Uncategorized
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison and Nokia use AI to reduce energy demand and emissions
Indonesian network operator Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison has deployed Nokia Energy Efficiency (part of the company’s Autonomous Networks portfolio – described below) to reduce energy demand and carbon dioxide emissions across its RAN network using AI. Nokia’s energy control system uses AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time traffic patterns, and will enable the operator to adjust or shut idle and unused radio equipment automatically during low network demand periods.
The multi-vendor, AI-driven energy management solution can reduce energy costs and carbon footprint with no negative impact on network performance or customer experience. It can be rolled out in a matter of weeks.
Indosat is aiming to transform itself from a conventional telecom operator into an AI TechCo—powered by intelligent technologies, cloud-based platforms, and a commitment to sustainability. By embedding automation and intelligence into network operations, Indosat is unlocking new levels of efficiency, agility, and environmental responsibility across its infrastructure.
Earlier this year Indosat claimed to be the first operator to deploy AI-RAN in Indonesia, in a deal involving the integration of Nokia’s 5G cloud RAN solution with Nvidia’s Aerial platform. The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the three firms included the development, testing, and deployment of AI-RAN, with an initial focus on transferring AI inferencing workloads on the AI Aerial, then the integration of RAN workloads on the same platform.
“As data consumption continues to grow, so does our responsibility to manage resources wisely. This collaboration reflects Indosat’s unwavering commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable innovation, using AI to not only optimize performance, but also reduce emissions and energy use across our network.” said Desmond Cheung, Director and Chief Technology Officer at Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison.
Indosat was the first operator in Southeast Asia to achieve ISO 50001 certification for energy management—underscoring its pledge to minimize environmental impact through operational excellence. The collaboration with Nokia builds upon a successful pilot project, in which the AI-powered solution demonstrated its ability to reduce energy consumption in live network conditions.
Following the pilot project, Nokia deployed its Energy Efficiency solution to the entire Nokia RAN footprint within Indonesia, e.g. Sumatra, Kalimantan, Central and East Java.
“We are very pleased to be helping Indosat deliver on its commitments to sustainability and environmental responsibility, establishing its position both locally and internationally. Nokia Energy Efficiency reflects the important R&D investments that Nokia continues to make to help our customers optimize energy savings and network performance simultaneously,” said Henrique Vale, VP for Cloud and Network Services APAC at Nokia.
Nokia’s Autonomous Networks portfolio, including its Autonomous Networks Fabric solution, utilizes Agentic AI to deliver advanced security, analytics, and operations capabilities that provide operators with a holistic, real-time view of the network so they can reduce costs, accelerate time-to-value, and deliver the best customer experience.
Autonomous Networks Fabric is a unifying intelligence layer that weaves together observability, analytics, security, and automation across every network domain; allowing a network to behave as one adaptive system, regardless of vendor, architecture, or deployment model.
References:
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
Bloomberg News reports that AT&T is in talks to acquire Lumen Technologies’ consumer fiber operations, in a deal that could value the unit at more than $5.5 billion, citing people with knowledge of the matter. The companies are in exclusive discussions about a transaction valuing the unit at more than $5.5 billion, said one of the people, who requested to not be identified discussing confidential information. The terms of the unfinalized deal could change or the talks might still collapse, according to the report.
“If the rumored price is correct, it is a great deal for AT&T,” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors. “The value per [fiber] location at $5.5 billion would be about $1,300 which compares to Frontier at $2,400, Ziply at $3,800, and Metronet at $4,700,” the analysts continued.

https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/is-at-t-getting-a-screaming-deal-on-lumen-s-fiber-
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
Microsoft choses Lumen’s fiber based Private Connectivity Fabric℠ to expand Microsoft Cloud network capacity in the AI era
Lumen, Google and Microsoft create ExaSwitch™ – a new on-demand, optical networking ecosystem
ACSI report: AT&T, Lumen and Google Fiber top ranked in fiber network customer satisfaction
Lumen to provide mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
WiFi 7: Backgrounder and CES 2025 Announcements
Backgrounder:
Wi-Fi 7, also known as the IEEE 802.11be-2024 [1.], is the latest generation of Wi-Fi technology, offering significantly faster speeds, increased network capacity, and lower latency compared to previous versions like Wi-Fi 6, by utilizing features like wider 320MHz channels, Multi-Link Operation (MLO), and 4K-QAM modulation across all frequency bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz). Wi-Fi 7 is designed to use huge swaths of unlicensed spectrum in the 6 GHz band, first made available in Wi-Fi 6E standard, to deliver a maximum data rate of up to 46 Gbps.
Note 1. The Wi-Fi Alliance began certifying Wi-Fi 7 devices in January 2024. The IEEE approved the IEEE 802.11be standard in 2024 on September 26, 2024. The standard supports at least one mode of operation capable of supporting a maximum throughput of at least 30 Gbps, as measured at the MAC data service access point (SAP), with carrier frequency operation between 1 and 7.250 GHz, while ensuring backward compatibility and coexistence with legacy IEEE Std 802.11 compliant devices operating in the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The role of 6 GHz Wi-Fi in delivering connectivity is changing, and growing. A recent report from OpenSignal, found that smartphone users spend 77% to 88% of their screen-on time connected to Wi-Fi. Further, the latest generations of Wi-Fi (largely due to the support of 320 MHz channels and critical features like Multi-Link Operation) are increasingly more reliable and deterministic, making them viable options for advanced applications like extended reality in both the home and the enterprise.
