Month: July 2020
Gartner: Market Guide for Small Cells- 5G, virtualization, disaggregation and Open RAN
Introduction:
Small cells are increasingly used to boost network densification and expand coverage for both private and public networks. They will be increasingly important in the deployment of 5G mmWave networks because of the very short propagation distances which require many small cells for adequate coverage in a given geographical area.
5G small cell market is gaining momentum due to the higher bands like mmWave limitation, in-depth in-building coverage requirement and strategic area densification. However, despite the hype surrounding 5G, 3G/4G deployments are expected to remain the dominant technology in terms of volume shipments until 2022 when 5G small cell deployment will overtake 3G/4G. Therefore, because small cell densification is moving forward, integrated small cell platforms supporting both 5G and 4G radio are essential for the next five years.
Small cells deployed in strategic areas have also accelerated the new virtualized and disaggregated architecture adoption, aiming for greater cost-efficiency and flexibility. Together with edge computing, they are enablers for enterprise digital services such as manufacturing applications, smart harbor/terminal, local contextual applications and IoT services.
Definition of Small Cells:
-
Femtocells
-
Picocells
-
Carrier-grade Wi-Fi
Gartner’s Key Findings:
-
The small cell solution is shifting from delivering in-build coverage to enable large-scale network densification. Increasing 5G and private network deployments further accelerate the trend.
-
In the small cell market, variety and diversity are replacing uniformity. Introduction of new spectrums, types of cells and architectures, vertical industries use cases, and business models like neutral host act as accelerators in this respect.
-
In addition, diversity increases the cost and complexity of small cell deployment and management, not just access points but also potentially edge computing, localized core and distributed radio units.
-
Traditional proprietary small cell systems are challenged by disaggregated, virtualized architecture. Communications service providers (CSPs) are looking for a more flexible, multivendor, cost-effective solution through breaking apart basebands and radio heads, and virtualizing some or all of the baseband functions in software.

Gartner’s Recommendations for Small Cell Deployment:
-
Build your small cell deployment strategy beyond coverage through prioritized investment in network densification and related digital services. Include 5G small cell and private networking requirements in your product plans.
-
Address diversity challenges through a multivendor approach. There is no one size fits all in the future small cell market, and a scenario-oriented product evaluations process needs to be implemented.
-
Reduce complexity and improve cost-efficiency through prioritizing the deployment feasibility as well as operation intelligence and automation.
-
Work closely with emerging suppliers and establish an objective and structured process to thoroughly evaluate and develop quick prototypes using disaggregated and virtualized architectures.
Small Cells Will Be at the Forefront of Virtualization and Open RAN:
The economic success of 5G is reliant on interoperable multi-vendor networks, which require open interfaces at both the silicon and network levels. Therefore, many CSPs are continually exploring the possibility of moving away from the proprietary hardware to more modern open and interoperable systems.
To support these, CSPs will need to adopt new network topologies such as cloud-RAN, virtualized RAN (vRAN) or open RAN (ORAN), together with integrated edge compute.The key to the open network lies in disaggregation — separating the key elements such as centralized units (CUs) and distributed units (DUs) — and the open reconfiguration — combining components from any suppliers because they are all interconnected in the same way.
For 5G, those central processes will usually be virtualized (run as software on off-the-shelf servers).The move to open network has been more advanced in small cell layer than macro network, and several suppliers already offer architectures in which a number of small cells are clustered around a centralized, virtualized controller. But there are two potential barriers to achieving a real multivendor environment: the need to be in agreement on where the network should be split between the central and the local elements and the need to be a single common interface between the elements in each preferred split.
Split RAN/SC architectures have multiple options, as identified by 3GPP. Of these, 3GPP has focused on Option-2 (RLC-PDCP), ORAN on Option-7.2 (PHY-PHY) and Small Cell Forum (SCF) on Option-6 (PHY-MAC). SCF will develop a 5G version of its networked FAPI spec, which will enable a split MAC and PHY in a disaggregated small cell network, supporting the 3GPP Option-6 split over Ethernet fronthaul and targeting, in particular, cost-effective indoor scenarios. SCF’s work on open interfaces such as nFAPI will play an important role in the market, alongside the work of partners such as O-RAN Alliance and Telecom Infra Project.
Many CSPs expect to take their first steps in their small cell layer, providing valuable experience of how to manage and orchestrate a network in which multiple radio units share common baseband functions, some of them deployed on cloud infrastructure. While there are still challenges in this domain, the disaggregation and virtualized architecture reduce the technology barrier to market and introduce new players into the market including software players as well as OEMs and ODMs.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Small Cell Hardware and Software Vendors:
The table below may be used as a quick reference guide to representative vendors and their 5G small cell solutions. It includes the major vendors who have a long history providing small cell, DAS solutions and also some new emerging vendors who are providing software-based small cell solutions.
Table of Small Cell Vendors:
|
Small Cell Software
|
|
|
Air5G
|
|
|
Virtualized RAN Software
|
|
|
M-RAN Virtual Small Cell
|
|
|
5G Open Platform Small Cell
|
|
|
ONECELL
|
|
|
Enterprise Radio Access Network (E-RAN)
|
|
|
Radio Dot System, Micro Radio, Lightpole Site
|
|
|
LampSite Family, BookRRU, Easy Macro
|
|
|
Viper Platform
|
|
|
Massive MIMO AAS Radio Unit
|
|
|
Flexi Zone, AirScale Indoor Radio system (ASiR), AirScale Micro Remote Radio Head (mRRH), AirScale mmWave Radio (ASMR), Smart Node Femtocells
|
|
|
CellEngine
|
|
|
Samsung 5G Small Cell
|
|
|
Qcell, 5G iMicro, 5G Pad RRU
|
UPDATED: Huawei now #1 global smartphone vendor
Despite the severe U.S. restrictions on Huawei, the company has succeeded in taking the top spot in the global smartphone market, according to figures from Canalys. The market research firm estimates Huawei shipped more smartphones worldwide than any other vendor for the first time in Q2 2020, marking the first quarter in nine years that a company other than Samsung or Apple led the market.
Note, however, that global smartphone sales DECLINED in the second quarter. Huawei shipped an estimated 55.8 million devices in the quarter, down 5 percent year on year. Samsung came second with 53.7 million smartphones, down 30 percent from a year earlier.
Huawei’s resilience was due to its strong position in China, where its shipments rose 8 percent in Q2. This offset an estimated 27 percent fall in its shipments abroad. Canalys estimates over 70 percent of Huawei’s smartphone sales are now in mainland China. That helps explains why the company can be so successful in selling smartphones, despite not being able to use licensed Google Android and associated apps on its latest flagship devices (that’s because Huawei was placed on the U.S. Entity list last year).
Canalys said the situation would likely not have happened without the Covid-19 pandemic. Huawei profited from the strong recovery in the Chinese economy, while Samsung has a very small presence in China, with less than 1 percent market share, and suffered from the restrictions in key markets such as the US, India, Brazil and Europe.

“This is a remarkable result that few people would have predicted a year ago,” said Canalys Senior Analyst Ben Stanton. “If it wasn’t for COVID-19, it wouldn’t have happened. Huawei has taken full advantage of the Chinese economic recovery to reignite its smartphone business. Samsung has a very small presence in China, with less than 1% market share, and has seen its core markets, such as Brazil, India, the United States and Europe, ravaged by outbreaks and subsequent lockdowns.”
“Taking first place is very important for Huawei,” said Canalys Analyst Mo Jia. “It is desperate to showcase its brand strength to domestic consumers, component suppliers and developers. It needs to convince them to invest, and will broadcast the message of its success far and wide in the coming months. But it will be hard for Huawei to maintain its lead in the long term. Its major channel partners in key regions, such as Europe, are increasingly wary of ranging Huawei devices, taking on fewer models, and bringing in new brands to reduce risk. Strength in China alone will not be enough to sustain Huawei at the top once the global economy starts to recover.”
As a result, it will be hard for Huawei to maintain its lead in the long term. Its major channel partners in key regions such as Europe are increasingly wary of stocking Huawei devices, taking on fewer models and bringing in new brands to reduce risk, as per the above Canalys quote from analyst Mo Jia.
