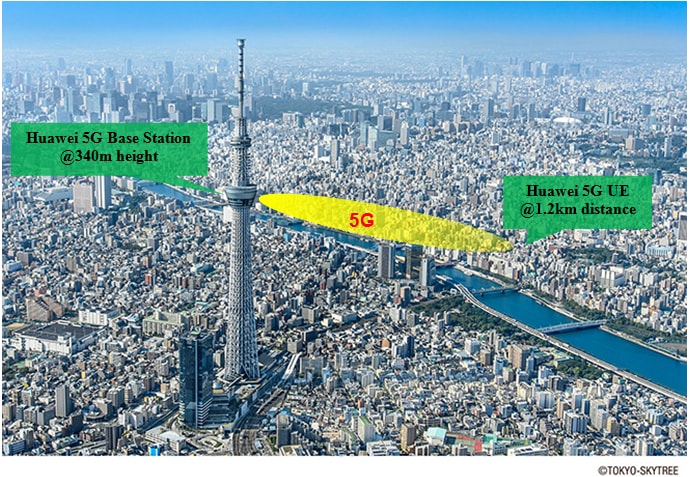
Huawei and NTT Docomo “5G” mmWave Field Trial in Tokyo
Huawei is highlighting a Tokyo, Japan trial in which the Chinese telecom/IT vendor achieved “5G” like download speeds of 4.52 gigabits per second over ~ three-quarters of a mile using 28 GHz millimeter-wave wireless technology. The trial took place in downtown Tokyo, where a base station working over 28GHz frequency was located at Tokyo Skytree’s viewing deck, 340m above the city.
Working with Japan’s NTT Docomo, Huawei said it was confident of launching a commercial 5G rollout by 2020 (NOTE: the IMT 2020 set of 5G standards are to be finalized by year end 2020).
“The high-speed and long distance support is one of important technical challenges for 5G mmWave conditions. This successful long distance live-demo on a 5G mmWave is a groundbreaking achievement in our joint effort with NTT DOCOMO to build a fundamental 5G commercial environment. This success makes us more confident in realizing the goal of commercializing 5G by 2020,” said Gan Bin, vice president of Huawei’s 5G product line.
Huawei utilized its 5G base station for the test, which supports Massive MIMO and beam forming technologies. Huawei also provided the 5G core network and the 5G mm wave test user equipment.
Huawei anticipates conducting further testing at the world’s biggest 5G testing site in Beijing’s Huairou District.
The test comes amid a flurry of 5G testing and trials around the world. For example, BT and Nokia announced plans for live “5G” tests in the UK earlier this month.
References:
http://www.huawei.com/en/news/2017/12/NTT-DOCOMO-5G-mmWave-Field-Trial-Tokyo
https://www.totaltele.com/498823/5G-testing-spurs-Huawei-to-deliver-5G-by-2020
IHS-Markit Forecast: Carrier NFV at $37B in 2021 for a CAGR of 30% from 2016-2021
by Michael Howard of IHS-Markit (co-founder and lead analyst at Infonetics)
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) MANO (management and network orchestration) and VNF (virtual network function) software revenue was $3.5B in 2016 and is expected to reach $5.9B for 2017, according to the NFV Hardware, Software, and Services biannual market tracker from IHS Markit.
NFV revenue is not all new: it includes displaced revenue and newly identified parts of existing market segments. In 2021, 49% of the NFV revenue will be new revenue from software and outsourced services, and 8% will be displaced revenue spent on NFVI server/storage/switch hardware purchased instead of purpose-built network appliances. The remaining 43% represent spend on VNF software.
“Operators around the world are planning or extending their NFV environments to customer sites on CPE (customer premises equipment), which we are calling uCPE (universal CPE). We expect operators will spend $11M on physical “uCPE” hardware in 2017, growing to $448M in 2021,” stated Michael Howard, Executive Director Research and Analysis for Carrier Networks at IHS Markit.
“In our 5th annual global carrier surveys on SDN and NFV, 82% of respondents indicated they are deploying or plan to execute VNFs on uCPE located at customer sites (with 97% in COs and 85% in DCs). Because this is such a large part of operator plans and products available now, we have sized and forecast the uCPE market,” Michael Howard added.
Above illustration courtesy of IHS-Markit
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Note: NFV and MANO Backgrounder:

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
NFV Reference Architecture showing NFV Orcestrator and VNF Manager

Above illustration extracted from the ETSI NFV MANO Specification
Recently, there’s been more innovation around the MANO portion of the NFV infrastructure and a recognition that MANO might need more development as a model given the gap between the MANO layer in NFV and the OSS/BSS (operations support systems/business support systems) portion of network operator businesses that handle the core orchestration and billing functions as shown above.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
More NFV Market Highlights (IHS-Markit):
· Revenue to vendors and systems integrators for outsourced services for NFV projects will grow to $16.6B in 2021 with a 2016-2021 CAGR of 23%.
· NFV software (NFV MANO and VNFs) revenue will grow to $15.5B in 2021 with a 2016-2021 CAGR of 36%.
· NFV hardware (NFVI server, storage, and switches) revenue will grow from $696M in 2016 to $3.1B in 2021 with a 2016-2021 CAGR of 35%.
· Service providers will invest $2B in hardware and software for the enterprise vCPE use case in 2021, and $293M for the consumer vCPE use case.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
NFV Hardware, Software and Services Report Synopsis:
The IHS Markit NFV Hardware, Software, and Services market tracker provides biannual worldwide and regional market size, forecasts through 2021, analysis and trends for:
(1) NFV hardware [servers, switches, storage and uCPE],
(2) software: NFV MANO, Virtual Network Functions (VNF) [SD-WAN, mobile core & EPC, PCRF & DPI, security, IMS, SBC & DCS, video CDN, vRouters, and other VNFs],
(3) outsourced services for NFV projects, plus NFV use case spending [consumer vCPE and enterprise vCPE].
Vendors tracked include Amdocs, ADVA, Ciena, Cisco, ClearPath, Ericsson, Fujitsu, HPE, Huawei, Juniper Networks, Metaswitch Networks, Nakina Systems, Nokia, Nuage Networks, NEC, NetCracker, Oracle, ZTE, and others.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Note:
I strongly respect Mr. Howard’s work ethic and primary market research findings. While not having read this latest report, I’m sure it’s excellent. However, I’m still much more pessimistic on the NFV market due to the lack of standards for exposed interfaces/APIs and backward compatibility (especially hybrid network management) with the installed base of non NFV equipment/boxes.
