MEF New Standards for SD-WAN Services; SASE Work Program; Dec 2022 UPDATE!
The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) [1.] has published new SD-WAN standards that add critical enhancements, including new service capabilities for underlay connectivity, important application performance metrics, and security zones for service providers deploying SD-WAN managed services.
Note 1. The MEF is an industry forum empowering enterprises to transform digitally with standard services and APIs for network, cloud, and technology providers. While initially focused on Carrier Ethernet, the MEF scope has broadened to encompass overlay services like SD-WAN. The ITU-T does not have an active SD-WAN standardization program so the industry must look to the MEF for service definitions and standards for that subject.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The new MEF standards include:
- MEF 70.1 updates MEF 70, the industry’s first global SD-WAN standard, to include new service attributes for underlay connectivity services, new measurable performance metrics that provide visibility into an application’s performance within the provider network and across multiple service providers, and the infrastructure to support application-based security defined in MEF 88 (see below).
- MEF 88, MEF’s first security standard, enhances an SD-WAN service to add security functions. These include defining threats, malware protections, security policy terminology and attributes, and describing what actions a policy should take in response to certain threats.
- MEF 95 provides a unified policy framework for MEF’s SD-WAN (MEF 70.1), Network Slicing (MEF 84), and SASE (MEF W117) and Zero Trust (MEF W118) standards coming in 2022.
“We’re seeing a healthy uptick in SD-WAN deployments driven by work from anywhere, as more users are connecting to the cloud and cloud-based applications. We estimate the global SD-WAN service market will grow from $2.85B in 2020 to $14.5B in 2025 (CAGR of 38%),” said Roopa Honnachari, vice president of research & global program leader – network & edge services, Frost & Sullivan.
“MEF’s work in standardizing and certifying SD-WAN managed services is helping to drive that adoption, and we believe certified services and professionals will continue to play an important role in moving the market forward.”
“MEF develops standards and certifications to provide clarity and assurance and remove complexity for SD-WAN managed services.
The new standards define the service behavior and associated policy language needed to deliver high-performance, secure SD-WAN managed services,” said Pascal Menezes, CTO, MEF.
Source: MEF
……………………………………………………………………………………..
“These standards, and the forthcoming SASE and Zero Trust standards, benefit both customers and providers—customers know what to expect when purchasing SD-WAN managed services from a provider, and providers have the tools needed to deliver secure SD-WAN services that drive customer satisfaction,” Pascal added.
Both service providers and vendors can attain certification for MEF’s SD-WAN standards in the MEF 3.0 SD-WAN certification program which validates compliance with MEF standards for delivering managed SD-WAN services and the underlying technology. The objective is to eliminate market confusion, and enable faster SD-WAN market adoption.
In 2022, secure SD-WAN requirements will be added to the MEF 3.0 certification program. Currently, 17 companies have achieved MEF 3.0 SD-WAN certification. In addition, the MEF-SDCP Professional Certification training and certification provides an opportunity for the engineers, architects, product managers, and others deploying SD-WAN solutions to demonstrate their expertise in MEF 3.0 service standards.
- Worldwide, there are over 700 MEF-SDCP professionals employed by more than 120 companies.
- Over 60 service providers have either the Carrier Ethernet or SD-WAN certification within the MEF 3.0 framework, and a handful have both.
- AT&T, Verizon, Comcast Business and Windstream are among the service providers with MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Certification. Those companies also rank within the top five of Vertical Systems Group’s 2020 US Carrier Managed SD-WAN Leaderboard.
MEF SASE Work:
MEF will also be releasing SASE (MEF W117) and Zero Trust (MEF W118) standards in 2022. MEF started developing its secure access service edge (SASE) framework last fall to clarify the service attributes and definitions for SASE.
The SD WAN market has already become bogged down by different SASE definitions, which has led to confusion among enterprise customers and frustration for service providers.
MEF defines SASE as a “service connecting users (machine or human) with their applications in the cloud while providing connectivity performance and security assurance determined by policies set by the Subscriber.” The networking and security functions within a SASE service include routing, VPN, path selection, traffic shaping, firewall, threat prevention and more.
Yet finding one vendor that meets all those requirements, and delivers a SASE service that is simple to deploy, is proving challenging for service providers that want to provide SASE as a managed service to enterprise customers.
“The ideal is one vendor, right? That’s the ideal, we all agree with it. But at least for enterprise customers, we’d haven’t found a single vendor solution that meets their needs yet from a SASE perspective,” said Verizon’s Vincent Lee.
MEF Media Contact: Melissa Power [email protected]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
MEF Introduces New Standards for High-Performance, Secure SD-WAN Services
https://www.mef.net/service-standards/overlay-services/sase/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
December 2022 UPDATE:
MEF SD-WAN and SASE Standards:
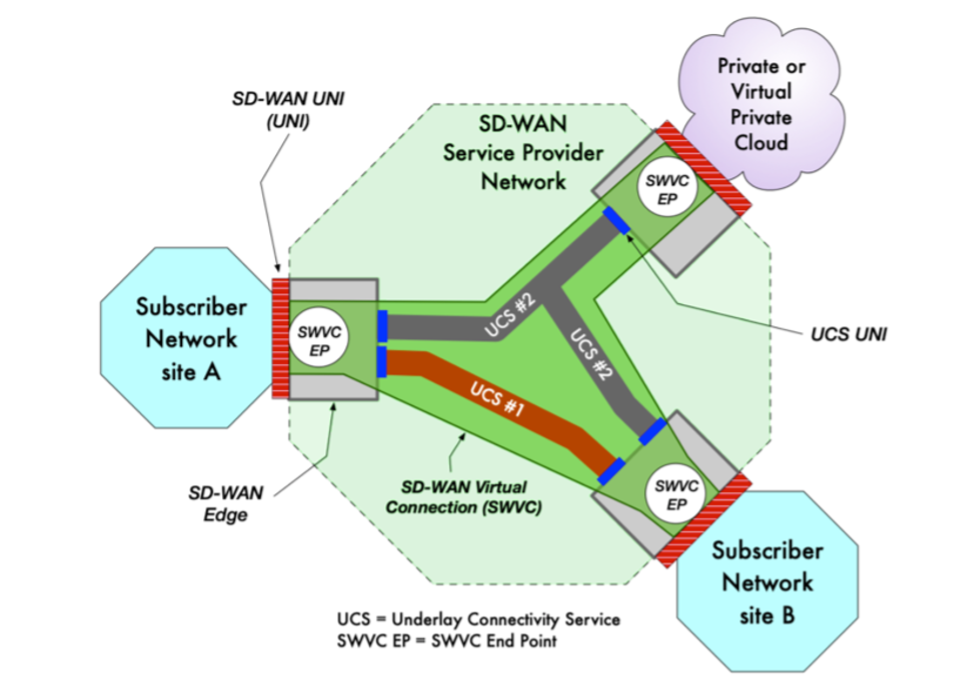
In August 2019, the MEF published the industry’s first global standard defining an SD-WAN service and its service attributes. SD-WAN Service Attributes and Services (MEF 70). The MEF SD-WAN standard describes requirements for an application-aware, over-the-top WAN connectivity service that uses policies to determine how application flows are directed over multiple underlay networks irrespective of the underlay technologies or service providers who deliver them. However, it does not address interoperability because it does not specify either a UNI or NNI protocol stack.
MEF 70 defines:
- Service attributes that describe the externally visible behavior of an SD-WAN service as experienced by the subscriber.
- Rules associated with how traffic is handled.
- Key technical concepts and definitions like an SD-WAN UNI, the SD-WAN Edge, SD-WAN Tunnel Virtual Connections, SD-WAN Virtual Connection End Points, and Underlay Connectivity Services.
SD-WAN standardization offers numerous benefits that will help accelerate SD-WAN market growth while improving overall customer experience with hybrid networking solutions. Key benefits include:
- Enabling a wide range of ecosystem stakeholders to use the same terminology when buying, selling, assessing, deploying, and delivering SD-WAN services.
- Making it easier to interface policy with intelligent underlay connectivity services to provide a better end-to-end application experience with guaranteed service resiliency.
- Facilitating inclusion of SD-WAN services in standardized LSO architectures, thereby advancing efforts to orchestrate MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services across automated networks.
- Paving the way for creation and implementation of certified MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services, which will give users confidence that a service meets a fundamental set of requirements.
In December 2022, MEF published two Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) standards defining 1.] SASE service attributes, common definitions & a framework and 2.] a Zero Trust framework that together allow organizations to implement dynamic policy-based actions to secure network resources for faster decision making and implementation for enterprises. MEF’s SASE standard defines common terminology and service attributes which is critically important when buying, selling, and delivering SASE services. It also makes it easier to interface policy with security functions for cloud-based cybersecurity from anywhere. MEF’s Zero Trust framework defines service attributes to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
- SASE Service Attributes and Service Framework Standard: specifies service attributes to be agreed upon between a service provider and a subscriber for SASE services, including security functions, policies, and connectivity services. The standard defines the behaviors of the SASE service that are externally visible to the subscriber irrespective of the implementation of the service. A SASE service based upon the framework defined in the standard enables secure access and secure connectivity of users, devices, or applications to resources for the subscriber. MEF’s SASE standard (MEF 117) includes SASE service attributes and a SASE service framework.
- Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services: The new Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services (MEF 118) defines a framework and requirements of identity, authentication, policy management, and access control processes that are continuously and properly constituted, protected, and free from vulnerabilities when implemented and deployed. This framework also defines service attributes, which are agreed between a subscriber and service provider, to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
3 thoughts on “MEF New Standards for SD-WAN Services; SASE Work Program; Dec 2022 UPDATE!”
Comments are closed.



SD-WAN provides a secure path from siloed enterprise networks to the public, private and hybrid cloud
SD-WAN is a reset in thinking about how a Wide Area Network (WAN) should work. It’s a virtual WAN architecture, an overlay that can work with different network transport services, including broadband. SD-WAN enables organizations to centrally manage traffic using the principles of Software Defined Networking (SDN), without the limitations imposed by physical network infrastructure.
SD-WAN centralizes network control, management, provisioning and security, despite the continued decentralization of data, as businesses move to the cloud. A few companies stand apart from the rest when it comes to offering SD-WAN solutions. Cisco is the market leader, followed by Fortinet and VMware, according to a report from Dell’Oro Group.
Enterprise spend on SD-WAN has accelerated in recent times. Businesses are upgrading network infrastructure to accommodate changing objectives and shifting workforce demands, as well. Sales of SD-WAN solutions rose 45% year-over-year for the third calendar quarter of 2021, according to Dell’Oro. The research firm noted that Cisco’s quarterly SD-WAN revenue nearly doubled in the quarter, with especially strong growth in North America.
The State of the WAN
For years, the literal backbone of enterprise WAN connectivity has been Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS). MPLS is a routing technique which directs data based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. Those paths labels speed network traffic by identifying virtual links between distant network nodes, eliminating routing delays.
MPLS supports a range of network transport services. And as the acronym implies, it supports multiple networking protocols: Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM) and Frame Relay, for example.
Regardless of protocol, MPLS connections all have one thing in common: They’re dedicated circuits, and require specialized routing hardware at both ends. This complicates provisioning and limits scale. What’s more, traditional WAN topologies typically backhaul all network traffic for security. This creates bottlenecks and complicates network traffic management.
A WAN topology that restricts the flow of network traffic to the cloud is at direct odds with enterprise digitalization strategies. Enterprises depend on more cloud-based services than ever to manage essential business functions. SaaS platforms like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) are examples. These platforms provide organizations with agility, flexibility, and scale, but being cloud-native demands a new approach when it comes to practical network management.
SD-WAN modernizes network operations for the cloud
As enterprises and users turn to the cloud, the difference between data center cloud and public cloud can get nebulous. Increasing public cloud-dependence and adjacency introduces complications to network security and compliance. Data sovereignty, compliance and security is top of mind for every IT professional.
Many enterprises leaning into to the cloud are implementing Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) to manage their networks. SD-WAN abstracts the networks’ transport service altogether. It’s a virtual WAN architecture which enables organizations to leverage whatever transport service they need — broadband, MLPS, 4G LTE, 5G.
By separating the network’s control plane altogether, SD-WAN enables businesses to centralize network management, security, and provisioning. SD-WAN replaces dedicated network hardware with Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) in place of physical networking hardware.
VNFs specifically replace devices like network routers and firewalls. VNFs are implemented as Virtual Machines (VMs) which run as software in the IT cloud, operating on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) server hardware. Accompanied by Cloud-native Network Functions (CNFs), they provide IT departments with the ability to scale services instantly to meet demand. As software rather than hardware, VNFs and CNFs can be continuous updated and optimized.
While VNFs are nothing new to enterprise IT, what’s new here in the SD-WAN equation is how SDN itself helps IT operations manage network operations and data security for branch and remote locations. There are some key differences, too.
“SDN advocates a central controller to dictate network behaviors. In contrast, SD-WAN generally manages based on central policy control, but decisions may also be made locally while taking into consideration the corporate policies. Or decisions can be made centrally while incorporating knowledge of local conditions reported by remote network nodes,” said VMware.
SD-WAN in the wild
SD-WAN has emerged as an opportunity for carriers and hyperscalers, Over-the-Top (OTT) service providers, and edge services. In December, Amazon introduced AWS Cloud WAN as a way to replace what it called a “patchwork” of services needed to handle private network control and management. AWS Cloud WAN connects on-prem data centers, branch offices and cloud resources together on AWS’ global backbone, consolidating management through a central dashboard.
Verizon features SD-WAN managed by Cisco as an option for its Network as a Service (NaaS). It comprises Cisco Umbrella security framework, manages zero trust application access and provides managed services through Cisco products including Pluggable Interface Modules and Catalyst Cellular Gateways.
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20220113/telco-cloud/what-is-software-defined-wide-area-networking-sd-wan
SD-WAN technology is a true WAN transformation from conventional inflexible WAN to next gen cloud ready WAN environment which are really easy to deploy, manage and scale in global environment. Dynamically sharing the load across the links adds great advantage to get both the links used in optimum way, not sitting idle as backup though it can be configured based on the need of the customer. SD-WAN has brought huge cost saving opportunity if Internet links are used replacing high cost MPLS services.
