Bloomberg: Chip Sales to Slow Further as Global Recession Fears Mount
Semiconductor sales are set to grow more slowly than previously expected as the international economy struggles under the weight of rapid interest-rate increases and rising geopolitical risks, fueling fears of a global recession. That will adversely effect telecom equipment and handset vendors that depend on advanced semiconductors to build their products.
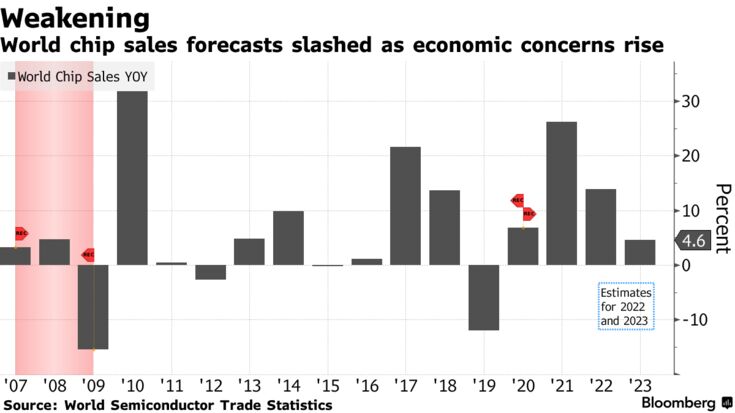
World Semiconductor Trade Statistics, a non-profit body that tracks shipments, lowered its market outlook to 13.9% growth this year from a previous 16.3%.
In 2023, it sees chip sales rising just 4.6%, the weakest pace since 2019.
The semiconductor market is still expected to surpass $600 billion this year, WSTS says. Next year’s forecast growth would be the weakest since a 12% drop in sales at the height of the U.S.-China trade war.
Chip sales are an important indicator of global economic activity as households and firms increasingly rely on digital devices and online services to consume and expand. President Joe Biden this month signed the so-called CHIPS and Science Act aimed at strengthening the U.S. semiconductor industry as China races to expand its own chip-making capacity. Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) is a partially state-owned publicly-listed Chinese pure-play semiconductor foundry company. It is the largest contract chip maker in mainland China and 5th largest globally behind TSMC, Samsung, United Microelectronics Corporation, and GlobalFoundries.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) last month downgraded its global growth forecast and said 2023 may be tougher than this year. A Bloomberg Economics model sees a 100% probability of a US recession within the next 24 months.
Based in Morgan Hill, California, WSTS includes among its members Texas Instruments Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corp and Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology Co., according to its website.
References: