Open Networking
Analysys Mason Open Network Index: survey of 50 tier 1 network operators
Open networks apply proven cloud concepts to the networking domain while enabling components to be sourced from a broad ecosystem of vendors. Open networks boast high levels of automation and programmability and are built around the concept of utilizing a common, horizontal cloud platform that supports cloud-native network functions from multiple vendors and from multiple network domains. Network operators can enhance the flexibility, agility, composability, innovation and operational efficiency of their networks by implementing open architectures and open operating models.
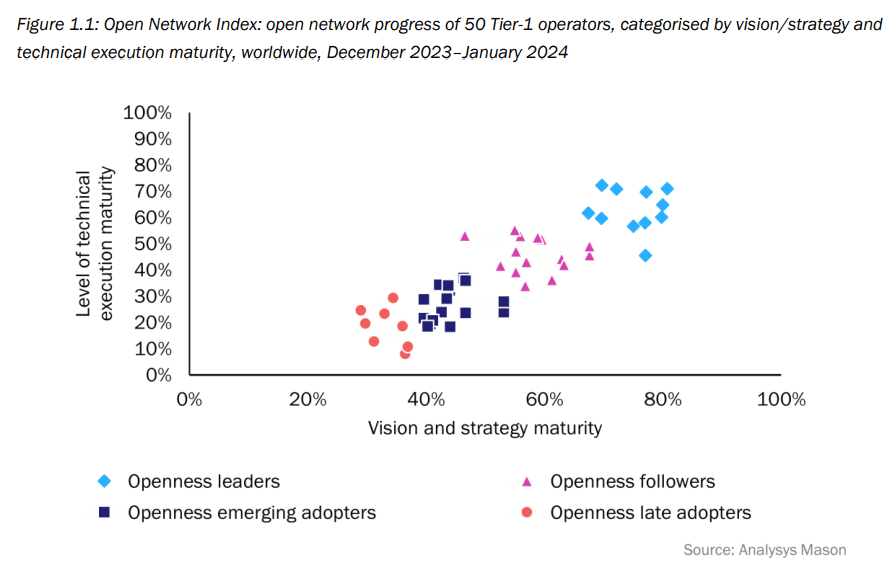
According to a survey conducted by Analysys Mason, ninety percent of global telecom service providers believe open networks are critical to their survival. However, only 20% have an open network strategy in place. Analysys Mason surveyed 50 leading Tier-1 operators worldwide between December 2023 and January 2024.
The analysts then benchmarked operator progress from a vision/strategy perspective and a technical perspective to form the first iteration of Analysys Mason’s Open Network Index (ONI). The survey and report were commissioned by Dell Technologies, but Analysys Mason says it does not endorse any of the vendor’s products or services.
The market research firm defines open networks as those based on non-proprietary technologies and standards, including open hardware and software developed by open communities, as well as software technologies that individual vendors are exposing, typically through open application programming interfaces (APIs), to anyone who wants to use them.
“Operators need to urgently develop an openness strategy and ensure that they approach openness in the right way,” the report authors said.
The analysts said that overall, survey respondents displayed a strong willingness to align themselves with open networking principles. But the technical implementation of open network architectures remains challenging.

The survey results partitioned the 50 network operators into four distinct categories:
- Openness leaders have a deep commitment to open networks and are supported at the highest levels of the organization. This category includes a higher proportion of operators from developed Asia–Pacific (APAC) than in any of the following categories.
- Openness followers are implementing aspects of open networks, but they take a more tactical approach because they lack the strong level of senior executive support that the openness leaders enjoy.
- Openness emerging adopters are operators that are just starting their journey. The category includes operators from developing markets that have a vision but have not yet started to deploy the architectures. The category also includes cautious adopters with lower ambitions for open networks.
- Openness late adopters do not have a clear concept of what an open network is, and they have not yet started to formulate a strategy for achieving openness or to win senior executive support. They have a low appetite for risk and perceive significant risks associated with moving away from incumbent vendors.
Many operators have strong engagements with well-established telecoms industry bodies such as the GSMA and the TM Forum. These bodies have traditionally aimed to improve standardisation and foster multi-vendor interoperability, but their activities in the areas of open cloud platforms and open operating models have been somewhat peripheral. Operators should deepen their involvement with initiatives such as the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), Nephio and Sylva, which champion open infrastructure and open operations, and support the fundamentals of horizontal cloud platforms.
In addition, operators should engage with the O-RAN Alliance (which is NOT a standards body/SDO), which is leading multi-vendor Open RAN interface and interoperability standards, with these standards leveraging distributed, cloud-native-based architectures. Participation in these initiatives facilitates knowledge sharing, enables operators to shape future standardization efforts and empowers operators to exert greater influence over their vendors.
References:
https://www.analysysmason.com/operator-network-index-rma16-rma18
Analysys Mason’s gloomy CAPEX forecast: “there will not be a cyclical recovery”
IEEE/SCU SoE May 1st Virtual Panel Session: Open Source vs Proprietary Software Running on Disaggregated Hardware
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
IEEE/SCU SoE May 1st Virtual Panel Session: Open Source vs Proprietary Software Running on Disaggregated Hardware
Complete Event Description at:
https://scv.chapters.comsoc.org/event/open-source-vs-proprietary-software-running-on-disaggregated-hardware/
The video recording is now publicly available:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RWS39lyvCPI
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Backgrounder – Open Networking vs. Open Source Network Software
Open Networking was promised to be a new paradigm for the telecom, cloud and enterprise networking industries when it was introduced in 2011 by the Open Networking Foundation (ONF). This “new epoch” in networking was based on Software Defined Networking (SDN), which dictated a strict separation of the Control and Data planes with OpenFlow as the API/protocol between them. A SDN controller running on a compute server was responsible for hierarchical routing within a given physical network domain, with “packet forwarding engines” replacing hop by hop IP routers in the wide area network. Virtual networks via an overlay model were not permitted and were referred to as “SDN Washing” by Guru Parulkar, who ran the Open Networking Summit’s for many years.
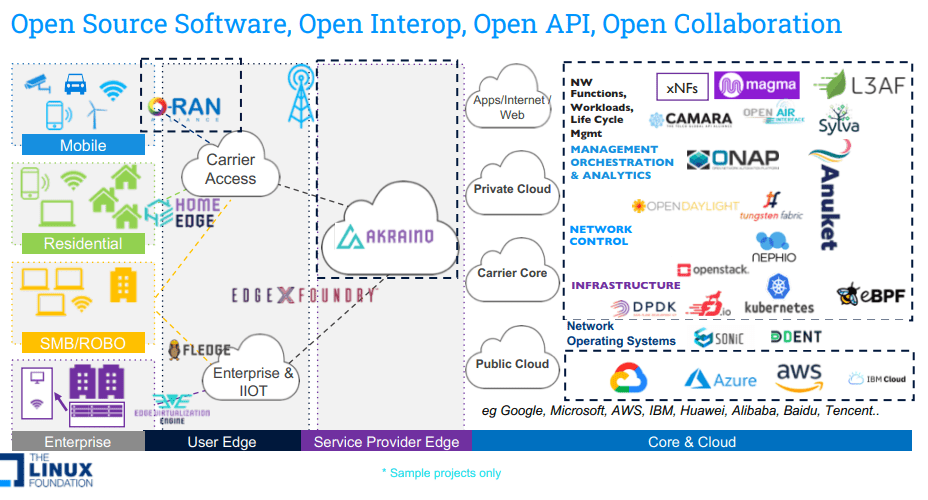
Today, the term Open Networking encompasses three important vectors:
A) Beyond the disaggregation of hardware and software, it also includes: Open Source Software, Open API, Open Interoperability, Open Governance and Open collaboration across global organizations that focus on standards, specification and Open Source software.
B) Beyond the original Data/Control plane definition, today Open Networking covers entire software stack (Data plane, control plane, management, orchestration and applications).
C) Beyond just the Data Center use case, it currently covers all networking markets (Service Provider, Enterprise and Cloud) and also includes all aspects of architecture (from Core to Edge to Access – residential and enterprise).
Open Source Networking Software refers to any network related program whose source code is made available for use or modification by users or other developers. Unlike proprietary software, open source software is computer software that is developed as a public, open collaboration and made freely available to the public. There are several organizations that develop open source networking software, such as the Linux Foundation, ONF, OCP, and TIP.
Currently, it seems the most important open networking and open source network software projects are being developed in the Linux Foundation (LF) Networking activity. Now in its fifth year as an umbrella organization, LF Networking software and projects provide the foundations for network infrastructure and services across service providers, cloud providers, enterprises, vendors, and system integrators that enable rapid interoperability, deployment and adoption.
Event Description:
In this virtual panel session, our distinguished panelists will discuss the current state and future directions of open networking and open source network software. Most importantly, we will compare open source vs. proprietary software running on disaggregated hardware (white box compute servers and/or bare metal switches).
With so many consortiums producing so much open source code, the open source networking community is considered by many to be a trailblazer in terms of creating new features, architectures and functions. Others disagree, maintaining that only the large cloud service providers/hyperscalers (Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Facebook) are using open source software, but it’s their own versions (e.g. Microsoft SONIC which they contributed to the OCP).
We will compare and contrast open source vs proprietary networking software running on disaggregated hardware and debate whether open networking has lived up to its potential.
Panelists:
- Roy Chua, AvidThink
- Arpit Joshipura, LF Networking
- Run Almog, DriveNets
Moderator: Alan J Weissberger, IEEE Techblog, SCU SoE
Host: Prof. Ahmed Amer, SCU SoE
Co-Sponsor: Ashutosh Dutta, IEEE Future Networks
Co-Sponsor: IEEE Communications Society-SCV
Agenda:
- Opening remarks by Moderator and IEEE Future Networks – 8 to 10 minutes
- Panelist’s Position Presentations – 55 minutes
- Pre-determined issues/questions for the 3 panelists to discuss and debate -30 minutes
- Issues/questions that arise from the presentations/discussion-from Moderator & Host -8 to 10 minutes
- Audience Q &A via ZOOM Chat box or Question box (TBD) -15 minutes
- Wrap-up and Thanks (Moderator) – 2 minutes
Panelist Position Statements:
1. Roy will examine the open networking landscape, tracing its roots back to the emergence of Software Defined Networking (SDN) in 2011. He will offer some historical context while discussing the main achievements and challenges faced by open networking over the years, as well as the factors that contributed to these outcomes. Also covered will be the development of open networking and open-source networking, touching on essential topics such as white box switching, disaggregation, OpenFlow, P4, and the related Network Function Virtualization (NFV) movement.
Roy will also provide insight into the ongoing importance of open networking and open-source networking in a dynamic market shaped by 5G, distributed clouds and edge computing, private wireless, fiber build-outs, satellite launches, and subsea-cable installations. Finally, Roy will explore how open networking aims to address the rising demand for greater bandwidth, improved control, and strengthened security across various environments, including data centers, transport networks, mobile networks, campuses, branches, and homes.
2. Arpit will cover the state of open source networking software, specifications, and related standards. He will describe how far we have come in the last few years exemplified by a few success stories. While the emphasis will be on the Linux Foundation projects, relevant networking activity from other open source consortiums (e.g. ONS, OCP, TIP, and O-RAN) will also be noted. Key challenges for 2023 will be identified, including all the markets of telecom, cloud computing, and enterprise networking.
