Month: January 2020
Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg’s technology related remarks on 4Q2019 earnings call
Note: Copy editing was done to correct grammar errors and delete extraneous words/phrases.
- Our partnership with AWS Amazon on the 5G mobile edge compute, is a totally new way of accessing a market that we have not been into.
- We fulfilled our 5G commitment to deploy in 30 cities. We made 31. We said we’re going to launch 5G Home with the NR standard. We did that, and we said we’re going to launch the first 5G mobile edge compute. We did that in Chicago in December.
- If you think about our priorities for 2020, first of all, continue to grow on the core business. We showed this year we can continue to grow 4G and our core business, and that we’ll continue to do in 2020 as well, including building our network to be the best network in this market. Secondly is leveraging our new assets that we’re building.
- We’re building out fiber. We’re building our 5G and seeing that we can start leveraging that with our customer.
- This year, we’ll continue to have a lot of focus on our 5G build-out and we will come back to that later on how we see the 5G market when we will have an Investor Day later in February.

Verizon claims 5G leadership with 31 mobile cities, 16 NFL stadiums, 4 basketball arenas; launched 5G Edge and NR-based 5G Home
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- We’re very excited about the opportunities that Verizon business group has, because that’s why we started building the Verizon Intelligent Edge Network some three, four years ago in order to actually address this market in the best way, and the traction we are seeing with our customers is really good.
- So I think that our technology department have no constraints on what they need to do in 2020. This is what they have plans for in order for us to continue to fortify our 4G network, to continue with strong additions in the 5G as well as continue with our fiber build. And when it comes to the monetization of the fiber build, we’re already starting to do that.
- Many of the fibers right now are going to our cell sites on air because that was a part of it. Then, of course, it has come a little bit later in monetization for our small and medium businesses and enterprise business, etc. But clearly, we’re already now seeing the benefits of doing that. So going into 2020, I think we have a very solid capital allocation for our capex.
- Ronan Dunne (VZ CTO) already said in the beginning of the year that we’re going to have some 20 5G devices coming out in the market this year. So of course, we’re going to see more 5G devices coming out. It’s going to be more build in the markets in 2020 than we had last year. So of course, this is a year that there is going to be even more 5G things coming in. When it comes to any particular phones coming out in the market, we cannot really comment on it because that, we’ll leave to the company to do.
- If this is a market which has a high degree of iOS, that means that when a 5G phone will come out from Apple, that will be important for many consumers to look into what they think is a good change. In our case, I think we’re building a unique 5G experience with our millimeter wave that nobody else is building and have the capability to do. So I think that’s really where the difference will come.
- We already have the best 4G network as you have seen in the latest J.D. Power and RootMetrics. We’re going to continue to have that. So we’re going to give the best experience for customers. And we — and I’m confident that how we are building the network will make a big difference. And that’s why we also feel very confident if — with all these devices coming out, including if the iPhone would come out, that we will have a good chance to actually grab more customers that want to be on our network. When it comes to the spectrum and all of that, I mean, I think that I might have talked about this so many times. We have all the assets to deploy our 5G strategy when it comes to millimeter wave and using dynamic spectrum sharing, be available nationwide when our customers are ready.
- Everything from spectrum to how you densify (wireless) networks and what type of software you put in, and that’s a long-term planning how to do that right. And I think that’s something where you — or people around us go wrong when I look at us because think about how we have been performing, and many actually thought that we would never sustain an unlimited. And the more the network is growing, we’re getting more and more headroom as we’re continuing deploying our software and the engineering capabilities we have in the company.
- We think the C-band (3.7-to-4.2 GHz) is an important spectrum for many reasons. That frequency will be global. So roaming will be done on it, and that’s very important for U.S. market to get into that. And it’s very important for Verizon to get into that. But it’s not hindering our strategy right now to deploy a great 5G network and be able to capture the market for 5G.
- On the CBRS, as you know, we have already started for quite a long time ago to do trials and see how it works, and it works fine. We think it’s a good addition to the portfolio that in order to see that we get good customer expectations. So we think CBRS is an important spectrum, even though it is sort of more share than anything else, but it’s going to be definitely something we’re using as it comes out.
- Secondly, when it comes to the 5G Home, you’re confirming, actually what we have in front of us. The next-generation chipset that goes into the CP for 5G Home will come out. At least, the plan right now is in third quarter, which means that commercial product is probably coming out a little bit later because it takes some time from the chipset to the device. By then, we will have, of course, deployed far more millimeter wave across the country, so we will be able to start launching many more markets when that happens. So that will come back to a little bit more about that when have our Investor Day the 13th of February, talk a little bit more about it. But that’s in the grand scheme, the plans for 5G Home, and that’s no different from what we said half a year ago.
- When it comes to the mix and match, we want to give our (residential) customers options on top of the broadband. If it’s the fiber broadband or if it’s the 5G Home broadband, we want to give them options. Of course, one option is always to have a broadband and having over-the-top services. But another is, of course, giving the mix and match option right now to see that they use the right packages that is more fitted for them. Still, of course, it’s what they can choose whatever channels you have because they come in packages. But the early — or early indication is, of course, that customers that has been on trial for a month, they clearly see what channels they’re using and what package we can suggest for that, that is going to be more optimized. So I think for us, we just think about our customers and where the market is going, and we want to give them the option of actually having different ways they can address the market when it comes to their content consumption. And I think it’s good for our customer experience, but it’s also good for our customers because all of them can do it. So as you said, it’s a little bit early, but I think that our customers are very happy that we’re giving them this option. And I think this is what everyone see where the market is going, meaning more and more over-the-top content is coming in and you want — you need thought, mixing and matching that. And here, we have a great opportunity given our service strategy, and we can work with all the type of option in the content market as we’re not owning any content.
- We always do the trade-off between owning and leasing or sharing fiber with someone, and that is a very prudent or financially disciplined way of looking at our deployment. In many cases, we see it as owning it has really an advantage for us because of the multi-use of our network. Now we’re doing sites all the time. We’re going to create revenue for our business side. So we probably have a couple of years left on doing that. But in general, I feel good about the pace we have right now and the multi-use of the fiber we have. And I think this is one of the most critical assets in a network today — in today’s world, especially as we build Verizon Intelligent Edge Network and you want actually to start delivering the 5G experience that we’re expecting. We need this fiber to be there. So that’s basically where we are with the fiber.
- We have already gotten Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to work from the software point of view. And the majority of our baseband is ready for taking DSS. So what we have said, I’m not going to give you an exact date, but I’m going to tell you, we’re going to be ready when we feel the market is ready and our customers need to have that coverage. And again, remember, we want to have the best network performance-wise. We don’t want to deploy it because it’s called 5G. We want to see that we actually give a superior performance to our customers. And that’s why we think that the millimeter wave, what we’re doing there is extremely important because we talked about 10 to 20x, at least more throughput and speed than we have on the 4G network, and we still have the best 4G network. So I think that’s what we already assessed. When we meet at the Investor Day, we’re going to talk a little bit more about the technology sector.
- When it comes to the 5G and where we are, I think that you saw last year that we had a strong deployment coming in during ’19, but of course, we have even higher ambitions in ’20. And we will also come back and talk a little bit about — more about that. But it goes in all three directions in our multipurpose network. It’s for the mobility case, for the home case, and it’s also for the 5G mobile edge compute case, not forgetting that, because all three of them are using our multipurpose network. And when it comes to use cases, I can do some of them.
- On the mobile edge compute, we see a lot of optimization in factories. We see private 5G networks in order to keep the data and the security and the throughput in a facility, if that’s a campus, whatever, that use case has come up very early on.
- What we can do with millimeter wave in the stadium, how we can use broadcasting cameras with 5G, a lot of new innovation, both with consumer, but also for the distribution of content. With our spectrum positioning, we basically are limited on the uplink when it comes to stadiums, which is the big blocker today in a stadium. So I think you’re going to see quite a lot next four or five days on consumer cases (at the NFL Superbowl in Miami, FL) as well as we will continue to give you more insights to it the next couple of weeks and when we meet in New York here.
- We have told you where 5G will come in, which is more of 2021. So we work with assets we have right now, but we build also a great foundation on 5G going forward for the years after.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2020 Priorities for Verizon: Executing 2020 from a position of strength
1. Strengthen & Grow Core Business
• Extend our network leadership through continued innovation
• Strengthen and grow core business in Consumer, Business & Media
2. Leverage Assets to Drive New Growth
• Scale 5G / MEC / OneFiber & other assets for new growth
• Differentiate brand through trust & innovation
3. Drive Financial Discipline & Strength in Balance Sheet
• Accelerate revenue and earnings growth to drive strong cash flows
• Disciplined capital and operating spend
4. Infuse a PurposeDriven & CustomerCentric Culture
• Put customers at the center of everything we do
• Drive responsible business as part of our strategy
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/investors/quarterly-reports/4q-2019-earnings-conference-call-webcast
U.K. Allows Huawei to Build Non Critical Parts of its 5G Network
Huawei is given permission to build noncritical parts of the network, despite U.S. security concerns:
As widely expected, the UK government today decided to allow Huawei’s network equipment to play a limited role in its national 5G networks. After a security review, the UK’s National Security Council (NSC) made the decision today following a meeting chaired by Prime Minister Boris Johnson.
British officials from senior government departments held a meeting last Wednesday and made the recommendation to allow the world’s #1 network equipment vendor to play a “limited role” in national 5G networks. Today, that recommendation was made final.
Huawei is the leading 5G global network equipment vendor, with relatively few alternative providers — such as the European firms Ericsson and Nokia — none of whom are considered to offer a like-for-like option at this stage.
UK Digital Secretary Baroness Morgan said:
“We want world-class connectivity as soon as possible but this must not be at the expense of our national security. High-risk vendors never have been and never will be in our most sensitive networks.
“The government has reviewed the supply chain for telecoms networks and concluded today it is necessary to have tight restrictions on the presence of high-risk vendors.”
Huawei has been under scrutiny over alleged ties to the Chinese government, an allegation the company has repeatedly denied. The U.S. has urged the UK to ban equipment from the Chinese vendor over national security concerns and American officials issued their British counterparts with a dossier highlighting perceived risks earlier this month.
The UK has always maintained that any decision on Huawei would be evidence-led and based on its own reviews, but the result will nonetheless anger the U.S. which has been pushing for Huawei to be totally banned from 5G networks of allies.
Huawei, and other “high-risk” vendors, will face the following restrictions:
- Excluded from all safety-related and safety-critical networks in critical national infrastructure.
- Excluded from security-critical ‘core’ functions, the sensitive part of the network.
- Excluded from sensitive geographic locations, such as nuclear sites and military bases.
- Limited to a minority presence of no more than 35 percent in the periphery of the network, known as the access network, which connects devices and equipment to mobile phone masts.
Governing that Huawei has no more than 35 percent presence in the periphery of the overall 5G network is particularly interesting. This restriction ensures that if Huawei’s equipment was later compromised, or deemed too risky, around two-thirds of the UK’s 5G network would remain unaffected.
The UK is upgrading its wireless network technology for the rollout of 5G. PHOTO: DANNY LAWSON/ZUMA PRESS ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
John Strand of Strand Consult wrote today in a note to subscribers:
- The decision relates to the use of Huawei equipment in the United Kingdom. In practice, this means that the May 2018 total ban on ZTE equipment by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre will continue.
- Huawei are now classified as a high risk vendor following the conclusions of the Telecoms Supply Chain Review.
- The use of Huawei equipment will be prohibited in core networks. This means that the backbone of UK mobile networks must not contain Huawei equipment. This policy demonstrates that UK authorities recognize the risk of equipment made by entities affiliated with the Chinese government. If Chinese-made equipment was safe, Huawei equipment would not be prohibited from the network core.
- The use of Huawei in the radio access network (RAN) will be limited to 35 percent of the active equipment. This limits the amount that Huawei can sell in the UK. It also means that UK operators will have to prioritize network upgrades in the Western part of the country where Huawei equipment is largely deployed. In practical terms, it will not be possible for an operator to use Huawei for more than 35 percent of the equipment and then use another Chinese or Huawei-white labeled product for the rest of the network, or a portion thereof. The goal of the policy is to limit equipment from Chinese owned and/or affiliated entities, even if it is not explicitly written.
- The use of Huawei equipment will be expressly prohibited in sensitive geographical areas in the UK, areas selected for national security reasons. Indeed, this is already practiced in France where Huawei equipment in restricted in Toulouse, home of Airbus and the European aerospace industry. A similar policy exists for Brest where French nuclear submarines are located. Read more about the French decision.
Overall, the UK policy will send a strong signal to the rest of Europe and the world that the use of Chinese equipment poses a security risk and should be limited. The UK and French decisions were developed to protect industries, institutions, and assets of national importance in specific geographical areas.
The U.S. model restricts its military from using Huawei and ZTE, regardless of location. Moreover, the Federal Communications Commission prohibits the use of its subsidies for the purchase of Huawei and ZTE equipment and is considering the requirement of removal of Huawei equipment for future subsidies.
Additional US policy restricts American firms from transacting business with Huawei for sensitive technologies. US telecom operators, noting the risk, have largely opted not for Huawei or ZTE, outside of a few exceptions. This is explained in Strand Consult’s research note The pressure to restrict Huawei from telecom networks is not driven by governments, but the many companies that have experienced hacking, IP theft, or espionage.
The UK new policy is a step in the right direction, and it underscores the need for greater scrutiny of technology from firms owned and/or affiliated with the Chinese government. The security risks are real and networks are key vulnerability. Indeed, scrutiny should extend beyond the network equipment to other vulnerable products and services; systems can be compromised by devices attached to networks as well as from software running over it. See Strand Consult’s research note “The debate about network security is more complex than Huawei. Look at Lenovo laptops and servers and the many other devices connected to the internet.”
Strand Consult expects that the security standards required for public safety networks will be strengthened and translated to commercial telecom networks. It is likely that some UK operators will claim that the new policy will be unduly expensive. Strand Consult examines such claims in the report ”The real cost to rip and replace Chinese equipment from telecom networks.”
Notably 2G / 3G / 4G equipment must be replaced anyway in the move toward 5G. Huawei is not the only vendor, and alternatives are price competitive. Moreover, when it comes to 5G, network rollout policy is far more consequential than the choice of equipment vendor. The view that Huawei is necessary for 5G is a myth; indeed, the US has taken a leadership position on 5G without using Huawei equipment.
Looking at the historical facts, it is not difficult to find operators which have swapped their networks with a new supplier. This need not come as a premium for shareholders. Strand Consult reviews the financial data and case studies from the major network swap it observed in 2010 – 2016.
The UK government, with Boris Johnson at the forefront, can improve the prospects for 5G in a meaningful way. In the UK, as in many other countries, it is both difficult and expensive to build mobile infrastructure. Strand Consult’s analysis show that the terms and costs associated with obtaining permits and leasing land for mobile masts and towers is artificially expensive. In the UK, operators have for many years and with limited success tried to change the terms.
In Denmark, on the other hand, Strand Consult has helped to create transparency so that authorities get the information they need to create the needed rollout policies. As a result, the total rental costs for mobile operators have fallen by over 20 percent, and it has become significantly cheaper and easier to upgrade and build existing and new mobile infrastructure. Learn more about the project here ”How to deploy 5G: Best practices for infrastructure, regulation and business models.”
Huawei will likely claim that the UK decision doesn’t hurt its prospects. This is probably to save face. The fact is that Huawei will be subject to increased restriction and will not be able to enlarge its market share. Moreover, there is no change on the ZTE ban. The UK makes clear that Chinese equipment is not allowed in the core network. Moreover, when it comes to RAN, there are also strict limitations.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In September 2018, a Canadian official argued that allowing Huawei to operate improves security. If a specific vendor’s equipment is compromised, having others in operation means less of the overall network is affected.
While Huawei will be breathing a sigh of relief at the UK’s decision – so will the country’s providers. In a statement, BT wrote:
“This decision is an important clarification for the industry. The security of our networks is an absolute priority for BT, and we already have a long-standing principle not to use Huawei in our core networks. While we have prepared for a range of scenarios, we need to further analyse the details and implications of this decision before taking a view of potential costs and impacts.”
All four of the UK’s major operators had already begun deploying 5G equipment from Huawei. Stripping Huawei’s gear and buying and installing replacements would have been costly and time-consuming.
Andrew Stark, cybersecurity director at Red Mosquito, said:
“With Huawei kit already integral to the UK 3G and 4G networks, shifting to 5G with them offers the path of least resistance and increases chances of telecom companies meeting tight roll-out targets. There are currently only two other tech players capable of providing hardware for 5G, namely Nokia and Ericsson.”
The UK says its decision was made after the NCSC “carried out a technical and security analysis that offers the most detailed assessment in the world of what is needed to protect the UK’s digital infrastructure.”
However, not all of the UK government will be so welcoming of today’s news. Conservative MP Bob Seely recently said “to all intents and purposes [Huawei] is part of the Chinese state” and involving the company would be “to allow China and its agencies access to our network.”
While UK intelligence officials clearly decided the benefits outweigh the risks, several concerns have been raised about Huawei’s equipment in recent years.
The dedicated Huawei Cyber Security Evaluation Centre (HCSEC) reported in 2018 that it could no longer offer assurance that the risks posed by the use of Huawei’s equipment could be mitigated following the “identification of shortcomings in Huawei’s engineering processes”. Concerns were raised about technical issues limiting security researchers’ ability to check internal product code and the sourcing of components from outside suppliers which are used in Huawei’s products.
A follow-up report from HCSEC in March 2019 slammed Huawei as being slow to address concerns and claimed that “no material progress has been made by Huawei in the remediation of the issues reported last year, making it inappropriate to change the level of assurance from last year or to make any comment on potential future levels of assurance.”
Just a month earlier, the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) – the world’s oldest independent think tank on international defence and security – warned about the use of Huawei equipment: “It is far easier to place a hidden backdoor inside a system than it is to find one,
“In the likely, but unacknowledged, battle between Chinese cyber attackers and the UK’s Huawei Cyber Security Evaluation Centre, the advantage and overwhelming resources lie with the former.”
The UK’s approach to Huawei has been decided, but it doesn’t feel like the end of the debate.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.telecomstechnews.com/news/2020/jan/28/huawei-reprieve-uk-government-permits-5g-gear/
https://techcrunch.com/2020/01/28/uk-will-allow-huawei-to-supply-5g-with-tight-restrictions/
https://www.wsj.com/articles/u-k-allows-huawei-to-build-parts-of-5g-network-11580213316
Continued Growth for South Korea’s 5G Vendors: Samsung + Many Others!
by Shim Woo-hyun of The Korea Herald (Korea)
The earnings of South Korean 5G equipment companies could regain momentum as global telecom firms seek to increase their capital expenditure on 5G network infrastructure.
The improved prospects of Samsung Electronics, the major provider of telecom equipment here, will also lead to earnings improvements of other companies, local financial reports said.
At large, 5G equipment providers here recorded significant growth so far until the third quarter last year. Their stock price had also skyrocketed until October when the global demand eased.
Radio frequency company KMW is one of the local 5G equipment firms that is expected to mark better earnings. It supplies massive multi-input and multi-output (MIMO) devices to global telecom and tech players such as Samsung, Huawei, Ericsson, ZTE and Nokia.
KMW is anticipated to mark 740 billion won ($633 million) in sales and 160 billion won operating income in 2019. In 2018, the company posted sales of 296.3 billion won, while its operating loss was 26.2 billion won.

Other local players that look forward to better performance this year include SeoJin System, OE Solutions and Ace Technologies.
- SeoJin manufactures cabinets, cases and enclosures for network equipment. The sales improvement of SeoJin is largely backed by the increase in remote radio head orders from Samsung’s 5G access unit. SeoJin’s sales in 2019 are estimated to have increased by 30 percent to reach 430 billion won, while its operating profit soared 70 percent to 63 billion won.
- Optical transceiver provider OE Solutions will also continue upward trend as it has been receiving orders from key players — Samsung, Ericsson and Huawei. The Gwangju-based firm started supplying its products to Japanese telecommunication firm KDDI last year through Samsung Electronics which has partnered with the Japanese firm to provide 5G equipment over the next five years.
- Ace Technologies, a local provider of telecom antennas, filters and massive MIMO devices, is also expected to show improved performance from its major customers — Ericsson, Samsung Electronics, KT and SK Telecom. Ace’s 2019 sales are estimated to reach 410 billion won, up 10 percent compared to 2018. Its operating profit is also expected to improve at 13 billion won, a 70 percent increase on-year.
Local financial reports said that the earnings of GaN-powered transistor manufacturer RFHIC could also rise along with the expansion of its partner Samsung Electronics. The company’s sales to Huawei, however, could remain stagnant, experts said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
According to reports, the sales of the above mentioned companies last year are expected to reach 1.8 trillion, an increase of 70 percent compared to the previous year. The combined operating profit of the firms are also anticipated to reach some 300 billion won, up 500 percent from 2018.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This article originally appeared at: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20200127000188
China has more than 1.6 billion mobile subscribers (> China’s entire population!)
China has a little more than 1.6 billion mobile subscribers as of year end 2019. That’s remarkable, considering China 2019 population is estimated at 1,433,783,686 people at mid year 2019 according to UN data.
- China Mobile gained more than 3.73 million new customers in December 2019, up from 2.95 new additions in November.
- China Telecom added 1.18 million new subscribers.
- China Unicom lost 2.7 million users in December.
China Mobile remains by far the largest Chinese cellular operator, with 950.2 million customers, of which 758 million are 4G users.
China Telecom, which has been growing steadily in the past year, has moved into second place with 335.57 million mobile customers, compared to 318.4 million at Unicom.
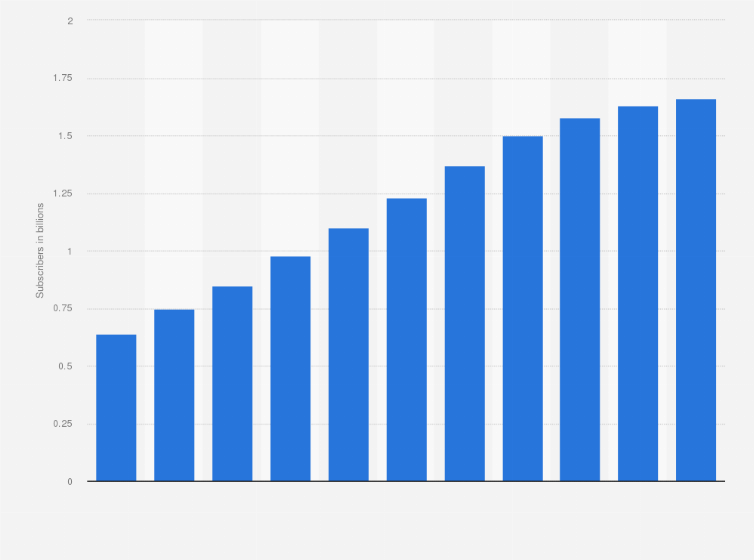
Number of mobile phone subscribers in China from 2008 to 2018 (Source: Statista.com)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Mobile is also biggest in the fixed broadband market, ending 2019 with a total of 187.04 million users. However, in December 2019, it lost 609,000 fixed broadband customers, compared to a net addition of 694,000 in November and more than 1.9 million customer adds in October. China Telecom saw its fixed broadband subscriber base drop by 0.62 million in the month to 153.13 million, and Unicom lost 975,000 for a total of 83.47 million fixed broadband subscribers.
On November 1, 2019, Chinese operators China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom announced the rollout of 5G mobile phone services to customers. The three operators started by offering 5G plans for CNY 128 per month.
While the rollout of 4G in China took 46 months, 5G is expected to be available within ten months. China Mobile, the biggest of the three operators, already has 10 million customers interested in 5G, who are the first to access the services at launch. China Mobile earlier announced it expects to end 2019 with 5G coverage of 50 cities, and add another 340 cities in 2020, covering a population of 600-700 million people.
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/china-ends-2019-with-more-than-16-billion-mobile-customers–1323638
China Internet penetration reached 61.2% in 1st half 2019; 99.1% access Internet via mobile phones!
BICS: 4G roaming traffic doubles for the third consecutive year
4G roaming traffic doubled in 2019 for the third consecutive year, according to a BICS report. Subscriber demand for high-capacity borderless connectivity continues to boom. The findings were from sourced from BICS’ global network, which connects over 700 operators and 500 digital service providers and carries over 50% of global data roaming traffic. The report show an uplift in roaming traffic across all continents, fueled by increased global travel, adoption of roaming tariffs, travel SIMs, and IoT devices.

“The exponential growth in roaming traffic highlights how important international connectivity has become to the subscriber experience,” commented Mikaël Schachne, CMO and VP Mobility & IoT Business at BICS. “Through the provision of seamless, cross-border 5G connectivity, operators will be able to create new revenue streams and support a wide range of new and innovative use cases in areas such as automotive, gaming, telemedicine and logistics. As carriers launch 5G networks, roaming must be at the heart of their offerings to deliver maximum value for subscribers.”
Carrying over a third of all global roaming traffic, BICS is connected to every single mobile network and has a presence in over 180 countries. Through BICS’ IPX platform, service providers can establish roaming and inter-working agreements with over 600 members on the network, enabling them to offer subscribers high-quality data roaming with other mobile and fixed network operators globally. In 2019 BICS consolidated its position at the center of the global connectivity ecosystem, with one in three operators worldwide now utilizing its 4G roaming services.
Last year also saw momentum build for both national and international 5G; approximately 50 national 5G networks are now live, while BICS pioneered several live 5G roaming services, including a 5G intercontinental roaming service between Europe and Asia. In 2020 BICS predicts 5G roaming will gain further traction, as service providers progress 5G deployments and launch 5G roaming to support increasing demand from both subscribers and industries requiring high-speed, ultra-low latency 5G data connectivity.
In July of last year, BICS launched a 5G roaming service between Swiss operator Swisscom and South Korean carrier SK Telecom. The 5G roaming service delivers high-speed, low latency 5G data connectivity between two continents, with operators using BICS’ 5G global IPX network.
Editor’s Caveat:
There won’t be much if any roaming on 5G until the industry agrees on IMT 2020 standards which must include a legitimate 5G Core network (as per 3GPP Release 16).
References:
https://bics.com/news/4g-roaming-traffic-doubles-for-the-third-year-as-industry-gears-up-for-5g/
SK Telecom: Over-the-Air Transmission on Multi-Vendor Commercial Stand Alone 5G Network
SK Telecom today announced that it has successfully accomplished the world’s first standalone (SA) 5G data session on its multi-vendor commercial 5G network in South Korea.
Editor Notes:
1. T-Mobile claimed they were the first carrier to successfully test 5G SA operation which we covered in this article: T-Mobile Claim: 1st Standalone 5G Data Session on a Multi-Vendor Radio and Core Network.
2. Definition: 5G Stand Alone (SA) refers to using 5G specifications (in cells/base stations and endpoints) for both signalling and information transfer. All 5G deployments to date use NSA operation which uses 4G-LTE signaling and 4G-Evolved Packet Core (EPC) as well as LTE network management
SA operation requires the new 5G Packet Core (5GC) architecture from 3GPP instead of relying on the EPC to allow the deployment of 5G without the LTE network.
Ericsson provides 5G Standalone 5G facts:
- New cloud-native 5G Core
- Simplified RAN and device architecture
- The only option to provide same 5G coverage for low band as legacy system
- Supports advanced network-slicing functions (not standardized yet – may be in 3GPP Release 16)
- Facilitates a wider range of use cases for new devices
- Brings ultra-low latency (that won’t happen to completion of 3GPP Release 16 in June 2020 if then)
3. South Korea was the first country in the world to launch 5G services and currently has some of the most wide ranging 5G networks anywhere in the world. That’s largely due to government co-ordination with the three large South Korean wireless network operators – SK Telecom, KT and LG Uplus.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
With this major breakthrough in 5G, SK Telecom says it is now fully set to provide standalone 5G services. SK Telecom said that it plans to launch the world’s first 5G SA service in the first half of this year.
The standalone 5G data call took place on January 16, 2020 in Busan, the second largest city in Korea, using SK Telecom’s commercial 5G network deployed in that region.
To achieve this standalone 5G milestone, the company applied standalone 5G New Radio (NR) software to its existing non-standalone (NSA) 5G base stations, and completed multi-vendor interoperability between network equipment of Ericsson and Samsung.
SK Telecom has also applied key 5G technologies such as network slicing and mobile edge computing (MEC) to its standalone 5G network. Network slicing is being highlighted as an essential technology for providing optimal support for different types of 5G services by partitioning a single physical network into multiple virtual mobile networks. MEC minimizes latency by providing a shortcut for data transmission through installation of small-scale data center at 5G base station or router. MEC can improve the performance of ultra-low latency 5G services such as cloud gaming, smart factory and autonomous driving.
“With the successful standalone 5G data call on our multi-vendor commercial 5G network, we are now standing on the threshold of launching standalone 5G service, a key enabler of revolutionary changes and innovations in all industries,” said Park Jong-kwan, Vice President and Head of 5GX Labs of SK Telecom. “SK Telecom will offer the best 5G networks and services to realize a whole new level of customer experience in the 5G era.”
About SK Telecom
SK Telecom (NYSE: SKM) is the largest mobile operator in Korea with nearly 50 percent of the market share. As the pioneer of all generations of mobile networks, the company has commercialized the fifth generation (5G) network on December 1, 2018 and announced the first 5G smartphone subscribers on April 3, 2019. With its world’s best 5G, SK Telecom is set to realize the Age of Hyper-Innovation by transforming the way customers work, live and play.
Building on its strength in mobile services, the company is also creating unprecedented value in diverse ICT-related markets including media, security and commerce.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or [email protected].
………………………………………………………………………………………….
Related—Big 3 Korean carriers vow to offer seamless telecom service during lunar new year:
Korea’s big three mobile network operators have committed to provide “seamless” connectivity over the Korean Lunar New Year festivities, according to reports in the Korean press.
SK Telecom, KT and LG Uplus all committed to provide extra capacity in their networks over the Seollal period, as Koreans travel home for the holiday, placing extra strain on the country’s networks, particularly in public spaces such as train stations and along the country’s roads.
“To respond to possible data traffic jams, LG Uplus checked out base stations for 4G and 5G networks and will run an emergency situation room. We will also increase the number of technicians for highly-populated areas such as airports,” the company told journalists from the Korea Times.
SK Telecom predicted that it would see a 24 per cent hike in data traffic over the holiday period, as vacationing Koreans make use of high demand services like UHD video streaming and geolocation services. SK Telecom identified 750 busy areas that will receive special attention over the period, while KT said that it would be proactively managing traffic in 970 locations across the country.
All three mobile network operators have said that they will have more technicians and service staff working over the holiday to help them cope with the increase in demand.

Technicians of SK Telecom check network quality at an airport, Sunday. Photo Courtesy of SK Telecom
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
LG Uplus will also run an emergency response center at its office in Magok, western Seoul during the holiday.
The company has completed inspections of 4G and 5G base stations installed at highway rest areas, SRT and KTX train stations and bus terminals throughout the country.
“To respond to possible data traffic jams, LG Uplus checked out base stations for 4G and 5G networks and will run an emergency situation room. We will also increase the number of technicians for highly-populated areas such as airports,” the company said.
KT designated 970 places including highways, department stores, bus terminals, airports, train stations and other busy areas in the country as data quality management zones.
South Korea was the first country in the world to launch 5G commercial services with the big three wireless carriers doing so on the same day.
References:
https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/tech/2020/01/133_282175.html
Verizon FioS will no longer offer home television and internet on bundled plans
On January 9, 2020, Verizon stated it was eliminating multi-year contracts, multi-service bundles, weird added fees at the bottom of bills, and other nickel and dime cable charges. Instead, Fios will offer Internet at a couple of speeds, priced at $40 to $80 monthly, and a couple of TV packages, priced from $50 to $90. The channel line ups of the TV packages will be more customizable than in the past, as well.
“Customers have been loud and clear about their frustrations with cable, and we’ve listened. As a result, we’re transforming our approach to Internet and TV offers by giving customers more choices and more transparency,” says Frank Boulben, Senior Vice President of Consumer Marketing and Products at Verizon. “Customers are tired of having to buy a bundle with services they don’t want to get the best rates, and then discover that those rates didn’t include extra fees and surcharges. We’re putting an end to the traditional bundle contract and putting customers in control.”
To replace bundles, Verizon has chosen to give consumers greater flexibility through what it calls Mix & Match. With Mix & Match, Verizon customers can choose between three internet tiers ranging from $40 to $80 per month, and from cable packages offered either through Verizon’s in-house Fios service or through the company’s partnership with YouTube TV. Verizon offers three Internet speed options for FiOS customers – 100 Mbps, 300 Mbps and Gigabit Connection.
NOTE: Triple-play bundles refer to long-term contracts with a company such as Comcast Corp. or Charter Communications Inc. that provide internet, television and landline phone service for one “discounted” rate. These packages force you to have an old-school home phone number, seemingly just for telemarketers to call, and dozens of TV channels you’ll never watch but will nevertheless subsidize. However, many subscribers only want a fast internet connection to binge on Netflix or Amazon Prime and gain access to a handful of their favorite network shows.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Mix & Match builds on Verizon’s strategy to adapt to changing consumer habits; the company has reported a net loss in Fios TV subscribers every quarter since 2016 – coinciding with the rise of subscription-based internet streaming services.
Consumers can change their service selection each month, whereas Verizon had previously offered one- and two-year contracts for discounted introductory bundles. This practice sowed frustration among consumers, as many wanted internet alone but were forced to also buy home television, or because the service price escalated after the introductory contract expired, Verizon SVP Frank Boulben told The Wall Street Journal.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T is emblematic of the limitations of bundling in a sufficiently competitive environment: The company used lots of debt to pay over $150 billion to purchase DirecTV and Time Warner ($67 billion acquisition of satellite television provider DirecTV in 2015 and $86 billion acquisition of Time Warner in 2018). The goal was to build up its media assets and combine with its wireline and wireless networks to distribute new content. Unfortunately for AT&T, it hasn’t been able to leverage those combined assets via bundles in a way that drives consumer interest and subscriptions. AT&T executives proclaimed the mergers would bring “a fresh approach to how the media and entertainment industry works for consumers, content creators, distributors and advertisers.”
Many Wall Street analysts at the time expressed concern that the debt incurred from the company’s mergers would make that goal untenable. And they were right! AT&T’s bottom line has been bleeding from loss of DirecTV customers while they have not yet been able to monetize the content obtained from Time Warner.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
As Verizon runs into similar problems in the home, it’s increasing the modularity of its product options and also expanding into segments like VR and cloud gaming. How Verizon fares with this new approach in its home business will be an instructive lesson for the wireless industry as a whole — particularly as mobile operators continue to pursue bundling as a strategy outside the home as well, pairing mobile offerings with media to draw in and retain mobile subscribers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-disrupts-cable-industry
https://www.businessinsider.com/verizon-discontinues-bundling-internet-cable-services-2020-1
https://www.latimes.com/business/story/2020-01-09/verizon-breaks-the-cable-bundle-but
Taiwan raises more than 138 billion TWD in 5G spectrum auction amongst fierce competition
Taiwan completed its 5G spectrum auction on 16 January, after 261 rounds of bidding. Total bids reached 138.08 billion TWD (approximately USD 4.6 billion), DigiTimes reports, citing a statement from Taiwanese regulator National Communications Commission (NCC).
- Chunghwa Telecom, Taiwan Mobile, Far EasTone Telecommunications and Taiwan Star Telecom won spectrum in the 3.5GHz band. Asia Pacific Telecom also participated in the auction. According to the same source, the unit price per 10MHz bandwidth in the 3.5GHz band reached TWD 5.075 billion, which made it “the most expensive 5G bandwidth in the world.”
- Chunghwa Telecom won 90MHz of spectrum in the 3.5GHz frequency band for TWD 45.675 billion and also secured 600MHz in the 28GHz band for TWD 618 million.
- Far EasTone won 80MHz in the 3.5GHz band with a bid of TWD 40.6 billion, as well as 400MHz in the 28GHz band for TWD 412 million.
- Taiwan Mobile secured 60MHz of spectrum in the 3.5GHz frequency band for TWD 30.4 billion and 200MHz in the 28GHz frequency band for TWD 206 million. Judging from Taiwan Mobile’s current business model, the company is likely to team up with Asia Pacific for rendering related 5G services, leveraging 60MHz bandwidths it won in the 3.5GHz band.
- Taiwan Star won 40MHz in the 3.5GHz band for TWD 19.708 billion, and
- Asia Pacific Telecom secured 40MHz of spectrum in the 28GHz frequency band for TWD 412 million.
- Chunghwa Telecom and Far EasTone secured 90MHz and 80MHz of spectrum in the 3.5GHz band, respectively. Digitimes says these two carriers are expected to compete fiercely in a number of 5G service segments, including IoT, AI and big data.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..

RCR Wireless: Taiwan to open 4.8GHz to 4.9GHz band for dedicated 5G testing
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Bloomberg had this to say about Taiwan’t 5G spectrum auction:
The rising costs for licenses shows carriers expect the faster networks — due later this year in Taiwan — will provide a market advantage over competitors. The auction results so far are “blowing away expectations,” New Street Research analysts said in a note dated Jan. 6.
“There is no sign that the bidding will end soon,” Sheih Chi-mau, chairman and chief executive officer of the island’s biggest carrier Chunghwa Telecom, said Monday night in remarks at a company event. “It may take a few more days. The competition is fierce.”
While some other sales of 5G spectrum in similar bands have drawn bigger totals, Taiwan’s is the richest relative to population, according to New Street.
Taiwan’s bidding war suggests strong demand for mid-spectrum airwaves like the 3.5Ghz band in other markets, including for a U.S. sale of the so-called C-Band that could bring about $50 billion. Taiwan has about 29 million mobile phone accounts, an average of more than one per person, but its neighbor China has more than a billion. What makes Taiwanese subscribers especially attractive is that they’re the biggest consumers of data in Asia, according to researcher Tefficient. Average per-user data consumption at Taiwan’s carriers reached as high as 17.6GB per month, compared with 7.6GB in China and 8.5GB in South Korea.
South Korean carriers established the world’s first full commercial 5G services last April. They are expected to have reached 5 million subscribers by the end of 2019. Operators in other countries including the U.S., U.K., Japan and Australia have also offered limited services to the public with plans to introduce wider networks this year.
From LightReading— Robert Clark, contributing editor:
Taiwan’s 5G auction has completed its first round in near-record territory, with the five operators committing NT$138 billion ($4.6 billion) for more than three times the government reserve price.
Just over NT$137 billion went to the 3.5GHz band, putting the medium-sized Asian economy third behind Italy and Germany in aggregate spending and second in terms of spending per megahertz. Bids for the 28GHz frequencies raised about NT$1 billion.
But the auction isn’t over. The regulator, NCC, called a halt Thursday morning after the smallest player, Hon Hai-backed Asia-Pacific Telecom, withdrew from 3.5GHz bidding.
The process will resume on February 21, when the operators are expected to negotiate with each other for specific frequencies within the spectrum bands. The NCC said it would step in only if they are unable to reach agreement.
The biggest winners were Chunghwa Telecom, the number-two operator, which bid NT$45.7 billion for 90MHz of 3.5GHz spectrum, FarEasTone, which committed $40.6 billion for 80MHz, and Taiwan Mobile, which will pay NT$30.45 billion for 60MHz.
Table 1: Current Bids in Taiwan’s 5G Auction
| Chungwha Telecom | FarEasTone | Taiwan Mobile | Taiwan Star | Asia-Pacific Telecom | |
| 3.5GHz | 90MHz; NT$45.67B | 80MHz; NT$40.6B | 60MHz; NT$30.45B | 40MHz; NT$19.71M | N/A |
| 28GHz | 600MHz; NT$618M | 400MHz; NT$412M | 200MHz; NT$206M | N/A | 400MHz; NT$412M |
| Source: NCC Units. | |||||
Local credit agency Taiwan Ratings has warned that with debt loads already expected to rise to fund the 5G rollout, the unexpected high cost of spectrum is adding further pressure. It forecasts operators may “adopt a more conservative approach to infrastructure deployment.”
Investors aren’t too thrilled, either. Since the auction began a month ago, they’ve marked Taiwan Mobile down 4.4% and FarEasTone 2.1%. Chunghwa’s stock is unchanged.
Chunghwa Telecom, the part state-owned giant, has forecast annual 5G investment of up to NT$9-10 billion ($300-334 million), with total cost expected to significantly overtake its total NT$60 billion investment in 4G.
The official Central News Agency reported that telco execs have said privately that, because the sum raised far exceeds the government’s anticipated revenue take, they expect relief measures in the form of tax cuts, incentives, basestation subsidies or other measures.
So far none of these has materialized, but NCC Acting Chairman Chen Yaw-shyang says the government can introduce “administrative measures” to ensure consumers enjoy access to “high-quality and affordable” 5G.
He said the Taiwan cabinet would hold an interdepartmental meeting to discuss distribution of the auction proceeds, including investment in upgrading telecom infrastructure, Taipei Times reported.
The Taiwan Telecommunications Industry Development Association (TTIDA) has also called for 5G to be exempt from spectrum usage charges and for a delay on the issue of spectrum for private network services. (See Taiwan’s Telcos Seek Govt. Help as 5G Auction Blows Out.)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.digitimes.com/news/a20200116PD221.html
https://www.lightreading.com/asia-pacific/taiwan-calls-temporary-halt-on-$46b-auction/d/d-id/756907?
Samsung acquires network services provider TWS; SK-Telecom launches Global MEC Task Force
1. Samsung Acquires Network Services Provider TeleWorld Solutions to Accelerate U.S. 5G Network Expansion
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. today announced the completion of an agreement to acquire TeleWorld Solutions (TWS), a network services provider headquartered in Chantilly, VA.

TWS provides network design, testing and optimization services to mobile service and cable operators, equipment OEMs and other companies across the U.S. With network builds associated with 5G and 4G LTE enhancements advancing in the U.S, the acquisition will address the need for end-to-end support in delivering network solutions.
TWS, a privately owned company, will operate as a wholly owned subsidiary of Samsung Electronics America, Inc. The service offerings and customers of TWS complement Samsung’s growth among networks infrastructure clients. With competencies in radio frequency (RF) and network design service—as well as installation, testing, and optimization services—TWS will continue to serve its existing customers and clients they currently support with Samsung. The TWS leadership team will continue to manage the business and, together with Samsung, address the network upgrade cycle occurring in the US.
With a growing position in the US networks industry, along with its 5G technology leadership, Samsung Networks has collaborated with major U.S. network operators to fulfill 5G’s network expansion. As its growth continues through network operator agreements and enterprises seeking their own cellular networks, the combination of Samsung and TWS will help customers address next-generation demands.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. SK Telecom Joins Forces with Bridge Alliance Members for Cooperation in 5G MEC
SK Telecom today announced the launch of the ‘Global MEC Task Force’ with Bridge Alliance member operators, including Singtel, Globe, Taiwan Mobile and PCCW Global, for cooperation in 5G mobile edge computing (MEC).
SK Telecom will share its lessons-learned in 5G and MEC areas with other members that are preparing to launch 5G, while making joint efforts for the development of MEC technologies and services. The company will also play a leading role in setting international MEC standards to build an interoperable MEC platform.
MEC is being highlighted as a key technology that can improve the performance of ultra-low latency services such as cloud gaming, smart factory and autonomous driving by creating a shortcut for mobile data communications.
Through the task force, SK Telecom expects to lead the expansion of the 5G MEC ecosystem to the Asian countries, and develop valuable overseas market opportunities for its 5G technologies/services including MEC.
As the first chair of the task force, SK Telecom will be hosting the first MEC workshop with Bridge Alliance from January 13 to 15 at its headquarters located in Seoul, Korea. The workshop will identify potential regional MEC-based use cases, and discuss business models and commercialization plans.
The company will introduce its 5G strategies, 5G MEC-based use cases including smart factory, and 5G clusters including ‘LoL Park.’
“As the global 5G pioneer, SK Telecom is committed to contribute to the expansion of the global 5G ecosystem,” said Lee Kang-won, Vice President and Head of Cloud Labs of SK Telecom. “SK Telecom will work closely with Bridge Alliance Member Operators to help accelerate their progress in 5G and MEC, and create a pan-Asian 5G MEC ecosystem.”
“As the role of telecommunications companies is expanding beyond simply providing mobile connectivity to offering new values based on infrastructure, Bridge Alliance believes that this cooperation will serve as a key driver for realizing win-win business opportunities to all members,” said Ong Geok Chwee, CEO of Bridge Alliance.Photo: (from left) Ha Min-yong, VP and Head of Global Alliance Group, SK Telecom, Ong Geok Chwee, CEO of Bridge Alliance, and Lee Kang-won, VP and Head of Cloud Labs, SK Telecom.
For more information, please contact [email protected] or [email protected]
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?page.page=1&idx=1439&page.type=all&page.keyword=
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
U.S. telcos on 5G rollouts (“vague promises”), devices, IoT/smart cities
Here’s what AT&T, Sprint, T-Mobile, and Verizon said about their 5G network rollouts, soon-to-be available devices, and Smart City plans at CES 2020:
AT&T on 5G Devices, Network Plans:
Carrier and media goliath AT&T talked about 5G devices at this year’s CES event in Las Vegas, NV. Currently, AT&T only sells one 5G-capable phone, the Samsung Galaxy Note 10 Plus 5G, but AT&T plans to have 15 5G phones available for use on its low-band 5G spectrum during 2020 (see Comment in the box below this article). The Dallas-based service provider said that other mobile devices, such as laptops, tablets, and hotspots will also be available this year, but no exact number of products were provided.
AT&T’s low-band 5G network went live in December 2019 and is currently available in parts of 19 cities. The carrier’s other 5G network that is built on millimeter-wave and is referred to as 5G Plus is live in parts of 35 cities. AT&T said that it plans to cover 200 million people with its 5G network by this summer.
Sprint IoT, Smart City Updates:
Wireless provider Sprint could merge with T-Mobile any day now, but the Overland Park, Kansas-based carrier hasn’t slowed down in the meantime. Sprint took to CES to launch several new offerings and update the market on its IoT plans.
Sprint unveiled its Certainty network design model, which unites its entire business wireline portfolio, including its wireless, IoT, and security solutions. The carrier also launched IoT Factory 2.0, a dedicated platform that solution providers and businesses can use to build custom IoT solutions for small-to-mid sized businesses in the food service, healthcare and agriculture space.
Chris Brydon, Regional Vice President Sales, Sprint Business Northwest Region via LinkedIn:
We believe hashtagIoT has the power to improve people’s lives. Here’s a story illustrating how an IoT application can be so much more than just a cold, lifeless piece of tech. Watch the very human difference it makes in the lives of a man and his family. https://lnkd.in/gdyeT9N hashtagWorksForBusiness
Sprint updated the market on its Smart City initiative on Tuesday. Specifically in Georgia, the provider said that in 2020 “micropositioning” technology, which combines next-generation wireless technologies and small cells will be installed within city infrastructure in areas to enable real-world navigation for autonomous machines, more connected sensors and IoT solution testing in its innovation Center for solutions such as refrigeration and monitoring, and security robots in Peachtree Corners’ Town Hall. Sprint also has plans to integrate additional Smart City technology in Greenville, South Carolina, and Arizona State University.
T-Mobile Talks 5G, Avoids Sprint Mega-Merger Talk:
T-Mobile didn’t address the main topic on everyone’s mind when thinking about the Magenta-colored carrier: its in-progress $26 billion mega-merger with wireless competitor Sprint. Instead, the “Un-Carrier” took to the show to highlight its 5G connectivity.
In a surprising move last month, the Bellevue, Wash.-based provider launched its nationwide 5G network using 600 MHz spectrum acquired in the recent incentive auction, as well as two 5G phones capable of using its 600 MHz spectrum. T-Mobile originally planned to launch the network in 2020.
Verizon 5G Devices and Ultra Wideband Availability:
AT&T’s biggest competitor, Verizon, also came to CES armed with 5G updates. Compared to AT&T’s 15 devices, Basking Ridge, N.J.-based Verizon vowed to have 20 5G-capable devices in 2020 and said these devices would be competitively priced anywhere between $600-$800. Currently, Verizon has four 5G-capable smartphones. Subscribers interested in 5G will have to pay an additional $10 on top of their current unlimited data plan, Verizon said, but the company didn’t name any specific device manufacturers.