New features:
- 320MHz channels: Double the bandwidth compared to Wi-Fi 6E.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Allows devices to connect using multiple channels across different bands simultaneously.
- K-QAM modulation: Enables more data to be transmitted per signal.
1. TP-Link unveiled the Deco BE68 Whole Home Mesh Wi-Fi 7 solution, which is claims delivers speeds of up to 14 Gbps, covering 8,100 sq. ft. and supporting up to 200 connected devices. “Featuring 10G, 2.5G, and 1G ports, it ensures fast, reliable wired connections. With Deco Mesh technology, the system delivers seamless coverage and uninterrupted performance for streaming, gaming, and more,” stated the company.
TP-Link also announced an outdoor mesh system to address the increasing demand for outdoor Wi-Fi connectivity. The Deco BE65-Outdoor and Deco BE25-Outdoor nodes are equipment with weather, water and dust proof enclosures. When combined with the Deco indoor models, a cohesive and reliable indoor-outdoor mesh network that allows a user to move seamlessly between the two environments can be achieved.
2. Intel Core Ultra Series 2) are all equipped with Wi-Fi 7 capabilities integrated into the silicon, Intel has made Wi-Fi its standard choice. On its website, the company explained that a “typical” Wi-Fi 7 laptop is a potential maximum data rate of almost 5.8 Gbps. “This is 2.4X faster than the 2.4 Gbps possible with Wi-Fi 6/6E and could easily enable high quality 8K video streaming or reduce a massive 15 GB file download to roughly 25 seconds vs. the one minute it would take with the best legacy Wi-Fi technology,” Intel added.
3. ASUS New Wi-Fi 7 Router Lineup

ASUS unveiled a range of new networking products at CES 2025, including the ASUS RT-BE58 Go travel router and ASUS 5G-Go mobile router – both recipients of the CES 2025 Innovation Award – alongside the ROG Rapture GT-BE19000AI gaming router and the ZenWiFi Outdoor series for home Wi-Fi setups.
- The RT-BE58 Go – is a dual-band, Wi-Fi 7-capable mobile router supports three use cases: 4G/5G mobile tethering, public Wi-Fi hotspot (WISP), and conventional home router. It also supports VPN from up to 30 service providers and subscription-free Trend Micro security for online protection, while AiMesh compatibility allows for the router to be paired with other ASUS routers to provide wider signal coverage.
- The ROG Rapture GT-BE19000AI is the iteration of the GT-BE19000 router released last year, this time with an NPU onboard coupled with CPU and MCU. This tri-core combination enables features like ROG AI Game Booster and Adaptive QoS 2.0 to reduce network latency by up to 34% for supported games, plus 46% power savings through its AI Power Saving mode that saves power based on usage patterns. Additional features include advanced ad and tracker blocking, network insights, and RF scanning.
References:
https://standards.ieee.org/ieee/802.11be/7516/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-Fi_7
https://www.mathworks.com/help/wlan/ug/overview-of-wifi-7-or-ieee-802-11-be.html
WiFi 7 and the controversy over 6 GHz unlicensed vs licensed spectrum
Highlights of GSA report on Private Mobile Network Market – 3Q2024
According to GSA, the private mobile network market (PMNM) continued to grow in 3Q2024, as the number of unique customer references for deployments reached 1,603. The market is being driven by sectors like manufacturing, education, and mining, which use these networks for enhanced data, security and mobility needs.
On average, 71% of references included in the GSA database are non-public and unique to this database, submitted by members of the GSA Private Mobile Networks Special Interest Group (SIG). This number can be higher for certain industries, with more than 80% of sectors such as military and defense, maritime and power plants not visible in the public domain. The referenced SIG includes 16 companies: 450Alliance, 5G-ACIA, AI-Link, Airspan, Celona, Dell, Ericsson, GSMA, JMA Wireless, Keysight Technologies, Mavenir, Nokia, OnGo Alliance, OneLayer, PrivateLTEand5G.com and TCCA. GSA would like to thank its members 450Alliance, Airspan, Celona, Ericsson, Keysight Technologies, Mavenir, Nokia and OneLayer for sharing general information about their network deployments to enable this report and data set to be produced. New data has resulted in a significant uplift in this update.
Other PMNM highlights in the 3rd quarter 2024 include:
• There are 80 countries around the world with at least one private mobile network.
• Of the top 10 reporting countries, the United States reported growth of 24%, followed by the United Kingdom, up 11%, Sweden by 9% and Japan and Australia by 5% each. Finland and the Republic of Korea grew by 4% each
• Seaports and oil and gas were the fastest-growing industries, up 9%. Manufacturing, education and academic research and mining remain the top three sectors for customer references, although this does not represent the actual size and scale of deployments, which vary by user type.
• There are 80 countries around the world with at least one private mobile network.
• There is typically a strong, positive correlation between the number of private mobile network references and countries with dedicated spectrum. Private mobile networks are mainly in high- and upper-middle-income regions so far, with the United States, Germany, the United Kingdom, China and Japan having the most references. It is sometimes reported that China has a high number of networks, reaching up to 30,000, but GSA believes a large portion use the public network and therefore do not meet our definition.