Separately, Gartner estimates that 10% of smartphone shipments, or about 220 million units in 2020, will have 5G capability, but they’ll work on “5G” networks with a LTE core (5G NSA).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Addendum:
Huawei’s just announced global licensing agreement with Qualcomm grants Huawei back rights to some of the San Diego-based company’s patents effective Jan. 1, 2020. It remains to be seen if Huawei will design smartphone components that use those patents in their next generation of 5G endpoint devices.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.canalys.com/newsroom/Canalys-huawei-samsung-worldwide-smartphone-market-q2-2020
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Update- August 3, 2020:
According to market research firm Omdia, overall Q2-2020 smartphone shipment volume was down a hefty 15.7%, year-on-year, to 229.7 million units.
Samsung will certainly hope there are better times ahead. Omdia figures show the South Korean behemoth lost its #1 position in Q2, dislodged by Huawei. Samsung’s Q2 shipments plummeted nearly 28%, year-on-year, to 54.3 million.
Many of Samsung’s most important markets, were significantly impacted by COVID-19, especially emerging markets, which apparently accounted for more than 70% of Samsung’s overall shipments in 2019.
For its part, Samsung is hopeful of a Q3 smartphone recovery, helped by the launch of new flagship models, including the Galaxy Note and a new foldable phone.
Huawei, helped by a resurgent domestic market in China, snagged a 20% global smartphone share during Q2 (55.8 million units), up from an 18% market share the previous quarter. Year-on-year, Huawei’s Q2 shipment units were down a comparatively modest 4.9%.
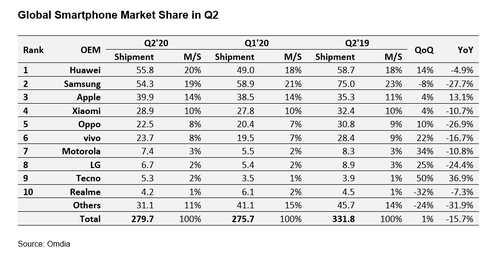
Apple was one of the few OEMs to increase Q2 shipment volumes, year-on-year (up 13.1%, to 39.9 million units). The iPhone SE, a model with mid-range pricing, coupled with the iPhone 11, helped Apple expand its unit shipments, and cement its third-spot position with a market share of 14% (up from 11% in Q2 2019).
“With the launch of the iPhone SE in April, Apple has released a long-desired product, with an attractive price,” said Jusy Hong, director of smartphone research at Omdia.
“For existing iPhone users who needed to upgrade their smartphones in the second quarter, the new SE represented an affordable option that does not require a large downpayment or high monthly repayment rates,” added Hong.
Reference:
https://www.lightreading.com/huawei-apple-buck-q2-smartphone-trends—report/d/d-id/762886?
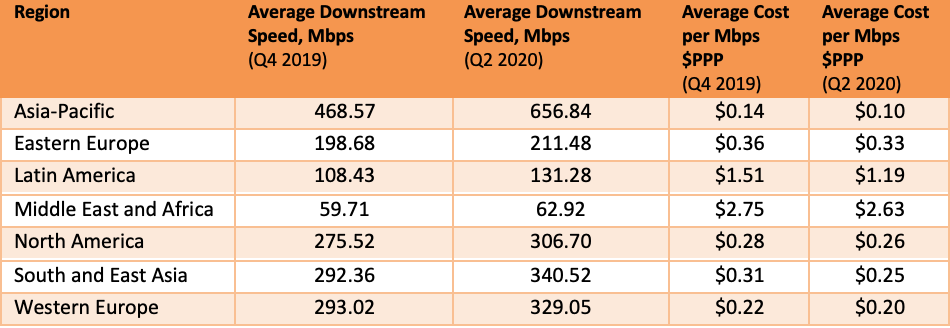
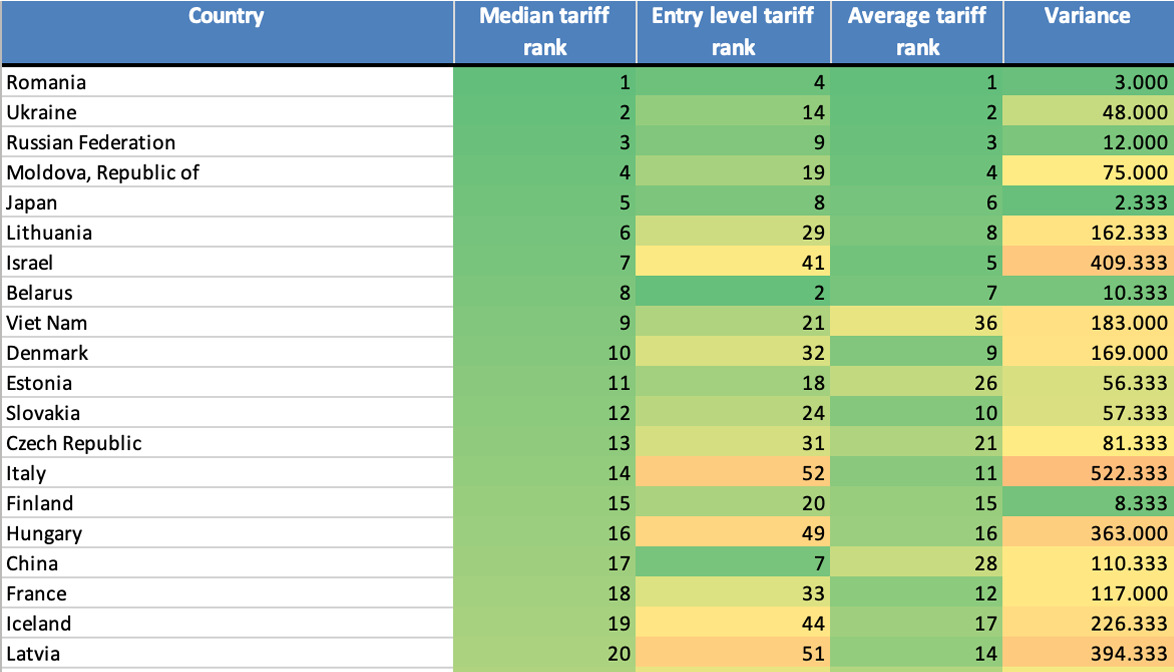
Point Topic Analysis of Fixed Broadband Tariffs from 300 Operators in 90 Countries
|
|
|
|
|
TSDSI’s 5G Radio Interface spec advances to final step of IMT-2020.SPECS standard
Telecommunications Standards Development Society of India (TSDSI)’s 5G Radio Interface Technology (RIT) has met step 7 of an 8 step process of ITU-R WP5D, thereby paving the way for its inclusion in the IMT-2020.SPECS. That impressive accomplishment was achieved at the ITU-R WP5D virtual meeting #35e which concluded on July 9, 2020. From the WP 5D Technology WG meeting report: “The RIT proposed in IMT-2020/19(Rev.1) (TSDSI) also passed Step 7 as “TSDSI RIT.”
As a penultimate step, the description of the TSDSI technology has been included in the draft IMT-2020 specification document. The TSDSI RIT is specified in Annex III. of the draft IMT-2020.SPECS standard, which is expected to be finalized at the WP5D meetings to be held in October and November 2020. Final approval is expected at the ITU-R SG 5 meeting November 23-24, 2020.
The TSDSI 5G RIT specification was described in a July 5, 2019 IEEE Techblog post. The ITU-R had earlier adopted the Low-Mobility-Large-Cell (LMLC) use case proposed by TSDSI as a mandatory 5G requirement in 2017. This test case addresses the problem of rural coverage by mandating large cell sizes in a rural terrain and scattered areas in developing as well as developed countries. Several countries supported this as they saw a similar need in their jurisdictions as well.
LMLC fulfills the requirements of affordable connectivity in rural, remote and sparsely populated areas. Enhanced cell coverage enabled by this spec, will be of great value in countries and regions that rely heavily on mobile technologies for connectivity but cannot afford dense deployment of base stations due to lack of deep fiber penetration, poor economics and challenges of geographical terrain.

Photo Credit: TSDSI
TSDSI successfully introduced an indigenously developed 5G candidate Radio Interface Technology (RIT), compatible with 3GPP’s 5G NR IMT-2020 RIT submission, at the ITU-R WP5D meeting in July, 2019 (as noted in the above referenced IEEE Techblog post). TSDI’s RIT incorporates India-specific technology enhancements that can enable larger coverage for meeting the LMLC requirements. It exploits a new transmit waveform that increases cell range developed by research institutions in India (IIT Hyderabad, CEWiT and IIT Madras) and supported by several Indian tech companies. It enables low-cost rural coverage and has additional features which enable higher spectrum efficiency and improved latency.
From TSDSI: Acceptance of TSDSI RIT as a 5G radio interface standard, a first for India, catapults India into the elite club of countries with expertise in defining global standards. It is a trailblazer that establishes India’s potential to deliver more such solutions that are appropriate to the specific requirements of the developing world and rely on indigenously developed technologies – Design Local, Deploy Global.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Addendum: Overview of TSDSI RIT
TSDSI RIT is a versatile radio interface that fulfills all the technical performance requirements of IMT 2020 across all the different test environments. This RIT focuses on connecting the next generation of devices and providing services across various sectors. In particular, this RIT focuses on:
1. Enhanced spectral efficiency and broadband access
2. Low latency communication
3. Support millions of IOT devices
4. Power efficiency
5. High speed connectivity
6. Large Coverage (in particular for Rural areas)
7. Support multiple frequency bands including mmWave spectrum
While, the current specifications provide a robust RIT, the specification also provides a framework on which future enhancements can be supported, providing a future-proof technology. In the following sections, we provide a basic description of the RIT. The complete details of the RIT can be found in the specification document IMT-2020/20 (ITU TIES account required for access).
References:
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status (?), and 3GPP’s 2 RIT submissions
Reliance Jio claim: Complete 5G solution from scratch with 100% home grown technologies
Deutsche Telekom: 40 million people have 5G coverage
Deutsche Telekom said today that its 5G network has reached 40 million people in Germany. This means that 50% of the population can use the new 5G mobile technology. Over 3,000 towns and municipalities received 5G after the company upgraded a further 18,000 antennas in recent weeks. In the coming weeks, Bremen and Dortmund, among other places, will receive high-speed 5G.
Deutsche Telekom uses spectrum on the 2.1 GHz band to supply as many people as possible with 5G. This band enables a long-range reach and increased speed. In rural areas, customers can surf at up to 225 Mbps, while in cities the network reaches 600-800 Mbps speeds at its peak.
With the 3.6 GHz frequency band, the network offers more speed and capacity. Antennas on this band achieve transmission rates of up to 1 Gbps. The company uses both the 2.1 GHz and 3.6 GHz frequency bands for the 5G rollout.
Deutsche Telekom said nearly 18,000 antennas have been upgraded for 5G and integrated into the live network in the past five weeks. This means that 40 million people can now have access to the telco’s 5G.

Image Credit: Deutsche Telekom
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“Half the population in Germany is now covered. 5G has arrived in all German states. This is a big step for our customers, our network and for digitization in Germany,” said Walter Goldenits, head of technology at Telekom Deutschland. The executive said that the carrier aims to cover two thirds of the country’s population with 5G before the end of the year.
“We will switch on 5G in 2.1 GHz in at least half of Germany already this year. 2.1 GHz is excellent for 5G because this spectrum range combines speed with good propagation,” the carrier’s CEO Timotheus Höttges recently said in a conference call with investors.
“We will have the top 20 cities covered with 3.6 GHz. Going forward, we will leverage other spectrum ranges, such as 700 MHz frequencies. So we have a mix of low band, mid band [and]high band, which is, compared to my competition, significantly better, and we will roll out faster than anybody else. So comparing the commitments of Vodafone with ours, we will have four times more coverage already by the end of the year with regard to 5G,” Höttges added.
As noted above, bands.Deutsche Telekom is using different frequencies for its 5G expansion. The focus is on the 2.1 GHz and 3.6 GHz frequency bands. Deutsche Telekom kicked off the rollout of its 5G network in a limited number of cities across Germany at the beginning of July 2019.
LTE is also receiving a further boost from the technology offensive. Customers will receive a further frequency band for the use of LTE and thus more bandwidth. The use of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) will make additional spectrum available to LTE customers. As a result, they too can surf even faster than before.
With DSS, Deutsche Telekom operates two mobile communications standards in parallel in one frequency band. The new technology distributes the spectrum between LTE and 5G users according to demand. The network automatically adapts to the needs of the respective customers within milliseconds. This leads to an even better user experience.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
| Germany 5G subscriptions 2020-22 (in thousands) – Omdia forecast | |||
| Company | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| 1&1 Drillisch | — | — | 702 |
| O2 Germany | — | 477 | 2,539 |
| T-Mobile Germany | 430 | 1,253 | 3,242 |
| Vodafone D2 | 494 | 1,426 | 3,536 |
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rival operator Vodafone Germany in its financial results statement last week said it planned to cover 10 million people with 5G technology by the end of 2020.
Telefonica Deutschland aims to cover 16 million people with its 5G network by 2022, with coverage across Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Frankfurt and Cologne this year.
Meanwhile, the construction of 1&1 Drillisch’s 5G network has been experiencing delays due to the COVID-19 pandemic. According to previous reports, 1&1 Drillisch expects to launch its 5G network in 2021.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/deutsche-telekom-touts-5g-for-40m-in-germany/d/d-id/762676
Verizon earnings beat estimates despite COVID-19 impact; wireless revenues down; 2H-2020 Priorities
Verizon’s reported today that 2nd-quarter adjusted earnings per share was $1.18, ahead of analysts’ consensus estimate of $1.15, but down from $1.23 in the same period last year. The company estimates that second-quarter 2020 EPS and adjusted EPS included approximately 14 cents of COVID-19-related net impacts, primarily driven by impacts to wireless service revenue and lower advertising and search revenue from Verizon Media.
Verizon added 173,000 wireless postpaid phone subscribers for the second quarter, as the COVID-19 pandemic weighed on wireless service and equipment revenue (see CFO Matt Ellis quote below).
Total wireless service revenue was down 1.7% from the same period a year ago, to $15.9 billion, while postpaid phone churn for Q2 was 0.51%. Verizon cited a significant drop in wireless equipment revenue because of low activations as the main driver behind a 4% drop in total consumer revenues to $21.1 billion and business to $7.5 billion.
Consumer wireless service revenue declined 2.7% from the year ago period to $13.1 billion. Business wireless revenue declined 3.7% YoY to $7.5 billion (see charts below).
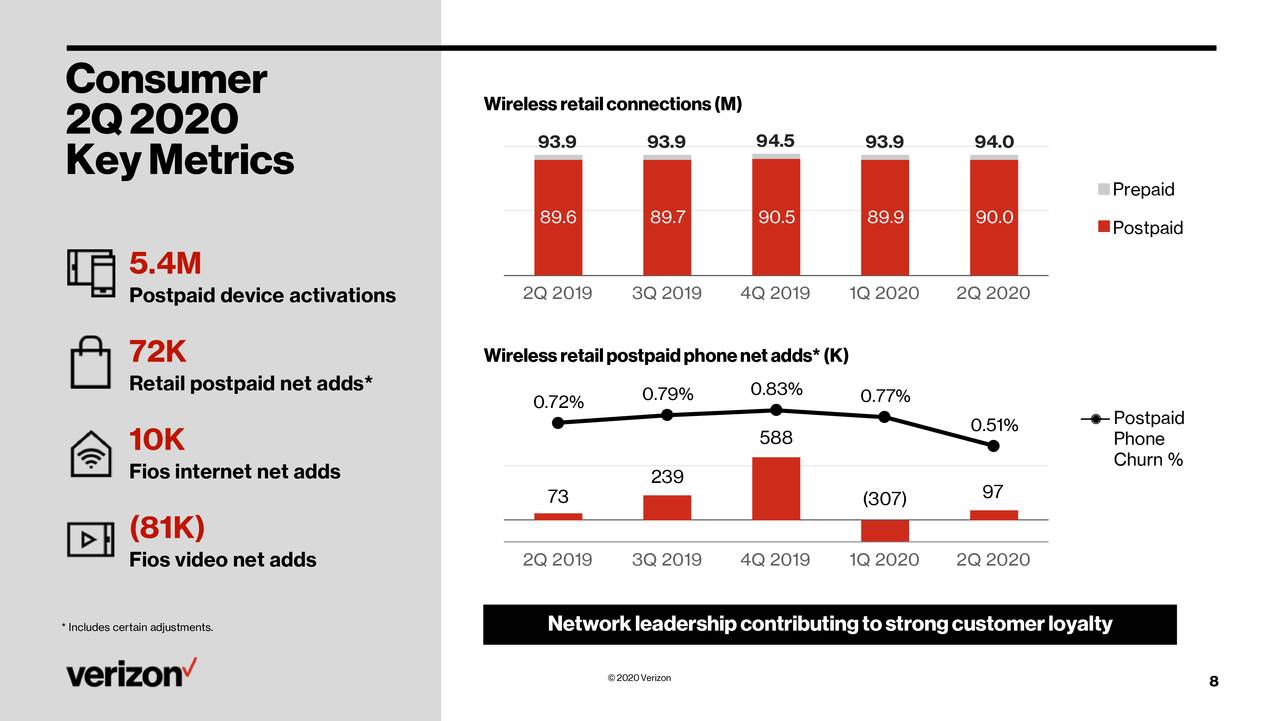
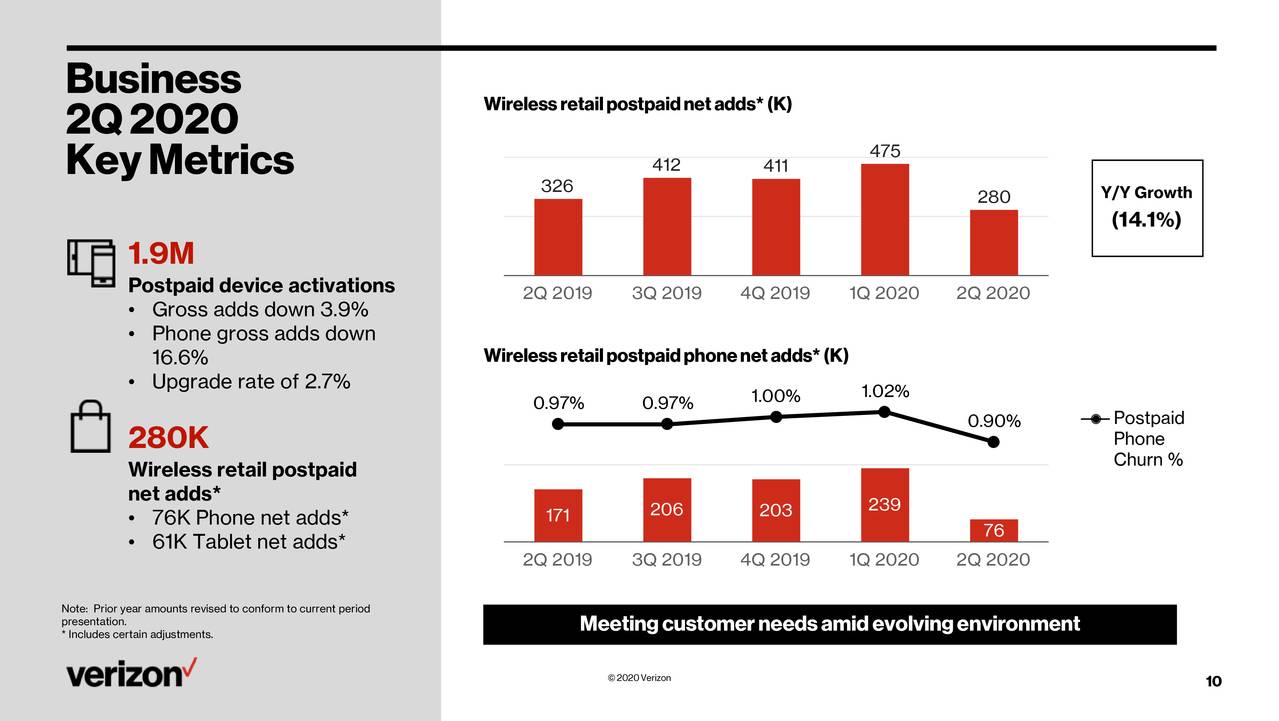
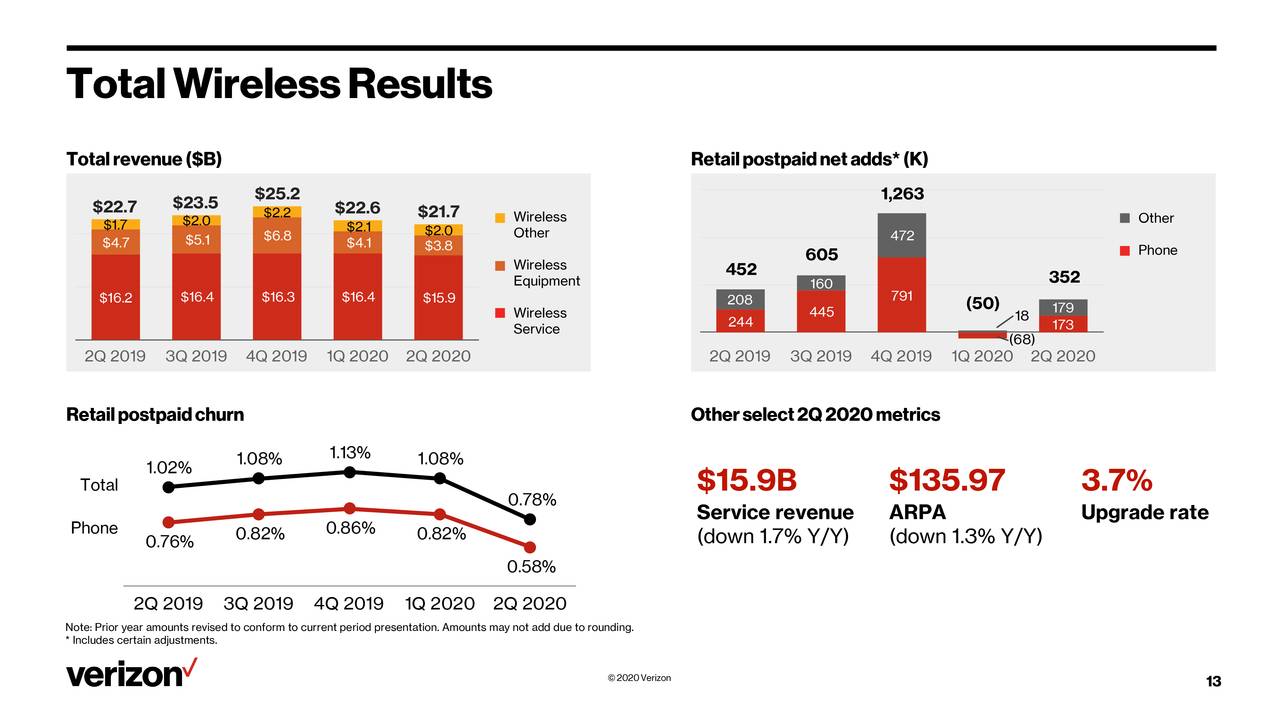
Like AT&T, which reported earnings yesterday, Verizon said the results include impacts from reduced roaming and usage as travel remains restricted, and waived fees. However, Verizon said it had record uptake of its premium Unlimited plans by new accounts. Wireless postpaid average service revenue per account (ARPA) declined 1.8% to $116.02.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Verizon continues to build-out its 5G network, with $9.9 billion in capital expenditures in the first half of the year. Those investments supported capacity and traffic growth across Verizon’s networks and included additional fiber and cell sites to expand its 5G UltraWideband rollout, which primarily uses 28 GHz millimeter wave spectrum. Verizon 5G network is in parts of 35 cities, while its fixed wireless 5G Home product is currently in six markets.
