Month: November 2024
Technavio: Silicon Photonics market estimated to grow at ~25% CAGR from 2024-2028
The global silicon photonics market size is estimated to increase by $5.24 billion from 2024-2028, according to Technavio. The market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of almost 24.88% during the forecast period. Increasing need for higher bandwidth is driving market growth, with a trend towards emergence of optical data centers. However, lack of global standards and guidelines poses a challenge.
The decades old global Silicon Photonics market is now experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for high-speed data transfer in various industries. With Internet traffic from cloud computing, 5G technology, IoT, and AI-powered devices, there is a need for more efficient and low-power solutions.
Silicon photonics uses integrated circuits (ICs) for optical communications, thereby reducing power consumption compared to electronic technologies.
Key components of silicon photonics include transceivers, optical interconnects, lasers, modulators, and photodetectors. These are used in data centers, telecommunication networks, and interconnection networks. The market is also driven by the adoption of 5G network, self-driving cars, and high-speed kits for point-of-care testing and imaging data. Silicon photonics uses optical waveguides, optical modulators, and photodetectors made from silicon, silicon nitride, and other photonic components. These components are more compact and less susceptible to thermal effects compared to traditional fiber-optic solutions. Additionally, the use of high-powered laser sources, thermal stress management, and liquid-crystal cladding helps mitigate thermal effects and improve performance.

The market for silicon photonics is expected to grow in IT & telecommunications and consumer electronics sectors, with applications in broadband services, telecom service providers, and broadband connections. This growth is driven by the need for high-speed data transfer and low power consumption, making silicon photonics a promising solution for the future of optical communications and data storage systems.
Silicon photonics is now targeted at optical data centers, providing enhanced capabilities for data transmission, processing, and storage. By integrating high-speed, high-bandwidth optical interconnects directly onto silicon chips, silicon photonics enables seamless communication between different data center components. This results in faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and increased scalability, making it an ideal solution for modern applications like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics. The continuous growth in cloud-based applications and big data analytics has significantly expanded the scale of data center networks. Silicon photonics, with its advantages over traditional copper-based interconnects, is a crucial technology in addressing the demands for faster and more efficient data center infrastructure.
The communications industry’s growth is driving the demand for silicon photonics due to its ability to transmit wider bandwidth signals with low latency and maintain signal quality during long-distance communication with minimal loss. Silicon photonics is a key technology in optical communication systems, enabling the transfer of large amounts of data at high speeds. Increased bandwidth and low latency requirements have fueled the demand for silicon photonics-based devices such as receivers, transmitters, and modulators.
Communications Industry – Market size and forecast 2018 – 2028 (USD Mn):
The global silicon photonics market is experiencing significant growth due to increasing demand for high-speed data transfer in various industries. With the Internet traffic from cloud computing, 5G technology, IoT, and AI-powered devices, there is a need for more efficient and low-power optical communications solutions.
The proliferation of data centers and cloud computing infrastructure is a major factor driving the market’s growth. Vendors like Cisco Systems Inc. And Intel Corp. Offer silicon photonics solutions for high-speed data transmission in data center environments. The evolution of 5G networks is another significant factor, as silicon photonics supports 5G networks with low latency and high capacity at a low cost and power per bit. With the increasing investment in 5G networks, the demand for silicon photonics is also expected to rise, boosting the growth of the global silicon photonics market through the communications segment.
Silicon photonics vendors include: AIO Core Co. Ltd., ams OSRAM AG, Broadcom Inc., Corning Inc., Hamamatsu Photonics KK, II VI Inc., Infinera Corp., Innolume GmbH, Intel Corp., International Business Machines Corp., IPG Photonics Corp., MACOM Technology Solutions Inc., NKT Photonics AS, Nokia Corp., NVIDIA Corp., OpenLight Photonics Inc., OSCPS Motion Sensing Inc, RANVOUS Inc., Sicoya GmbH, TRUMPF SE Co. KG, and Cisco Systems Inc.
Market Challenges:
- Lack of global standards and guidelines
- Availability of substitute technologies for silicon photonics
- High heat generation by photonic components
Silicon photonics offers a promising solution with its integration of photonics and electronic components on a single silicon chip. However, challenges such as thermal effects, power consumption, and thermal stress in high-powered laser sources remain. Transceivers, optical interconnects, and lasers are key components in this market, along with modulators, photodetectors, and optical waveguides. Data centers, telecommunication, and IT and telecommunications are major end-users, with consumer electronics and automotive industries also adopting silicon photonics for high-speed kits in self-driving cars and point-of-care testing. Optical network infrastructure, including fiber-optic and active optical cables, is a significant application area. The market is expected to grow further with advancements in silicon nitride, optical multiplexers, attenuators, and other photonic components.
The absence of standardized protocols and specifications in the silicon photonics market poses challenges for both manufacturers and customers. Without universally accepted standards, the integration of silicon photonics components into existing optical communication systems and networks becomes complicated. Compatibility issues arise, product development and manufacturing processes are complicated, and implementation costs increase. Furthermore, the lack of clear standards results in inconsistent performance metrics, making it difficult for customers to compare and evaluate different silicon photonics solutions effectively. Standardization is crucial for the widespread adoption of new technologies, and its absence in the silicon photonics market hinders its growth and potential impact on the optical communication industry.
References:
LightCounting: Silicon Photonics chip market to hit $3 billion in 2029
Light Counting on Silicon Photonics and Optical Switching at SC22
Synopsys and Juniper Networks form new company to pursue “open” silicon photonics platform
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
https://viodi.com/2013/11/08/silicon-photonics-cisco-intel-see-light-at-the-end-of-the-tunnel/
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
Ericsson’s November 2024 Mobility Report predicts that global 5G standalone (SA) connections will top 3.6 billion by 2030. That compares to 890 million at the end of 2023. Over that same period of time, 5G SA as a proportion of global mobile subscriptions is expected to increase from 10.5% to 38.4%, while average monthly smartphone data consumption will grow to 40 GB from 17.2 GB. By the end of the decade, 80% of total mobile data traffic will be carried by 5G networks.
