologies and innovation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Opinion: The rush to 6G R & D is incomprehensible to this author, as there are still so many holes in 5G specifications and standards. Moreover, 5G Advanced specs (3GPP Release 18) have not been completed. Hence, there is no ITU-R standards work even started for that. There isn’t even an ITU-R recommendation that specifies 6G functionality or features!
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

The development of the G project “has become crucial”, according to Telefónica, as it has become evident that 6G networks need to be “more adaptable and intelligent” so that they can give rise to a future vision that tackles “greater levels of complexity, contextualisation, and data traffic” – all the while consuming less energy, and providing enhanced security and privacy measures so that anyone developing future technology is given the level of trust required for the “widespread implementation of next-generation devices and nodes”.
A main objective for the Enable-6G project is to ensure “advanced privacy protections are built into the architecture,” given that precise mapping and sensing, as well as data privacy and security, are major concerns but also provide a great opportunity for new service development.
The initiative will also focus on designing and implementing software-defined networks (SDN) that can operationalise optimised edge-to-cloud processing, with the end goal being to support time-critical and geo-distributed network orchestration.
Enable-6G will look to provide “environmental sensing” which, according to Telefónica, will significantly reduce the energy footprint per device and prevent a large increase in overall network power usage.
While 5G networks and services are still being deployed and developed, many players in the industry are already exploring the potential of wireless 6G.
As well as Enable-6G, Telefónica is also active in another European 6G project, called Hexa-X-II, which involves participation from Orange and Telecom Italia, as well as vendors Nokia and Ericsson.
Also in Europe, German operator Deutsche Telekom is leading a consortium of 22 partners as part of the 6G-TakeOff research project within the broader 6G industrial projects funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) – see Deutsche Telekom, Nokia take lead roles in European 6G projects. Ericsson is launching a €5.7m research and innovation consortium in Europe, called Deterministic6G, with which Orange is also involved, as well as several other members – see News brief: 6G R&D gathers pace in Europe.
Meanwhile, China plans to launch 6G by 2025 – way in advance of any standards which imply no interoperability! India has their Bharat 6G vision document with plans to launch a 6G research and development testbed.
In the UK, the government has invested £110m in 5G, 6G and telecom security research and development initiatives, in collaboration with BT, Cellnex, Virgin Media O2, Ericsson, Mavenir, Nokia, Parallel Wireless and Samsung, among others – see UK government pumps £110m into 5G, 6G R&D.
More recently, the UK Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) announced that it plans to invest up to £100m into “a new long-term national mission to ensure that the UK is at the forefront of both adopting and developing 6G – the future of digital connectivity.”
Elsewhere, Japanese telco NTT Docomo is also taking strides towards shaping the future of 6G, including issuing advice in the form of whitepaper reports in partnership with its South Korean peer SK Telecom (SKT).
While in India, Prime Minister Narendra Modi has recently set out a vision, dubbed Bharat 6G, that aims to put India on the global map of leaders in the 6G era – see India eyes global leadership role in 6G.
North American is also involved into the 6G R&D sector. US industry group The Next G Alliance has been active in depicting a 6G vision for North America, drawing up a roadmap of necessary steps to secure the region’s leadership in wireless technology from the next decade onwards.
References:
Enable-6G launched to unlock the potential of Future 6G Networks
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/6g/telef-nica-joins-europe-s-latest-6g-r-d-effort-47305/
China to introduce early 6G applications by 2025- way in advance of 3GPP specs & ITU-R standards
India unveils Bharat 6G vision document, launches 6G research and development testbed
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
Juniper Research: 5G to Account for 80% of Operator Revenue by 2027; 6G Requires Innovative Technologies
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
Summary of ITU-R Workshop on “IMT for 2030 and beyond” (aka “6G”)
Arista Networks unveils cloud-delivered, AI-driven network identity service
At the RSA Conference today, Arista Networks announced a cloud-delivered, AI-driven network identity service for enterprise security and IT operations. Based on Arista’s flagship CloudVisionⓇ platform, Arista Guardian for Network Identity (CV AGNI™) expands Arista’s zero trust networking approach to enterprise security. CV AGNI helps to secure IT operations with simplified deployment and cloud scale for all enterprise network users, their associated endpoints, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
“Proliferation of IoT devices in the healthcare network creates a huge management and security challenge for our IT and security operations. The ease of securely onboarding devices on the network by CV AGNI and its integration with Medigate by Claroty for device profiling greatly simplifies this problem for a healthcare network,” said Aaron Miri, CIO of Baptist Healthcare.
AI-Driven Network Identity brings Simplicity and Security at Scale
While enterprise networks have seen massive transformation in recent years with the adoption of cloud and the acceleration of a post-pandemic, perimeter-less enterprise, Network Access Control (NAC) solutions have changed little for decades. Traditional NAC solutions continue to suffer from the complexity of on-premises deployment and administration and have been unable to adapt to the explosion of SaaS-based identity stores, users, devices and their associated profiles across the enterprise.
CloudVision AGNI takes a novel approach to enterprise network identity management. Built on a modern, cloud-native microservices architecture, the CV AGNI solution leverages AI/ML to greatly simplify the secure onboarding and troubleshooting for users and devices and the management of ever-expanding security policies.
CV AGNI is based on Arista’s foundational NetDL architecture and leverages AVA™ (Autonomous Virtual Assist) for a conversational interface that removes the complexity inherent in managing network identity from a traditional legacy NAC solution. AVA codifies real-world network and security operations expertise and leverages supervised and unsupervised ML models into an ‘Ask AVA’ service, a chat-like interface for configuring, troubleshooting and analyzing enterprise security policies and device onboarding. CV AGNI also adds user context into Arista’s network data lake (NetDL), greatly simplifying the integration of device and user information across Arista’s products and third-party systems.
CloudVision AGNI delivers key attributes from client to cloud across the cognitive enterprise:
- Simplicity: CV AGNI is a cloud service that eliminates the complexity of planning and scaling the compute resources for an on-premises solution. Administrative actions take a fraction of the time compared to a traditional NAC solution. It also natively integrates with industry-leading identity stores.
- Security: CV AGNI leapfrogs legacy NAC solutions by redefining and greatly simplifying how enterprise networks can be secured and segmented by leveraging user and device context in the security policies.
- Scale: With a modern microservices-based architecture, the CV AGNI solution scales elastically with the growing needs of any enterprise.
CloudVision Delivers Network Identity as-a-Service
Based on the CloudVision platform, CV AGNI delivers network identity as a service to any standards-based wired or wireless network.
CloudVision AGNI’s key features include the following:
- User self-service onboarding for wireless with per-user unique pre-shared keys (UPSK) and 802.1X digital certificates.
- Certificate management with a cloud-native PKI infrastructure
- Enterprise-wide visibility of all connected devices. Devices are discovered, profiled and classified into groups for single-pane-of-glass control.
- Security policy enforcement that goes beyond the traditional inter-group macro-segmentation and includes intra-group micro-segmentation capabilities when combined with Arista networking platforms through VLANs, ACLs, Unique-PSK and Arista MSS-Group techniques.
- AI-driven network policy enforcement based on AVA for behavioral anomalies. When a threat is detected by Arista NDR, it will work with CV AGNI to quarantine the device or reduce its level of access.
Tailored for Multi-vendor Integration
CloudVision AGNI leverages cognitive context from third-party systems, including solutions for mobile device management, endpoint protection, and security information and event management. This greatly simplifies the identification and onboarding process and application of segmentation policies. Examples include:
- Endpoint Management: Medigate by Claroty, CrowdStrike XDR, Palo Alto Cortex XDR
- Identity Management: Okta, Google Workspace, Microsoft Azure, Ping Identity and OneLogin.
- MDM: Microsoft Intune, JAMF
- SIEM: Splunk
- Networking devices: Multi-vendor interoperability in addition to Arista platforms
Availability
CV AGNI is integrated into Arista CloudVision to provide a complete identity solution. CV AGNI is in trials now with general availability in Q2 2023.
Visit us at booth #1443 at RSA. Learn more about AI-driven network identity at Arista’s webinar on May 18, register here. For more insight on this announcement, read Jayshree Ullal’s blog here.
About Arista
Arista Networks is an industry leader in data-driven, client to cloud networking for large data center, campus and routing environments. Arista’s award-winning platforms deliver availability, agility, automation, analytics and security through an advanced network operating stack. For more information, visit www.arista.com.
Competing Product:
SailPoint’s AI driven Identity Security Platform
References:
https://www.arista.com/en/company/news/press-release/17244-pr-20230424
https://www.sailpoint.com/platform/?campaignid=11773644133
Arista’s WAN Routing System targets routing use cases such as SD-WANs
China increases funding for semiconductor companies as TSMC warns of 16% revenue fall
Chinese chipmaking suppliers plan to spend 50 billion yuan ($7.26 billion) with backing from the state to strengthen the domestic supply chain as the U.S. curbs tech exports.
“We cannot avoid decoupling in semiconductors,” Chiu Tzu-Yin, president of state-backed wafer giant National Silicon Industry Group (NSIG), said at a chip supply chain conference hosted in Guangzhou for two days through Wednesday.
“This will be the greatest opportunity for Chinese enterprises that make production machinery and materials.”
As imports of foreign-made chipmaking machines have slowed due to U.S. restrictions, Chinese companies that produce chipmaking equipment and materials have gained visibility, aided by subsidies and investment under the auspices of the government’s Made in China 2025 initiative.
About 35% of Chinese semiconductor factories used domestic equipment in 2022, up from 21% in 2021, Chinese media report. Domestic players have won nearly half of all public bids for equipment by leading chipmakers here so far in 2023, a Chinese brokerage reports.
“Global political frictions will likely usher in a golden age to China’s semiconductor manufacturing machinery sector,” said David Wang, CEO of ACM Research, which specializes in wafer-cleaning equipment.
Naura Technology Group, China’s top manufacturer of chipmaking devices, earned 14.6 billion yuan in revenue last year, more than six times the figure in 2017. The state-linked company bought a U.S. wafer cleaning device maker in 2018 and extended its business profile to include products for etching.
 Naura Technology Group is China’s biggest manufacturer of chipmaking devices. (Photo by Shunsuke Tabeta)
Naura Technology Group is China’s biggest manufacturer of chipmaking devices. (Photo by Shunsuke Tabeta)Naura is said to supply leading Chinese foundry Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp. (SMIC) as well as Yangtze Memory Technologies. Naura is investing 3.8 billion yuan on building a plant in Beijing due to begin operations next year.
Advanced Micro-Fabrication Equipment, China’s No. 2 manufacturer of chipmaking tools and a producer of etching devices, roughly quintupled its sales last year from 2017. Products from the state-backed enterprise can handle advanced 5-nanometer semiconductors. Construction is underway for a 1.5 billion yuan plant in Shanghai.
Sales of chipmaking equipment in China totaled 52 billion yuan last year, an industry group estimates, roughly six times more than in 2017.
About 62 billion yuan worth of chipmaking materials was sold in 2022 as well, nearly triple the 2017 figure. NSIG’s revenue roughly quintupled during that span, and the company raised 10 billion yuan in funds last year alone.
“We plan to increase the monthly production capacity of 300-millimeter wafers up to 1.2 million units, quadruple the current level,” Chiu said.
 National Silicon Industry Group broke ground on a research hub in November 2022. (Photo courtesy of National Silicon Industry Group)
National Silicon Industry Group broke ground on a research hub in November 2022. (Photo courtesy of National Silicon Industry Group)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Beijing plans further support to domestic companies in light of its growing rivalry with Washington. Speculation centers on a package worth 1 trillion yuan or more.
“Upstream and downstream industries will work together on innovation, accelerating efforts for a Chinese-style self-reliance in semiconductors,” said Tsinghua University professor Wei Shaojun, a policy adviser on semiconductors.
China ranked first worldwide in chipmaking equipment sales for the third consecutive year in 2022 despite a 5% decrease, industry group SEMI reports. Demand is expected to grow in 2023, especially as Chinese chipmakers anticipate new American export restrictions. SMIC plans a similar level of investment in 2023 as in 2022.
Overseas players also have an eye on opportunities in China, the world’s largest market for chips. The three largest U.S. equipment makers generated around 30% of their total sales last year in China, according to Chinese research institution ChipInsights.
Sponsors for this week’s Guangzhou conference included U.S.-based Applied Materials, KLA and Lam Research, as well as Germany’s Siemens. A Singaporean executive from KLA used the event to highlight the company’s expertise in automotive chips.
Current U.S. restrictions on tech exports to China focus on cutting-edge areas, like 10- and 14-nm logic chips. Shipments in more mature fields, like equipment, are still allowed.
One executive from a foreign company noted that losing the Chinese market would harm overall earnings, in turn impacting research and development.
In Japan, Disco and Hitachi Group were listed as sponsors for the Guangzhou event. But they kept a low profile, largely watching for U.S. moves.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC), the world’s #1 semiconductor company in total sales, said revenue could fall as much as 16% in the three months to the end of June, as the weak global economy and high energy prices weigh on demand from customers.
The world’s biggest contract chip maker said Thursday (April 20th)that it expected second-quarter revenue of between $15.2 billion and $16 billion, from $18.16 billion a year earlier. On an earnings call with analysts, Chief Executive C.C. Wei said the company will likely post a low- to mid-single digit percentage decline in full-year sales—a more gloomy outlook than the one he gave in January.
Contrary to market expectations that it would cut spending, TSMC left its full-year capital expenditure budget unchanged. This underscores its commitment to maintain a high level of spending in anticipation of a pickup in orders in the second half of the year, the chip maker’s executives said, warning that demand for smartphones and PCs will likely remain weak all year.
TSMC in January cut its capital spending plans for 2023 to a range of $32 billion to $36 billion, down from $36.3 billion last year.
Mr. Wei said he forecasts the global semiconductor industry, excluding memory chips, will post a full-year revenue decline in a similar range to TSMC’s—and which would also be worse than he predicted in January.
Analysts say TSMC’s sales have been squeezed as many clients clear their inventory.
The auto-related business was the only segment to post an increase in sales from the previous three months, with the company’s usual growth drivers, such as smartphone and high-performance computing, all falling.
Still, TSMC’s dominant position in chip making ensures strong demand from customers, including tech companies such as Apple Inc. and Nvidia Corp.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/taiwan-semiconductor-manufacturing-tsm-q1-earnings-report-2023-2ebf2836
Multi-G Initiative to drive Open RAN Software Interfaces and increase innovation
Cohere Technologies, Intel, Juniper Networks, Mavenir and VMware intend to collaborate to develop the industry’s first framework for a multi-generational (Multi-G), software-based Open RAN architecture. The Multi-G initiative would define frameworks, interfaces, interoperability testing, and evaluation criteria that would provide the interfaces to support full coexistence of 4G, 5G, and future waveforms.
Intel’s FlexRAN platform is used by most current virtualized RAN (vRAN) deployments; Mavenir has a strong presence in providing open RAN equipment and software; and Juniper Networks and VMware are both contributing their work with the RAN intelligent controller (RIC). Cohere’s contribution is through its Universal Spectrum Multiplier software that can be integrated by RAN vendors or as an “app” into a telco cloud platform.
Intel’s involvement in this initiative is significant from an industry perspective due to the breadth of FlexRAN adoption. It also puts the chip giant a step ahead of competitors like Qualcomm, Arm and AMD that are aggressively targeting the Open RAN silicon market.
The new Multi-G framework would disaggregate RAN intelligence and scheduling functions, enabling future code releases of Intel’s FlexRAN reference architecture to support higher capacity, software-defined deployments for 4G, 5G and next generation wireless waveforms and standards.
This effort would help drive higher performance and connectivity across satellite, private and ad-hoc networks, and autonomous vehicles, increasing new service and revenue opportunities for telecommunications and mobile operators.
“This is going to make the network programmable all the way from layer one to the highest layers of the architecture,” said Cohere Technologies’ CEO Ray Dolan. “It’s not that open RAN is incomplete or not vibrant or not working, it is.” Right now, it has opened most of the parts that are what I’ll say are less controversial than the E2 interface. It’s opened the radio interfaces and the antenna interfaces, and so it’s established. But it hasn’t established the proper E2 interfaces completely. And that’s widely accepted as a fact. And in order for, I believe, for open RAN to really achieve its full vision, it needs to open that E2 interface because that’s where the innovation will come. Because that’s where all of the complexity in the marketplace is.”
The E2 work basically taps into the near real-time xApps running in a RIC to monitor and optimize an operator’s RAN deployment – typically either a vRAN or open RAN – and across different spectrum bands. This in turn allows an operator to support more stringent service-level agreements (SLAs) and private network deployments that can generate more revenues.
Ahead of the group’s first meeting in May 2023, telecommunications leaders worldwide are already sharing support for the collaborative initiative:
Vodafone Group
“This commitment from Intel, Mavenir, Juniper Networks, and Cohere, with a software programmable L1 stack, is fully aligned with the vision of Open RAN and will bring us one step closer to the scale deployment of software-defined RAN,” said Yago Tenorio, Vodafone Fellow and Director of Network Architecture, and Chairman of the Telecom Infra Project (TIP). “This has huge potential for significant performance and capacity benefits for all existing cellular networks. We strongly endorse this initiative, and we look forward to seeing the critical interfaces published into the relevant O-RAN Alliance and TIP Working Groups.”
