Chinese companies’ patents awarded in the U.S. increased ~10% while U.S. patent grants declined ~7% in 2021
Chinese companies’ patents granted in the United States surged last year, even as total patent awards in the U.S. trended downward, according to a renowned U.S. patent service provider. Data from IFI Claims (more below) showed that Chinese companies’ patents earned in the U.S. increased ~10% to 20,679 in 2021, up from 18,792 in 2020.
The progress came as total U.S. patent grants declined about 7% from 2020 to 327,329 awards last year, the most precipitous drop in the past decade, said IFI Claims.
Several Chinese companies are now among the Top 50 in U.S. patent rankings, including world’s #1 chip maker Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC) at No 4, telecom giant Huawei at No 5, display maker BOE at No 11, tech heavyweight Oppo at No 49, while China’s Advanced New Technologies was ranked #43. Oppo was granted 719 patents in the U.S. last year, marking a surge of 33% year-on-year.
When it comes to total global patents held, China possesses 29% of the global 250 patent families – collections of patent applications covering the same or similar technical content – compared to the U.S. (24%) and Japan (19%), said IFI Claims.
A deeper analysis shows that the U.S. and Japanese portfolios are stronger and more mature. Nevertheless, it is clear that China has stimulated a research and development culture that is serious about intellectual property, said Mike Baycroft, CEO of IFI Claims Patent Services in a statement (see below).
The progress comes as Chinese companies increasingly strengthen their R&D push. Huawei, for instance, invested 141.9 billion yuan ($22.3 billion) in R&D in 2020, accounting for about 15.9% of its revenue.
Jason Ding, head of the intellectual property department at Huawei, said earlier that the company has become one of the world’s largest patent holders through investment in innovation.
Oppo is also beefing up its R&D push. Chen Mingyong, CEO of Oppo, said earlier that the company aims to be a tech pioneer by increasing R&D spending.
“We’ve been working hard for many years to ramp up our products,” Chen said. So far, Oppo has filed for patents in more than 40 countries and regions around the world as it accelerates efforts to expand its global business. As of Dec 31, 2021, Oppo had filed 75,000 patent applications globally, and its global number of authorized patents exceeds 34,000, the company said.
For more information, email: [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IFI Claims Patent Services – China Surges, as Others Decline:
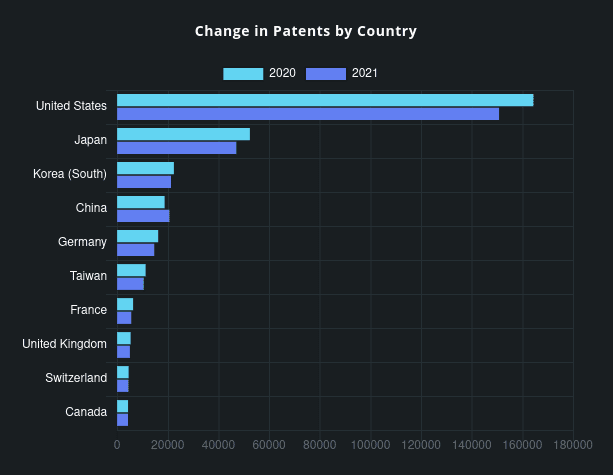
In a year that saw U.S. patent grants decrease anywhere from 8 to 12% among worldwide corporations, China-based companies stood out with an increase of 10 percent, going from 18,792 awards in 2020 to 20,679 during the past year. A total of four Chinese companies are now in the U.S. Top 50 including Huawei at #5, BOE at #11, Advanced New Technologies at #43, and Guangdong Oppo at #49. US company grants were down commensurate with the worldwide total decline, 8%.
“Last year saw the steepest decline in patent grants in the past decade. There could be many reasons for this – and clearly some are pandemic-related – but what we’re seeing is that corporations are still innovating at an impressive clip despite a challenging environment, particularly U.S. and Asia-based entities,” said Mike Baycroft, CEO of IFI CLAIMS Patent Services.
Consistent with the overall decline in U.S. patent activity from 2020 to 2021, all regions except China had a negative growth rate Year over Year (2021 vs 2020). That is depicted on this chart:
Source: IFI Claims Patent Services
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://mobile.chinadaily.net.cn/cn/html5/2022-01/14/content_013_61e07f4ced500fb050170922.htm
3 thoughts on “Chinese companies’ patents awarded in the U.S. increased ~10% while U.S. patent grants declined ~7% in 2021”
Comments are closed.



Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the dominant maker of the world’s most advanced chips, is in bullish mood.
On the back of another robust set of quarterly financials (Q4 FY21) and a strong balance sheet, TSMC is upping once again its capex budget. By doing so, it hopes to be better placed to exploit future market growth.
“We are witnessing a structural increase in underlying semiconductor demand underpinned by the industry megatrends of 5G-related and HPC [high-performance computing] applications,” explained TSMC CTO Wendell Huang, speaking on the company’s Q4 earnings conference call.
The CFO said the capital budget for 2022 was slated at between $40 billion and $44 billion, well up on the $30 billion splashed out in 2021. TSMC’s capex in 2019, by way of comparison, was $14.9 billion.
Huang said between 70% and 80% of the 2022 budget will be allocated to “advanced process technologies” including 2-nanometer (nm), 3nm, 5nm and 7nm. “About 10% will be spent for advanced packaging and mask making,” he added, “and 10% to 20% will be spent for specialty technologies.”
TSMC should have no trouble in funding its largesse on advanced chips (7mn and below). “With $38 billion in cash and $40 billion in operating cash flow before capex, TSMC can afford to take some risk,” said Richard Windsor at analyst firm Radio Free Mobile. “The sheer size of its investments in 2022 demonstrates that TSMC is intent on leaving its rivals in the dust come what may.”
Windsor argued, however, that the cyclical semiconductor industry had most likely reached a peak. “The return on these investments will be felt over a period of years, meaning that TSMC thinks that the industry is in a period of secular expansion with no real dip in sight,” he said. “This is precisely the view that when uttered by semiconductor companies is most often an indicator of a peak in the semiconductor cycle.”
Thin wafers, fat margins
Shipments of 5nm during Q4 accounted for 23% of TSMC’s total wafer revenue, while the 7nm share was 27%. It meant that advanced technologies (7nm and below) accounted for 50% of total wafer revenue, up from 41% in 2020.
Moreover, TSMC continues to post very respectable margins. Gross margin for Q4 was 52.7%, operating margin was 41.7%, and net profit margin came in at 37.9%. Revenue for the quarter, at $15.74 billion, was a 24.1% jump year-over-year (and up 5.8% compared with the previous quarter).
“Moving into first quarter 2022, we expect our business to be supported by HPC-related demand, continued recovery in the automotive segment, and a milder smartphone seasonality than in recent years,” said Wuang in prepared remarks.
TSMC is guiding for Q1 FY22 revenue of between US$16.6 billion and US$17.2 billion. Based on the exchange rate assumption of 1 US dollar to 27.6 NT dollars, gross profit margin is expected to be between 53% and 55%, while operating profit margin is guided at between 42% and 44%.
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/tsmc-massively-ups-capex-on-advanced-chips/d/d-id/774601?
Not only have patents awarded Chinese companies increased, but their telecommunications standards contributions also increased significantly in the last decade. This has been a strategic objective of the CCP (Chinese Communist Party).
From my studies, Huawei and other Chinese companies work very hard to produce the number of patents and standards contributions. Relative to overall revenue, Huawei is actually spending more on R&D (14.2% of revenue) than Microsoft (12%) and Amazon (10.4%), and isn’t far behind Google (14.9%). There is no doubt their quality of R&D has also improved year by year.
However, China still lacks key technologies, such as semiconductor fabrication and manufacturing (They are way behind TSMC). That prevents China from dominating the entire tech world, which is the ambition of the CCP.
This increase in “China Inc’s” patent portfolio should be a wake-up call to the western world, which should increase and extend their R&D efforts.
Reference:
What tech companies spent on R&D relative to revenue
Despite a very repressive political system, China has emerged as a major global technology leader in many areas. Those include: AI, high-end transportation systems (e.g. railways, ships, trucks and buses), agricultural equipment, advanced batteries, Electric Vehicles (EVs), robotics, infrastructure development and energy equipment. China also has a growing presence in space, biomedicine, and low to mid-range medical equipment.
China’s speed and breadth of technology development is exceptionally remarkable while it has simultaneously grown its manufacturing leadership in all the key areas. Excluding semiconductor chips and equipment, China can easily be ranked in the top three industrial categories amongst all leading nations.
China today has the technology breadth and the scale. Patents are one of the key metrics to measure innovation and China is succeeding! No one imagined, let alone predicted, China’s meteoric rise over the last thirty odd years when it generally decided to embrace commercial development of non-state enterprises.
I agree with the comment that Huawei, along with Chinese EV companies, and others become leaders in their fields via “home grown” innovations, which were the direct result of massive R&D investments.
In my opinion, the U.S. is at a crossroads, perhaps not unlike the one it faced in October, 1957 when the Soviet Union launched its Sputnik satellite into the earth’s orbit The jury is out whether we have the will and the courage this time around to rise to the challenge!