“Through extraordinary circumstances, Verizon delivered a strong operational performance in the second quarter,” said Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg in a statement. “We remain focused on our strategic direction as a technology leader, quickly adapting to the new environment and providing our customers with reliable and vital connections and technology services, while working to keep our employees safe and accelerating our 5G network deployment. We have embraced, engaged in and responded to important social movements happening throughout the world, and will continue to be at the forefront of initiatives that move the world forward for everyone. We are proud of what we have done, and continue to do, for our customers, shareholders, employees, and society.”
Other Q2 metrics for Verizon:
- Total revenue of $30.4 billion, down 5.1%
- Adjusted EBITDA of $11.5 billion and adjusted EBITDA margin of 37.9%
- Earnings per share of $1.18, down 4.1%
- Verizon Media revenues were down 24.5% to $1.4 billion
Commenting on the impact of COVID-19, Verizon Chief Financial Officer Matt Ellis told Barron’s Friday morning:
“Certainly this was a very different quarter than others, not part of our plan for the year, but when you look at the results I think you see strong operational performance and very good cash flow coming from that. I think it speaks to the nature of our business model and the importance of our products in our customers’ lives.”
Guidance and 2nd Half 2020 Priorities:
Verizon expects wireless revenue in a range of -1% to flat year over year in the 3rd quarter. Capital spending is forecast to be in the range of $17.5 billion to $18.5 billion.
Stated 2nd half 2020 initiatives are:
- 5G adoption
- Network monetization
- Next-gen B2B applications
- Customer differentiation
- New revenue opportunities
“Regardless of how results match up against expectations for Verizon, these results should be seen as good compared to what AT&T reported yesterday,” wrote New Street Research analyst Jonathan Chaplin on Friday morning. This author certainly agrees, as Verizon is not encumbered by DirecTV and Warner Media as AT&T is.
In February, we made some bold statements about our deployment on 5G in 2020 all the way from the Mobile Edge Compute, 5G Home cities, 5x more small cells on 5G and some 60 cities on the 5G Ultra-Wideband as well as a nationwide coverage on 5G with DSS. I’m happy to report we’re on track on that, and in some cases even ahead of the plan. We are continuing to deploy our technology.
Our test with DSS is going very well and as well, we have launched some of the 60 markets when it comes to mobility and some additional markets on 5G Home. However, you’re going to see that in the second half of this year we have a lot of new things happening and building on the foundation of the strategy and the strategic priorities that Verizon has outlined the last couple of years.
For Verizon Business Group, 5G Mobile Edge Compute, an important piece of our growth strategy, we have said that we are going to have 10 5G Mobile Edge Compute sites this year deployed. And now we’ve also started gearing up our partners. We have announced IBM and we also talked about SAP as two very important application providers that are going to take part of our deployment and that we’re collaborating with right now. So we’re creating a lot of excitement around the 5G Mobile Edge Compute and a lot more to come in the second half. Verizon Business Group, 5G Mobile Edge Compute, an important piece of our growth strategy, we have said that we are going to have 10 5G Mobile Edge Compute sites this year deployed. And now we’ve also started gearing up our partners. We have announced IBM and we also talked about SAP as two very important application providers that are going to take part of our deployment and that we’re collaborating with right now. So we’re creating a lot of excitement around the 5G Mobile Edge Compute and a lot more to come in the second half.
We are on plan to deploy more than 5x more millimeter wave base stations this year compared to last year, so the footprint will be much broader and we will be into 60 cities and those cities will be much more covered than they were last year. And we are disclosing that – usually on a fairly frequent basis how that map is growing. As you have seen, we have launched fairly few markets the first half when it comes to the 60, so you should expect quite a lot of noise from us in the second half and we’re really excited about that. But you also need to think about our model will also include nationwide, so think about our model being a millimeter wave that is transformative. No one is even close to it in the world. Then we will have national coverage on top of that. And then in the bottom, we have the best 4G network in the world. And then I don’t think that our customer will be disappointed with that. We build things that are transformative that are so different than others. So I would be excited for the second half if I would be you. It’s crunch time for Verizon. We have been talking about this for one and a half year. I think our customers will be very excited in the second half.
One year ago, we didn’t talk about DSS. But of course, our team was working to prepare all the networks so we can actually deploy DSS in all the radio base stations we have. So we constantly are ahead of the game thinking what is needed to be preparing for the network. But right now our focus is very much about the commitments we have to our customers when it comes to 5G, but also to keeping the best network on 4G. That’s where we’ll have it and then do that fiber reach. Those are the priorities and it will continue so. Then any speculation on the future spectrum or something, that’s a little bit early to have right now. But I can tell you my team is always proactively thinking about how to do this network continue to be the best in America. There’s no debate about that. And I have a high confidence that they will continue to do so when it comes to our CapEx allocation as well.
If you think about the Mobile Edge Compute, just last week we announced partnership with IBM and with SAP. That’s going to be part of the 5G Mobile Edge Compute in order to serve our customers. So you’re going to see that how we are doing, sort of laying out early indicators on that path to revenue that we have outlined both internally as well as externally.
5G Mobile Edge Compute. I think that the use cases we see today is very much real-time decision-making. If that’s a big distribution center that’s going to have 5G-enabled distribution center to actually take real-time decisions, or if it’s a big manufacturing plant that’s going to use 5G Mobile Edge Compute by wireless connecting to all the robotics, we’re in many of those cases. And then you also see cases where sort of IoT devices with 5G will actually enable a new way of delivering a service. And finally, the whole VR and AR for large enterprises where you need a low latency on the campus or in the manufacturing or whatever it might be, those are all the early cases. Many of them right now are based on low latency. We see it’s creeping into security because the data can then be contained with the company, meaning they can actually process and have all the processing and storage at the edge, which means they can keep the data for themselves. So those two capabilities are the first one. I think in the next, we’re going to see enormous bandwidth of enterprise that need to send a lot of data to the edge in order to take decisions. But so far, latency and security, that’s how the 5G Mobile Edge Compute scenarios are working out. And we basically have two, three – or two, I would say, per industry vertical that are lead customers for us. And we work with them to do the solutions and sometimes we are the third party as we don’t have all application ourselves. That’s how we’re working it right now and I’m encouraged. And, of course, as I said before, acceleration has been seen, because all the digitalization and touchless that is needed going forward.
We feel really good about our model. As we have said before, minimum of 10 5G Home cities. We’re going to have the cities with a much better chipset. That’s on plan for this second half.
And the self-install, which I have been talking about now for one and half year, which excites me that our customers should be able to receive the gear, the CPs and be able to install themselves in a short timeframe. It’s not that I’m down to the times that I have envisioned. I wanted to be below one hour, but we have come a far way from the eight hours we started with. And compared to a fiber installation where you need to first put it on the agenda, you wait for a couple of weeks and you have to come there and install it, and it takes hours to do. This is a totally different way. It’s transformative. As I said, we are building 5G that’s transformative, not the me-too to my 4G.
I think one thing that we have learned also is that, of course, fixed wireless access, we think a lot about consumers, but there is an opportunity clearly when you see this also as a fixed wireless access opportunity for small and medium business, et cetera, that we will start working on later on.
CFO Matt Ellis:
We’re driving these (5G Home) revenues off of the same (wireless) network that you are getting 5G mobility revenues on. So this is the first time we’ve had that opportunity to drive multiple revenue streams off of the same investment. And so as we roll out the network, we’ll have the opportunity to add more market share. And so we’re very excited about that as we head into ’21 with the progress we’re making this year.
We’re certainly excited about the opportunities that come with the C-band auction. One of the great things about having got the balance sheet in position that we have is it gives us the opportunity to take advantage of items like that when they come along. And I don’t think that – as I look at the balance sheet and I look at the auction that that will provide any inhibitor [ph] to us either in terms of what we do in the auction or how we invest in the rest of the business. In terms of the free cash flow, so the second quarter as you say, a couple of items in there. We had the tax benefit from the item that we recognized in the fourth quarter last year. We also had a timing difference of about $2 billion moving just regular cash payments from second quarter to last week. But all-in-all, look, our cash flow will continue to be strong because we have – obviously we have a strong business with a recurring revenue stream that will continue into the second half of the year. Working capital provided a benefit in the first half with the lower volumes. We’ll see how that plays out in the second half of the year. And I think that will be one of the key determinants of how cash flow looks for the full year on a year-over-year basis. So we’ll see how it plays out, but I certainly expect free cash flow to continue to be strong for the business.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
AT&T Loses Subscribers, Revenues and Earnings drop due to COVID-19 Pandemic
AT&T suffered subscriber and revenue losses across the board in the spring quarter as the novel coronavirus infected every aspect of its business. Overall revenues sank to $41 billion, down 9% from $45 billion a year earlier, with the COVID-19 pandemic accounting for about $2.8 billion of that $4 billion hit.