Since Internet is uncontrolled, Business grade premium internet link with good SLA must be considered to get desired application throughput. To balance cost vs technology, combination of Business Grade and Low SLA internet can be used. Redundant infrastructure can be easily deployed with low cost compared to dual MPLS services to ensure business continuity and disaster recovery.
Internet and O365 or other Cloud specific applications can be securely offloaded locally using Cloud Service brokers to have faster access compared to backhauling or express route in the central office in other region.
Since the SD-WAN service is cloud ready and majorly over Internet which is not secured enough, Security is always key and high focus from all the layers, management plane, control plane and data plane. Traffic are encrypted as per industry standard with TLS 1.2 or IPSC with higher encryption or proprietary protocols to ensure CIA. Built in basic firewall function can have policy enforcement which is application aware, on top of that Network Based Firewall function can be deployed if stateful packet filter firewall is required with Anti X function.
Based on the requirement of the customer, segmentation will add value to have completely isolated segment and associated routing in the same box, like business user’s traffic and guest user’s internet traffic can be completely separated and traversed on same internet links.
Journey begins with this with the key focus how to secure end user’s behavior which may lead to opening up vulnerabilities. SASE solution now being added on top of SD-WAN where security for end to end traffic flow can be ensured. DLP can be integrated with role based access control along with malware protection such that only trusted source will have desired access to designated application and attempt to unauthorized access can be blocked. Same policy can be harmonized across the region for users who can connect from office LAN, Home VPN or Office Wi-Fi segments. SASE POP, gateways will have integration with real time scanning engine, sandboxing to minimize the threat landscape.
Thank you MEF, Gartner to define SD-WAN and SASE standard that Solution providers are complying to ensure solution is meeting security guideline.
SD-WAN Architecture Design plays a pivotal role to create a concrete standard solution framework. Number of Hubs (Interconnect point of MPLS and SD-WAN Internet) should be minimum to simplify WAN infrastructure. Combination of MPLS and Internet as underlying transport can create routing complexity of the hybrid site. BGP routing must be managed with right attributes to prevent asymmetric routing or routing loop. Redundancy must be considered based on business requirement, Single router dual link or dual router dual link etc.
SASE readiness analysis will be interested study for organizations. It will be essential to identify the applications, type of users, connectivity methods and 3rd party support partner’s access requirement to define SASE business policy to provide right security posture across the organize to protect the communication from Internal and External threats.
Thank you !
Dr. Sudip Sinha
MEF SDCP SD-WAN Specialist
VMWare SD-WAN Master Specialist
Member IEEE
[email protected]
Security Service Edge vs. SASE: What Is the Difference?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a category of networking solutions defined by Gartner in 2019, which combines traditional network security functions with wide area networking (WAN) capabilities. The goal of SASE is to provide secure and reliable connectivity for users and devices, regardless of their location or the type of network they are connected to.
Gartner defines SASE as a cloud-delivered, network security as a service platform that provides secure network connectivity and network security functions in a unified offering, delivered through a common infrastructure and management. SASE combines network security functions, such as zero trust networking, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), with cloud-based networking services like SD-WAN (software-defined wide area networking) and internet connectivity.
……………………………………………………………………..
Secure Services Edge (SSE) is a set of integrated, cloud-delivered secure services that use identities and policies to establish secure connections between authenticated users and business resources. First introduced by Gartner in 2021, SSE is a security category that will secure connectivity in the future of hybrid environments and remote work.
As more employees work outside corporate boundaries, SaaS applications become the norm, and applications move to the public cloud, organizations cannot continue to backhaul user traffic to corporate networks. Many IT organizations are replacing their existing network security appliances, such as firewalls, VPN gateway appliances, and web gateways, with cloud-based options that can better protect data, provide a better user experience, and reduce costs.
SSE platforms provide cloud services that extend secure connectivity to user locations, without connecting users to corporate networks, exposing IT infrastructure to the public internet, or requiring complex network segmentation. Instead, SSE allows IT to provide secure access from anywhere to on-premise applications, secure access to the internet, and fast access to the cloud and SaaS applications.
………………………………………………………………………………………..
Security Service Edge vs. SASE: What Is the Difference?
The main difference between Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Security Service Edge (SSE) is the focus of the solutions. SASE combines traditional network security functions with wide area networking (WAN) capabilities, while SSE focuses specifically on security functions.
SASE solutions are designed to provide secure and reliable connectivity for users and devices, regardless of their location or the type of network they are connected to. This can include traditional networking functions like VPNs and SD-WAN (software-defined wide area networking), as well as security functions like firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and other controls. SASE solutions are often used by organizations with remote and hybrid workforces to ensure secure access to corporate resources and protect against cyber threats.
https://wire19.com/security-service-edge-vs-sase-difference/