3. Run will provide an overview of Israel based DriveNets “network cloud” software and cover the path DriveNets took before deciding on a Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) architecture for its proprietary software. He will describe the reasoning behind the major turns DriveNets took during this long and winding road. It will be a real life example with an emphasis on what didn’t work as well as what did.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://lfnetworking.org/
https://lfnetworking.org/how-
https://lfnetworking.org/
https://lfnetworking.org/open-
Intel quietly acquires private 5G software provider Ananki
Intel has acquired private 5G network provider Ananki, several months after the startup spun out of the non-profit Open Networking Foundation (ONF) to commercialize open-source network technologies.
The acquisition was confirmed Monday on LinkedIn by Guru Parulkar, PhD, who was co-founder and CEO of Ananki and executive director of the Open Networking Foundation.
–>His ONF successor was not disclosed, despite my LI comment enquiring about it.
Intel declined to comment on the Ananki acquisition and instead only confirmed a development that Parulkar said was related: that the ONF’s development team has joined Intel’s Networking and Edge Group. Intel’s statement echoed a quote provided by top Intel networking executive and former Stanford Professor Nick McKeown, PhD in a press release published by the non-profit. McKeown was previously a part-time Intel Senior Fellow who joined the company after its 2019 acquisition of Barefoot Networks, which he co-founded.
“The addition of these developers will support [Intel’s Network and Edge Group’s] mission to drive the shift toward software-defined and fully programmable infrastructure – from the cloud, through the Internet and 5G networks, all the way out to the Intelligent Edge. Intel intends to continue to support and contribute to ONF’s open-source efforts,” an Intel spokesperson said. No financial terms were disclosed.
Ananki provides an open-source, software-defined service that aims to make private 5G networks “as easy to consume as Wi-Fi” for enterprises working on so-called Industry 4.0 projects. This involves connecting a variety of things, including cameras, sensors, robots, and autonomous vehicles, over high-speed networks in various settings, from factories to retail stores.
Ananki has a diverse range of products, including a SaaS-based 5G software stack, small cell radios, SIM cards, and a dashboard for monitoring and analyzing network activity. These are provided through a subscription-based service that charges organizations based on how much 5G coverage they need.

Source: Ananki
If Intel continues to offer Ananki’s products as a subscription service, it would fall in line with the semiconductor giant’s plan to buoy hardware sales with a significant increase in software revenue, as The Register has previously reported. Less than two weeks ago, The Register reported that Intel plans to offer the cloud optimization software of Granulate, another startup it plans to acquire, in Xeon CPU sales pitches.
The Ananki transaction is part of a broader effort by the Open Networking Foundation to support the increasing commercialization of its open-source, software-defined networking technologies, which it originally developed with the financial support of its more than 100 members. Those include Intel as well as several other prominent tech companies, such as AMD, AT&T, Broadcom, Cisco, Google, Microsoft, Nvidia, and T-Mobile.
The Open Networking Foundation said this new commercialization shift involves open-sourcing the entirety of its production-ready software, which includes private 5G, SD-RAN, SD-Fabric and SD-Core technologies that serve as the basis of Ananki’s products. The nonprofit has also made its software-defined broadband and P4 programmable network technologies available as open source.
“We have built platforms that naysayers said were doomed to fail, we’ve proven what’s possible, and today a number of our platforms have been deployed in production networks and others are now production ready and expected to be broadly adopted,” said Parulkar, who is now vice president of software within Intel’s Network and Edge Group.
The ONF seems to want to move development from internal open source teams to member organizations. As such, the nonprofit is transitioning a majority of its development team to Intel’s Network and Edge Group, which is also the new home of Ananki.
References:
https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/12/intel_ananki_5g/
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/edge-computing/what-is-the-network-edge.html
https://networkbuilders.intel.com/events2022/big-5g-event
ONF Enters a New Era Focused on Growing Adoption and Community for its Leading Open Source Projects
ONF’s Private 5G Connected Edge Platform Aether™ Released to Open Source
Furthering its mission to seed the industry with innovative open source platforms to advance 5G and software-defined open networking, the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) today announced that its Aether Private 5G + Edge Cloud platform, and related component projects SD-Core™, SD-RAN™ and SD-Fabric™ have now all been released under the permissive Apache 2.0 open source license.
Aether is the first open source 5G Connected Edge platform for enabling enterprise digital transformation. Aether provides 5G mobile connectivity and edge cloud services for distributed enterprise networks. Aether represents a complete, open 5G solution, addressing RAN through Core, democratizing availability of a robust and complete software-defined 5G platform for developers.
In just 2 years, Aether has achieved significant milestones and demonstrated numerous industry firsts:
- Aether was selected for the $30M DARPA Pronto project for building secure 5G
- Aether was deployed in an ongoing field trial with Deutsche Telekom in Berlin
- Aether has been deployed in over 15 locations, operating 7×24 and delivering production-grade uptime
- Aether is the only private 5G solution leveraging the benefits of open RAN for private enterprise use cases
In the process of achieving these remarkable milestones, Aether has matured to the point where it is ready to be released to the community for broad consumption.
Aether is built upon a number of world-class component projects that are each in their own right best-in-class. Today, all the component projects are also being open sourced, including:
SD-Core 4G/5G dual-mode cloud native mobile core
SD-Fabric SDN P4 Programmable Networking Fabric
SD-RAN Open RAN implementation with RIC and xApps
Demonstrating Aether at MWC:
The ONF stand #1F66 at Mobile World Congress (MWC) will showcase an Aether deployment, demonstrated as a cloud managed offering optimized for enterprise private networks. In the demo, devices (UEs), such as mobile phones, cameras, sensors and IoT devices, can be aggregated into device-groups, and each device-group assigned a 5G slice and connected to specific edge applications thereby extending the slicing concept to individual applications and services. Each slice is attached to specific Industry 4.0 application(s), thereby creating distinct slices for different use cases and guaranteeing each slice secure isolation for security along with bandwidth, latency, quality of service (QoS) and resource assurances.
Two Industry 4.0 applications are demonstrated running over the Aether Private 5G using Intel technologies enabling ONF SD-RAN and SD-Core ranging from Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Intel vRAN accelerator ACC100, Intel Tofino Intelligent Fabric Processors, to software offerings such as Intel’s FlexRAN reference architecture, Intel Smart Edge Open, and the Intel Distribution of OpenVINO. The first is a security application built on Intel’s Distribution of OpenVINO toolkit, an intelligent AI/ML edge platform running on Aether 5G and leveraging Aether’s Industry 4.0 APIs to dynamically change the network slice to suit the application’s real time requirements for connectivity. The demo first creates an application slice for video surveillance, grouping together a set of streaming cameras. Next, whenever a human is detected in the field of vision for a camera, the solution automatically increases the 5G bandwidth for the impacted camera and instructs the camera to increase its resolution so a high-def recording can be made. With this approach, 5G wireless capacity is reserved for mission critical applications, and bandwidth is dynamically allocated precisely when and where needed. All of this is performed in real time without human intervention.
Anomaly detection is featured in the second Industry 4.0 application. Based on Intel’s Anomalib, an Aether application slice carries a mission critical video feed of a manufacturing / packaging line which is channeled into an anomaly detection edge-app. The edge app is trained using defect free data and uses probabilistic AI to detect anomalies like spoiled fruit (bananas). Given the time critical nature of detecting faults early, the app is built to work in a real time fashion over Aether to deliver results at line rate for typical industrial and packaging production lines.
