Strategy Analytics: Huawei 1st among top 5 contributors to 3GPP 5G specs
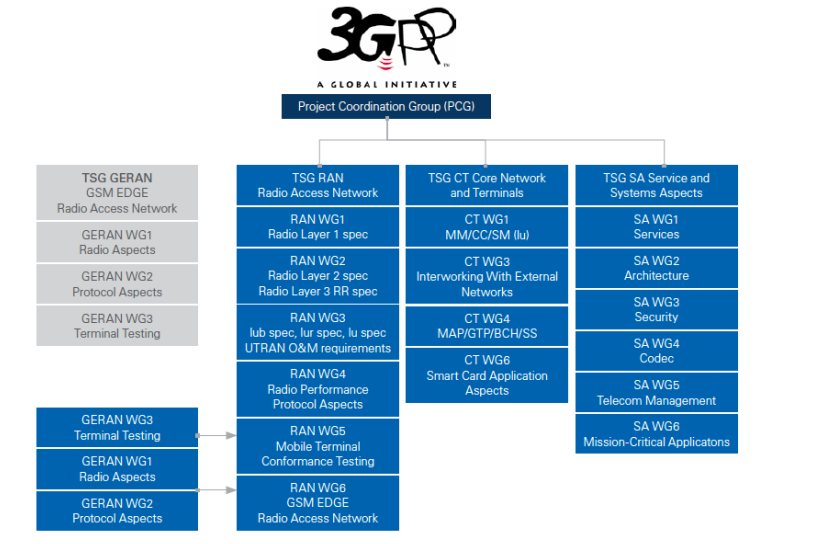
Even though there are more than 600 member companies participating in 3GPP, their 5G specification process is actually led by only a few leading telecom companies. New research from Strategy Analytics analyzes the contributions to 3GPP 5G specifications (Release 15 and Release 16) and finds that 13 companies contributed more than 78% 5G related papers and led 77% of the 5G related Work Items and Study Items.
The Strategy Analytics report “Who Are the Leading Players in 5G Standardization? An Assessment for 3GPP 5G Activities” is available to clients and registered guests here . The report assesses the 13 leading companies’ contributions to 3GPP 5G standards for the period of Releases 15 and 16 so far, based on the following criteria:
- Volume of 5G related papers, including submitted papers, approved/agreed papers and the ratio of approved/agreed papers to total submissions in all Technical Specification Groups (TSGs) and Working Groups (WGs)
- Chairmanship positions, i.e. Chairman and Vice Chairmen for all TSGs and WGs
- Rapporteurs of 5G related Work Items (WIs) / Study Items (SIs) in all TSGs and WGs
The results indicate that the top 5 companies in 3GPP 5G specification activities are Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm and China Mobile.
Guang Yang , Director at Strategy Analytics, noted, “3GPP plays the central role in the ecosystem of global 5G standardization. By analyzing the contributions of industry players to 3GPP 5G standards, we can get an idea of different companies’ positions in 5G innovation as well as their influence in the global mobile industry. So we looked at 3GPP organization and work procedures to assess each company’s influence from multiple aspects.”
Sue Rudd , Director Networks and Service Platforms service, added, “According to our assessment, leading infrastructure vendors – Huawei , Ericsson and Nokia – made more significant contributions to 5G standards than other studied companies. Huawei leads in terms of overall contributions to the end-to-end 5G standards, while Ericsson leads in TSG/WG chairmanship and Nokia in approved/agreed ratio of 5G contribution papers .”
Phil Kendall , Executive Director at Strategy Analytics, added, “It is important to remember that the true nature of the standardization process is actually one of industry collaboration rather than competition. 3GPP standardization continues to be a dynamic process. It is expected that emerging players and new market requirements will increasingly impact priorities for 3GPP Release 17 standards.”