That rosy forecast is in sharp contrast to the extremely slow and disappointing pace of 5G SA deployments to date. In January, Dell’Oro counted only 12 new 5G SA deployments in 2023, compared to the 18 in 2022. “The biggest surprise for 2023 was the lack of 5G SA deployments by AT&T, Verizon, British Telecom EE, Deutsche Telekom, and other Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) around the globe. As we’ve stated for years, 5G SA is required to realize 5G features like security, network slicing, and MEC to name a few.”
Fifty 5G Standalone enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) networks commercially deployed (2020 – 2023):
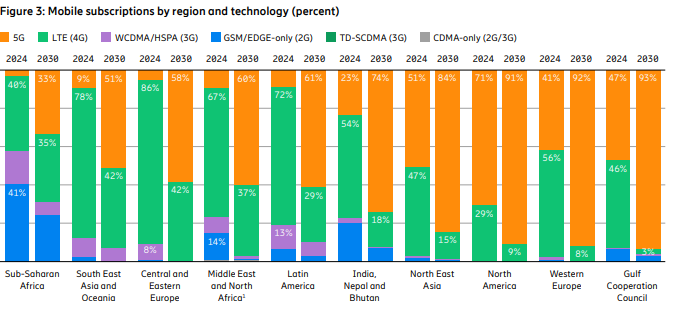
The report states, “Although 5G population coverage is growing worldwide, 5G mid-band is only deployed in around 30% of all sites globally outside of mainland China. Further densification is required to harness the full potential of 5G.” Among the report highlights:
- Global 5G subscriptions will reach around 6.3 billion in 2030, equaling 67% of total mobile subscriptions.
- 5G subscriptions will overtake 4G subs in 2027.
- 5G is expected to carry 80% of total mobile data traffic by the end of 2030.
- 5G SA subscriptions are projected to reach around 3.6 billion in 2030.
Source: Ericsson Mobility Report -Nov 2024
“Service differentiation and performance-based opportunities are crucial as our industry evolves,” said Fredrik Jejdling, EVP and head of Ericsson’s networks division. “The shift towards high-performing programmable networks, enabled by openness and cloud, will empower service providers to offer and charge for services based on the value delivered, not merely data volume,” he added.
The Mobility Report provides two case studies in T-Mobile US and Finland’s Elisa – both of which have rolled out network slicing on their 5G SA networks and co-authored that section of the report:
- T-Mobile has been testing a high priority network slice to carry mission-critical data during special events.
- Elisa has configured a slice to support stable, high-capacity throughput for users of its premium fixed-wireless access (FWA) service, called Omakaista.
The Mobility Report doesn’t say if those two telcos are deriving any monetary benefit from network slicing, or more broadly from their 5G SA networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) market has momentum:
- Ericsson predicts FWA connections will reach 159 million this year, up from 131 million in 2023.
- By 2030, connections are expected to hit 350 million, with 80% carried by 5G networks.
- In four out of six regions, 83% or more wireless telcos now offer FWA.
- The number of FWA service providers offering speed-based tariff plans – with downlink and uplink data parameters similar to cable or fiber offerings – has increased from 30% to 43% in the last year alone.
- An updated Ericsson study of retail packages offered by mobile service providers reveals that 79% have a FWA offering.
- There are 131 service providers offering FWA services over 5G, representing 54 percent of all FWA service providers.
- In the past 12 months, Europe has accounted for 73%of all new 5G FWA launches globally.
- Currently, 94% of service providers in the Gulf Cooperation Council region offer 5G FWA services.
- In the U.S. two service providers (T-Mobile US and Verizon) originally set a goal to achieve a combined 11–13 million 5G FWA connections by 2025. After reaching this target ahead of schedule, they have now revised their goal to 20–21 million connections by 2028.
- The market in India is rapidly accelerating, with 5G FWA connections reaching nearly 3 million in just over a year since launch. • An increasing number of service providers are launching FWA based on 5G standalone (SA).
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/reports/november-2024
https://www.ericsson.com/4ad0df/assets/local/reports-papers/mobility-report/documents/2024/ericsson-mobility-report-november-2024.pdf
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
FWA a bright spot in otherwise gloomy Internet access market
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Vodafone UK report touts benefits of 5G SA for Small Biz; cover for proposed merger with Three UK?
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Google’s Bosun subsea cable to link Darwin, Australia to Christmas Island in the Indian Ocean


“Vocus is thrilled to have the opportunity to deepen our strategic network partnership with Google, and to play a part in establishing critical digital infrastructure for our region. Australia Connect will bolster our nation’s strategic position as a vital gateway between Asia and the United States by connecting key nodes located in Australia’s East, West, and North to global digital markets,” said Jarrod Nink, Interim Chief Executive Officer, Vocus.
“The combination of the new Australia Connect subsea cables with Vocus’ existing terrestrial route between Darwin and Brisbane, will create a low latency, secure, and stable network architecture. It will also establish Australia’s largest and most diverse domestic inter-capital network, with unparalleled reach and protection across terrestrial and subsea paths.
“By partnering with Google, we are ensuring that Vocus customers have access to high capacity, trusted and protected digital infrastructure linking Australia to the Asia Pacific and to the USA. “The new subsea paths, combined with Vocus’ existing land-based infrastructure, will provide unprecedented levels of diversity, capacity and reliability for Google, our customers and partners,” Nink said.
“Australia Connect advances Google’s mission to make the world’s information universally accessible and useful. We’re excited to collaborate with Vocus to build out the reach, reliability, and resiliency of internet access in Australia and across the Indo-Pacific region,” said Brian Quigley, VP, Global Network Infrastructure, Google Cloud.
Perth, Darwin, and Brisbane are key beneficiaries of this investment and are now emerging as key nodes on the global internet utilizing the competitive and diverse subsea and terrestrial infrastructure established by the Vocus network. Vocus will be in a position to supply an initial 20-30Tbps of capacity per fiber pair on the announced systems, depending on the length of the segment.
References:
Google’s Equiano subsea cable lands in Namibia en route to Cape Town, South Africa
Google’s Topaz subsea cable to link Canada and Japan
“SMART” undersea cable to connect New Caledonia and Vanuatu in the southwest Pacific Ocean
Telstra International partners with: Trans Pacific Networks to build Echo cable; Google and APTelecom for central Pacific Connect cables
HGC Global Communications, DE-CIX & Intelsat perspectives on damaged Red Sea internet cables
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
NEC completes Patara-2 subsea cable system in Indonesia
SEACOM telecom services now on Equiano subsea cable surrounding Africa
Bharti Airtel and Meta extend 2Africa Pearls subsea cable system to India
China seeks to control Asian subsea cable systems; SJC2 delayed, Apricot and Echo avoid South China Sea
Intentional or Accident: Russian fiber optic cable cut (1 of 3) by Chinese container ship under Baltic Sea
Altice Portugal MEO signs landing party agreement for Medusa subsea cable in Lisbon
2Africa subsea cable system adds 4 new branches
Echo and Bifrost: Facebook’s new subsea cables between Asia-Pacific and North America
Equinix and Vodafone to Build Digital Subsea Cable Hub in Genoa, Italy
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Meta Platforms and Elon Musk’s xAI start-up are among companies building clusters of computer servers with as many as 100,000 of Nvidia’s most advanced GPU chips as the race for artificial-intelligence (AI) supremacy accelerates.
- Meta Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg said last month that his company was already training its most advanced AI models with a conglomeration of chips he called “bigger than anything I’ve seen reported for what others are doing.”
- xAI built a supercomputer called Colossus—with 100,000 of Nvidia’s Hopper GPU/AI chips—in Memphis, TN in a matter of months.
- OpenAI and Microsoft have been working to build up significant new computing facilities for AI. Google is building massive data centers to house chips that drive its AI strategy.
xAI built a supercomputer in Memphis that it calls Colossus, with 100,000 Nvidia AI chips. Photo: Karen Pulfer Focht/Reuters
A year ago, clusters of tens of thousands of GPU chips were seen as very large. OpenAI used around 10,000 of Nvidia’s chips to train the version of ChatGPT it launched in late 2022, UBS analysts estimate. Installing many GPUs in one location, linked together by superfast networking equipment and cables, has so far produced larger AI models at faster rates. But there are questions about whether ever-bigger super clusters will continue to translate into smarter chatbots and more convincing image-generation tools.
Nvidia Chief Executive Jensen Huang said that while the biggest clusters for training for giant AI models now top out at around 100,000 of Nvidia’s current chips, “the next generation starts at around 100,000 Blackwells. And so that gives you a sense of where the industry is moving. Do we think that we need millions of GPUs? No doubt. That is a certainty now. And the question is how do we architect it from a data center perspective,” Huang added.
“There is no evidence that this will scale to a million chips and a $100 billion system, but there is the observation that they have scaled extremely well all the way from just dozens of chips to 100,000,” said Dylan Patel, the chief analyst at SemiAnalysis, a market research firm.
Giant super clusters are already getting built. Musk posted last month on his social-media platform X that his 100,000-chip Colossus super cluster was “soon to become” a 200,000-chip cluster in a single building. He also posted in June that the next step would probably be a 300,000-chip cluster of Nvidia’s newest GPU chips next summer. The rise of super clusters comes as their operators prepare for Nvidia’s nexgen Blackwell chips, which are set to start shipping out in the next couple of months. Blackwell chips are estimated to cost around $30,000 each, meaning a cluster of 100,000 would cost $3 billion, not counting the price of the power-generation infrastructure and IT equipment around the chips.
Those dollar figures make building up super clusters with ever more chips something of a gamble, industry insiders say, given that it isn’t clear that they will improve AI models to a degree that justifies their cost. Indeed, new engineering challenges also often arise with larger clusters:
- Meta researchers said in a July paper that a cluster of more than 16,000 of Nvidia’s GPUs suffered from unexpected failures of chips and other components routinely as the company trained an advanced version of its Llama model over 54 days.
- Keeping Nvidia’s chips cool is a major challenge as clusters of power-hungry chips become packed more closely together, industry executives say, part of the reason there is a shift toward liquid cooling where refrigerant is piped directly to chips to keep them from overheating.
- The sheer size of the super clusters requires a stepped-up level of management of those chips when they fail. Mark Adams, chief executive of Penguin Solutions, a company that helps set up and operate computing infrastructure, said elevated complexity in running large clusters of chips inevitably throws up problems.
The continuation of the AI boom for Nvidia largely depends on how the largest clusters of GPU chips deliver a return on investment for its customers. The trend also fosters demand for Nvidia’s networking equipment, which is fast becoming a significant business. Nvidia’s networking equipment revenue in 2024 was $3.13 billion, which was a 51.8% increase from the previous year. Mostly from its Mellanox acquisition, Nvidia offers these networking platforms:
- Accelerated Ethernet Switching for AI and the Cloud

- Quantum InfiniBand for AI and Scientific Computing

- Bluefield® Network Accelerators

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Nvidia forecasts total fiscal fourth-quarter sales of about $37.5bn, up 70%. That was above average analyst projections of $37.1bn, compiled by Bloomberg, but below some projections that were as high as $41bn. “Demand for Hopper and anticipation for Blackwell – in full production – are incredible as foundation model makers scale pretraining, post-training and inference, Huang said. “Both Hopper and Blackwell systems have certain supply constraints, and the demand for Blackwell is expected to exceed supply for several quarters in fiscal 2026,” CFO Colette Kress said.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/nvidia-chips-ai-race-96d21d09?mod=tech_lead_pos5
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/
https://nvidianews.nvidia.com/news/nvidia-announces-financial-results-for-third-quarter-fiscal-2025
HPE-Juniper combo + Cisco restructuring create enterprise network uncertainty
Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s (HPE) pending acquisition of Juniper Networks and Cisco’s recent corporate restructuring (which de-emphasizes legacy networking products like access/core routers and Ethernet switches) is putting enterprise networking customers in a holding pattern. They are pausing investments in network equipment as they wait out the uncertainty.
“I’ve had customers put things on hold right now, and not just the Juniper side but both sides,” Andre Kindness, principal analyst at Forrester Research, said in an interview with SDxCentral about how Juniper and HPE customers are reacting to uncertainty around the deal. “Typically, if customers are strong enough to look outside of Cisco and they’re not a Cisco shop, then HPE, Aruba, Juniper are the primary ones that they’re looking at. I’ve had customers put some of that on hold at this point.”