On the wireless side of the business, which makes up more than half of revenues, AT&T shed 151,000 postpaid customers in Q2-2020, much worse than Wall Street’s consensus estimates of a 4,000-subscriber gain. That loss included 338,000 customers who stopped paying their bills but the company kept on the network to comply with the FCC’s Keep America Connected program. AT&T added 72,000 wireless postpaid subscribers in the year-ago period.
As a result, wireless revenues slipped to $17.1 billion in the quarter, down from $17.3 billion a year ago. But the company’s earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) margin did edge up to 45.6% from 44.9% the year before.
AT&T’s shrinking traditional-TV business showed why the company needs its new online service to succeed. The division holding its DirecTV satellite unit lost 886,000 U.S. premium-TV subscribers and another 68,000 online-only channel bundles. That figure included 91,000 past-due accounts kept connected under the Keep Americans Connected pledge.
The U.S. TV unit ended June with 18.4 million accounts, down from more than 25 million two years ago. AT&T reported its traditional pay TV services, including DIRECTV and its newer streaming option AT&T TV, saw a combined net loss of 897,000 subscribers in the quarter. Meanwhile, its over-the-top streaming service, AT&T TV Now, also lost 138,000 subscribers, following a number of price hikes. In addition, AT&T lost 68,000 streaming video subscribers. Due to that loss, its AT&T Now “skinny” bundle service closed the quarter with 720,000 subs, down 46% from a year earlier.
The company’s newer pay TV service, AT&T TV, only just became available nationwide in March. But despite its “streaming” nature — it ships with an Android TV-powered box to deliver TV over the internet — consumers may now have the opinion that it’s the worst of pay TV wrapped up in a new delivery mechanism. The streaming service is expensive compared with today’s over-the-top and video-on-demand options. It’s also laden with fees for things like activation, early termination and additional set-top boxes. And its bundle with AT&T Internet offers each service for $39.99/month for the first 12 months, but ties subscribers into two-year contracts where prices climb in the second year.
AT&T’s Q1 TV subscriber numbers indicate how quickly the pay TV market is imploding. And perhaps it will decline even more rapidly now that people no longer want to risk coronavirus exposure by having service techs install equipment in their homes. While AT&T TV’s DIY installation may help in that area, it’s unclear if the new service will ever broadly appeal to consumers in the streaming era. AT&T ended the quarter with 18.6 million pay TV subscribers, down from 19.5 million in Q4 when it lost 945,000 subscribers. As a result, AT&T has now lost 3.9 million premium TV subs over the past 12 months, shrinking its customer base by 18%.

Speaking on their earnings call Thursday morning, AT&T executives said they expect those numbers to improve in the third quarter as their retail stores gradually reopen throughout the U.S. However, they also said some stores may not reopen or may close as they consolidate and streamline their retail outlets.
CapEx was $4.5 billion, with gross capital investment at around $5 billion, a difference primarily attributable to the timing of underpayments. AT&T invested an additional $1 billion in new 5G spectrum in the quarter, and invested nearly $400 million in HBO Max, in line with our full year estimate of $2 billion.
Even with the launch of HBO Max this spring, AT&T took its biggest financial hit on the media side of its business. Revenues at its WarnerMedia unit fell to $6.8 billion, down 23% from $8.8 billion last year, because of the absence of theatrical releases, lower TV ad sales and the lack of live sports. Company officials estimated that COVID-19 accounted for $1.5 billion of that decline.
Following what new AT&T CEO John Stankey termed “a flawless launch” of HBO Max, the supersized streaming video service that the company rolled out nationally in late May, the company reported that it closed out June with 36.3 million U.S. subscribers to HBO Max and HBO, up from 34.6 million subs at the end of last year. Citing “strong customer engagement” with HBO Max, Stankey said about 4.1 million customers have signed up so far, including about 1 million wholesale subscribers to AT&T.
AT&T reported an overall loss of 102,000 home broadband subscribers in the quarter, which included about 159,000 past-due accounts. The unit ended the quarter with 13.9 million connections, including DSL. That broadband customer shrinkage came despite 225,000 AT&T Fiber net adds. The latest AT&T broadband decrease marks the company’s fourth consecutive quarterly net loss of advanced broadband subscribers as it continues to fall further behind such big cable rivals as Comcast and Charter in the U.S. broadband market.
The telecom giant posted the overall broadband sub losses because it dropped 304,000 U-verse and other “advanced” broadband subscribers, according to the company’s latest earnings report. It also shed another 23,000 DSL subscribers as that business continues to wind down.
CFO John Stevens said on the earnings call:
Broadband customers continue to look for faster speeds. We added more than 220,000 AT&T Fiber subscribers, and a number of customers opting for gigabit speeds increased by more than 750,000 in the quarter. We now have 4.3 million AT&T Fiber customers, with nearly 2 million of them on 1 gigabit speeds.
On the broadband side, look, I have an appetite to get back to building footprint on fiber, and I think I’ve indicated that before. And I wouldn’t quite pigeon hole it in the way you asked the question relative to households. I have an appetite to build fiber that serves a combination of our needs in the consumer space, what we need to do to deploy 5G and what can help our business segment.
And really, the unique position we’re in as a business is we have lines of business in all those areas, and that should give us leverage in fiber deployment that I think others that are either only a fixed line provider and reselling wireless services or those that are only wireless providers and trying to deploy more fiber-intensive 5G networks don’t enjoy. And my investment thesis and my point of view on our company is that if we do our engineering correctly, and we think about our planning properly, we should be getting yields off of every millennial foot of fiber we put in that nobody else can achieve. And so as I think about this, and as we’re working them through from a planning perspective right now, it’s how we get the leverage across all 3 segments, not just the homes that we pass. Although, ideally, the net effect of that will be there will be communities that we build. I personally do not believe that 5G is a replacement in the near term for suburban, residential, single-family living units. It is an optimal strategy. I think it’s going to be a tough one to beat when there’s embedded gigabit-capable fixed line networks in place. And so I think there’s clearly going to be stuff on the margin that makes sense around that. But I don’t believe in the near term that 5G is the right fixed line replacement strategy in what I would call a typical single-family home infrastructure. And look, if it ultimately moves that way, and we start to see the technology stabilizing, we’re as well positioned as anybody to pivot to that. We certainly got the spectrum and the assets to make that happen; but I’m just not of the mindset right now that, that’s the optimal place to win in the market.
AT&T’s total broadband subscriber base is now shrinking by 3.3% on a year-over-year basis, according to the latest calculations by Craig Moffett, principal analyst at MoffettNathanson. In a report to investors today, he noted that this pace represents “another marked acceleration from the 2.8% decline” the company was experiencing just one quarter ago.Due to these accelerating subscriber losses, AT&T’s broadband financial metrics are clearly trending down as well.
“As with video, they had been pushing ARPU steadily higher, reflecting both mix as well as a clear intention to extract more cash from the business,” Moffett wrote in his report. But, he added: “Growth of just 1.6% YoY in premium broadband ARPU only (they don’t report DSL ARPU) wasn’t enough to offset the 2.5% YoY decline in subscribers; as with video, IP broadband revenue growth is now negative YoY.”
“HBO Max has gotten off to a rather inauspicious start,” Moffett added.
The company said it will continue investing in strategic growth areas like fiber, 5G, FirstNet, HBO Max. Here are the company’s 2020 priorities:
Executing our plan with a market focus on:
• Wireless – Nationwide 5G and FirstNet
• Fiber-based connectivity – for wireless, consumer and business
• Software-based entertainment – HBO Max and AT&T TV
• Increased customer engagement – insights across all platforms’
AT&T withdrew its financial guidance due to the “lack of visibility related to COVID-19 pandemic and recovery,” the company said in a press release, which also stated:
“Our solid execution and focus in a challenging environment delivered significant progress in the quarter, most notably the successful launch of HBO Max, resilient free cash flow and a strengthened balance sheet,” said John Stankey, AT&T chief executive officer. “Our resilient cash from operations continues to support investments in growth areas, dividend payments and debt retirement. We are aggressively working opportunities to sharpen our focus, transform our operations and continue investing in growth areas, with the customer at the center of everything we do.”
“Our resilient cash from operations continues to support investments in growth areas, dividend payments and debt retirement. We are aggressively working opportunities to sharpen our focus, transform our operations and continue investing in growth areas, with the customer at the center of everything we do………I expect we’re going to be dealing with some of these economic challenges in a Covid environment” through the current quarter, Mr. Stankey said. “We’re operating accordingly,” he added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/covid-19-stings-atandt-despite-5g-hbo-max-rollouts/d/d-id/762618?
http://www.broadbandworldnews.com/author.asp?section_id=472&doc_id=762628&
AT&T Execs Talk up “Broadband Resiliency” and 5G with mixed impact from COVID-19
AT&T loses 897K more pay TV subscribers in Q1 2020, adding pressure to HBO Max launch
FCC CBRS Auction for 5G mid-band spectrum in the 3.5GHz band
The FCC’s Citizens Broadband Radio Systems (CBRS) auction is scheduled to start tomorrow, July 23, 2020. 271 qualified bidders are expected to bid for spectrum in what is referred to as the “5G mid-band.”
FCC Auction 105 will offer 22,631 Priority Access Licenses (PALs) in the 3550-3650 MHz portion of the 3.5 GHz band.
In 2015, the Commission adopted rules for shared commercial use of the 3550-3700 MHz band (3.5 GHz band). The Commission established the CBRS and created a three-tiered access and authorization framework to accommodate shared federal and non-federal use of the band. Rules governing the Citizens Broadband Radio Service are found in Part 96 of the FCC’s rules.
Access and operations will be managed by an automated frequency coordinator, known as a Spectrum Access System (SAS). When managing spectrum access, SASs may incorporate information from an Environmental Sensing Capability (ESC), a sensor network that detects transmissions from Department of Defense radar systems and transmits that information to the SAS. Both SASs and ESCs must be approved by the Commission. SASs will coordinate operations between and among users in three tiers of authorization in the 3.5 GHz band: Incumbent Access, Priority Access, and General Authorized Access.
Past sales offered licenses covering entire metropolitan areas at prices that only large carriers such as AT&T Inc. and Verizon Communications Inc. could afford. This one offers smaller licenses — seven in each county in the country for a total of 22,631. That means smaller telecoms, and other companies with new uses for the technology, can bid on spectrum rights in their local areas.
Mid-tier telecoms like Carolina West Wireless and Cincinnati Bell are on the list as well as electric co-ops like the Benton Rural Electric Association and the Illinois Electric Cooperative, Inside Towers reported. Several businesses and schools plan to bid, including: Deere & Company, Duke University and Health System, and the University of Kentucky. Utilities and electricity distributors could use their winnings to expand wireless broadband networks, manage electricity distribution, and install remote meter-reading.
“It’s really a game-changer for all of these non-traditional users,” said Kurt Schaubach, chief technology officer with Federated Wireless, a company based in Arlington, Virginia, that helps coordinate use of the spectrum being auctioned.
“We’ve never had an auction of this size,” FCC Commissioner Michael O’Rielly told Bloomberg. Auction winners can only buy four of the seven licenses available in each county, ensuring that no single user can get all of an area’s licenses. Each of the seven licenses provides rights to use the spectrum across an entire county.
A Raymond James analyst estimates the total value of the mid-band spectrum licenses at potentially $10 billion.
UPDATE:
Gross proceeds reached roughly $3.54 billion at the end of the 39th round of bidding for Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum. Auction tracker Sasha Javid of BitPath says, “Bidders have left the most expensive markets like Los Angeles and San Diego and moved into markets that remain relative bargains compared to their predicted prices derived from past auctions.”
“The last few rounds have been a period of bargain hunting,” Javid told Fierce Wireless after Tuesday’s bidding closed. “Bidders have left the most expensive markets like Los Angeles and San Diego and moved into markets that remain relative bargains compared to their predicted prices derived from past auctions.”
References:
https://insidetowers.com/cell-tower-news-bidding-starts-tomorrow-in-cbrs-auction/
https://www.fcc.gov/auction/105
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/cbrs-auction-tops-3-5-billion-as-bidders-bargain-hunt
TrendForce forecast: Chinese 5G smartphones to hold 4 of top 6 spots by production volume in 2020
Annual 5G smartphone production is expected to reach 235 million units in 2020, an 18.9 percent penetration rate, according to the latest research from TrendForce. Total smartphone production is forecast to reach 1.24 billion in 2020.
Ranked by production volume, Chinese brands are expected to account for 4 of the top 6 spots for 5G smartphone brands in 2020. Huawei tops the ranking, and is expected to produce around 74 million 5G smartphones in 2020. Apple is in 2nd place with a forecast yearly 5G smartphone production of around 70 million units. Samsung will be in 3rd place with production of 29 million 5G smartphones. They are followed by Chinese brands Vivo, Oppo and Xiaomi in 4th, 5th and 6th place with 5G smartphone production volumes of 21 million, 20 million and 19 million units respectively.

Note that this is a forecast, especially for Apple which has not yet announced a 5G smartphone.
Mid-to-low end 5G chipsets released by AP suppliers are expected to raise the penetration rate of 5G smartphones in 2021
TrendForce’s analysis of future developments in the 5G market shows that an aggressive push by mobile processor manufacturers will lead to the rapidly increasing presence of 5G chipsets in the mid-to-low end market, driving 5G smartphone production to surpass 500 million units in 2021, which will potentially account for about 40% of the total smartphone market. Once 5G chip prices reach a stable level this year, smartphone brands may look to gain additional shares in the 5G smartphone market by sacrificing gross margins. In doing so, they are likely to accelerate the drop of 5G smartphones’ retail prices, and the market may see the arrival of 5G smartphones around the RMB 1000 price level by the end of this year. Incidentally, it is worth noting that the penetration rate of 5G smartphones does not equal the usage rate of the 5G network, which depends on the progress of base station construction. Since the current 5G infrastructure build-out is pushed back as a result of the pandemic, the global 5G network coverage will be unlikely to surpass 50% before 2025 at the earliest, with complete coverage taking even longer.

Editor’s Questions:
In the absence of any true 5G standard, e.g. IMT-2020.SPECs, will any of these 5G smartphones work on a 5G network other than the one they are subscribed to? Or will they fall back to 4G-LTE? Will the 5G smartphones sold in 2020 be upgraded to comply with IMT-2020.SPECs and/or 3GPP Release 16 specs?
References:
http://www.trendforce.com/presscenter/news/20200722-10398.html
T-Mobile US: 5G SA Core network to be deployed 3Q-2020; cites 5G coverage advantage
Yet another wireless telco is moving to a 5G Stand Alone (SA) core network, without any standard or even specification (yes, we know about 3GPP TS 23.501 5G Systems Architecture spec in R15 and R16) in place.
In a blog post to assess the progress in the (new) T-Mobile US network four months after the Sprint acquisition, CTO Neville Ray wrote:
We’re also hard at work getting ready to light up standalone 5G this quarter, having recently completed the world’s first standalone 5G data session on a multi-vendor radio and core network, and the first standalone 5G data session of any kind in North America. Standalone 5G will expand our coverage and bring with it improved latency and faster uploads. It will also pave the way for applications that require real-time responses and massive connectivity such as mobile augmented and virtual reality, cloud gaming, smart factories and meters and even connected vehicles.
Analysis:
To the best of our knowledge, there are no 5G SA core networks deployed yet. All the so called “5G” deployments are based on NSA or a LTE anchor via EPC. With a rush of recent 5G SA core announcements, that will soon change
Yet it’s critical to note that ALL of the 5G core work is done in 3GPP– not in any SDO. Moreover, ITU-T SG 13 which is responsible for IMT 2020 Non Radio Aspects recommendations has not received any of the 3GPP R16 documents. And finally, URLLC for both the 5G radio access network and core are not yet complete as there has been no performance testing yet. So how will “improved latency” be realized?
In the absence of any standard or detailed implementation spec, any 5G SA core network deployed within the next year (or longer) will be based on a joint specification effort between the wireless network operator and its 5G core vendor (e.g. Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, possibly Cisco and NEC?).
Here’s what Dell-Oro had to say about 5G SA/5G Core:
During 2020, the industry will progress toward 5G SA. Lab proof-of-concepts and field trials are well underway around the world. Vendors and SPs are working together to learn about the intricacies of implementing 5G SA, which primarily means implementing the 5G Core for 5G NR base stations (a.k.a. Option 2). Some SPs will operate multiple 5G Cores dedicated to consumers, enterprise, public safety, and Internet of Things (IoT). They believe that dedicated 5G Core networks will be able to deliver new agile business solutions at a quicker pace for their respective user bases and more efficient network management.
The 3GPP release schedule is highlighted to emphasize that 5G, and especially the 5G Core standard (3GPP TS 23.501, the overarching specification), still has a long way to go before the full potential of 5G will be achieved. While the industry has been touting 5G for several years, it cannot be realized without the 5G Core.
The 5G Core is known as a Service-Based Architecture (SBA). At a high level, it consists of the User Plane, the Control Plane, and the Shared Data Layer Network Functions. This enables a more resilient core network (CN). Hardware and software disaggregation creates what is known as stateless Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) that run on COTS Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVi). If a hardware failure occurs, a new virtual machine (VM) or Container can spin up on a new server without loss of data because it resides in the Shared Data Layer.
This structure allows for Cloud computing with container-based Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) that permit microservices tailor-made for smaller groups of subscribers. CNFs enable SPs to build a web-scale core with greater degrees of orchestration and automation to bring new services to the market in a few hours or days, as compared to months or years.
More specifically, TS 23.501 -Release 16 provides guidelines for 5G Core virtualized deployments, but does not specify how to implement any of those deployments. Here’s the relevant text:
5.21.0 General
5GC supports different virtualized deployment scenarios, including but not limited to the options below:
– A Network Function instance can be deployed as distributed, redundant, stateless, and scalable NF instance that provides the services from several locations and several execution instances in each location.
– This type of deployments would typically not require support for addition or removal of NF instances for redundancy and scalability. In the case of an AMF this deployment option may use enablers like, addition of TNLA, removal of TNLA, TNLA release and rebinding of NGAP UE association to a new TNLA to the same AMF.
– A Network Function instance can also be deployed such that several network function instances are present within a NF set provide distributed, redundant, stateless and scalability together as a set of NF instances.
– This type of deployments may support for addition or removal of NF instances for redundancy and scalability. In the case of an AMF this deployment option may use enablers like, addition of AMFs and TNLAs, removal of AMFs and TNLAs, TNLA release and rebinding of NGAP UE associations to a new TNLA to different AMFs in the same AMF set.
– The SEPP, although not a Network Function instance, can also be deployed distributed, redundant, stateless, and scalable.
– The SCP, although not a Network Function instance, can also be deployed distributed, redundant, and scalable.
Also, deployments taking advantage of only some or any combination of concepts from each of the above options is possible.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other T-Mo Highlights:
Ray referred to recent analysis from OpenSignal and Ookla on T-Mobile US’ 5G network availability. T-Mo’s reliance on far-reaching 600 MHz spectrum for its “5G foundation,” assures that its 5G footprint significantly outstrips the other national carriers’ 5G coverage areas. Ray wrote:
A new report from Opensignal ranks the T-Mobile network first for 5G availability, meaning Un-carrier customers get a 5G signal more often than customers on any other network – more than twice as often as AT&T and 56 times more often than Verizon! Plus, a new report from Ookla measuring 4G and 5G from over one million customer devices shows that T-Mobile has 5G in nearly 4X more cities than Verizon and AT&T (and 32X more cities than Verizon alone). And T-Mobile customers with a 5G-capable device experience faster overall download and upload speeds than Verizon customers. And look at the Verizon availability score – yep – no typo here – that’s 0.4%…..
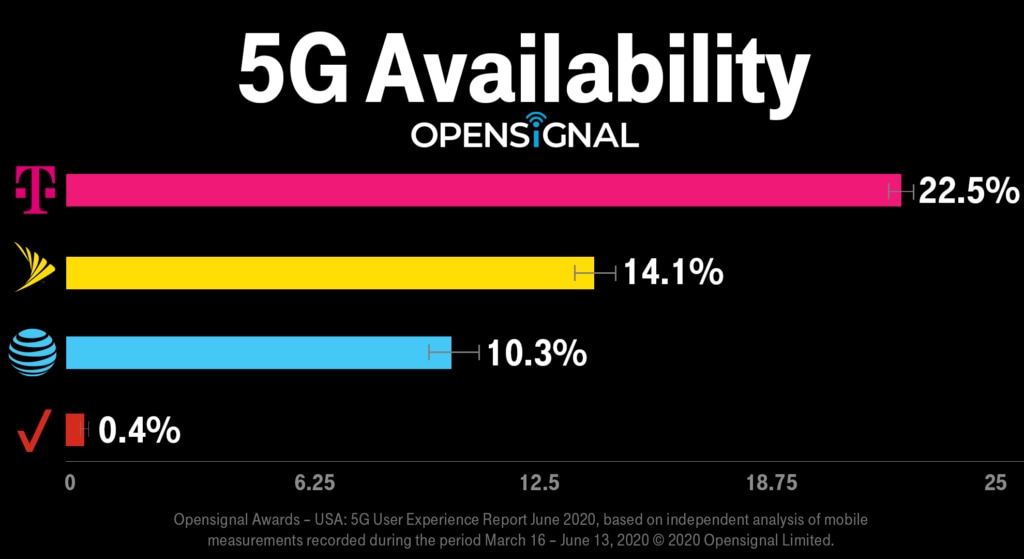
Verizon in particular relied on millimeter wave for its initial deployments, and AT&T has moved to a mix of high- and low-band 5G deployments. Verizon expects to be able to dramatically expand its 5G coverage via the use of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing later this year.
T-Mo’s 5G Spectrum holdings are depicted in this graphic (courtesy of T-Mobile US):

Image Credit: T-Mobile USA
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Regarding 5G speeds, low-band 5G performance tends to look pretty similar to 4G, while mmWave-based 5G is spotty but speedy. Post-Sprint merger, T-Mo is leveraging Sprint’s mid-band spectrum holdings to boost its 5G speed performance and also utilizes mmWave in some urban areas, per its “layer cake” 5G spectrum strategy as per the above graphic.
Ray said in his blog post that T-Mobile US is “rapidly deploying critical mid-band 2.5 GHz spectrum from Sprint” to increase capacity and speed, and announced that mid-band 5G from T-Mo is now live in parts of Chicago, Illinois; Houston, Texas; and Los Angeles, California.
Ray said that mid-band 5G testing is showing average download speeds of more than 300 Mbps and peak speeds of 1200 Mbps. T-Mobile US has also tested the reach of its low-band 5G, recently completing tests with Ericsson, Qualcomm and OnePlus that demonstrated a 5G connection reaching 60 miles from the base station (on 600 MHz).
The T-Mo exec also said that the carrier’s 600 MHz spectrum is finally repacked and cleared of broadcasters, a little more than three years after being auctioned. Virginia Beach, Norfolk and Richmond, Va., Topeka, Kan., Sussex County, Del., and coming soon in Buffalo, N.Y.
Related to the carrier’s commitments to the Federal Communications Commission as part of the merger with Sprint, Ray said that T-Mo is moving ahead with the expansion of its wireless broadband internet service pilot. In Grand Rapids, Michigan, the carrier has started offering the service to people who aren’t existing T-Mobile US customers. Ray noted that the carrier plans to offer T-Mobile Home Internet in more than 50% of all U.S. zip codes.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/network/accelerating-5gforall