ONF and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate Fully Disaggregated Open RAN and SD-WAN
Deutsche Telekom is working with the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) and eight vendors to test software-defined radio access networks (SD-RAN) and Open RAN in what it calls a fully disaggregated system. This is the first field trial implementing fully disaggregated open RAN solutions using ONF’s RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) software platform as defined by the O-RAN architecture. This 4G and 5G Standalone (SA) outdoor trial is live at Deutsche Telekom in Berlin, Germany.
In addition, the Facebook-backed Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is taking part by providing hardware and facilities out of the TIP Community Lab in Berlin hosted by Deutsche Telekom.
Carriers are investing in open RAN to enable a new breed of modular and customizable 5G solutions to accelerate innovation and enable the mix-and-match of best-of-breed components from multiple vendors. Open RAN gives operators choice and flexibility to customize and optimize their networks. This SD-RAN trial hosted by DT highlights the promise and flexibility of open RAN by integrating components from eight companies: AirHop, Edgecore, Facebook, Foxconn, Intel, Radisys, Supermicro and Wiwynn. Additionally, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is participating by providing hardware and facilities out of the TIP Community Lab in Berlin hosted by DT. The on-site field trial integration and testing is being coordinated and supported by Highstreet Technologies.
The live trial features horizontally disaggregated hardware (separate RU, DU, and CU units), as well as vertically disaggregated software components including an open source near real-time RIC (nRT-RIC) and xApps coming from the ONF’s SD-RAN project. By integrating proprietary and open source components, including a near real-time RIC and xApps, this ground-breaking trial exemplifies a model for how future open RAN deployments are envisioned to take shape.
The entirety of the trial is operationalized leveraging ONF’s Aether platform, a centrally-managed, multi-cloud, cloud-native platform providing Connectivity-as-a-Service, and highlights network slicing with multiple UPFs running at the edge. The SD-Core component of Aether provides 5G connectivity and the control plane running from the public cloud while SD-Fabric is a fully programmable network fabric optimized for the edge cloud used to instantiate a P4-based 4G/5G UPF in hardware.
Aether hosts the Radisys containerized CU while the Intel® Smart Edge Open (formerly known as OpenNESS) software toolkit hosts the Radisys DU to enable cloud-native deployment of the RAN workload with optimization on the 3rd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor and Intel® vRAN Dedicated Accelerator ACC100. The CU and DU are integrated with ONF’s nRT-RIC, xApps, SD-Core 5G core and Foxconn O-RU.
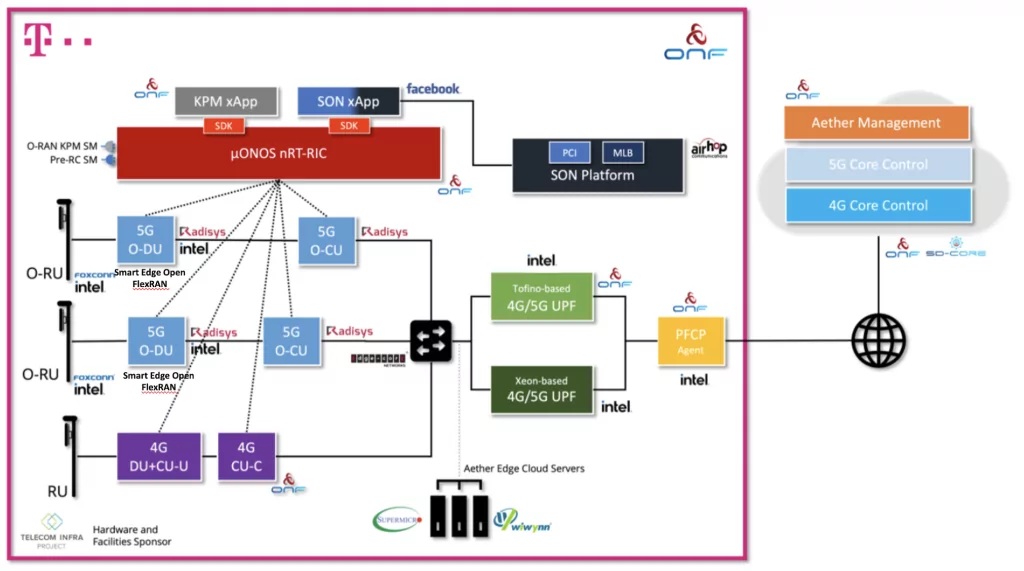
“The Berlin SD-RAN Open RAN Trial, is a momentous step towards realizing the vision of fully disaggregated and intelligent RAN, leveraging ONF’s leading open source RAN Intelligent Controller software platform. In addition to open fronthaul, this trial includes disaggregated RU/DU/CU units, and also vertically disaggregates the RIC and xApps according to SDN principles. Together, we are demonstrating the power of truly open RAN and ecosystem collaboration to accelerate innovation.”