That holding pattern is tied to uncertainty over what systems and platforms will emerge from a combined HPE-Juniper. Mr. Kindness noted in a blog post when the deal was announced that “the journey ahead will be rife with obstacles for Juniper and HPE/Aruba customers alike.” Kindness explained that one important move for HPE would be to “rationalize/optimize the portfolio, the products and the solutions.”
“HPE will try to reassure you that nothing will change; it doesn’t make sense to keep everything, especially the multiple AP [access point] product lines (Instant On, Mist, and Aruba Aps), all the routing and switching operating systems (Juno, AOS-CX, and ArubaOS) and both management systems (Central and Mist),” Kindness wrote.
“Though not immediately, products will need to go and the hardware that stays will need to be changed to accommodate cloud-based management, monitoring, and AI.” HPE CEO Antonio Neri and his management team has attempted to temper these concerns by stating there is virtually no overlap between HPE and Juniper’s product lines, which Kindness said, “just boggles my mind,” he added.
Juniper’s AI product, called Marvis (part of the Mist acquisition in 2019), is by far the most advanced AI solution in the networking market. That’s not a profound statement; no vendor has anything close to it. The quick history: Juniper’s acquisition of Mist brought the company a cloud-based Wi-Fi solution with a leading AI capability, Marvis. Juniper quickly started integrating its switching and routing portfolio into Marvis. Walmart, Amazon, and others took notice. Fast-forward to today: This gives HPE Aruba a two-year lead against its competitors by bringing Juniper into the fold.
“I think [Neri’s] got to worry about the financial analyst out there in the stock market or the shareholders to pacify them, and then at the same time you don’t want to scare the bejesus out of your customer base, or Juniper customer base, so you’re going to say that there’s going to be either no overlap or no changes, everything will coexist,” Kindness said.
While overlap and other concerns could alter what a potential Juniper HPE combo looks like, Kindness said he expects the result to lean heavily on Juniper’s telecom and networking assets. That includes HPE products like Aruba networking gear being replaced by Juniper’s artificial intelligence (AI)-focused Mist and Marvis platforms.
“Mist has been really a game changer for the company and just really opened a lot of doors,” Kindness explained. “[Juniper] really did a 180 degree turn when they bought [Mist], and just the revenue that’s brought in and the expansion of the product line itself, and the capabilities of Mist and actually Marvis in the background would be hard for [HPE] to replicate at this point. My perception was HPE looked at it and said, Marvis and Mist is just something that would take too long to get to.” Kindness added that he does not expect significant platform thinning to happen for a couple of years after a potential closing of the deal, but the interim could be filled with challenges tied to channel partners and go-to-market strategies that could chip away at market opportunities similar to what is happening at VMware following the Broadcom acquisition. “Broadcom is ruthless, right or wrong, it’s its business model,” Kindness said. “HPE is not quite that dynamic.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Cisco CFO Scott Herren told the audience at a recent investor conference that HPE’s pending Juniper acquisition is causing “uncertainty” in the enterprise WLAN market that could be benefit Cisco. “I think for sure that’s created just a degree of uncertainty and a question of, hey, should I consider if I was previously a vendor or a customer of either of those, now is the time to kind of open up and look at other opportunities,” Herren said. “And we’ve seen our wireless business, our orders greater than $1 million grew more than 20% in the fourth quarter.”
Cisco is also working through its own networking drama as part of the vendor’s recently announced restructuring process. Those moves will see Cisco focus more on high-growth areas like AI, security, and cloud at the expense of its legacy operations, including the pairing down of its networking product lines.
“It looks like Cisco’s realizing that all the complexity of customer choice and all these variations and offering a zillion features is probably not the way to go. I think Chuck realized it,” Kindness said of Cisco’s efforts. “If you look at the ACI [Application Centric Infrastructure] and Cloud Dashboard for Nexus starting to consolidate, and then the Catalyst line and the Aironet line and the Meraki line are consolidating, it’s just the right move. The market has told them that for the last 10 years, it just took them a while to recognize it.”
References:
https://www.juniper.net/us/en.html
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
Canalys & Gartner: AI investments drive growth in cloud infrastructure spending
According to market research firm Canalys, global spending on cloud infrastructure services [1.] increased by 21% year on year, reaching US$82.0 billion in the 3rd quarter of 2024. Customer investment in the hyperscalers’ AI offerings fueled growth, prompting leading cloud vendors to escalate their investments in AI.
Note 1. Canalys defines cloud infrastructure services as services providing infrastructure (IaaS and bare metal) and platforms that are hosted by third-party providers and made available to users via the Internet.
The rankings of the top three cloud service providers – Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud – remained stable from the previous quarter, with these providers together accounting for 64% of total expenditure. Total combined spending with these three providers grew by 26% year on year, and all three reported sequential growth. Market leader AWS maintained a year-on-year growth rate of 19%, consistent with the previous quarter. That was outpaced by both Microsoft, with 33% growth, and Google Cloud, with 36% growth. In actual dollar terms, however, AWS outgrew both Microsoft and Google Cloud, increasing sales by almost US$4.4 billion on the previous year.
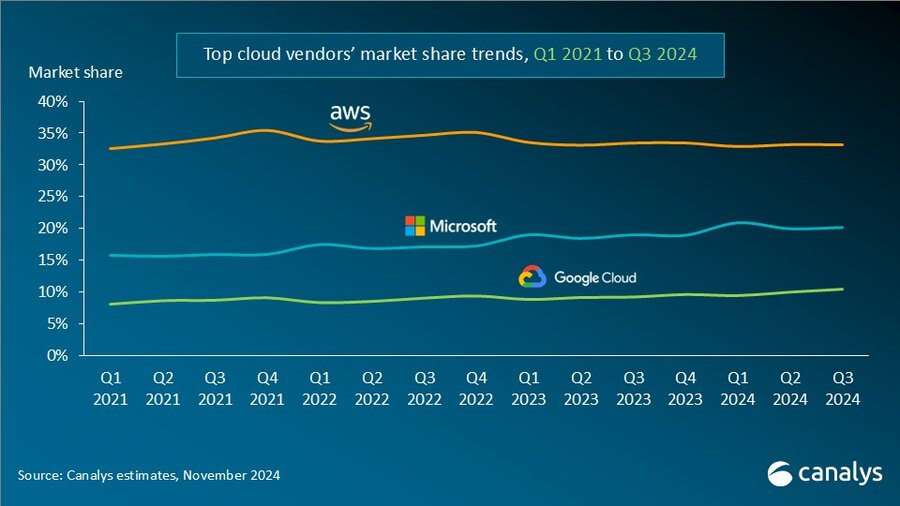
In Q3 2024, the cloud services market saw strong, steady growth. All three cloud hyperscalers reported positive returns on their AI investments, which have begun to contribute to their overall cloud business performance. These returns reflect a growing reliance on AI as a key driver for innovation and competitive advantage in the cloud.