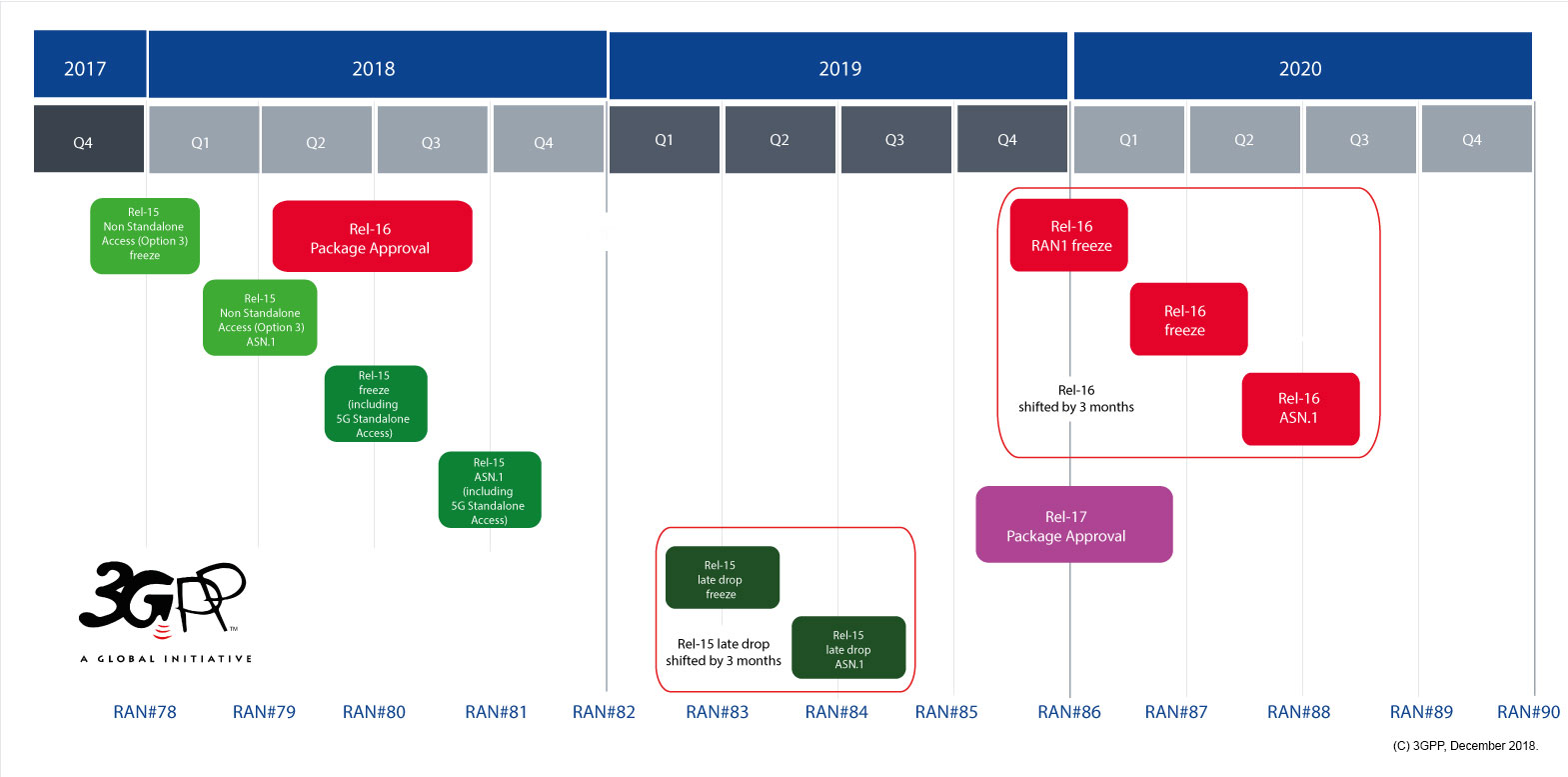
3GPP Timeline:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mike Dano of Lightreading says “Huawei being the biggest contributor to the 3GPP’s 5G specs will undoubtedly worry U.S. lawmakers and regulators, who for years have argued the company poses a security threat to the nation. Huawei denies those allegations.”
“We must have a vocal presence at the standards bodies that are defining the rules for 5G. We have been woefully absent and need to make participation a priority,” wrote Mike Rogers in a recent opinion column. Rogers is a former US representative who co-authored the 2012 US government report initially outlining the security threats posed by Chinese equipment vendors like Huawei and ZTE.
“We need to work with our allies to staunch the spread of Huawei and other Chinese companies owned by the state. We need to better communicate what Chinese dominance of 5G means. This is something we have not successfully done, as shown by Britain deciding to allow Huawei into certain elements of the 5G network,” Rogers added.
Rogers now chairs the “5G Action Now” 501(c)4 advocacy organization, which has been working with the now-disbanded C-Band Alliance to speed up the C-Band spectrum auction in the US for 5G.
Indeed, legislation introduced early this year would require the Trump administration to develop a strategy to “promote United States leadership at international standards-setting bodies for equipment, systems, software, and virtually-defined networks relevant to 5th and future generation mobile telecommunications systems and infrastructure, taking into account the different processes followed by the various international standard-setting bodies.” That legislation passed the House and is now headed to the Senate.
Companies’ 3GPP contributions to the 5G specs [1.] don’t necessarily translate into revenues. For that, companies must patent their inventions.
Note 1. 3GPP specs vs 5G standards:
3GPP 5G specs in Release 15 and 16 have and will continue to be input to ITU-R WP 5D, but only some of those contributions will be in IMT 2020 which is currently restricted to the Radio Interface Technologies (RITs) or sets of RITs (SRITs). Other essential 5G specs like signaling, 5G packet core, 5G network management, etc will be standardized by SDOs (like ETSI) but the real work is done in 3GPP. Also note that IMT 2020 will have several NON 3GPP RITs from ETSI/DECT Forum and India (TSDSI).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
According to one study, Huawei leads in that respect also. IPlytics recently reported that the Chinese firm has far and away the most “declared 5G families” of patents, and the most filed since 2012.
However, it’s worth noting that UK law firm Bird & Bird argues that the reliance on such patent calculations isn’t very insightful, and that different methodologies yield different results.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:


