IHS Markit: $5 Billion to Be Spent on Outdoor Small Cell Backhaul Equipment: 2016 to 2020
By Richard Webb, research director, mobile backhaul and small cells, IHS Markit
Highlights:
- The outdoor small cell backhaul market accelerated in 2016, with revenue growing more than 200 percent year-over-year
- Just over $5 billion will be spent globally on outdoor small cell backhaul equipment from 2016 to 2020
- By 2020, deployments of outdoor small cell backhaul connections are projected to approach nearly 700,000
IHS Analysis:
The small cell backhaul market is still in experimentation mode and has been since early trials commenced in 2013. Market growth started to look more meaningful this year—with revenue up 233 percent year-over-year, albeit from a very modest base—but we anticipate the market to really kick into higher gear in 2018.
IHS Markit is forecasting that a cumulative $5.1 billion will be spent worldwide on outdoor small cell backhaul equipment between 2016 and 2020, driven by an increasing number of mostly modest-scale projects to augment 3G and Long Term Evolution (LTE) capacity in urban areas and to provide mobile coverage in rural markets. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the five-year period is 78 percent.
It’s worth noting that the $5.1 billion for outdoor small cells is in addition to the nearly $43 billion that’s being spent on macrocell backhaul equipment during the same five-year period.
Deployments of outdoor small cell backhaul connections are expected to grow to 109,000 in 2016, up from 35,000 in 2015. And by 2020, deployments are projected to reach 693,000—for a total installed base of around 1.9 million.
Wireless microwave makes up nearly 60 percent of small cell backhaul gear revenue today, climbing to over 80 percent in 2020 led by E band millimeter.
Geographically, small cell deployments generally reflect the regional share of the overall mobile infrastructure market. By 2020, the regional breakdown for small cell backhaul equipment will be: Asia Pacific (48 percent), Europe, the Middle East and Africa (27 percent), the Caribbean and Latin America (14 percent) and North America (11 percent).
Small Cell Report Synopsis:
The IHS Markit biannual small cell mobile backhaul equipment report tracks equipment used for transporting traffic from outdoor small cell sites, such as those attached to light poles, utility poles, and the sides and tops of buildings. It provides worldwide and regional market size, forecasts through 2020, analysis and trends for equipment, connections and cell sites by type. The report covers equipment including digital subscriber line (DSL) modems and digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAMs); Ethernet over copper and fiber; <6GHz microwave; point-to-point (P2P) microwave; point-to-multipoint (P2MP) microwave; and licensed and unlicensed millimeter wave.
For information about purchasing this report, contact the sales department at IHS Markit in the Americas at (844) 301-7334 or [email protected]; in Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) at +44 1344 328 300 or [email protected]; or Asia-Pacific (APAC) at +604 291 3600 or [email protected]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, a report “Mobile and Wireless Backhaul Market – by Equipment (Microwave, Millimeter Wave, Sub 6 GHZ, Test and Measurement), by Services (Network, System Integration, Professional) – Worldwide Market Forecasts and Analysis to 2015 – 2020″, the market is estimated to grow from USD 17.85 Billion in 2015 to USD 33.15 Billion by 2020, at an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.18% from 2015 to 2020.
The growing need to remain connected and increasing adaption rate of 3G and 4G (Long-Term Evolution) networks has enhanced the market of mobile and wireless backhaul. Increasing usage of smart phones and tablets has increased the mobile data traffic and this has fueled the market for a fast and reliable connectivity. Technical advancements such as small cells, has to quench the high bandwidth needs.
Growing mobile data traffic is spurring the market of mobile and wireless backhaul
Nowadays, spectrum band has been increased to up to 42GHz owing to the need for faster connectivity. Also, the introduction of 5G is offering great opportunity for mobile and wireless backhaul market. Popularity of data exhaustive such as video on demand, online streaming and video connectivity is continually growing and driving the mobile traffic data. The installation of small cells enables the network operators to offload the mobile data on the unlicensed spectrum using Wi-Fi, hence reducing the congestion on the macro-cells and licensed spectrum.
The microwave equipment segment is estimated to account for majority of the total mobile and wireless backhaul market in 2015, but is slowly losing its market share because of the increasing adoption of millimeter wave equipment. The major trends seen in the service market are the increasing use of system integration services by end user to effectively deploy mobile and wireless backhaul solutions and the easy integration of these solutions with the existing ones.
The North America region is expected to contribute the maximum market share to the overall mobile and wireless backhaul market
North America will witness the highest market share in 2015, and will continue to dominate the globe during the forecast period. The mobile and wireless backhaul markets in Asia-Pacific (APAC), Middle East and Africa (MEA), and Latin America are expected to witness substantial growth, as large enterprises as well as SMBs are yet to adopt the solutions. Major enterprises in these emerging economies are expected to increase investments in mobile and wireless backhaul solutions, due to the huge demand for managing aging infrastructure and assets.
The major vendors in the mobile and wireless backhaul market include Alcatel Lucent, Cisco Systems, Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, Broadcom Corporation, Brocade Communications Systems, Fujitsu, Nokia Networks, Tellabs, and ZTE Corporation. A detailed analysis on key industry players is done to provide key insights about their businesses, products and services, key strategies, and recent developments associated with the mobile and wireless backhaul market.
The mobile and wireless backhaul market has been segmented into equipment, services, and regions. The equipment is further segmented into Microwave, Millimeter wave, Sub 6 GHz, and Test and Measurement. The service types are Network services, System Integration, and Professional Services. Furthermore, the report classifies the market according to the regions of North America, Europe, APAC, MEA, and Latin America.
More on MarketsandMarkets Wireless Backhaul report:
Contact:
Mr. Rohan
Markets and Markets
UNIT no 802, Tower no. 7, SEZ
Magarpatta city, Hadapsar
Pune, Maharashtra 411013, India
1-888-600-6441
Email: [email protected]
US Telcos Way Behind MSOs in Broadband Deployment & Subscribers
Bottom Line:
In a new research note, Moody’s Investor Services stated that the overall U.S. telecom industry has not kept pace with cable companies (cablecos or MSOs) in terms of broadband deployments and speeds.
“Except for Verizon’s FiOS footprint, the US telecom industry has under-invested in broadband,” said Mark Stodden, VP and senior credit officer for Moody’s Investor Service. “Market share gains of cable operators (MSO’s) will persist given the capital required to catch up,” he added.
Stodden concluded that “wireline revenues will continue eroding as cable operators gain broadband share.”
Fierce Telecom also reported Moody’s research on telcos under-investing in broadband.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Telcos Lose While MSO’s Gain Broadband Subscribers:
In 3Q-2016, the top telcos collectively lost about 150,000 subscribers, widening the loss of about 145,000 they saw in the same period a year ago.
Leichtman Research Group (LRG) reported in a press release that the fourteen largest cable and telephone providers in the US — representing about 95% of the market — acquired about 625,000 net additional high-speed Internet subscribers in 3Q 2016. These top broadband providers now account for 92.5 million subscribers — with top cable companies having 57.8 million broadband subscribers, and top phone companies having 34.7 million subscribers. Among the individual telcos tracked by LRG for the Q3 study, only Verizon (24,000) and Cincinnati Bell (3,100) came away with net sub additions in the period.
Other broadband findings for the quarter include:
- Overall, broadband additions in 3Q 2016 were 99% of those in 3Q 2015
- The top cable companies added about 775,000 subscribers in 3Q 2016 — 99% of the net additions for the top cable companies in 3Q 2015
- The top phone companies lost about 150,000 broadband subscribers in 3Q 2016 — similar to the loss of about 145,000 in 3Q 2015
- Telco providers have had net broadband losses in five of the past six quarters
- In the first three quarters of 2016, cable companies (MSOs) added about 2,440,000 broadband subscribers, while Telcos lost about 475,000 subscribers
“While major providers now account for nearly 92.5 million broadband subscribers in the US, the broadband market continues to expand with top cable providers driving the growth,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for LRG, in a statement. “Over the past year, cable companies added more than 3.5 million broadband subscribers, accounting for 118% of the 2.995 million net broadband additions.”