With the increasing adoption of AI technologies, demand for high-performance computing and storage continues to rise, putting pressure on cloud providers to expand their infrastructure. In response, leading cloud providers are prioritizing large-scale investments in next-generation AI infrastructure. To mitigate the risks associated with under-investment – such as being unprepared for future demand or missing key opportunities – they have adopted over-investment strategies, ensuring their ability to scale offerings in line with the growing needs of their AI customers. Enterprises are convinced that AI will deliver an unprecedented boost in efficiency and productivity, so they are pouring money into hyperscalers’ AI solutions. Accordingly, cloud service provider capital spending (CAPEX) will sustain their rapid growth trajectories and are expected to continue on this path into 2025.
“Continued substantial expenditure will present new challenges, requiring cloud vendors to carefully balance their investments in AI with the cost discipline needed to fund these initiatives,” said Rachel Brindley, Senior Director at Canalys. “While companies should invest sufficiently in AI to capitalize on technological growth, they must also exercise caution to avoid overspending or inefficient resource allocation. Ensuring the sustainability of these investments over time will be vital to maintaining long-term financial health and competitive advantage.”
“On the other hand, the three leading cloud providers are also expediting the update and iteration of their AI foundational models, continuously expanding their associated product portfolios,” said Yi Zhang, Analyst at Canalys. “As these AI foundational models mature, cloud providers are focused on leveraging their enhanced capabilities to empower a broader range of core products and services. By integrating these advanced models into their existing offerings, they aim to enhance functionality, improve performance and increase user engagement across their platforms, thereby unlocking new revenue streams.”
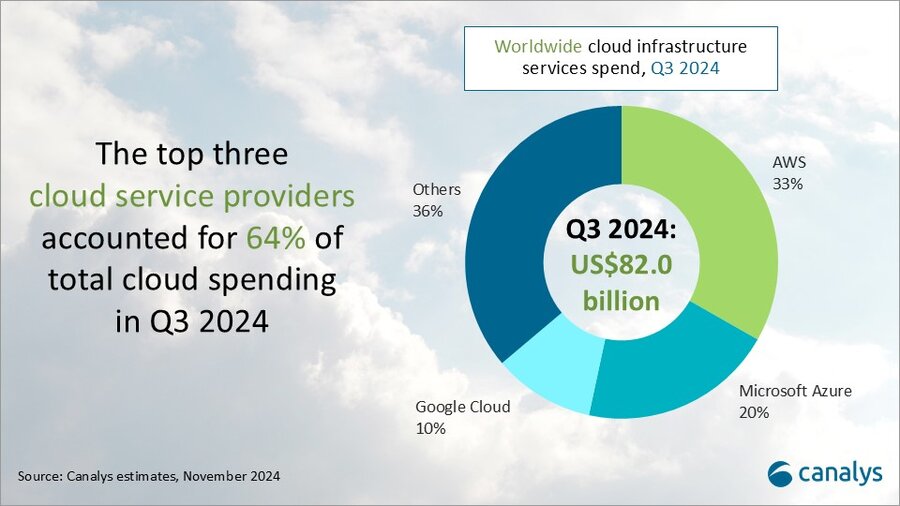
Amazon Web Services (AWS) maintained its lead in the global cloud market in Q3 2024, capturing a 33% market share and achieving 19% year-on-year revenue growth. It continued to enhance and broaden its AI offerings by launching new models through Amazon Bedrock and SageMaker, including Anthropic’s upgraded Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Meta’s Llama 3.2. It reported a triple-digit year-on-year increase in AI-related revenue, outpacing its overall growth by more than three times. Over the past 18 months, AWS has introduced nearly twice as many machine learning and generative AI features as the combined offerings of the other leading cloud providers. In terms of capital expenditure, AWS announced plans to further increase investment, with projected spending of approximately US$75 billion in 2024. This investment will primarily be allocated to expanding technology infrastructure to meet the rising demand for AI services, underscoring AWS’ commitment to staying at the forefront of technological innovation and service capability.
Microsoft Azure remains the second-largest cloud provider, with a 20% market share and impressive annual growth of 33%. This growth was partly driven by AI services, which contributed approximately 12% to the overall increase. Over the past six months, use of Azure OpenAI has more than doubled, driven by increased adoption by both digital-native companies and established enterprises transitioning their applications from testing phases to full-scale production environments. To further enhance its offerings, Microsoft is expanding Azure AI by introducing industry-specific models, including advanced multimodal medical imaging models, aimed at providing tailored solutions for a broader customer base. Additionally, the company announced new cloud and AI infrastructure investments in Brazil, Italy, Mexico and Sweden to expand capacity in alignment with long-term demand forecasts.
Google Cloud, the third-largest provider, maintained a 10% market share, achieving robust year-on-year growth of 36%. It showed the strongest AI-driven revenue growth among the leading providers, with a clear acceleration compared with the previous quarter. As of September 2024, its revenue backlog increased to US$86.8 billion, up from US$78.8 billion in Q2, signaling continued momentum in the near term. Its enterprise AI platform, Vertex, has garnered substantial user adoption, with Gemini API calls increasing nearly 14-fold over the past six months. Google Cloud is actively seeking and developing new ways to apply AI tools across different scenarios and use cases. It introduced the GenAI Partner Companion, an AI-driven advisory tool designed to offer service partners personalized access to training resources, enhancing learning and supporting successful project execution. In Q3 2024, Google announced over US$7 billion in planned data center investments, with nearly US$6 billion allocated to projects within the United States.
Separate statistics from Gartner corroborate hyperscale CAPEX optimism. Gartner predicts that worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is on course to reach $723.4 billion next year, up from a projected $595.7 billion in 2024. All segments of the cloud market – platform-as-a-service (PaaS), software-as-a-service (SaaS), desktop-as-a-service (DaaS), and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) – are expected to achieve double-digit growth.