Verizon’s ultra wideband 5G network is available in parts of 30 cities today, including Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York City, as well as Hoboken, N.J. Des Moines, Iowa; and Providence, RI. Please see Comment in the box below this article.
………………………………………………………………………………………
Mike Dano of Lightreading wrote that AT&T and Verizon made “vague (uncertain?) promises” for their 5G mmWave networks:
in a New Year-themed post, AT&T’s Scott Mair wrote that “you’re in for an exhilarating ride on the AT&T 5G network in 2020 and beyond,” but he did not offer any specifics about what the carrier will do with its “5G+” network. Then, during a subsequent appearance at an investor event this week, AT&T CFO John Stephens said only that the operator’s 5G network would “continue to improve and grow.”
Similarly, Verizon touted its “vision” for its network in 2020 in a release issued this week, but said only that customers should “expect more great innovations and technology advancements from us in 2020 including a more aggressive build out of our 5G network.” At that same investor event, Verizon’s Ronan Dunne said “we will be continuing to drive hard” in 5G, but didn’t offer any specifics.
The bottom line here is that neither operator is offering any concrete information on the number of cities, cell sites or customers it plans to touch with mmWave 5G in 2020. As Heavy Reading analyst Gabriel Brown writes, it’s time for these operators to show their hands.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
From a marketwatch.com article titled: The long-promised ‘Year of 5G’ arrives with more promises and little 5G
For years, telecommunications companies and gadget makers have invaded CES to talk about how big 5G was going to be in 2020.
At CES 2020 though the promise was still unfulfilled as the faster wireless service is still spotty and not entirely what was envisioned.
Without the premier connections that were promised, it is questionable how many consumers will buy the more expensive 5G-enabled devices that were introduced at the giant trade show this year, even though the same glowing predictions of a new future were readily available throughout Las Vegas.
5G promises faster data speeds, a reduction in lag time, and greater density for smart devices, all things that could eventually be catalysts for futuristic applications like autonomous driving and connected cities. More immediately, carriers are focused on exposing businesses and customers to those faster data speeds, where and when they can.
Verizon Communications Inc. expects to launch 20 devices with access to 5G by the end of the year, up from the seven that currently exist, according to Tami Erwin, who heads the company’s business group. AT&T Inc. mobility executive Kevin Petersen told MarketWatch at CES that accessibility will also be a key theme in the year ahead.
T-Mobile US claimed that it conducted a nationwide 5G rollout at the end of last year, providing access over a greater area but at slower data speeds than competitors. Verizon and AT&T both plan to add new cities to their coverage later this year, with AT&T still expecting to have nationwide coverage this year also.
Bob O’Donnell, president of TECHnalysis Research, cautions that these upgrades won’t happen right away due to some technical aspects of the 5G rollout. The more exciting type of 5G, millimeter-wave spectrum, primarily works outdoors and on campuses where it’s been specifically deployed. Sub-6 5G service works indoors and offers some benefits in speed and latency, but it’s a less dramatic step up from the 4G service consumers have come to know.
“The pieces are coming together but the forward-looking benefits are still a few years off,” O’Donnell said. Part of the issue is that 5G currently runs on top of 4G, rather than in a stand alone manner. Moving to stand alone 5G requires that carriers “refarm” spectrum frequencies from 4G to 5G, but they’re hesitant to make that big leap right away while most customers are still using 4G connections and while few phones support 5G.
“That’s like opening a 10-lane highway only for people with electric cars,” he said, since only a small minority of drivers would have access.
Making 5G a reality is a bit of a “chicken and egg” scenario, according to O’Donnell, given that carriers thinking about moving away from 4G want there to be enough devices in the market to take advantage of the new wireless standard, and consumers want to make sure 5G networks are broad enough before investing in a mobile device that works on the network.
The device part of the equation showed signs of progress at CES, with connected PCs being one notable category. Lenovo Group Ltd. announced it will launch in the spring the Yoga 5G two-in-one device, which it says is the first 5G PC. Always-connected PCs let customers rely on cellular connectivity rather than hunt for WiFi networks, and the 5G products shown by Lenovo, HP Inc. HPQ, and others offer faster speeds than 4G ones currently on the market.
Those devices are more expensive than competitive gadgets without access to the technology, though, and that will most likely continue to be the case. Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. will be holding a smartphone launch in early February, where the company is expected to introduce a family of 5G Galaxy devices, and Apple is thought to be planning a 5G iPhone rollout later this year, with analysts expecting the 5G versions of those popular smartphones to carry a higher price tag.
Instinet analyst Jeffrey Kvaal expects “a large increase” in 5G unit sales for 2020, up from a small base of sales last year, but he thinks most of these sales will come at the expense of 4G devices, rather than a rush of upgrades. He estimates that 5G could boost a phone’s retail price by at least $75.
Today’s devices tend to be in the $1,000-plus range, but consumers should “start to see prices coming down, which ultimately helps the adoption curve,” as more mid-tier devices come to market this year equipped with 5G capabilities. Verizon’s consumer chief executive Ronan Dunne said at a Citi investor conference earlier this week that there could be 5G devices priced below $600 by the end of the year.
AT&T Chief Financial Officer John Stephens told investors at the Citi conference that trying to predict 5G unit sales is missing the point a bit, since handset sales are “not a profitable enterprise for a business like ours.” The company sees various new service revenue opportunities from being able to compete “in the geographies where our service has gotten much better.”
The promise of 5G goes well beyond smartphones, and executives pointed out that the services that have developed in the past decade likely wouldn’t have existed without the move to 4G.
“If someone was watching a streaming video on a connection 10 years ago, you would’ve swatted the phone out of their hand and said they were going to use up the whole monthly data plan in 13 seconds,” Qualcomm’s vice president of engineering John Smee told MarketWatch. Now, streaming over wireless is commonplace. Verizon’s Erwin noted that the proliferation of ride hailing also wouldn’t have been possible without the upgrade in data speeds.
AT&T’s Petersen thinks it’s too soon to know what the killer use case for 5G will be, but he’s upbeat about its ability to provide upgraded experiences in gaming, translation and medicine. A reduction in latency, or lag time, could create better responsiveness for gamers and reduce awkward pauses when people are using mobile devices to translate from one language to another in real time. Doctors could more easily monitor patients remotely after procedures by using connected devices.
Over time, the expected benefits of 5G and the growth of accessible smart devices could change the way consumers and workers think about doing data-heavy tasks. Smee even suggested that it could replace the need for Wi-Fi for most users.
“If you think of your cable modem or your DSL and you look at the rates you get compared to the 5G data rate, all of a sudden wireless is the preferred medium and that’s a big game changer versus the idea that you have to have wired connectivity to have high data rates,” he said.
References:
https://www.crn.com/slide-shows/networking/ces-2020-top-telecom-carriers-talk-5g-new-devices-and-iot