– Alex Choi, Senior Vice President Strategy & Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom and Founding Board Member, O-RAN Alliance
“The SD-RAN Berlin Trial with DT is a significant industry milestone for open RAN. At ONF we are seeing tremendous interest from the mobile community for our open source implementation of the O-RAN architecture, and this trial demonstrates the maturity of the SD-RAN open source RIC and xApp development platform.”
– Guru Parulkar, Executive Director, ONF
“AirHop is thrilled to be participating in this DT SD-RAN trial. We are contributing commercially hardened 5G xApps that work with the complete Open RAN end-to-end solution. The trial demonstrates that commercial xApps can be quickly integrated and deployed using O-RAN defined standard interfaces to deliver automated performance optimization.”
– Yan Hui, CEO, AirHop
“Open systems are the future, and Edgecore is pleased to be leading the charge and to be providing open network hardware that is running software from ONF as part of this DT SD-RAN trial. It has been amazing working with this dynamic community, and a real pleasure to be collaborating with DT on this effort.”
– Jeff Catlin, VP of Technology, Edgecore Networks
“We are excited to see multiple ecosystem partners collaborating to test and trial this disaggregated Open RAN solution. We have made great progress with the RIC-xApp portability paradigm and we look forward to continuing to make contributions to the SD-RAN project.”
– Manish Singh, Head of Wireless Ecosystem Programs, Facebook
“Foxconn has contributed the Radio Units (RUs) that are deployed in the SD-RAN trial. Given that this represents the first deployment of a truly disaggregated RAN solution, we’ve been very pleased with the collaboration and commitment shown by the whole SD-RAN community.”
– Dr. Benjamin Wang, Sr. 5G RD Director, Infrastructure Product Division, Foxconn
“Our long-standing collaboration with ONF and its partners reflects our priority to collaborate with the Open Source community and aligns very well to initiatives such as Intel Smart Edge Open® targeted for open innovation and developer acceleration. It is great to see an entire portfolio of Intel technologies enabling ONF SD-RAN and SD-Core ranging from Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, vRAN accelerators to software offerings such as Intel® FlexRAN and Smart Edge Open® get featured in this trial, paving the way to the next wave of disaggregated and intelligent networks.”
– Renu Navale, VP & GM in the Network Platforms Group, Intel
“The OCP and ONF have a synergistic relationship, with OCP focused on open hardware and ONF focused on open software that can run on OCP hardware. The SD-RAN trial with DT exemplifies this relationship, demonstrating OCP Inspired™ openEdge servers from Wiwynn, an OCP Certified Solution Provider, running critical components of the SD-RAN solution.”
– Steve Helvie, VP of Channel, Open Compute Project (OCP)
“As a founding member of the SD-RAN initiative with ONF, Radisys is excited to participate in this important SD-RAN trial at DT, demonstrating use cases of RAN optimization and multi-vendor interoperability. We worked closely with the ONF community to develop service models, use cases and in the end-to-end integration of this field trial. This is a significant step towards commercial adoption of O-RAN based solutions by operators.”
– Arun Bhikshesvaran, CEO, Radisys
“Supermicro is excited to have our servers included in the SD-RAN Berlin trial. This trial is a significant step in realizing the potential of open RAN, and it has provided a great opportunity for multi-vendor collaboration and learning. We are a strong supporter of open source and disaggregation, and believe that it is essential for enabling 5G edge, core and cloud networks.”
– Jeff Sharpe, Director, 5G / IoT Edge Solutions, Supermicro
“TIP is pleased to be collaborating to support the SD-RAN Berlin Trial. The RIA sub-group of the TIP OpenRAN project is prioritizing use cases for open RAN that are being highlighted by this effort, so we see terrific synergies working with ONF and the broader SD-RAN community to support this first-of- its-kind trial featuring a multi-vendor mix of RU/DU/CU controlled by an open RIC and xApps.”
– Attilio Zani, Executive Director, Telecom Infra Project
“Wiwynn is pleased to be providing our edge cloud optimized servers as part of the DT SD-RAN trial. These systems are designed for edge and telco applications, and are certified by ONF for the Aether platform used for this DT trial. We are committed to building solutions optimized for open RAN deployments, and we’re very excited to see this DT trial advancing the state-of-the-art for open RAN.”
-Steven Lu, Senior Vice President, Wiwynn
DEUTSCHE TELEKOM SD-RAN TRIAL EVENT:
ONF and DT will be co-hosting a virtual event October 19th offering an in-depth view into the trial and key learnings from the community. Featuring live keynotes and on-demand talks from operator and vendor leaders from across the open RAN movement. Register to hear about lessons learned directly from the experts who have deployed the first trial of its kind! The event is open to anyone.:
Deutsche Telekom SD-RAN Trial – Webinar
October 19th, 2021
5pm CEST, 11am EDT, 8am PDT
REGISTER HERE
References:
ONF and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate Fully Disaggregated Open RAN with Open RIC Platform
One thought on “ONF and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate Fully Disaggregated Open RAN and SD-WAN”
Comments are closed.



SD-WAN provides a secure path from siloed enterprise networks to the public, private and hybrid cloud
SD-WAN is a reset in thinking about how a Wide Area Network (WAN) should work. It’s a virtual WAN architecture, an overlay that can work with different network transport services, including broadband. SD-WAN enables organizations to centrally manage traffic using the principles of Software Defined Networking (SDN), without the limitations imposed by physical network infrastructure.
SD-WAN centralizes network control, management, provisioning and security, despite the continued decentralization of data, as businesses move to the cloud. A few companies stand apart from the rest when it comes to offering SD-WAN solutions. Cisco is the market leader, followed by Fortinet and VMware, according to a report from Dell’Oro Group.
Enterprise spend on SD-WAN has accelerated in recent times. Businesses are upgrading network infrastructure to accommodate changing objectives and shifting workforce demands, as well. Sales of SD-WAN solutions rose 45% year-over-year for the third calendar quarter of 2021, according to Dell’Oro. The research firm noted that Cisco’s quarterly SD-WAN revenue nearly doubled in the quarter, with especially strong growth in North America.
The State of the WAN
For years, the literal backbone of enterprise WAN connectivity has been Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS). MPLS is a routing technique which directs data based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. Those paths labels speed network traffic by identifying virtual links between distant network nodes, eliminating routing delays.
MPLS supports a range of network transport services. And as the acronym implies, it supports multiple networking protocols: Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM) and Frame Relay, for example.
Regardless of protocol, MPLS connections all have one thing in common: They’re dedicated circuits, and require specialized routing hardware at both ends. This complicates provisioning and limits scale. What’s more, traditional WAN topologies typically backhaul all network traffic for security. This creates bottlenecks and complicates network traffic management.
A WAN topology that restricts the flow of network traffic to the cloud is at direct odds with enterprise digitalization strategies. Enterprises depend on more cloud-based services than ever to manage essential business functions. SaaS platforms like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) are examples. These platforms provide organizations with agility, flexibility, and scale, but being cloud-native demands a new approach when it comes to practical network management.
SD-WAN modernizes network operations for the cloud
As enterprises and users turn to the cloud, the difference between data center cloud and public cloud can get nebulous. Increasing public cloud-dependence and adjacency introduces complications to network security and compliance. Data sovereignty, compliance and security is top of mind for every IT professional.
Many enterprises leaning into to the cloud are implementing Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) to manage their networks. SD-WAN abstracts the networks’ transport service altogether. It’s a virtual WAN architecture which enables organizations to leverage whatever transport service they need — broadband, MLPS, 4G LTE, 5G.
By separating the network’s control plane altogether, SD-WAN enables businesses to centralize network management, security, and provisioning. SD-WAN replaces dedicated network hardware with Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) in place of physical networking hardware.
VNFs specifically replace devices like network routers and firewalls. VNFs are implemented as Virtual Machines (VMs) which run as software in the IT cloud, operating on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) server hardware. Accompanied by Cloud-native Network Functions (CNFs), they provide IT departments with the ability to scale services instantly to meet demand. As software rather than hardware, VNFs and CNFs can be continuous updated and optimized.
While VNFs are nothing new to enterprise IT, what’s new here in the SD-WAN equation is how SDN itself helps IT operations manage network operations and data security for branch and remote locations. There are some key differences, too.
“SDN advocates a central controller to dictate network behaviors. In contrast, SD-WAN generally manages based on central policy control, but decisions may also be made locally while taking into consideration the corporate policies. Or decisions can be made centrally while incorporating knowledge of local conditions reported by remote network nodes,” said VMware.
SD-WAN in the wild
SD-WAN has emerged as an opportunity for carriers and hyperscalers, Over-the-Top (OTT) service providers, and edge services. In December, Amazon introduced AWS Cloud WAN as a way to replace what it called a “patchwork” of services needed to handle private network control and management. AWS Cloud WAN connects on-prem data centers, branch offices and cloud resources together on AWS’ global backbone, consolidating management through a central dashboard.
Verizon features SD-WAN managed by Cisco as an option for its Network as a Service (NaaS). It comprises Cisco Umbrella security framework, manages zero trust application access and provides managed services through Cisco products including Pluggable Interface Modules and Catalyst Cellular Gateways.
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20220113/telco-cloud/what-is-software-defined-wide-area-networking-sd-wan