While SaaS will be the biggest single segment, accounting for $299.1 billion, IaaS will grow the fastest, jumping 24.8 percent to $211.9 million.
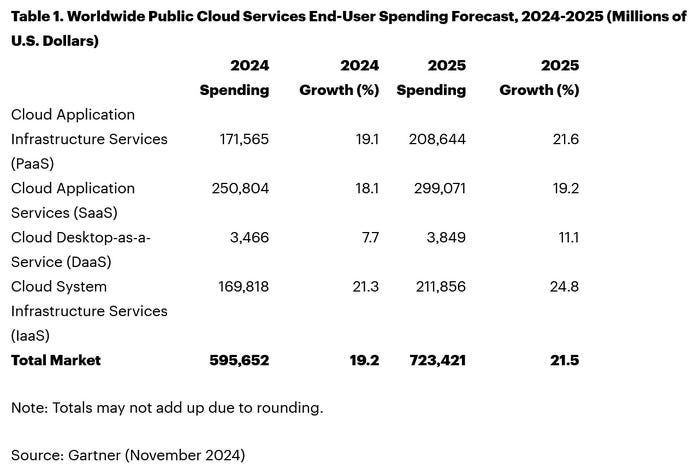
Like Canalys, Gartner also singles out AI for special attention. “The use of AI technologies in IT and business operations is unabatedly accelerating the role of cloud computing in supporting business operations and outcomes,” said Sid Nag, vice president analyst at Gartner. “Cloud use cases continue to expand with increasing focus on distributed, hybrid, cloud-native, and multicloud environments supported by a cross-cloud framework, making the public cloud services market achieve a 21.5 percent growth in 2025.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://canalys.com/newsroom/global-cloud-services-q3-2024
https://www.telecoms.com/public-cloud/ai-hype-fuels-21-percent-jump-in-q3-cloud-spending
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
MTN Consulting: Top Telco Network Infrastructure (equipment) vendors + revenue growth changes favor cloud service providers
IDC: Public Cloud software at 2/3 of all enterprise applications revenue in 2026; SaaS is essential!
IDC: Cloud Infrastructure Spending +13.5% YoY in 4Q-2021 to $21.1 billion; Forecast CAGR of 12.6% from 2021-2026
IDC: Worldwide Public Cloud Services Revenues Grew 29% to $408.6 Billion in 2021 with Microsoft #1?
Synergy Research: Microsoft and Amazon (AWS) Dominate IT Vendor Revenue & Growth; Popularity of Multi-cloud in 2021
Google Cloud revenues up 54% YoY; Cloud native security is a top priority
WSJ: T-Mobile hacked by cyber-espionage group linked to Chinese Intelligence agency
According to the Wall Street Journal, T-Mobile’s network was hacked in a damaging Chinese cyber-espionage operation that successfully gained entry into multiple U.S. and international telecommunications companies.
Hackers linked to a Chinese intelligence agency were able to breach T-Mobile as part of monthslong campaign to spy on the cellphone communications of high-value intelligence targets. It is unclear what information, if any, was taken about T-Mobile customers’ calls and communications records.
“T-Mobile is closely monitoring this industry-wide attack, and at this time, T-Mobile systems and data have not been impacted in any significant way, and we have no evidence of impacts to customer information,” a company spokeswoman said. “We will continue to monitor this closely, working with industry peers and the relevant authorities.”
China’s multipronged spying operations have drawn warnings in the U.S. about their economic implications. Photo: Andy Wong/Associated Press
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Salt Typhoon used sophisticated methods to infiltrate American telecom infrastructure through vulnerabilities including Cisco Systems routers, and investigators suspect the hackers relied on artificial intelligence or machine learning to further their espionage operations , people familiar with the matter said. The attackers penetrated at least some of that infrastructure over eight months or more.
In the broader hacking campaign, attackers were able to access cellphone lines used by an array of senior national security and policy officials across the U.S. government, in addition to politicians. The access allowed them to scoop up call logs, unencrypted texts and some audio from targets, in what investigators believe may have significant national-security ramifications.
Additionally, the hackers were able to access information from systems maintained by the carriers to comply with U.S. surveillance requests, raising further counterintelligence concerns. Investigators are still endeavoring to fully understand and have said the attack was carried out by the Salt Typhoon group. At Lumen, which doesn’t provide wireless service, the attackers didn’t steal any customer data or access its wiretap capabilities, according to people familiar with the matter.
Further investigation has revealed that the hackers sought access to data managed under U.S. law enforcement programs, including those governed by the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA). This act authorizes American intelligence agencies to monitor suspected foreign agents’ communications. By targeting these programs, Chinese hackers may have aimed to infiltrate sensitive government communications channels, gaining insights into U.S. surveillance efforts.
Some foreign telecommunications firms were also compromised in the hacks, including in countries that maintain close intelligence-sharing partnerships with the U.S., people familiar with the matter said. Earlier this week, the Biden administration acknowledged in a public statement some details about the nature of the “broad and significant” hack that were previously reported by the WSJ.
Chinese government-linked hackers had compromised networks at multiple telecommunications companies “to enable the theft of customer call records data, the compromise of private communications of a limited number of individuals who are primarily involved in government or political activity, and the copying of certain information that was subject to U.S. law enforcement requests pursuant to court orders,” the statement from the FBI and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) said. “We expect our understanding of these compromises to grow as the investigation continues,” they added.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/cybersecurity/u-s-wiretap-systems-targeted-in-china-linked-hack-327fc63b
https://www.newsweek.com/fbi-chinese-cyber-espionage-multiple-telecom-networks-1985617
China backed Volt Typhoon has “pre-positioned” malware to disrupt U.S. critical infrastructure networks “on a scale greater than ever before”
FBI and MI5 Chiefs Issue Joint Warning: Chinese Cyber Espionage on Tech & Telecom Firms
Cybersecurity threats in telecoms require protection of network infrastructure and availability
FT: A global satellite blackout is a real threat; how to counter a cyber-attack?
Demythifying Cyber security: IEEE ComSocSCV April 19th Meeting Summary
StrandConsult Analysis: European Commission second 5G Cybersecurity Toolbox report
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Pente Networks, MosoLabs and Alliance Corp collaborate for Private Cellular Network in a Box
Pente Networks, a private wireless network core, orchestration and management software company; MosoLabs, a global company building solutions for LTE and 5G private and neutral host networks; are collaborating with Alliance Corporation to deliver a complete Private Cellular Network in a Box. It’s a pre-built, plug and play kit with multiple options available (see below) to cater to different use cases, such as surveillance, fixed wireless access and point of sale.
By including already provisioned devices, customers can use their own highly secure and robust private cellular network almost immediately. The solution speeds up and simplifies private network deployment for integrators, IT departments and small businesses; even those with little to no private wireless experience.
Alliance’s Network in a Box is a pre-configured bundle designed with everything needed to deploy and then operate an end-to-end private wireless 4G LTE or 5G wireless network. Alliance’s professional services team uses the Pente HyperCore platform to pre-integrate with MosoLabs’ Canopy indoor and outdoor radios and provision selected end-user devices, SIMs and eSIMs. Alliance then assembles an enclosure that houses all the network equipment, including the HyperCore EdgeMini, a full Evolved Packet Core (EPC) and 5G Core in one. The pre-built kits and radios are ready for simple installation at the desired location. Once connected, the network is immediately up and running, with the devices instantly recognized by the network. No additional programming or configuration is needed.
Three ready made bundles are:
- Network in a Box with Fixed Wireless Access WiFi
- Network in a Box with Video Surveillance
- Network in a Box with Point of Sale
Each bundle includes the Pente HyperCore EdgeMini, Moso Canopy Small Cell Radios, and select devices all preconfigured to work together instantly.

“Our goal is to make private networks accessible to everyone,” says Dan Ortega, Senior Sales Engineer, Alliance Corporation. “With Pente and MosoLabs, we can pre-configure an out-of-the-box functional kit so that all our customers, regardless of their size or use case, can take advantage of everything private networks have to offer.”
Alliance support is available for any questions, and they offer additional services needed such as RF planning, SAS registration, and network monitoring and management. Alliance can also support customers who want to scale their network to support additional services, applications, and IoT devices.
Alliance Corporation distributes equipment for wireless network infrastructure, in-building signal enhancement solutions, cellular broadband systems, next-generation 5G networks, fixed wireless and private enterprise networks, as well as cellular solutions that connect the Internet of Things. Alliance provides pre and post-sale technical support, engineering, radio configuration, and training services. Alliance serves telecommunication carriers, fixed wireless broadband service providers, OEMs, systems integrators, resellers, and contractors in education, enterprise, federal government, military, healthcare, industrial, municipal government, oil and gas, mining, public safety, security, utilities, and transportation industries.
Alliance US Holding, LP owns Alliance Corporation, GetWireless, TESSCO Technologies, and DiscountCell and is owned by entities affiliated with Lee Equity Partners and Twin Point Capital
About Pente:
Pente provides the world’s most advanced LTE & 5G SA mobile core and network management solution supporting operators and enterprises with both fully virtualized mobile core networks and private cellular network solutions. With over 1000 APIs, Pente’s mobile core and network orchestration platform, enables the fastest implementation and integration available on the market today. Pente currently manages millions of IT-grade SIMs for customers around the globe on networks serving corporate enterprise, industrial, healthcare, education, the public sector and military applications. Pente has strategic customers and partnerships with leading MNOs, MVNOs, enterprises, device manufacturers, managed service providers and system integrators.
Visit pentenetworks.com or call 1-888-821-4797.
About MosoLabs:
MosoLabs is focused on building world-class 4G and 5G hardware with a unified network management platform and an innovative application software suite for private wireless and neutral hosts networks. Our mission is to simplify the entire private network experience – from planning to deployment to management – and create products to support new use cases. We develop fully integrated products that simplify time-to-market and deployment complexity for global enterprises and managed service providers. Learn more at www.mosolabs.com.
References:
https://www.pentenetworks.com/networkinabox
Tata Consultancy Services: Critical role of Gen AI in 5G; 5G private networks and enterprise use cases
SNS Telecom & IT: $6 Billion Private LTE/5G Market Shines Through Wireless Industry’s Gloom
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G Network market annual spending will be $3.5 Billion by 2027
HPE Aruba Launches “Cloud Native” Private 5G Network with 4G/5G Small Cell Radios
Nokia and Kyndryl extend partnership to deliver 4G/5G private networks and MEC to manufacturing companies
BT and Ericsson in partnership to provide commercial 5G private networks in the UK
Ericsson and e& (UAE) sign MoU for 6G collaboration vs ITU-R IMT-2030 framework
Ericsson and United Arab Emirates (UAE) network operator e& have signed of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), for the collaborative exploration of 6G technology, its use cases and future network evolution. It will also include a series of technical discussions and engagements aimed at jointly exploring key 6G technology concepts.
The purpose of this MoU is unclear, as the definition work for 6G RANs will be done in ITU-R WP5D with the specs likely to come from 3GPP. So any 6G MoU would have to be based on the ITU-R IMT-2030 framework (see figures below and References).
Khalid Murshed, Chief Technology and Information Officer, e& UAE, says: “e& UAE has pioneered new technologies since 1976 powering people and societies. This collaboration is a testament to our dedication for driving the digital future and pushing the boundaries of a more connected and technologically advanced future. We are thrilled to partner with Ericsson on exploring 6G and its future network evolution.”
Ekow Nelson, Vice President and Head of Global Customer Unit for e& at Ericsson Middle East and Africa, says: “We have barely scratched the surface with 5G which will overtake 4G and become the dominant mobile technology after 2027 and, with 5G Standalone and 5G Advanced, realize its transformative potential over the next several years. At the same time, we have started the proactive approach to 6G research with our partners to shape the next generation of mobile networks. Collaborating closely with e& UAE, we aim to leverage our shared expertise to drive progress in the development of 6G for the United Arab Emirates, and the wider region.”