ABI Research on NFV Market:
ABI Research forecasts that North America will lead the NFV market, accumulating $13 billion in NFV-related investments during 2022, while Europe will experience the highest growth rate at an estimated 53% CAGR between 2017 and 2022. Early adopters claim several benefits to NFV-enabled systems, which include reductions in network CAPEX & OPEX, service agility, and reduced deployment times for new network elements.
“In 2015 and 2016, the market experienced some early successes but mostly reconsiderations and failures with NFV,” says Neha Pachade, Senior Analyst at ABI Research. “Early adopters conducted proof of concept testing and NFV-integrated system demonstrations with the aim to understand the true impact of NFV in the technical, operational, and cultural domains. Our forecasts indicate that NFV will become a sizeable opportunity for vendors, although it is not yet clear whether it will cannibalize existing hardware-based product lines or create new market use cases.”
ABI Research estimates that total NFV market revenues will reach $38 billion in 2022. Hardware spend—including servers, storage devices, and switches—will reduce with time, while software and services will have higher growth rates of 55% and 50%, respectively. Although the market is evolving and technical expertise is starting to mature, the standardization and multi-vendor involvement challenges will remain stagnant for the next couple of years. Software and services vendors will have opportunities to identify NFV use-cases in enterprise verticals and use these to offer end-to-end integrated systems.
“Early contracts and market trends illustrate the biggest winners are likely to be the established vendors, including Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia, as well as specialists like Amdocs and Netcracker, with systems integration becoming more important each day,” concludes Pachade. “Several vendors also place heavy and risky bets on open source software, which may increase business opportunities but may also create difficult choices for them in the future, particularly if telco interest in specific open source projects fizzles out. For the time being, NFV is mostly considered as a cost-cutting exercise, since new revenue opportunities require a transformation in a much broader context, which is more likely to be driven by 5G, after 2020.”
These findings are from ABI Research’s Network Functions Virtualization Tracker and Forecasts report.
Small Cell Forum Operator Survey: 36% compound annual growth between 2015 and 2025 in small cells
Overview:
The Small Cell Forum (SCF) commissioned an in-depth survey from Rethink Technology Research to understand more about their deployment plans and business drivers for a dense HetNet, and the barriers they need to overcome. Over 50 tier 1 and 2 mobile and converged operators responded to this survey, which illuminates operators’ deployment plans for network densification, as well as the barriers they expect to have to overcome.
The results showed that cell densification has begun in today’s LTE networks and will intensify in the 5G era, enabled by profound changes to the architecture and economics of small cells.
The SCF forecasts that between 2015 and 2025, new non-residential small cell deployments will grow at a compound annual rate of 36%, to reach almost 8.5 million, and by 2025 deployments will be 22 times higher than in 2015.
Densification is starting in LTE networks and will intensify in the 5G era, enabled by profound changes to the architecture and economics of small cells.
Key findings:
It is clear from the results of the survey that most mobile network operators (MNOs) are starting to plan for dense HetNets, even if they do not intend to deploy the 5G radio network at scale until well into the 2020s. The biggest uptick in new deployments of small cells will be seen in the 2018-2020 period, with a 50% increase, with a second sharp increase in 2023-2024 as 5G densification gets into full swing.
This indicates that many operators are densifying their networks long before they upgrade to 5G – the start of 5G small cell deployment will come in 2020, with 68% of respondents planning to embark on this upgrade before the end of 2022 and the rest later than that. While a smooth migration path to 5G will be important, most MNOs’ main concerns are with immediate issues of deployment in 4G.
Against that context, the following is a summary of some of the key findings of the survey:
• Only 17% of respondents have no plans for large-scale densification. By
contrast, by 2020, 40% of operators expect to deploy between 100 and 350
small cells per square kilometer in the areas they densify (led by transport
hubs, urban downtown regions and business parks).
• When it comes to 5G, 69% of operators planning 5G deployment before 2023
expect to start small cell deployment in tandem with the macro, or ahead of
it. In the first 2-3 years of deploying 5G New Radio, 58% expect to focus
primarily on small cells, 37% mainly in order to densify the network for
enhanced mobile broadband, and 21% mainly to enable new use cases.
• However, densification will happen well in advance of 5G. When asked to
rank their critical requirements for small cells, operators prioritized those
which relate to the here-and-now, not just 5G futures. Low total cost of
ownership (TCO), multivendor interoperability, ease of deployment and good
macro network interworking were the most commonly cited as top three
demands.
• It is vital for the industry to support the key requirements as soon as
possible, since the survey shows that many operators would be keen to
accelerate their deployment timeline if their concerns were addressed. For
instance, 19% would ideally like to start at-scale deployment within one year,
but only 7% believe that will be practical and affordable.
• The key factors which would enable them to bring their deadlines forward
would be new sources of affordable fiber for backhaul and fronthaul (53%
cited this), followed by lower overall TCO (50%) and easier access to sites
(46%).
• The commercial drivers which are creating this new urgency are becoming
more diverse and business-critical. Supporting improved quality of experience
(QoE) – the main determinant of customer satisfaction – through improved
and targeted capacity emerged as the most important driver (placed in the
top three by 40%). This was followed by lower total cost of ownership (TCO)
for the mobile network (38%), and the ability to deploy new services and
revenue streams based on small cells (36%).
• There is increasing diversity of business cases. On top of mobile broadband,
40% plan to introduce new enterprise services enabled by small cells before
2020 – and two-thirds after that – while for IoT services, the figures are 29%
and 39%.
• Density will allow MNOs to address new enterprise requirements. The areas
where the largest number see a business case for density would be transport
hubs, business parks and corporate buildings or campuses, while significant
opportunities are also seen in medium-sized enterprises and the hospitality
and property development sectors.
• To support business case diversity, there is a need for architectural diversity
too. As well as standalone access points, by the end of 2019, 50% also
expect to have deployed distributed radio systems and 33% clusters of small
cells managed by a virtualized controller.
• Other architectural changes are being actively adopted to make densification
easier and support additional use cases. For instance, by the end of 2019,
75% of operators will have implemented small cell SON (self-optimizing
networks), while 25% will have started to deploy end-to-end orchestration of
physical and virtual cells.
• To improve the small cell business case further, especially in the enterprise,
79% expect to support edge computing integrated with small cells, by the
end of 2022. Enterprise edge applications are seen as the leading driver
(40% placed it in their top three).
• To boost capacity, there is a rising need to tap into new sources of spectrum.
By 2022, 66% expect to be using LTE in unlicensed spectrum, and 45% plan
to have deployed small cells in spectrum above 20 GHz.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
You can download the entire survey (after filling out a form) here.
IHS Markit: VMware acquires top SD-WAN vendor VeloCloud; 3Q17 SD-WAN revenue reaches $116M
Highlights:
SD-WAN (appliance + control and management software) revenue reached $116M in 3Q17, up 18% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) and up 2.8x year-over-year (YoY). VeloCloud led the SD-WAN market with 22% share of 3Q17 revenue, Aryaka was in second place with 18%. Silver Peak rounded out the top 3 with 12%, according to the DC Network Equipment market tracker early edition from IHS Markit.
“The majority of SD-WAN solutions at first focused on virtualizing the WAN connection problem bringing automation, reliability, and agility to the enterprise WAN using overlays. Current use cases include direct connect for branch offices to the Internet and increased reliability through automated fail-over for a better user experience,” said Cliff Grossner, Ph.D., Senior Research Director and Advisor for the Cloud and Data Center Research Practice at IHS Markit.
Worldwide SD-WAN revenue (US$M)-3Q-2017:
|
VeloCloud |
|
$26.0 |
|
|||
|
Aryaka |
|
$21.3 |
|
|||
|
Silver Peak |
|
$14.1 |
|
|||
|
Viptela |
|
$9.5 |
|
|||
|
InfoVista |
|
$4.4 |
|
|||
|
Citrix |
|
$4.4 |
|
|||
|
Talari |
|
$4.1 |
|
|||
|
TELoIP |
|
$3.9 |
|
|||
|
FatPipe |
|
$3.8 |
|
|||
|
Cisco |
|
$3.1 |
|
|||
|
Huawei |
|
$2.8 |
|
|||
|
CloudGenix |
|
$2.5 |
|
|||
|
Riverbed |
|
$1.7 |
|
|||
|
ZTE |
|
$0.6 |
|
|||
|
Other |
|
$14.2 |
|
|||
|
Total SD-WAN |
$116.2 |
|||||
| Source: IHS-Markit | ||||||
“With the WAN connectivity problem well understood and solutions ramping in deployments, SD-WAN vendors are beginning to offer additional services such as WAN optimization and virtual firewall. The next important challenge for SD-WAN vendors to solve is providing connectivity with SLAs and security for the multi-cloud,” said Cliff Grossner.
More Market Highlights:
· 3Q17 ADC revenue increased 5% from 2Q17 and decreased 5% from 3Q16
· Virtual ADC appliances stood at 28% of 3Q17 ADC revenue
· F5 garnered 45% ADC market share in 3Q17 with revenue down 4% YoY. Citrix had the #2 spot with 29% of revenue, and A10 (8%) rounded out the top 3 market share spots.
Data Center Network Equipment Report Synopsis:
The IHS Markit Data Center Network Equipment market tracker is part of the Data Center Networks Intelligence Service and provides quarterly worldwide and regional market size, vendor market share, forecasts through 2021, analysis and trends for (1) data center Ethernet switches by category [purpose built, bare metal, blade and general purpose], port speed [1/10/25/40/50/100/200/400GE] and market segment [enterprise, telco and cloud service provider], (2) application delivery controllers by category [hardware-based appliance, virtual appliance], and (3) software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) [appliances and control and management software]. Vendors tracked include A10, ALE, Arista, Array Networks, Aryaka, Barracuda, Cisco, Citrix, CloudGenix, Dell, F5, FatPipe, HPE, Huawei, InfoVista, Juniper, KEMP, Radware, Riverbed, Silver Peak, Talari, TELoIP, VeloCloud, Viptela, ZTE and others.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From a Nov 15, 2017 press release:
According to the IHS Markit Data Center and Enterprise SDN Hardware and Software Biannual Market Tracker, SD-WAN is currently a small market, totaling just $137 million worldwide in the first half of 2017 (H1 2017). However, global SD-WAN hardware and software revenue is forecast to reach $3.3 billion by 2021 as service providers partner with SD-WAN vendors to deploy overlay solutions — and as virtual network function (VNF)–based solutions become more closely integrated with carrier operations support systems (OSS) and business support systems (BSS).
“Currently, the majority of SD-WAN revenue is from appliances, with early deployments focused on rolling out devices at branch offices,” Grossner said. “Moving forward, we expect a larger portion of SD-WAN revenue to come from control and management software as users increasingly adopt application visibility and analytics services.”
More highlights from the IHS Markit data center and enterprise SDN report:
- Globally, data center and enterprise software-defined networking (SDN) revenue for in-use SDN-capable Ethernet switches, SDN controllers and SD-WAN increased 5.4 percent in H1 2017 from H2 2016, to $1.93 billion
- Based on in-use SDN revenue, Cisco was the number-one market share leader in the SDN market in H1 2017, followed by Arista, White Box, VMware and Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Looking at the individual SDN categories in H1 2017, White Box was the frontrunner in bare metal switch revenue, VMware led the SDN controller market segment, Dell held 45 percent of branded bare metal switch revenue and Hewlett Packard Enterprise had the largest share of total SDN-capable (in-use and not-in-use) branded Ethernet switch ports
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Notes:
We’ve repeatedly pounded the table that there are no standards for SD-WANs, despite efforts by MEF [1]. That implies single vendor SD WAN with vendor lock-in and no interoperability between SD-WANs from different vendors.
Note 1. MEF says it will standardize the managed services that SD-WAN network operators deliver, by developing open APIs, along with common terminology and components. This effort builds on MEF’s Lifecycle Service Orchestration effort. Please refer to this MEF document.
Note 2. Gartner’s definition of SD-WAN

More from Gartner on SD-WANs:
Enterprise network leaders face enormous challenges adapting and changing their managed WAN services to meet constantly changing business needs for new applications, new offices, more users, cloud services and digital business. Based on hundreds of client inquiries and recent Research Circle surveys, a key obstacle is that traditional network services are too slow in meeting these needs, and network leaders need alternative solutions that can meet their evolving needs faster. Compared to traditional WAN services, managed SD-WAN services (including various WAN connectivity services) are emerging with promises of greater agility, flexibility, control and cost-efficiency.
Gartner recommends that network leaders seeking managed WAN services use end-to-end managed SD-WAN and connectivity services to create agile and cost-effective managed WAN services. However, they must avoid buying into overinflated expectations created by the market hype that ignores the limitations of current services. To avoid the inevitable disappointment that follows unfulfilled expectations, network leaders should outline their service requirements, and use these to define evaluation criteria for a balanced analysis of service benefits and limitations.’

Source: Gartner (December 2017)
Enterprise network leaders face enormous challenges adapting and changing their managed WAN services to meet constantly changing business needs for new applications, new offices, more users, cloud services and digital business. Based on hundreds of client inquiries and recent Research Circle surveys, a key obstacle is that traditional network services are too slow in meeting these needs, and network leaders need alternative solutions that can meet their evolving needs faster. Compared to traditional WAN services, managed SD-WAN services (including various WAN connectivity services) are emerging with promises of greater agility, flexibility, control and cost-efficiency.
Gartner recommends that network leaders seeking managed WAN services use end-to-end managed SD-WAN and connectivity services to create agile and cost-effective managed WAN services. However, they must avoid buying into overinflated expectations created by the market hype that ignores the limitations of current services. To avoid the inevitable disappointment that follows unfulfilled expectations, network leaders should outline their service requirements, and use these to define evaluation criteria for a balanced analysis of service benefits and limitations.’

Source: Gartner (December 2017)
Current WAN services take too long to roll out and are too difficult to relocate or terminate, and network leaders are looking for ways to improve this. Network leaders see SD-WAN as a new opportunity to create more agile branch office connectivity due to appliances’ support of “zero-touch-configuration.” Vendors are fueling these expectations with reports of very fast site rollout with reports of 20 to 30 sites deployed overnight, compared to six to 10 sites per week for a traditional managed router service. However, SD-WAN does not change fundamental limitations of connectivity services, for example:
- Fast site deployments are only available for 4G/LTE access services or in cases where the provider already has a wired access service to the building (although in many cases these still require one to two weeks to provision).
- Network leaders who need new wired access services still need to plan for 14 to 90 days (or longer) from order to provisioning.
- All wired branch office connections, private or public, still require network leaders to sign a contract of fixed duration, making it a problem for network leaders to move or terminate a site without financial penalties.
Network leaders who need new WAN sites deployed with short notice should request managed SD-WAN with embedded LTE services. While many providers do not yet offer this service, there are providers in select countries that courier SD-WAN appliances with LTE embedded to customer sites instead of sending a technician. The best-case scenario is only six hours from order placement to on-site delivery of the appliance. Combined with self-service, where the enterprise plugs in the SD-WAN appliance to the LAN and powers up the device, the site can be operational within a day in the best case. However, network leaders who do not want their office staff to plug in the appliance need to plan for up to a week for a technician to be on-site, depending on location.
However, besides expense, the performance limitations of 4G/LTE include lower bandwidth than fiber, lack of geographic coverage and lack of QoS. Also, most of these services are based on using the internet as backhaul to the provider’s internet gateway. This means that, for larger sites and critical applications, network leaders should only employ 4G/LTE connectivity as an interim primary connection until a fiber connection has been deployed.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Because of the performance issues that still plague the internet in most parts of the world, the majority of enterprises are not replacing MPLS with internet services. Instead, based on client inquiries, Gartner estimates that around 60% of global WANs use both internet and MPLS in concert in a hybrid WAN that sends critical application traffic over the MPLS and everything else over the internet.
Enterprise experience has shown that for a global managed hybrid WAN, network planners can obtain at least 30% expense savings compared to traditional managed WAN (see “Cloud Adoption Is Driving Hybrid WAN Architectures” ). Network planners that want to replace their global MPLS with internet should progress selectively, and choose a few sites in areas where the internet is most likely to be of good quality. For these sites, demand a two- to four-month pilot as a condition of signing a new WAN contract. Remember that all internet providers and services are not the same. Use only a select few and do not disaggregate internet providers, as WAN and application performance will suffer.
IoT Tech Expo Highlights + Wirepas’ Distributed Intelligence Mesh Network
IoT Tech Expo Takeaways:
This was one of the most chaotic, disorganized, frustrating trade shows I’ve attended in many decades. [Please contact me if you’re interested in why that was the case]. However, there were several interesting booths I visited on the show floor, a few enlightening panel sessions and one novel presentation proposing a completely different approach to IoT wireless connectivity (see Wirepas discussion below).
Caroline Wong’s talk on cyber security for IoT was very illuminating and pointed out the huge dangers of exposed IoT devices/things which might be hacked.
Here are a few quick takes from a couple of IoT panels:
- Despite several standards available, strong cyber-security has not been embedded in IoT devices or gateways because it’s seen as too expensive by the hardware vendors.
- Industrial IoT demands massive connectivity, but the ability to scale to manage thousands of devices is questionable.
- A mutual understanding between IoT hardware vendors and cloud software providers is urgently needed. Business models for each seem to be at odds.
- Key questions:
-What will be the ROI for a company that deploys IoT for its business?
-What’s the IoT customer willing to pay for WAN connectivity, activation, services, management, etc. Suggested that recurring fees should be avoided. Sprint offers a pre-paid billing model without recurring fees for IoT connectivity.
- Metering for home automation offers the possibility of disaggregation of electrical signals for improved data collection and integration.
- In most IoT applications, sampled data should be analyzed and/or processed at the network edge rather than in a cloud resident data center.
- In some IoT applications, the IoT controller only needs to be informed of a status change.
- Sprint is offering a private LTE network where data and commands/status are routed off to an on site data center or to a remote host via Sprint’s wireless network. It offers secure, wireless WAN connections.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Massive IoT – Building shared success in IoT, by Youssef Kamel, GM Wirepas:
Youssef began by providing his company’s vision and requirements for IoT connectivity:
- Everything that can be connected will be connected.
- Need a fully decentralized operations to manage large scale infrastructure.
- Long life: IoT devices are expected to last up to 15 or 20 years vs 2 to 3 years for an iPhone.
- IoT devices generally require latency of a few msecs and micro amps of power.
- Currently, there’s a huge fragmentation of the IoT market with tremendous diversity of use cases (see illustration below). What’s common among them is requirement to manage on a large scale and density of devices.
- The IoT connectivity network needs to have very low cost (ideally free), use a small amount of energy per device, self configure network nodes according to the use cases (NOTE that is generally not the case in any existing large scale network we know of).
- Wirepas commissioned Northstream to do a whitepaper on IoT requirements for massive connectivity. It’s titled: “Massive IoT- different technologies for different needs” and available for free download (see Reference and chart below).
 …………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Evolution of IoT connectivity – from millions to billions:
- Local area and small installations – Zigbee, Thread, BLE Mesh, Z-wave,etc.
- Wide area and sparse installations with limited bandwidth – SigFox, LoRA, Ingenu, NB-IoT, LTE-M, etc.
- Massive IoT: Any scale, any density, any location installations, Over the Air (OTA), open platform with a Wide Area Mesh Network.
Following that backgrounder, Mr. Kamel’s presentation focused on massive IoT based on a decentralized, wireless mesh network, where all the interconnected network nodes locally decide actions to take by themselves via Wirepas’ Connectivity software. The local decision-making ensures that the devices always operate the similar way, independent of the network size or the devices’ locations within the network. No central network management is needed in this approach.
The multi-hop topology is optimized continuously and adapts to changes in the environment and the network. For each node, there are multiple routing options (next hops), and multiple Gateways (back haul connections) that may be used in the same network.
Different operational parameters can be changed to provide trade-offs between bandwidth, latency, range and power consumption. The network can be chosen according to the requirements.
The wireless connectivity protocol stack is described on Wirepas’ website as follows:
“Wirepas Connectivity is a de-centralized radio communications protocol for large-scale IoT applications. What we offer is the protocol software that can be used in any device, with any radio chip and on any radio band.”
Wirepas Connectivity (WPC) white paper may be downloaded here. From that paper:
“Device-to-device range can be adjusted with the used Physical layer. The selection of different Physical layers is enabled by the Physical layer independent architecture and operation of WPC. Different frequency bands and radio data rate vs. range options can be used depending on application needs. E.g. 2.4 GHz can be used for dense indoor installations and sub-GHz if longer device-to-device range is needed for inter-building communication.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In answer to this author’s question, Youssef said that BlueTooth Low Energy (BLE) was one of several wireless LAN technologies being used with the Wirepas Connectivity software which contains the network intelligence.
Author’s Note:
Wirepas provides the software protocol stack (starting at Data Link layer) that runs on their partner company’s radio and baseband (Physical layer and MAC sub-layer) hardware. Then OEMs deploy the smart devices (with embedded connectivity hardware from partner companies and Wirepas’ software) to complete the network infrastructure. That approach is shown in this illustration, courtesy of Wirepas:
Real World Example – Smart Metering with a Wide Area Mesh:
This real world deployment was done by Hafslund Nett – an electric utility company in greater Oslo, Norway that serving approximately 1.5 million people in a 100 x 200 km area. Highlights:
•> 700k electricity meters in a single Wide Area Mesh network.
• No infrastructure for connectivity – just the smart meters.
• Benefits of Wireless Area Mesh for utility: 100% network coverage, SLA >99.9%, Future proof, Free wireless connectivity.
A whitepaper on this deployment may be downloaded here.
Market Segments Wirepas is Pursuing:
- Smart metering for electricity, gas and water
- Asset tracking, e.g. within a post office
- Lighting systems within a building
- Street lights and smart cities
Wirepas claims 3 world records:
- Largest scale – 700 000+ devices in a single mesh network
- Highest density – 1000+ devices inside m3 without a single packet collision
- Smallest power IPv6 router – 25 μA stand by, continuously connected
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Next Up: Wirepas is partnering with K.Hartwall to deploy connected roller cages (AKA load carriers). The initiative is called Visimore.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Wirepas:
Reference:
Downloadable white papers: https://wirepas.com/download/
Verizon will offer residential “5G” fixed broadband service in 2018
Fully two years before the IMT 2020 “5G” standards are completed, Verizon announced at a “sell side analyst meeting” that it will launch a “5G” fixed wireless broadband service for residential customer Internet access in three to five U.S. markets in the second half of next year (2018). The company plans to use what they claim is “an early version of 5G” for the fixed wireless services. It’s supposedly the same technology that AT&T is testing in several cities.
Author’s Note:
As I’ve been saying for quite some time, these so called “5G” commercial service offerings are way to premature, because the ITU-R WP5D won’t even complete evaluation of the IMT 2020 Radio Access Network (RAN) technologies by end of 2020!
This piece in Barron’s seems to sum the mood up. Light Reading found out the “5G” equipmentt being used is supplied by Ericsson and Samsung.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Verizon’s first commercial launch is planned to be in Sacramento, CA in the second half of 2018. Details of that launch, and the announcement of additional markets, will be provided at a later date, the company said. Verizon plans to commercially deploy this broadband fixed wireless access service to a total of three to five markets in 2018.
Verizon already trialed 5G residential applications in 11 markets in 2017. The commercial launch is based on customer experience and on Verizon’s confidence in new technology powered by mmWave spectrum, the #1 US mobile operator said.
The company sees a potential market of 30 million households in the US for “5G” residential broadband services. The initial launch in 2018 is not expected to require significant capex. Speaking at an investor conference, Verizon said its capex in 2018 would be “consistent with the past several years.” The top U.S. mobile operator previously said that its 2017 capex will be between $16.8 billion and $17.5 billion.
“This is a landmark announcement for customers and investors who have been waiting for the 5G future to become a reality,” said Hans Vestberg, Verizon CTO. “We appreciate our strong ecosystem partners for their passion and technological support in helping us drive forward with 5G industry standards, for both fixed and mobile applications. The targeted initial launches we are announcing today will provide a strong framework for accelerating 5G’s future deployment on the global standards.”
This “5G” fixed wireless broadband access (FWBA) will use the 28 GHz spectrum band. Verizon forecasts the total addressable U.S. market for that technology is approximately 30 million homes. FWBA seems like a great idea as no fiber or wires have to be installed, but it has many challenges. Those include: poor propagation characteristics of millimeter wave spectrum.
A few slides from Verizon’s presentation:




At the investor conference, Verizon said that 25% to 30% of the “residential broadband market” in the US is “addressable by 5G.” Verizon says that could be up to 30 million households. According to the US Census Bureau, in 2016 there were 125.82 million across the US.
In the trials so far, Verizon said that it has served a 19 floor apartment building with the 28GHz millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G connection. The operator has been testing “home units” and “optional outdoor antennas” in the tests. Verizon has also been testing outdoor window-mount antennas that use an optical connection to an indoor WiFi router to distribute the signal.
Verizon is continuing to test its own fixed 5G specification in multiple markets. It will test the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) release 15 New Radio (NR) specification in the US in 2018.
–>Note yet again that 3GPP’s NR has not even been presented to ITU-R WP5D nor have any other Radio Interface Technologies (RITs). However, 3GPP has indicated it’s intent to submit NR for consideration late in 2018 when WP 5D will start to evaluate RITs.
References:
http://www.verizon.com/about/investors/analyst-meeting-including-5g-launch-news-release
http://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-launch-5g-residential-broadband-services-5-markets-2018
…………………………………………………………
Addendum:
Matt Ellis, EVP & CFO, will speak at the UBS 45th Annual Global Media and Communications Conference on December 5th at approximately 8:00 AM ET.
Ericsson Forecast: 1 Billion Global 5G Subscriptions in 2023
Global 5G subscriptions will reach 1 billion by the end of 2023, with 5G covering more than 20% of the global population, Ericsson has predicted.
Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report predicts that the first 5G new radio deployments will go live in 2019, with major deployments from 2020. Early 5G deployments are expects in markets including South Korea, Japan, China and the US.
LTE will meanwhile become the dominant mobile access technology by the end of this year. But after reaching a peak in 2021, subscriptions are expected to drop off slightly as they are supplanted by 5G.
Global LTE subscribers are tipped to reach an estimated 5.5 billion subscriptions by the end of 2023, with a global LTE population coverage of 85%.
VoLTE subscriptions are also expected to reach 5.5 billion by end-2023, accounting for more than 80% of combined LTE and 5G subscriptions.
The report also projects that global mobile data traffic will pass 100 exabytes per month in 2023, the equivalent of 5.5 million years of HD video streaming.

- 5G will cover more than 20 percent of the global population six years from now, according to the latest Ericsson Mobility Report
- Mobile data traffic continues to grow, primarily fueled by increased viewing of video content
- LTE will be the dominant access technology by end of this year, driven by demand for improved user experience and faster networks
“The latest report highlights trends in mobile subscription and data traffic growth, as well as the industry’s effort to tackle the increasing demands on mobile networks globally,” Ericsson chief strategy officer and head of technology and emerging business Niklas Heuveldop said.
“In addition, the report examines the emergence of new use cases as network capabilities evolve – smartwatches, IoT alarms, and augmented reality-assisted maintenance and repair, to name a few. As we prepare for 5G, these trends will continue to set the agenda for the mobile industry going forward.”
References:
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/global-5g-subs-pass-1b-2023
LG U+ & Huawei complete 5G network test in Seoul, South Korea
South Korea telco LG U+ and its wireless network equipment partner Huawei confirmed that they have completed what they say is the world’s first large-scale 5G network test in a pre-commercial environment. The test network was situated in the Gangnam District of Seoul, South Korea and consisted of both 3.5GHz and 28GHz base stations (the two most popular frequency bands for 5G globally so far).
The partners said the test also helped to successfully verify the technologies of UHD (4K) IPTV video and other commercial 5G services in a typical dense, urban environment. High-speed mobility, dual connectivity, and inter-cell handovers under continuous networking conditions were also validated.
LG U+ reported that the test results for the end-to-end network trial returned average data rates of 1Gbit/s over the 3.5GHz frequency band and more than 5Gbit/s for dual connectivity over both high and low bands.
During the trial in a typical dense urban area, the companies achieved average data rates of 1Gbps over the low band and more than 5Gbps for dual connectivity under both low and high bands. A peak data rate of 20Gbps was attained through this dual connectivity.
“The world’s first large-scale joint 5G pre-commercial test indicated a significant breakthrough in 5G,” said Kim Dae Hee, VP of the 5G Strategy Unit at LG U+. “We believe that Huawei is set to help LG U+ implement the world’s first Commercial 5G network over 3.5GHz”
LG U+ took to the road with its 5G Tour Bus to showcase 4K IPTV (picture below). It also demonstrated a VR drone designed by Huawei’s Wireless X Labs and kitted out with what the vendor says is the world’s first 5G customer premise equipment (CPE) operating in the 3.5GHz band. The demonstration reportedly showed throughput speeds of up to 1.5Gbit/s whilst the drone was flying at an altitude of over 100m.

“In the Gangnam District of Korea, we have successfully validated the 5G pre-commercial network and released the world’s first 3.5GHz CPE.,” said Zhou Yuefeng, CMO of Huawei’s Wireless Product Line.
“This demonstrates that Huawei will maintain its capability to provide competitive E2E 5G network products in 2018. LG U+ and Huawei will continue to conduct further research into 5G technologies and build a robust E2E industry ecosystem to achieve business success in the upcoming 5G era.”
The test results returned average data rates of 1 Gbps over the low band and more than 5 Gbps for dual connectivity over high and low bands. A peak data rate of 20 Gbps and an average data rate of more than 5 Gbps were achieved through dual connectivity over 3.5 GHz and 28 GHz. During the test, a 5G tour bus delivered 5G-based IPTV 4K, and a VR drone was demonstrated in the ‘5G for All’ experience room at the LG U+ headquarters, which required data rates ranging from 20 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
Editor’s Notes:
- South Korea’s mobile network operators are expected to roll out trial 5G services in time for the 2018 Winter Olympics. SK Telecom (SKT) completed a successful test of five-band carrier aggregation (5C). SK Telecom, KT and LG U+‘ launched the world’s first commercial interconnected VoLTE service.
- South Korea’s mobile market has slow growth over the last few years due to a highly mature market. Organic growth by the three main mobile operators, together with the multitude of niche MVNOs will result in further growth to 2018 however growth rates will taper off further over the next few years as the market further matures. Market penetration reached 117% in 2016 and is predicted to reach between 119% and 122% by 2021 driven by the uptake of both 4G and 5G services. The split in mobile operator market share has remained relatively constant over the last two decades. LG U+ (formerly known as LG Telecom) has made a marginal increase in market share over that time.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
http://www.telecomtv.com/articles/5g/the-lg-u-5g-tour-bus-makes-a-stop-in-gangnam-16187/
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20171127/5g/lg-huawei-5g-network-test-seoul-tag23
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/lg-u-completes-pre-commercial-5g-test
Cignal AI & Del’Oro: Optical Network Equipment Market Decline Continues
Executive Summary & Overview:
Does anyone remember the fiber optic build out boom of the late 1990’s to early 2001? And the subsequent bust, which the industry still has not recovered from!
Fast forward to today, where we hear more and more about huge fiber demand from mega cloud service providers/Internet companies for intra and inter Data Center Connections. And the huge amount of fiber backhaul for small cells and cell towers.
Yet two respected market research firms- Cignal AI and Del’Oro Group– both say that optical network transport equipment revenue declined yet again.
Cignal AI said: “global spending on optical network equipment dropped for a third consecutive quarter, led by a larger than normal seasonal decline in China and weakening trends in EMEA.” However, Cignal AI (Andrew Schmitt) stated that “North American spending increased again quarter-over-quarter, with positive results reported by most vendors. Spending on Metro WDM continues to grow at the expense of LH WDM.”
Del’Oro Group reported in a press release: “revenues for Optical Transport equipment in North America continued to decline in the third quarter of 2017.”
“Optical Transport equipment purchases in North America was about 10 percent lower in the first nine months of 2017,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “This has been one of the more challenging years for optical equipment manufacturers selling into North America. However, a few vendors in the region performed really well considering the tough market environment. For the first nine months of the year, Ciena was able to hold revenues steady, Cisco was able to grow revenues 14 percent, and Fujitsu experienced only a slight revenue decline,” Mr. Yu added.
–>Please see Editor’s Notes below for additional optical network equipment market insight and vendor perspective.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Cignal AI Report Summary:
- North American spending increased again quarter-over-quarter, with positive results reported by most vendors. Spending on Metro WDM continues to grow at the expense of LH WDM.
- EMEA revenue fell sharply though this was the result of weakness at larger vendors – smaller vendors performed better. As in North America, LH WDM bore the brunt of the decline.
- Last quarter was the weakest YoY revenue growth recorded in China in over 4 years as momentum from 2Q17 spending failed to continue into the third quarter. Spending trends in the region remain difficult to predict.
- Revenue in the rest of Asia (RoAPAC) easedfollowing breakout results in India during 2Q17 though spending remains at historically high levels.
- Quarterly coherent 100G+ port shipments broke 100k units for the first time on a global basis. 100G+ Port shipments in China were flat QoQ and are substantially up YoY.
Cignal AI’s October 29, 2017 Optical Customer Markets Report discovered an unexpected weakness in 2017 optical transport equipment spending from cloud and co-location (colo) operators (see Cignal AI Reports Unexpected Drop in Cloud and Colo Spending). This surprising trend was then further supported by public comments later made by Juniper and Applied Optoelectronics.
Contact Info:
Cignal AI – 225 Franklin Street FL26 Boston, MA – 02110 – (617) 326-3996
Email: [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Notes:
1.One prominent Optical Transport Network Equipment vendor evidently feels the effect of the market slowdown. On November 8, 2017, Infinera reported a GAAP net loss for the quarter of $(37.2) million, or $(0.25) per share, compared to a net loss of $(42.8) million, or $(0.29) per share, in the second quarter of 2017, and net loss of $(11.2) million, or $(0.08) per share, in the third quarter of 2016.
Infinera also announced it is implementing a plan to restructure its worldwide operations in order to reduce its expenses and establish a more cost-efficient structure that better aligns its operations with its long-term strategies. As part of this restructuring plan, Infinera will reduce headcount, rationalize certain products and programs, and close a remote R&D facility.
2. Astonishingly, there’s an India based optical network equipment vendor on the rise. Successful homegrown Indian telecom vendors are hard to come by. That makes Bengaluru-based Tejas Networks something of an anomaly. Started 17 years ago (in 2000), Tejas is one of India’s few hardware producers.
Tejas Networks India Ltd. has made a name for itself in the optical networking market, especially within India, which looks poised for a boom in this sector (mainly due to fiber backhaul of 4G and 5G mobile data traffic). Nearly two thirds of its sales come from India, with the rest earned overseas.
“We are growing at 35% year-on-year and we hope to grow by at least 20% over the next two to three years,” says Sanjay Nayak, the CEO and managing director of Tejas, during an interview with Light Reading. “Overseas, we mainly target south-east Asian, Latin America and African markets.” Telcos in these markets have similar concerns to those in India, explains Nayak, making it easy for Tejas to address their demands.
“R&D is in our DNA and we believe that unless you come up with a differentiated product the market will not take you seriously,” says Nayak. “We have a huge advantage as an Indian player … [which] allows us to provide the product at a lesser price.”
Nayak believes that the experience of developing solutions for the problems faced by Indian telcos has helped the company to address overseas markets as well.
“Our products do very well for networks evolving from TDM to packet, which is a key concern of the Indian telcos,” he explains. “We realized that the US-based service providers were facing a similar problem of cross connect, which we were able to resolve. So, as we say, you can address any market if you are able to handle the Indian market.”
Read more at: http://www.communicationstoday.co.in/daily-news/17152-india-s-tejas-eyes-bigger-slice-of-optical-market
3. The long haul optical transport market is dominated by OTN (Optical Transport Network) equipment (which this editor worked on from 2000 to 2002 as a consultant to Ciena, NEC, and other optical network equipment and chip companies).
The OTN wraps client payloads (video, image, data, voice, etc) into containers or “wrappers” that are transported across wide area fiber optic networks. That helps maintain native payload structure and management information. OTN offers key benefits such as reduction in transport cost and optimal utilization of the optical spectrum.
OTN technology includes both WDM and DWDM. The service segment includes network maintenance and support services and network design & optimization services. On the basis of component, the market is divided into optical switch and optical transport. Based on end user, it is classified into government and enterprises.
According to Allied Market Research, OTN equipment market leaders include: Adtran, Inc., ADVA Optical Networking, Advanced Micro Devices Inc., Fujitsu, Huawei Technologies., ZTE Corporation., Belkin Corporation., Ciena Corporation., Coriant, and Allied Telesyn.
Above illustration courtesy of Allied Market Research
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note that Cisco offers OTN capability on their Network Convergence System (NCS) 4000 – 400 Gbps Universal line card. Despite that and other OTN capable gear, Cisco is not covered in the above mentioned Allied Market Research OTN report.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Global Switching & Router Market Report:
Separately, Synergy Research Group said in a press release that:
Worldwide switching and router revenues were well over $11 billion in Q3 and were $44 billion for last four quarters, representing 3% growth on a rolling annualized basis. Ethernet switching is the largest of the three segments accounting for almost 60% of the total and it is also the segment that has by far the highest growth rate, propelled by aggressive growth in the deployment of 100 GbE and 25 GbE switches.
In Q3 North America remained the biggest region accounting for over 41% of worldwide revenues, followed by APAC, EMEA and Latin America. The APAC region has been the fastest growing and this was again the case in Q3, with growth being driven in large part by spending in China, which benefited Huawei in particular.
Cisco’s share of the total worldwide switching and router market was 51%, with shares in the individual segments ranging from 63% for enterprise routers to 38% for service provider routers. Cisco is followed by Huawei, Juniper, Nokia and HPE. Their overall switching and router market shares were in the 4-10% range in Q3. There is then a reasonably long tail of other vendors, with Arista and H3C being the most prominent challengers.
![S&R Q317[1]](http://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2017/11/27/1206112/0/en/photos/494670/0/494670.jpg?lastModified=11%2F27%2F2017%2004%3A20%3A07&size=3)
“The big picture is that total switching and router revenues are still growing and Cisco continues to control half of the market,” said John Dinsdale, a Chief Analyst at Synergy Research Group. “Some view SDN and NFV as existential threats to Cisco’s core business, with own-design networking gear from the hyperscale cloud providers posing another big challenge. While these are genuine issues which erode growth opportunities for networking hardware vendors, there are few signs that these are substantially impacting Cisco’s competitive market position in the short term.”
Contact Info:
To speak to a Synergy analyst or to find out more about how to access Synergy’s market data, please contact Heather Gallo @ [email protected] or at 775-852-3330 extension 101.
New ITU-T Standards for IMT 2020 (5G) + 3GPP Core Network Systems Architecture
New ITU-T standards related to “5G”:
ITU-T has reached first-stage approval (‘consent’ level) of three new international standards defining the requirements for IMT-2020 (“5G”) network systems as they relate to network operation, softwarization and fixed-mobile convergence.
The standards were developed by ITU-T’s standardization expert group for future networks, ITU-T Study Group 13.
Note: The first-stage approvals come in parallel with ITU-T Study Group 13’s establishment of a new ITU Focus Group to study machine learning in 5G systems.
End-to-end flexibility will be one of the defining features of 5G networks. This flexibility will result in large part from the introduction of network softwarization, the ability to create highly specialized network slices using advanced Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and cloud computing capabilities.
The three new ITU-T standards are the following:
- ITU Y.3101 “Requirements of the IMT-2020 network” describes the features of 5G networks necessary to ensure efficient 5G deployment and high network flexibility.
- ITU Y.3150 “High-level technical characteristics of network softwarization for IMT-2020” describes the value of slicing in both horizontal and vertical, application-specific environments.
- ITU Y.3130 “Requirements of IMT-2020 fixed-mobile convergence” calls for unified user identity, unified charging, service continuity, guaranteed support for high quality of service, control plane convergence and smart management of user data.
ITU’s work on “International Mobile Telecommunications for 2020 and beyond (IMT-2020)” defines the framework and overall objectives of the 5G standardization process as well as the roadmap to guide this process to its conclusion by 2020.
ITU’s Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is coordinating the international standardization and identification of spectrum for 5G mobile development. ITU’s Telecommunications Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is playing a similar convening role for the technologies and architectures of the wireline elements of 5G systems.
ITU standardization work on the wireline elements of 5G systems continues to accelerate.
ITU-T Study Group 15 (Transport, access and home networks) is developing a technical report on 5G requirements associated with backbone optical transport networks. ITU-T Study Group 11 (Protocols and test specifications) is studying the 5G control plane, relevant protocols and related testing methodologies. ITU-T Study Group 5 (Environment and circular economy) has assigned priority to its emerging study of the environmental requirements of 5G systems.
ITU-T Study Group 13 (Future networks), ITU’s lead group for 5G wireline studies, continues to support the shift to software-driven network management and orchestration. The group is progressing draft 5G standards addressing subjects including network architectures, network capability exposure, network slicing, network orchestration, network management-control, and frameworks to ensure high quality of service.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
The “5G” wireline standards developed by ITU-T Study Group 13 and approved in 2017 include:
- ITU Y.3071 “Data Aware Networking (Information Centric Networking) – Requirements and Capabilities” will support ultra-low latency 5G communications by enabling proactive in-network data caching and limiting redundant traffic in core networks.
- ITU Y.3100 “Terms and definitions for IMT-2020 network” provides a foundational set of terminology to be applied universally across 5G-related standardization work.
- ITU Y.3111 “IMT-2020 network management and orchestration framework” establishes a framework and related principles for the design of 5G networks.
- ITU Y.3310 “IMT-2020 network management and orchestration requirements” describes the capabilities required to support emerging 5G services and applications.
- Supplement 44 to the ITU Y.3100 series “Standardization and open source activities related to network softwarization of IMT-2020”summarizes open-source and standardization initiatives relevant to ITU’s development of standards for network softwarization.
Reference:
http://news.itu.int/5g-update-new-itu-standards-network-softwarization-fixed-mobile-convergence/
…………………………………………………………….
“5G” Core Network functions & Services Based Architecture:
The primary focus of ITU-R WP5D IMT 2020 standardization efforts are on the radio aspects (as per its charter). That includes the Radio Access Network (RAN)/Radio Interface Technology (RIT), spectral efficiency, latency, frequencies, etc.
To actually deliver services over a 5G RAN, a system architecture and core network are required. The core network provides functions such as authentication, session management, mobility management, forwarding of user data, and (possibly) virtualization of network functions.
3GPP Technical Specification (TS) 23.501 — “System Architecture for the 5G System” — is more commonly referred to as the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) for the 5G Core network. It uses service-based interfaces between control-plane functions, while user-plane functions connect over point-to-point links. This is shown in the figure below. The service-based interfaces will use HTTP 2.0 over TCP in the initial release, with QUIC transport being considered for later 3GPP releases.
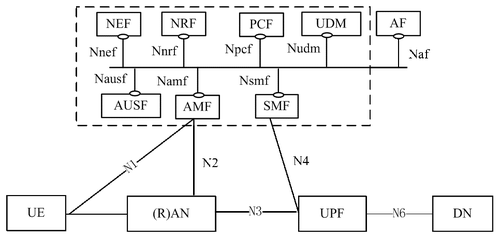
There are many aspects to this, but the white paper highlights:
- How the idea of “network function services” (3GPP terminology) aligns with the micro-services based view of network service composition
- How operators may take advantage of decoupled control- and user-plane to scale performance
- How the design might enable operators to deploy 5GC functions at edge locations, such as central offices, stadiums or enterprise campuses
The first 5G core standards (really specifications because 3GPP is not a formal standards body) are scheduled to be included in 3GPP Release 15, which “freezes” in June next year and will be formally approved three months later. This will be a critical release for the industry that will set the development path of the 5G system architecture for years to come.
Download white paper: Service-Based Architecture for 5G Core Networks
Editor’s Note:
From http://www.3gpp.org/specifications:
“The 3GPP Technical Specifications and Technical Reports have, in themselves, no legal standing. They only become “official” (standards) when transposed into corresponding publications of the Partner Organizations (or the national / regional standards body acting as publisher for the Partner).”
References:
http://www.lightreading.com/mobile/5g/5g-core-and-the-service-based-architecture/a/d-id/738456?
https://img.lightreading.com/downloads/Service-Based-Architecture-for-5G-Core-Networks.pdf