Telco CAPEX Declined in 2015:
USTelecom, the champion of the traditional telcos, revealed in its annual broadband investment research report that broadband provider network capital expenditures (capex) declined nearly $1 billion in 2015 to $76 billion.
US Telecom wrote in its report that wireline broadband investment “remains critical to modernizing the nation’s network infrastructure and maintaining strong international leadership.”
…………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T’s GigaPower:
AT&T maintains it’s continuing to invest in next-generation broadband networks under the company’s GigaPower brand. Earlier this week, AT&T announced that it has reached 46 markets with its 1 Gbps FTTH service. AT&T plans to expand GigaPower in parts of 23 more areas – at least 67 metros in total.

Image Courtesy of AT&T
Deepening its FTTH footprint continues to be a priority for AT&T. However, it’s unclear how broad the coverage is in these markets and what the take rate for true high speed Internet and TV will be.
AT&T says on its GigaPower website: “With internet speeds 20x faster than the average cable customer, you can download 25 songs in 1 second or your favorite 90-minute HD movie in less than 34 seconds.”
The latest AT&T GigaPower map is here.
………………………………………………………………………..
Please feel free to comment in the box below this post if you have a ComSoc techblog account. You can get one by filling out this application: https://techblog.comsoc.org/new-user-request-form/
Akamai: Global Internet Speeds Increased 21% Y-o-Y
Akamai’s “Third Quarter, 2016 State of the Internet Report,” states that global average Internet speeds increased 21% year over year during the quarter, and peak speeds increased 16% year over year. The report includes data gathered from across the Akamai Intelligent Platform about connection speeds, broadband adoption metrics, notable Internet disruptions, IPv4 exhaustion and IPv6 implementation, and other relevant topics concerning the Internet and its usage, as well as trends seen in the data over time. Here are a few highlights by category:
Global Average Connection Speeds and Global Broadband Adoption:
- Global average connection speed increased 2.3% to 6.3 Mbps in the third quarter, a 21% increase year over year.
- South Korea had the highest average connection speed at 26.3 Mbps in the third quarter.
- US lags far behind, ranking No. 16 with average connection speed of 15.3 Mbps, a 7.7% rise from the prior quarter.
- Global average peak connection speed increased 3.4% to 37.2 Mbps in the third quarter, rising 16% year over year.
- Singapore had the highest average peak connection speed at 162 Mbps in the third quarter.
- Global 10 Mbps broadband adoption rate rose 5.4% quarter over quarter, and 15 Mbps and 25 Mbps broadband adoption rates increased 6.5% and 5.3%, respectively.
- Average mobile connection speeds ranged from a high of 23.7 Mbps in the United Kingdom to a low of 2.2 Mbps in Venezuela.
IPv4 and IPv6:
- The number of unique IPv4 addresses connecting to the Akamai Intelligent Platform was just over 806 million, which is 0.7% more than the second quarter of 2016.
- Belgium remained the clear global leader in IPv6 adoption with 39% of its connections to Akamai occurring over IPv6, up 3.3% from the previous quarter.
- Cable and wireless/mobile providers continued to drive the largest volumes of IPv6 requests, with Comcast, AT&T and Verizon Wireless topping the list with 44%, 43% and 80% of their requests to Akamai being made over IPv6 in their regions, respectively.
AT&T network uses open ROADM technology on 100 Gbps optical wavelength
AT&T says it has implemented a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer to deliver a 100 gigabits-per-second optical wavelength on a production network. The deployment, said to be a first with multi-vendor interoperability, was in the Dallas, TX area. AT&Ts new network provided the connection of two IP multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) routers with transponders and ROADMs from Ciena and Fujitsu.
Andre Fuetsch, President and CTO at AT&T Labs writes in a blog that the company is pursuing two goals with new ROADMs: 1. software control and 2. open hardware specs. Fuetsch also said the new ROADM is an industry-first, multi-vendor interoperability implementation.
“We recently implemented in the Dallas area a 100 gigabit per second optical wavelength in our production network using Open ROADM-compliant technology,” he wrote.
Controlling and managing the optical network is done via the NetConf/YANG APIs and information models defined in the Open ROADM Multi-Source Agreement standards. This is an industry-first demonstration of model-driven control and management of optical equipment. The 100G wavelength was provisioned using an SDN ROADM Controller developed by Fujitsu and integrated into the AT&T ECOMP architecture.
Learn more about the project and see the latest specs and project participants at OpenROADM.org.
AT&T says it “welcomes new suppliers and service providers to join our open ecosystem!”
In a 2015 research note, Global Industry Analysts forecast that the worldwide reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) market would surpass $10.8 billion by 2020. The firm saw much of that growth coming from the need for data, video, and voice service providers to address the immense network traffic generated by the likes of social networks, data center virtualization, file sharing, video downloads, cloud computing, and online gaming.
Vodafone Trials Nokia’s Cloud RAN; Other 5G Research Partnerships
Vodafone is keenly interested in Nokia’s Cloud RAN architecture for switching between 4G, 5G and IoT. Trials of Nokia’s AirScale Cloud RAN platform conducted at a Vodafone R&D site in Italy assessed the suitability of C-RAN to provide the same service level as existing RAN architecture used for the company’s LTE networks. The tests also evaluated the potential added efficiencies and benefits associated with deploying cloud technology, which Nokia stated includes improved scalability and flexibility.
The trials examined the use of cloud-based radio access technology for macro networks. A major reason, over and above the usual efficiency/agility ones, to move RANs to the cloud is the hybrid nature of future networks, with 4G expected to coexist with both new 5G air interfaces and LPWANs for IoT.
Splitting baseband processing functionality between real-time and non real-time functions is the name of the game, apparently, because that allows the most time sensitive functions to be performed at the edge of the network, while others are virtualized and run in the cloud, allowing all the expected cloudy goodness.
“Working with Nokia on this trial we have seen how the application of Cloud RAN architecture can help the network react to changing demands quickly,” said Santiago Tenorio, Head of Networks at Vodafone Group. “It speeds up the delivery of services and will help with the transition to 5G.”
“Our Cloud RAN technology can help operators optimize network performance even as they cope with the increasing demands being placed upon them,” said Roberto Loiola, Head of Vodafone Global Customer Business Team at Nokia. “This trial with Vodafone builds on this promise, enabling Nokia to apply its longstanding working relationship with them to explore how we can enable the smooth and efficient transition from 4G to 5G.”
Other 5G trials in the works:
- Telefónica recently announced a 5G Proof of Concept trial with Huawei and last week dabbled in a spot of Pre5G massive MIMO live testing with ZTE.
- Huawei and BT have established a 5G research partnership, including how faster mobile communication technologies might be applied, as well as the technical and commercial feasibility of deploying them.
- We reported last week that Verizon was testing “Wireless Fiber” in a 5G trial.
- Ericsson believes most large wireless network operators are already planning 5G trials.
References:
http://telecoms.com/478183/nokia-and-vodafone-take-to-the-clouds-in-italy/
Cincinnati Bell’s Fiber Expansion will enable SD-WAN as a virtual network service
Cincinnati Bell’s bold three-year plan to expand its fiber networks will open the door for more opportunities to explore virtual network infrastructure, said Leigh Fox, COO of Cincinnati Bell, on December 6th during the UBS 44th Annual Global Media and Communications Conference.
“This project we just kicked off to look at this will be a 36 month or longer project,” Fox said. “As we build more fiber into our footprint, we also begin to hit thresholds where true network transformation is possible.” Fox said that the first tangible benefit of the transformation could be to offer an SD-WAN service to business customers.
“In the short run something like SD-WAN is more of an opportunity from a product standpoint for us,” said COO Leigh Fox. “We’ll launch an SD-WAN product in April next year so we see more growth from a revenue standpoint.”
Fox said that while the provider has no immediate plans to extend fiber into new territories, SD-WAN and other cloud-based services could strengthen the telco’s bond with multi-site customers.
“From an enterprise standpoint, I think that’s where you get into SD-WAN or more network as a service NaaS-type products,” Fox said. “I don’t think that you have build network and the way the product innovations are going we can combine unique products to follow them anywhere.”
Comments (not from this author who’s a SD-WAN skeptic):
Any technology needs to focus on the business proposition. Here are a few points that I think are most important:
- The WAN is really expensive and often more than 70% of the IT network budget. Even a 10% reduction in WAN cost has a substantial impact on the bottom line.
- Typically 50% of WAN spending is unused or “zombie” bandwidth as it is wasted for redundancy. (Imagine having 50% of your employees sitting around waiting for something to do)
- SD-WANs include such as cost of assets, remote administration, and cost of operation, but these two items are headline issues that need urgent solutions.
https://opennetworkingusergroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/ONUG-SD-WAN-WG-Whitepaper_Final1.pdf
Verizon to test 5G “wireless fiber” for Internet & TV in Spring 2017
Verizon Communications CEO Lowell McAdam described the teleco’s first 5G fixed-wireless trial, planned for early next year, as “wireless fiber.” The trial will focus on several small towns and will support gigabit speeds and over-the-top (OTT) video.
“We won’t be charging for the service, but we will be learning from it and figuring out the distance between the transmitter and the receiver in a 5G environment,” McAdam said at a UBS investor conference in New York.
Verizon has long touted 5G technology, well in advance of the ITU-R standard. 5G can be up to 100 faster than current 4G wireless service, as the basis for a new cable and Internet service. Analysts claim 5G is needed for Verizon’s six year, $300 million plan to offer TV and Internet in Boston, for example. But McAdam had not previously given the early 2017 timeline and additional details about Verizon’s efforts.
“We could go to a 300-channel bundle,” McAdam commented. But he noted that the industry is seeing increased demand for “skinny bundles” with fewer channels and that a “skinny bundle” would be part of the Verizon 5G fixed wireless trial. The customer premises equipment (CPE) supporting the offering will be “very simple,” according to McAdam. It essentially will be a traditional home router with a 5G chip in it, he said.
The carrier is looking for ways to save money and crack new markets as growth in its two main lines of business, wired and wireless phone service, have slowed. In addition to 5G video service, McAdam has also targeted service for smart, connected devices in the Internet of things and online advertising, via the acquisition of AOL and pending purchase of Yahoo.
Verizon’s FiOS unit, which offers TV and Internet service, largely ceased expanding years ago because of the expense of building fiber optic lines to customers. But the 5G wireless plan could dramatically reduce those costs. A customer would only need a typical router placed by a window to receive signals for high speed Internet and TV service from a neighborhood-based cell tower. Verizon has even discussed deploying more numerous microcells, with new technology that can put a 5G transmitter inside a street light, for example.
“This will allow you to stop anywhere from 200 feet to 1,000 feet, somewhere in that range, we think, from the home and then make it a wireless last leg into the home,” McAdam said. “And I think that is going to be the predominant architecture for wireless service going forward,” he added.
Author Notes:
- FiOS is available in about 54% of the three-state territory Frontier acquired from Verizon in September, 2015. While Verizon’s wireless network operates nationwide, the telco has reduced wireline operations to focus on the Northeast US.
- Google Fiber has apparently been put on hold as parent company Alphabet contemplates moving away from fiber to the home service towards a wireless platform that could provide high speed Internet access and TV service in urban areas for much less money. Google is hoping to use wireless technology to connect homes, rather than cables, in about a dozen new metro areas, including Los Angeles, Chicago and Dallas, according to people familiar with the company’s plans. As a result Alphabet has suspended projects in San Jose, Calif., and Portland, OR. http://www.wsj.com/articles/googles-high-speed-web-plans-hit-snags-1471193165
References:
Verizon’s Wireless TV And Internet Service Coming To Small Towns Soon
CEO: Verizon 5G Fixed Wireless Trial Will Offer Gigabit Broadband via ‘Wireless Fiber’
Verizon to Sell Data Centers to Equinix for $3.6 Billion
Verizon Communications will reap $3.6 billion when it sells the 24 data center sites it gained in its $1.3 billion acquisition of Terremark Worldwide five years ago to Equinix, a real estate investment trust. The deal will enable Verizon to raise cash after its expected $4.83 billion purchase of Yahoo! Inc. and the acquisition of wireless spectrum licenses.
For Verizon, the nation’s largest wireless carrier, the deal marks a retreat from the data-centers business five years after it bought Terremark Worldwide Inc. for $1.3 billion. As prospects faded and Verizon invested in more areas like mobile video and advertising, the company decided to put the data-centers unit up for sale about two years ago.
As the telecommunications industry matures, Verizon is shedding assets and turning the business in a new direction. Using go90, its video-streaming business, AOL’s web properties and the pending purchase of Yahoo! Inc., Verizon is entering a mobile video and advertising arena to challenge Google and Facebook Inc.
……………………………………………………………………………….
The acquisition of these assets will enable Equinix customers to further respond to a key market trend that is enabling their evolution from traditional businesses to “digital businesses” — the need to globally interconnect with people, locations, cloud services and data. Additionally, customers will have the opportunity to operate on an expanded global platform to process, store and distribute larger volumes of latency sensitive data and applications at the digital edge, closer to end-users and local markets.
The data centers to be acquired include approximately 900 customers, with a significant number of enterprise customers new to Equinix’s platform, and it adds approximately 2.4 million gross square feet. It will bring Equinix’s total global footprint to 175 data centers in 43 markets and approximately 17 million gross square feet across the Americas, Europe and Asia-Pacific markets.
The transaction is expected to close by mid-2017, subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions.
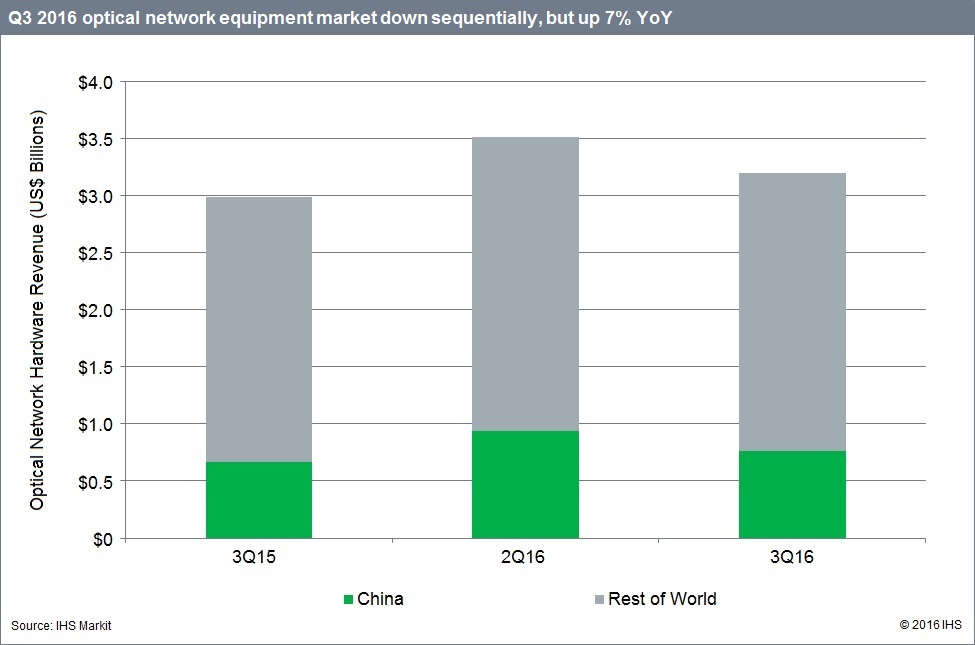
IHS: China’s Optical Spending Spree Slows; WWide +7% YoY but -9% QoQ
By Heidi Adams, senior research director, transport networks, IHS Markit
Highlights:
- In the third quarter of 2016 (Q3 2016), optical equipment revenue was down sequentially, but up on a year-over-year basis
- The extremely high growth rates seen in the Chinese optical market in the first half of 2016 have moderated
- 100G wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) long haul and data center interconnect (DCI) applications continue to be hot areas for optical equipment investment
IHS Analysis:
Worldwide, the optical equipment market totaled $3.2 billion in Q3 2016, gaining 7 percent year-over-year, but declining 9 percent quarter-over-quarter. The market was buoyed by continuing spend in China—although at lower levels—and solid year-over-year performance across all regions. The sequential drop was a result of the typical seasonal slowdown in Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA) and the Caribbean and Latin America (CALA)—and also a dip in Asian Pacific investment from an extremely high Q2 2016.
The great China optical gear spending spree seen in the first half of the year began to slow down in Q3 2016, with optical spending in the country down more than 19 percent sequentially. Although the high growth rates experienced in Q1 and Q2 2016 could not be sustained over the long run, spending increased over 14 percent year-over-year, as 100G infrastructure investment led by China Mobile continued.
North America was the only region to see both quarter-over-quarter and year-over-year growth. 100G long haul continues to perform well despite a drop in investment from Infinera customers. And the DCI market driven by the internet content providers (ICPs) is also driving growth.
The WDM equipment segment, at $2.9 billion in Q3 2016, was down 6 percent sequentially but up a solid 10 percent year-over-year. WDM is and will continue to be the growth engine for optical networks, and we forecast a 2015‒2020 compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7 percent for this segment. Meanwhile, the Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) segment reverted back to its secular decline, with revenue down 18 percent from the year-ago quarter.
Looking at Q3 market share, Huawei continued to lead by a wide margin, supported by strong spending on 100G projects in China, as well as strength in EMEA and CALA. Ciena maintained its commanding lead in the North American market and maintained second place overall. Nokia edged out ZTE to regain third place overall based on solid performance in the submarine line terminating equipment (SLTE) segment, where it regained the number-one market share position.
Optical Report Synopsis:
The quarterly IHS Markit optical network hardware report tracks the global market for metro and long-haul WDM and SONET/SDH equipment and ports. The report provides market size, market share, forecasts through 2020, analysis and trends.
For information about purchasing this report, contact the sales department at IHS Markit in the Americas at (844) 301-7334 or[email protected]; in Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) at +44 1344 328 300 or [email protected]; or Asia-Pacific (APAC) at +604 291 3600 or [email protected]
SVIEF 2017 Silicon Valley Smart Future Summit: January 9, 2017
Organized by SVIEF (Silicon Valley Innovation and Entrepreneurship Forum), the SV Smart Future Summit (January 9, 2017 at the Santa Clara Convention Center) is an international conference designed to foster innovation and promote business partnerships connecting US and Asia-Pacific region. The Summit includes two parts: Smart Future keynotes and panel discussions, and SVIEF-Star Demos.
During the Summit, attendees will experience first-hand demos of next-generation applications run on this new network. Learn from engaging keynotes, tech presentations, and panel discussions lead by visionaries in the field. Hear from community leaders highlighting recent case studies, success stories, and best practices to improve your group’s next-generation technology initiatives.
The Summit has been carefully designed to offer value to all experience levels, from students to investors, senior researchers, software architects, network engineers and senior management. SVIEF staff looks forward to having you join us for this exciting event.
IEEE ComSoc is a co-sponsor of this event.