Photo credit: Ericsson
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From the ITU-R IMT-2030 framework:
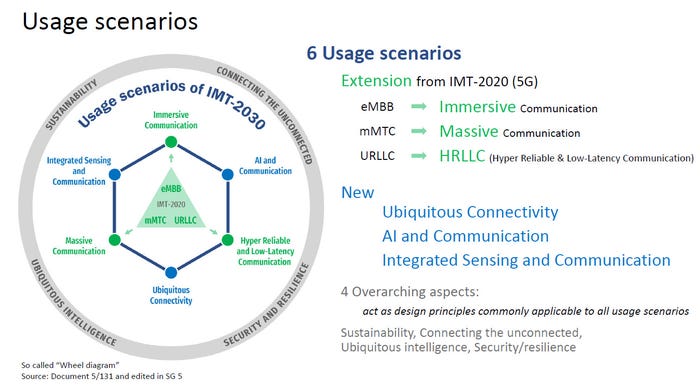
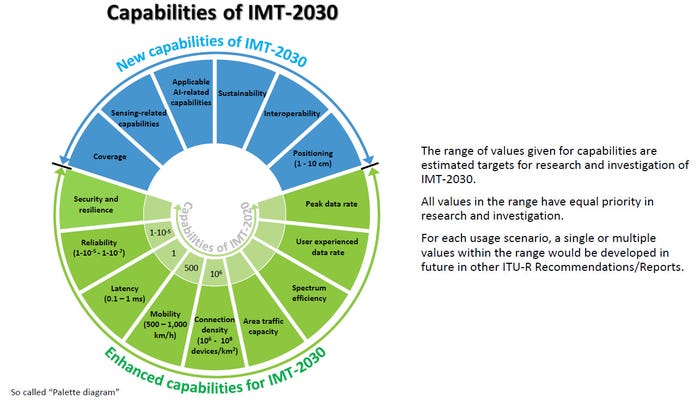
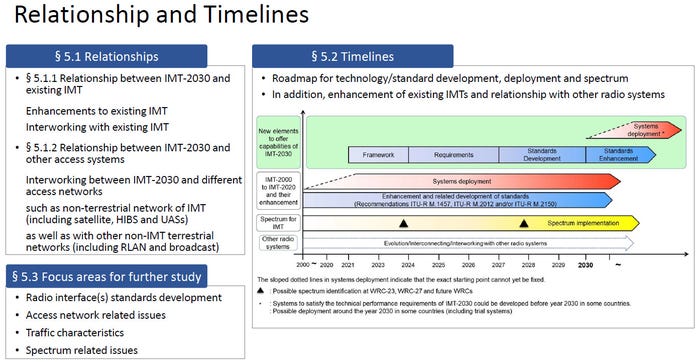
References:
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
FT: New benchmarks for Gen AI models; Neocloud groups leverage Nvidia chips to borrow >$11B
The Financial Times reports that technology companies are rushing to redesign how they test and evaluate their Gen AI models, as current AI benchmarks appear to be inadequate. AI benchmarks are used to assess how well an AI model can generate content that is coherent, relevant, and creative. This can include generating text, images, music, or any other form of content.
OpenAI, Microsoft, Meta and Anthropic have all recently announced plans to build AI agents that can execute tasks for humans autonomously on their behalf. To do this effectively, the AI systems must be able to perform increasingly complex actions, using reasoning and planning.
Current public AI benchmarks — Hellaswag and MMLU — use multiple-choice questions to assess common sense and knowledge across various topics. However, researchers argue this method is now becoming redundant and models need more complex problems.
“We are getting to the era where a lot of the human-written tests are no longer sufficient as a good barometer for how capable the models are,” said Mark Chen, senior vice-president of research at OpenAI. “That creates a new challenge for us as a research world.”
The SWE Verified benchmark was updated in August to better evaluate autonomous systems based on feedback from companies, including OpenAI. It uses real-world software problems sourced from the developer platform GitHub and involves supplying the AI agent with a code repository and an engineering issue, asking them to fix it. The tasks require reasoning to complete.
“It is a lot more challenging [with agentic systems] because you need to connect those systems to lots of extra tools,” said Jared Kaplan, chief science officer at Anthropic.
“You have to basically create a whole sandbox environment for them to play in. It is not as simple as just providing a prompt, seeing what the completion is and then evaluating that.”
Another important factor when conducting more advanced tests is to make sure the benchmark questions are kept out of the public domain, in order to ensure the models do not effectively “cheat” by generating the answers from training data, rather than solving the problem.
The need for new benchmarks has also led to efforts by external organizations. In September, the start-up Scale AI announced a project called “Humanity’s Last Exam”, which crowdsourced complex questions from experts across different disciplines that required abstract reasoning to complete.
Meanwhile, the Financial Times recently reported that Wall Street’s largest financial institutions had loaned more than $11bn to “neocloud” groups, backed by their possession of Nvidia’s AI GPU chips. These companies include names such as CoreWeave, Crusoe and Lambda, and provide cloud computing services to tech businesses building AI products. They have acquired tens of thousands of Nvidia’s graphics processing units (GPUs) through partnerships with the chipmaker. With capital expenditure on data centres surging, in the rush to develop AI models, the Nvidia’s AI GPU chips have become a precious commodity.
Nvidia’s chips have become a precious commodity in the ongoing race to develop AI models © Marlena Sloss/Bloomberg
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The $3tn tech group’s allocation of chips to neocloud groups has given confidence to Wall Street lenders to lend billions of dollars to the companies that are then used to buy more Nvidia chips. Nvidia is itself an investor in neocloud companies that in turn are among its largest customers. Critics have questioned the ongoing value of the collateralised chips as new advanced versions come to market — or if the current high spending on AI begins to retract. “The lenders all coming in push the story that you can borrow against these chips and add to the frenzy that you need to get in now,” said Nate Koppikar, a short seller at hedge fund Orso Partners. “But chips are a depreciating, not appreciating, asset.”
References:
https://www.ft.com/content/866ad6e9-f8fe-451f-9b00-cb9f638c7c59
https://www.ft.com/content/fb996508-c4df-4fc8-b3c0-2a638bb96c19
https://www.ft.com/content/41bfacb8-4d1e-4f25-bc60-75bf557f1f21
Tata Consultancy Services: Critical role of Gen AI in 5G; 5G private networks and enterprise use cases
Reuters & Bloomberg: OpenAI to design “inference AI” chip with Broadcom and TSMC
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
AI winner Nvidia faces competition with new super chip delayed