Telstra
“Cohere’s Universal Spectrum Multiplier technology has the potential to unlock new architectural capabilities and opportunities for the RAN beyond today’s architecture,” said Iskra Nikolova, Network and Infrastructure Engineering Executive at Telstra. “We’re pleased to support this initiative and look forward to working with Cohere and the group to define the framework and accompanying critical interfaces.”
Bell
“A genuine Multi-G framework will enhance the benefits of Cohere’s Universal Spectrum Multiplier, strengthen Open RAN vendor flexibility down to the silicon layer, and allow old and new waveforms to coexist— beyond 5G,” said Mark McDonald, Bell’s Vice President, Wireless Access. “Bell looks forward to working with Cohere and partners later this year to further test this architecture.”
Hear from the Collaborators:
Intel Corporation
“This Multi-G framework, enabled by Intel FlexRAN – which is fully software programmable down to L1 – will enable faster O-RAN adoption and unlock new innovations,” said Sachin Katti, senior vice president and general manager of the Network and Edge Group at Intel Corporation.
Mavenir
“As the leading Open RAN partner, we’re excited to be part of the Multi-G initiative which promises to bring 4G and 5G spectral efficiencies gains not possible with incumbent solutions,” said Bejoy Pankajakshan, EVP-Chief Technology and Strategy Officer at Mavenir. “Unlike traditional DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing) techniques which reduces 4G and 5G performance, with our Multi-G collaboration with Cohere and Intel, Mavenir can provide a true spectrum co-existence solution, which deploys 5G on the same spectrum assets as 4G dramatically improving the ROI per Hz on the existing 4G spectrum.”
Juniper Networks
“As more 5G deployments are underway, there is still a large installed base of 4G networks that can benefit from the intelligence, control and automation enabled by an Open RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) architecture,” said Raj Yavatkar, CTO of Juniper Networks. “Juniper Networks has already demonstrated innovative 4G and 5G use cases with our Juniper Non-RealTime RIC and Near-RealTime RIC that can provide more flexibility to network operators. We are excited to add our expertise and join the Multi-G framework initiative, which will not only help to accelerate Open RAN adoptions but will also spur further innovation across multiple generations of mobile networks to enhance the network operator experience.”
VMware
“VMware is already paving the way for more programmable and intelligent Open RAN networks with our VMware RIC and our Service Management Orchestration Framework (SMO) for end-to-end RAN automation, assurance and optimization,” said Sanjay Uppal, GM & SVP, Service Provider Business Unit, VMware. “We are pleased to join other industry leaders to pioneer in the development of the industry’s first framework for a Multi-G, software-programmable architecture that will further encourage innovation and fast-track the adoption of Open RAN globally.”
Open RAN Policy Coalition
“Defining new interfaces that supercharge developing and future networks is critical for the success of open networks,” said Diane Rinaldo, Executive Director of the Open RAN Policy Coalition. “This will foster innovation and add flexibility, which will improve our competitiveness.”
Cohere Technologies
“We are pleased to work with world-class partners and operators to accelerate the deployment of Multi-G, open networks with significant performance improvements,” said Ray Dolan, CEO of Cohere Technologies. “Cohere is committed to a software-based, open architecture that can drive faster innovation and deliver critical revenue growth and profitability for the industry.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Cohere Technologies:
Cohere is the innovator of Universal Spectrum Multiplier (USM) software for 4G, 5G, and Multi-G O-RAN. USM improves mobile networks up to 2x by MU-MIMO, enabling existing devices in any FDD and TDD spectrum band. Cohere is the creator of the Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) wireless system, and is headquartered in San Jose, Calif. (USA). Website: www.cohere-tech.com Twitter: @Cohere_MultiG
References:
https://www.cohere-tech.com/press-releases/multi-g-initiative
LightCounting: Open RAN/vRAN market is pausing and regrouping
ATIS and O-RAN Alliance MOU may be a prelude to Open RAN standards in North America
SNS Telecom & IT: Open RAN Intelligent Controller, xApps & rApps to reach $600 Million by 2025
Intel FlexRAN™ gets boost from AT&T; faces competition from Marvel, Qualcomm, and EdgeQ for Open RAN silicon