Image Credit: GSA
Notes:
The definition of a private mobile network used in this report is a 3GPP-based 4G LTE or 5G network intended for the sole use of private entities, such as enterprises, industries and governments. They can use only physical elements, RAN or Core, or a combination of physical and virtual elements — for example hosted by a public land mobile network — but as a minimum, a dedicated network core must be implemented. The definition includes MulteFire or Future Railway Mobile Communication System. The network must use spectrum defined in 3GPP, be generally intended for business-critical or mission-critical operational needs, and where it is possible to identify commercial value, the database includes contracts worth more than €50,0000 and between €50,000 and €100,000 to filter out small demonstration network deployments. Private mobile networks are usually not offered to the general public, although GSA’s analysis does include the following: educational institutions that provide mobile broadband to student homes; private fixed wireless access networks deployed by communities for homes and businesses; city or town networks that use local licenses to provide wireless services in libraries or public places (possibly offering Wi-Fi with 3GPP wireless backhaul), which are not an extension of the public network.
Non-3GPP networks such as those using Wi-Fi, TETRA, P25, WiMAX, Sigfox, LoRa and proprietary technologies are excluded from the data set. Network implementations using solely network slices from public networks or placement of virtual networking functions on a router are also excluded. Where identifiable, extensions of the public network (such as one or two extra sites deployed at a location, as opposed to dedicated private networks) are excluded. These items may be described in the press as a type of private network.
References:
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G and 4G LTE cellular networks for the global defense sector is a $1.5B opportunity
SNS Telecom & IT: $6 Billion Private LTE/5G Market Shines Through Wireless Industry’s Gloom
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G Network market annual spending will be $3.5 Billion by 2027
Dell’Oro: Private RAN revenue declines slightly, but still doing relatively better than public RAN and WLAN markets
Pente Networks, MosoLabs and Alliance Corp collaborate for Private Cellular Network in a Box
HPE Aruba Launches “Cloud Native” Private 5G Network with 4G/5G Small Cell Radios
U.S. Weighs Ban on Chinese made TP-Link router and China Telecom
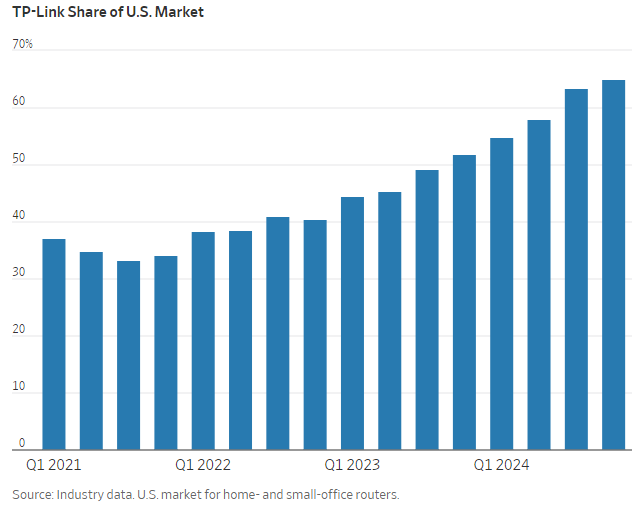
Today, the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported that the U.S. is considering banning the sale of China made TP-Link internet routers over concerns the home networking devices pose a security risk. Government authorities may ban the popular routers which have been linked to Chinese cyberattacks. TP-Link has roughly 65% of the U.S. market for routers for homes and small businesses. It is also the top choice on Amazon.com, and powers internet communications for the Defense Department and other federal government agencies.
Investigators at the U.S. Commerce, Defense and Justice departments have opened their own probes into the company, and authorities could ban the sale of TP-Link routers in the U.S. next year, according to people familiar with the matter. An office of the Commerce Department has subpoenaed TP-Link, some of the people said. If its routers are banned from the U.S., it would mark the biggest extraction of Chinese telecom equipment from the country since the Trump administration in 2019 ordered Huawei Technologies ripped out of American infrastructure.
TP-Link routers are routinely shipped to customers with security flaws, which the company often fails to address, according to people familiar with the matter. While routers often have bugs, regardless of their manufacturer, TP-Link doesn’t engage with security researchers concerned about them, the WSJ said. However, TP-Link told CBS MoneyWatch that the company’s “security practices are fully in line with industry security standards in the U.S.”
TP-Link router. Photo: Meghan Petersen/WSJ
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
TP-Link has also joined with more than 300 internet providers in the U.S. to be the router that is mailed to new homes that sign up for their services. Federal contracting documents show TP-Link routers supply everything from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration to the Defense Department and Drug Enforcement Administration, and the routers are sold at online military exchanges. The company’s market dominance has been achieved in part through lower prices. Its routers are cheaper than competitors, often by more than half, according to market data.
TP-Link sells in the U.S. through a business unit based in California. According to business records, TP-Link co-founder Zhao Jianjun is the chief executive of the California operation and he and his brother still ultimately control all global TP-Link entities. A spokeswoman for that unit said TP-Link assesses potential security risks and takes action to address known vulnerabilities.
“We welcome any opportunities to engage with the U.S. government to demonstrate that our security practices are fully in line with industry security standards, and to demonstrate our ongoing commitment to the U.S. market, U.S. consumers, and addressing U.S. national security risks,” the spokeswoman said.
Asked to comment about potential actions against TP-Link, Liu Pengyu, a spokesman for the Chinese Embassy in Washington, said the U.S. was using the guise of national security to “suppress Chinese companies.” He added that Beijing would “resolutely defend” the lawful rights and interests of Chinese firms.
TP-Link’s U.S. growth took off during the pandemic, when people were sent home to work and needed reliable internet. The company climbed from around 20% of the U.S. market for home and small-business routers in 2019 to around 65% this year. It took an additional 5% of the market in just the third quarter of this year, according to industry data. The TP-Link spokeswoman disputed the industry data but said the company’s market share has grown in the U.S.
An analysis from Microsoft published in October found that a Chinese hacking entity maintains a large network of compromised network devices mostly comprising thousands of TP-Link routers. The network has been used by numerous Chinese actors to launch cyberattacks. These actors have gone after Western targets including think tanks, government organizations, nongovernment organizations and Defense Department suppliers.
The Defense Department earlier this year opened an investigation into national-security vulnerabilities in Chinese routers, according to people familiar with the matter. The House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party in August urged the Commerce Secretary to investigate TP-Link because it presents an “unusual degree of vulnerabilities.” The House of Representatives in September passed legislation that called for a study of the national-security risks posed by routers with ties to foreign adversaries, on which the Senate has yet to act.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, the U.S. Commerce Department is moving to further crack down on China Telecom’s U.S. unit over concerns it could exploit access to American data through their U.S. cloud and internet businesses by providing it to Beijing, a source told Reuters. The source confirmed a New York Times report that the department last week sent China Telecom Americas a preliminary determination that its presence in U.S. networks and cloud services poses U.S. national security risks and gave the company 30 days to respond.
Previously, the FCC moved to shrink China Telecom’s presence in the U.S. In October 2021, nine months into Mr. Biden’s term, the Commission revoked all licenses for China Telecom Americas to provide ordinary phone services in the United States, saying it was “subject to exploitation, influence and control by the Chinese government.” That left in place China Telecom’s network nodes on U.S. telecom networks and carrier neutral data centers with the power to “peer in” to internet and phone traffic. That ability would be stripped under the Commerce Department order, assuming that the Trump administration went along. China Telecom Americas did not respond to messages left at its office in Herndon, Va.
“We’ve been taking a hard look at where Chinese technologies are in the United States and asking ourselves the question of, is this an acceptable level of risk?” Anne Neuberger, the deputy national security adviser for cyber and emerging technologies, said in an interview on Monday. “For a number of years, these companies have operated networks and cloud service businesses in the U.S., which involved network equipment that’s co-located with our internet infrastructure. And while in the past we may have viewed this as an acceptable level of risk, that is no longer the case.”
The F.C.C. action to block China Telecom from most of its business in the United States did not prevent Volt Typhoon — China’s placement of malicious code in the electric grid and water and gas pipeline networks — or Salt Typhoon, the surveillance effort that was uncovered over the summer. Taken together, officials say, they amount to the most significant assault on American critical infrastructure in the digital age.
Speaking last week at the Paley Center for Media in Manhattan, Gen. Timothy D. Haugh, the director of the National Security Agency and commander of U.S. Cyber Command, said, “If I look at today, the PRC is not deterred,” using the initials for the People’s Republic of China. He declined to say whether his forces were conducting offensive operations against China in retaliation for any of its recent incursions into American networks.
On Sunday, President-elect Donald J. Trump’s incoming national security adviser, Representative Mike Waltz, a Florida Republican, suggested on CBS’s “Face the Nation” that the new administration would be much more tempted to use offensive cyber-actions against China. “We need to start going on offense and start imposing, I think, higher costs and consequences to private actors and nation-state actors that continue to steal our data, that continue to spy on us and that, even worse, with the Volt Typhoon penetration, that are literally putting cyber time bombs on our infrastructure, our water systems, our grids, even our ports,” he said.
Officials have said they do not believe that the Chinese hackers have been ousted from the networks of at least eight telecommunications firms, including the nation’s two largest, Verizon and AT&T. That suggests that China’s hackers retain the capability to escalate.
Since Microsoft first alerted the telecommunications firms over the summer that they had found evidence of hackers deep in their systems, the Biden administration has struggled to come up with a response. It created a task force inside the White House, and the issue is considered so serious that the group meets almost daily. Chief executives of the affected firms have been summoned to the Situation Room to come up with a joint plan of action.
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/tp-link-router-china-us-ban/
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/12/16/us/politics/biden-administration-retaliation-china-hack.html
Aftermath of Salt Typhoon cyberattack: How to secure U.S. telecom networks?
WSJ: T-Mobile hacked by cyber-espionage group linked to Chinese Intelligence agency
China backed Volt Typhoon has “pre-positioned” malware to disrupt U.S. critical infrastructure networks “on a scale greater than ever before”
FBI and MI5 Chiefs Issue Joint Warning: Chinese Cyber Espionage on Tech & Telecom Firms
Quantum Technologies Update: U.S. vs China now and in the future
SKT-Samsung Electronics to Optimize 5G Base Station Performance using AI
SK Telecom (SKT) has partnered with Samsung Electronics to use AI to improve the performance of its 5G base stations in order to upgrade its wireless network. Specifically, they will use AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology (AI-RAN Parameter Recommender) to commercial 5G networks.
The two companies have been working throughout the year to learn from past mobile network operation experiences using AI and deep learning, and recently completed the development of technology that automatically recommends optimal parameters for each base station environment. When applied to SKT’s commercial network, the new technology was able to bring out the potential performance of 5G base stations and improve the customer experience.
Mobile base stations are affected by different wireless environments depending on their geographical location and surrounding facilities. For the same reason, there can be significant differences in the quality of 5G mobile communication services in different areas using the same standard equipment.
Accordingly, SKT utilized deep learning, which analyzes and learns the correlation between statistical data accumulated in existing wireless networks and AI operating parameters, to predict various wireless environments and service characteristics and successfully automatically derive optimal parameters for improving perceived quality.
Samsung Electronics’ ‘Network Parameter Optimization AI Model’ used in this demonstration improves the efficiency of resources invested in optimizing the wireless network environment and performance, and enables optimal management of mobile communication networks extensively organized in cluster units.
The two companies are conducting additional learning and verification by diversifying the parameters applied to the optimized AI model and expanding the application to subways where traffic patterns change frequently.
SKT is pursuing advancements in the method of improving quality by automatically adjusting the output of base station radio waves or resetting the range of radio retransmission allowance when radio signals are weak or data transmission errors occur due to interference.
In addition, we plan to continuously improve the perfection of the technology by expanding the scope of targets that can be optimized with AI, such as parameters related to future beamforming*, and developing real-time application functions.
* Beamforming: A technology that focuses the signal received through the antenna toward a specific receiving device to transmit and receive the signal strongly.
SKT is expanding the application of AI technology to various areas of the telecommunications network, including ‘Telco Edge AI’, network power saving, spam blocking, and operation automation, including this base station quality improvement. In particular, AI-based network power saving technology was recently selected as an excellent technology at the world-renowned ‘Network X Award 2024’.
Ryu Tak-ki, head of SK Telecom’s infrastructure technology division, said, “This is a meaningful achievement that has confirmed that the potential performance of individual base stations can be maximized by incorporating AI,” and emphasized, “We will accelerate the evolution into an AI-Native Network that provides differentiated customer experiences through the convergence of telecommunications and AI technologies.”
“AI is a key technology for innovation in various industrial fields, and it is also playing a decisive role in the evolution to next-generation networks,” said Choi Sung-hyun, head of the advanced development team at Samsung Electronics’ network business division. “Samsung Electronics will continue to take the lead in developing intelligent and automated technologies for AI-based next-generation networks.”
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
 SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
SK Telecom and Samsung Electronics researchers discussing verification of AI-based 5G base station quality optimization technology.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SKT said it is expanding the use of AI to various areas of its communications network, such as “Telco Edge AI,” network power reduction, spam blocking and operation automation, including basestation quality improvement.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SK Telecom (SKT) and Nokia to work on AI assisted “fiber sensing”
South Korea has 30 million 5G users, but did not meet expectations; KT and SKT AI initiatives
SKT Develops Technology for Integration of Heterogeneous Quantum Cryptography Communication Networks
India Mobile Congress 2024 dominated by AI with over 750 use cases
Dell’Oro: Private RAN revenue declines slightly, but still doing relatively better than public RAN and WLAN markets
Dell’Oro Group reports that Private Wireless Radio Access Network (RAN) revenue growth slowed slightly in the second quarter on a year-over-year basis relative to the ~40 percent increase in 2023. Still, the tapering is in line with expectations and private wireless is performing significantly better on a relative basis than both public RAN and enterprise WLAN. [However, it’s a much smaller market.]
“With public MBB investments slowing, the expectations with new growth opportunities such as Fixed Wireless Access and private wireless are rising,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “The results in the quarter and the trends over the past year validate this message that we have communicated now for some time, namely that the enterprise is a very large and mostly untapped opportunity. The market will continue to grow faster than both public RAN and enterprise WLAN, but because of the lower starting point, it will take some time before enterprise RAN revenues are large enough to stabilize public MBB swings,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from the September 2024 Private Wireless Report:
- Contract activity is slowing but the quality of the contracts is improving and increasingly includes larger, multi-site, and even multi-country agreements.
- Regional activity is mostly stable. The three largest regions in 1H24 from a revenue perspective include China, North America, and EMEA.
- Vendor rankings did not change in 1H24. The evolving scope of private wireless taken together with the fact that the $20 B+ enterprise RAN opportunity remains largely untapped is spurring interest from a broad array of participants across the ecosystem. Still, the traditional RAN suppliers are currently well-positioned in this initial phase.
- Top 3 Private Wireless RAN suppliers in 1H24 are Huawei, Nokia, and Ericsson.
- Top 3 Private Wireless RAN suppliers in 1H24 excluding China are Nokia, Ericsson, and Samsung.
- Projections are mostly unchanged. Private wireless RAN revenues are projected to grow at a 21 percent CAGR over the next five years, while public RAN revenues are set to decline at a 3 percent CAGR over the same time period.
Dell’Oro Group’s Private Wireless Advanced Research Report includes both quarterly vendors share data and a 5-year forecast for Private Wireless RAN by RF Output Power, technology, spectrum, and region. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, and data center markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit https://www.delloro.com.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ericsson and Nokia – Private Wireless Network Initiatives:
- Last week, Ericsson shared details of its enterprise 5G strategy, formulated after its 2020 Cradlepoint acquisition which provides both private 5G and neutral host solutions. “Ericsson’s strategic and comprehensive approach to evolving its private networking portfolio is addressing the growing demand for secure, high-performance connectivity in enterprises,” the vendor quoted Pablo Tomasi, Principal Analyst for Private Networks and Enterprise 5G at Omdia, as saying in its strategy announcement. “Ericsson’s ability to meet customers where they are in their 5G journey with a unified experience will be critical in helping the market scale and enabling enterprises leveraging 5G to transform in a meaningful way,” Tomasi added.
- Nokia has made myriad private networking deal announcements in the past couple of years and recently revealed the results of a market study it commissioned that paints the sector in a very positive light. Early adopters have been scaling up deployments, adding new locations for example, and the vast majority of those surveyed – 93%, to be exact – claimed to have generated a return on investment within a year; almost a quarter did so in just one month. That’s a strong message and one designed to help drive the market forwards.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

References:
Private Wireless RAN Revenues up 24 percent in 2Q 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.telecoms.com/telecoms-infrastructure/private-ran-revenues-continue-to-grow-amid-vendor-push
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
Highlights of Dell’Oro’s 5-year RAN forecast
Dell’Oro: 2023 global telecom equipment revenues declined 5% YoY; Huawei increases its #1 position
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Dell’Oro: Private 5G ecosystem is evolving; vRAN gaining momentum; skepticism increasing
HPE Aruba Launches “Cloud Native” Private 5G Network with 4G/5G Small Cell Radios
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G Network market annual spending will be $3.5 Billion by 2027
Ericsson and Vodafone enable Irish rugby team to use Private 5G SA network for 2023 Rugby World Cup
Wipro and Cisco Launch Managed Private 5G Network-as-a-Service Solution
Japan to support telecom infrastructure in South Pacific using Open RAN technology
Japan’s government and private sector will offer support for telecommunications infrastructure in Pacific island countries, starting with a data center and telecom project in Palau, in an effort to improve the security of vital networks connecting Asia and North America. The initiative will be led by Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and is expected to include telecom company NTT Group, internet service provider Internet Initiative Japan and other companies. It aims to increase Japan’s participation in the South Pacific, a region crisscrossed with undersea communications cables linking East Asia, the U.S., Australia and Southeast Asia. Funding will come from the ministry’s international cooperation budget. Several billion yen (1 billion yen equals $7.1 million) in public-private investment is expected to be mobilized over the first two years.
The infrastructure improvements will use Open Radio Access network (RAN) technology, which Japan has sought to promote as a low-cost way of building wireless networks from components made by different manufacturers.
Japan, the U.S., and Australia — which, along with India, make up the security dialogue known as the Quad — all support improving communications security in Pacific island countries. These island countries are reliant on equipment from Chinese telecom company Huawei Technologies for their land-based networks. The U.S. and others say Huawei has ties to the Chinese military and poses a security risk. Western officials have raised concerns about the potential for eavesdropping on communications and other activities. Huawei denies such accusations.
Quad members have agreed to support the modernization of Palau’s telecommunications infrastructure. Japan’s communications ministry will start putting this initiative to work as early as fiscal 2025, which begins in April. It will then seek to expand aid in fiscal 2026 to other countries in the region. Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands — two of the dwindling number of countries to maintain formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan — are likely to be candidates for such support. The effort will also seek to train cybersecurity personnel. Island countries with understaffed cybersecurity capabilities are seen as a potential vulnerability that can be exploited to launch attacks against Japan, experts say.
Tuvalu-an island country roughly halfway between Australia and Hawaii-is expected to be a candidate to receive Japanese support for telecommunications infrastructure. © Reuters
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China has worked to extend its influence in the South Pacific. In recent years, the Solomon Islands, Kiribati and Nauru have all cut diplomatic ties with Taiwan in favor of relations with Beijing. The Solomon Islands also formed a security agreement with China. Including Palau, only three countries in the region still maintain diplomatic relations with Taiwan.
Telecommunications infrastructure is becoming increasingly important for island countries in their own right.
“A stable network connecting a country with the rest of the world is essential for receiving remittances from migrant workers. Better telecommunications infrastructure is of great significance in improving ties between countries,” said Motohiro Tsuchiya, a professor at the Keio University Graduate School of Media and Governance in Japan.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://market.us/report/open-ran-market/
https://www.o-ran.org/otics/japan-otic
https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/japan-s-5g-ambitions-quad
NTT advert in WSJ: Why O-RAN Will Change Everything; AT&T selects Ericsson for its O-RAN
NTT DOCOMO OREX brand offers a pre-integrated solution for Open RAN
New venture to sell Network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) on a global scale
Overview:
Some of the world’s largest telecom operators, including América Móvil, AT&T, Bharti Airtel, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Reliance Jio, Singtel, Telefonica, Telstra, T-Mobile, Verizon and Vodafone, together with network gear maker Ericsson (the largest shareholder) are announcing a new venture to combine and sell network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) on a global scale to spur innovation in digital services. Network APIs are the way to easily access, use and pay for network capabilities. The venture will drive implementation and access to common APIs from multiple telecom service providers to a broader ecosystem of developer platforms. All the APIs on offer will be based on CAMARA – the open source API project led by the GSMA and the Linux Foundation.
Modern mobile networks have advanced and intelligent capabilities, which have historically been inaccessible to developers. Additionally, it has been impractical for developers to integrate the different capabilities of hundreds of individual telecom operators. The newly formed company will combine network APIs globally, with a vision that new applications will work anywhere and on any network, making it easier and quicker for developers to innovate.
Easily accessible advanced network capabilities will open up the next frontier in app development and empower developers to create new use cases across many sectors. These could include anti-fraud verification for financial transactions and the ability to check device status so streaming providers can dynamically adjust video quality.
The newly formed company will provide network APIs to a broad ecosystem of developer platforms, including hyperscalers (HCPs), Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers, System Integrators (SIs) and Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), based on existing industry-wide CAMARA APIs (the open-source project driven by the GSMA and the Linux Foundation). Vonage and Google Cloud will partner with the new company, providing access to their ecosystems of millions of developers as well as their partners. The new venture shareholders will bring funding and important assets, including Ericsson’s platform and network expertise, global telecom operator relationships, knowledge of the developer community and each telecom operator’s network APIs, expertise and marketing.
Ericsson-owned Vonage and Google Cloud have already agreed to partner with the new venture, providing access to their respective ecosystems of millions of developers as well as their partners.
“We have a common concern that we’ve made it difficult for developers to program on wireless networks,” said Niklas Heuveldop, CEO of Vonage, stressing that this initiative is all about removing any friction and roadblocks that may be preventing developers taking full advantage of the programmable networks opportunity. He added that, for Vonage, this means a smaller piece of a bigger network API pie.
Closing of the transaction is expected early 2025, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary conditions. Upon closing, Ericsson will hold 50% of the equity in the venture while the telecom providers will hold 50% in total. Built on a deep understanding of developer and enterprise needs and in keeping with the industry-body GSMA Open Gateway principles, the new venture’s platform and partner ecosystem will remain open and non-discriminatory to maximize value creation across the industry.
Comment and Analysis:
Much has already been made of the industry’s decision to open up and (attempt) to monetize network APIs. Optimistic estimates, like the one proffered by McKinsey, claim that network APIs represent a $300 billion opportunity for telcos between now and the end of the decade. However, some like Kearney, have warned that all will be for naught without proper industry coordination and collaboration to drive software developer uptake.
“Today’s announcement is an important step in that direction by addressing one of the major challenges for developers seeking to engage with mobile operators – sector fragmentation,” said Kester Mann, director of consumer and connectivity at CCS Insight. “In the past, the telecom industry – with many competing players each deploying different strategies for their specific regions – has struggled to present a united and coherent front.” Despite their dubious track record, Mann reckons this particular venture stands a better chance of success than most, thanks to the urgent need for operators to earn a return on 5G, and due to the involvement of major technology partners in the form of Google and Ericsson. “There should be fresh optimism that the new company unveiled will enjoy more success than previous failed ventures,” he added.
While open network APIs will work on compatible hardware from any vendor – whether it’s Nokia or Ericsson or Huawei – this new venture represents an opportunity for Ericsson to play a central role in the emerging ecosystem.
Quotes from the partners:
América Móvil
Daniel Hajj, Chief Executive Officer, AMX: “We are very excited to join Ericsson and other key players in our industry in this innovative global platform initiative that will benefit the digital ecosystem as a whole. New API solutions will establish exciting value-added offerings to our customers on the top of our networks’ infrastructure.”
AT&T
Jeremy Legg, Chief Technology Officer, AT&T: “At AT&T, we’ve been creating API tools to empower developers for well over a decade. Now, with a broad-based, interoperable API platform, we’re giving innovators a new global toolbox where the world’s best app developers can create exciting user experiences at scale. This high-performance mobile ecosystem will usher in a new era of greater possibility for customers and mobile users around the world.”
Bharti Airtel
Gopal Vittal, Managing Director and CEO, Bharti Airtel: “Today marks a defining moment as the industry comes together to form a unified platform that will allow more developers and businesses to utilize our networks and explore API opportunities through open gateway principles. This move will enhance network monetization opportunities. Airtel is delighted to partner in this initiative that will help enable the telecom sector to drive growth and innovation across the ecosystem.”
Deutsche Telekom
Tim Höttges, CEO of Deutsche Telekom: “The new company accelerates our leading work with MagentaBusiness APIs to expose our network capabilities for customers and developers. We believe that this company will open up new monetization opportunities for the industry. We encourage and look forward to more telecom operators joining us to expand and develop this ecosystem.”
Ericsson
Börje Ekholm, President and CEO, Ericsson: “Today is a defining moment for the industry and milestone in our strategy to open up the network for increased monetization opportunities. A global platform built on Ericsson’s deep technical capabilities and with a comprehensive ecosystem, that provides millions of developers with a single connection, will enable the telecom industry to invest deeper into the network API opportunity, driving growth and innovation for everyone.”
Orange
Christel Heydemann, Chief Executive Officer, Orange: “This is a critical first step in our innovation journey to fully harness the power of our networks at scale, providing secure access to new on-demand network services and advanced network capabilities. By delivering a common and simple set of network APIs for developers globally, we can unleash this network value for businesses, large and small. This is a definitive gamechanger for businesses, opening up the possibility of a new wave of digital services.”
Reliance Jio
Mathew Oommen, President, Reliance Jio: “We spearheaded the transformation of both mobile and fixed home broadband by delivering affordable, high-quality broadband to everyone, across India. As we rapidly adopt an AI and API-driven technology ecosystem—by collaborating with global leaders, Jio is thrilled to offer a suite of innovative and transformative APIs to enterprises and developers worldwide. Together, we are not just building networks; we are laying the foundation for a smarter, more connected, and inclusive world in the AI era.”
Singtel
Mr Yuen Kuan Moon, Group Chief Executive Officer, Singtel: “This unified platform and global eco-system will enable even more developers and businesses to leverage 5G quality networks to exploit API opportunities using GSMA’s open gateway principles. We look forward to helping even more enterprises and organizations in Asia to use network API solutions to drive growth and innovation through this timely collaboration.”
Telefonica
José María Álvarez-Pallete, Chairman & CEO of Telefónica: “This collaboration will drive the GSMA Open Gateway initiative and provide customers with a consistent set of Camara APIs. Our belief is that this industry movement, which will be open to all networks, can set the stage for unprecedented innovation and value creation for the sector, by unlocking the potential of network capabilities.”
Telstra
Vicki Brady, CEO of Telstra: “This is a groundbreaking initiative for our industry. This new global venture will create an ecosystem that provides developers, partners and customers with access to programmable, advanced network capabilities that will unleash a new wave of innovation in digital services and further unlocks the benefits of our 5G network. We’ve been making good progress locally with Ericsson and other partners, and we look forward to further accelerating digital transformation for our Australian customers and bringing value and simplicity to application developers around the world.”
T-Mobile
Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology, T-Mobile: “At T-Mobile, we’ve always been laser focused on championing change across the industry to create the best customer experiences, while fueling growth and innovation across the entire wireless ecosystem. That level of transformation takes unprecedented collaboration and expertise. We are excited about the possibilities this venture will create for developers and wireless customers around the world.”
Verizon
Joe Russo, EVP & President, Global Network and Technology of Verizon: “The depth and value of the services and data insights accessible through Verizon’s renowned 5G network are practically boundless. Verizon has been at the forefront of developing various network APIs to assist developers in enhancing customer security, reducing pain points in customer interactions, and enabling the creation of novel experiences. This exciting collaboration with global partners will broaden the availability of these services and accelerate adoption of APIs worldwide.”
Vodafone
Margherita Della Valle, Vodafone Group Chief Executive, said: “Network APIs are reshaping our industry. This pioneering partnership will enable businesses and developers to use the collective strength of our global networks to develop applications that drive growth, create jobs, and improve public services. Just as 4G and smartphones made apps integral to our everyday life, the power of our 5G network will stimulate the next wave of digital services.”
Google Cloud
Thomas Kurian, CEO of Google Cloud: “We understand the power of an open platform and ecosystem in driving innovation. We are proud to participate in this important partnership in the telco industry to create value for our global customers via network APIs – and ultimately deliver on the promise of the public cloud.”
Vonage
Niklas Heuveldop, CEO Vonage: “This groundbreaking, open industry collaboration effectively removes the single largest barrier for developers to leverage mobile networks to their full potential. Developers across the world’s leading developer platforms will benefit from accessing advanced network capabilities in partner networks globally through common APIs, accelerating the digital transformation of businesses and the public sector. As one of the leading developer platforms, we look forward to engaging our developer community as we grow the network API business.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Analysts: Telco CAPEX crash looks to continue: mobile core network, RAN, and optical all expected to decline
Analysys Mason Open Network Index: survey of 50 tier 1 network operators
Ericsson expects continuing network equipment sales challenges in 2024
Nvidia enters Data Center Ethernet market with its Spectrum-X networking platform
Nvidia is planning a big push into the Data Center Ethernet market. CFO Colette Kress said the Spectrum-X Ethernet-based networking solution it launched in May 2023 is “well on track to begin a multi-billion-dollar product line within a year.” The Spectrum-X platform includes: Ethernet switches, optics, cables and network interface cards (NICs). Nvidia already has a multi-billion-dollar play in this space in the form of its Ethernet NIC product. Kress said during Nvidia’s earnings call that “hundreds of customers have already adopted the platform.” And that Nvidia plans to “launch new Spectrum-X products every year to support demand for scaling compute clusters from tens of thousands of GPUs today to millions of DPUs in the near future.”
- With Spectrum-X, Nvidia will be competing with Arista, Cisco, and Juniper at the system level along with “bare metal switches” from Taiwanese ODMs running DriveNets network cloud software.
- With respect to high performance Ethernet switching silicon, Nvidia competitors include Broadcom, Marvell, Microchip, and Cisco (which uses Silicon One internally and also sells it on the merchant semiconductor market).

Image by Midjourney for Fierce Network
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In November 2023, Nvidia said it would work with Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Lenovo to incorporate Spectrum-X capabilities into their compute servers. Nvidia is now targeting tier-2 cloud service providers and enterprise customers looking for bundled solutions.
Dell’Oro Group VP Sameh Boujelbene told Fierce Network that “Nvidia is positioning Spectrum-X for AI back-end network deployments as an alternative fabric to InfiniBand. While InfiniBand currently dominates AI back-end networks with over 80% market share, Ethernet switches optimized for AI deployments have been gaining ground very quickly.” Boujelbene added Nvidia’s success with Spectrum-X thus far has largely been driven “by one major 100,000-GPU cluster, along with several smaller deployments by Cloud Service Providers.” By 2028, Boujelbene said Dell’Oro expects Ethernet switches to surpass InfiniBand for AI in the back-end network market, with revenues exceeding $10 billion.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a recent IEEE Techblog post we wrote:
While InfiniBand currently has the edge in the data center networking market, but several factors point to increased Ethernet adoption for AI clusters in the future. Recent innovations are addressing Ethernet’s shortcomings compared to InfiniBand:
- Lossless Ethernet technologies
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
- Ultra Ethernet Consortium’s AI-focused specifications
Some real-world tests have shown Ethernet offering up to 10% improvement in job completion performance across all packet sizes compared to InfiniBand in complex AI training tasks. By 2028, it’s estimated that: 1] 45% of generative AI workloads will run on Ethernet (up from <20% now) and 2] 30% will run on InfiniBand (up from <20% now).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/cloud/data-center-ethernet-nvidias-next-multi-billion-dollar-business
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/spectrumx/