Getting Started with Aether:
It is easy to get started using Aether Private 5G. Aether can be deployed by developers on a laptop using Aether-in-a-Box, a simple pre-packaged end-to-end development environment including RAN through mobile core. By making such a complete solution available in a footprint that can run on a laptop, developers can get started with minimal friction. Developers can then organically grow the test deployment at their own pace into a fully disaggregated production-grade deployment, including production-grade RAN radios, disaggregated UPF edge processing and cloud-native mobile core. This makes it easy to get started with Aether, while assuring developers that Aether can scale to meet the needs of even the most demanding commercial applications.
The ONF Community:
Aether has been an amazing collaboration between ONF engineering resources and an active community that includes: Aarna Networks, AirHop, AT&T, Binghamton University, China Mobile, China Unicom, Ciena, Cohere Technologies, Cornell University, Deutsche Telekom, Edgecore Networks, Facebook Connectivity, Foxconn, Google, GSLab, HCL, Intel, NTT Group, Microsoft, Princeton University, Radisys, Sercomm, Stanford University and Tech Mahindra.
About the Open Networking Foundation:
The Open Networking Foundation (ONF) is an operator-led consortium spearheading disruptive network transformation. Now the recognized leader for open source solutions for operators, the ONF first launched in 2011 as the standard bearer for Software-Defined Networking (SDN). Led by its operator partners AT&T, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Google, NTT Group and Türk Telekom, the ONF is driving vast transformation across the operator space. For further information visit http://www.opennetworking.org
References:
To learn more about the project and join our growing community by reviewing the Aether documentation, by visiting the ONF booth at MWC Barcelona (#1F66), or registering here to be sent a pointer to the recorded demo to be released after MWC. Developers can also easily get started by running Aether-in-a-Box on a bare metal machine or VM.
Cignal AI: Metro WDM forecast cut; IP-over-DWDM and Coherent Pluggables to impact market
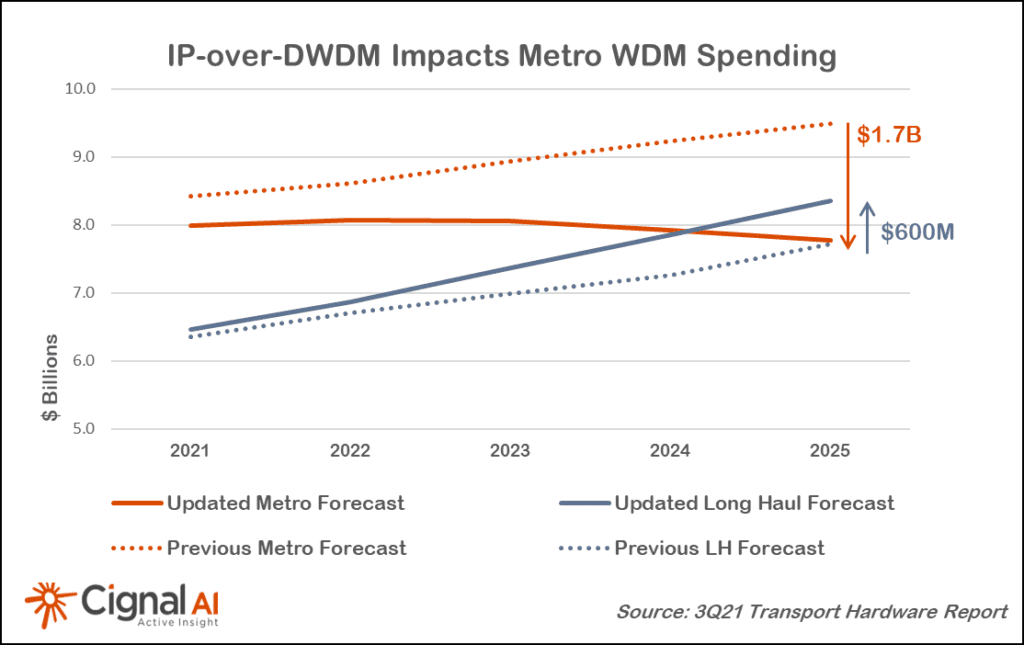
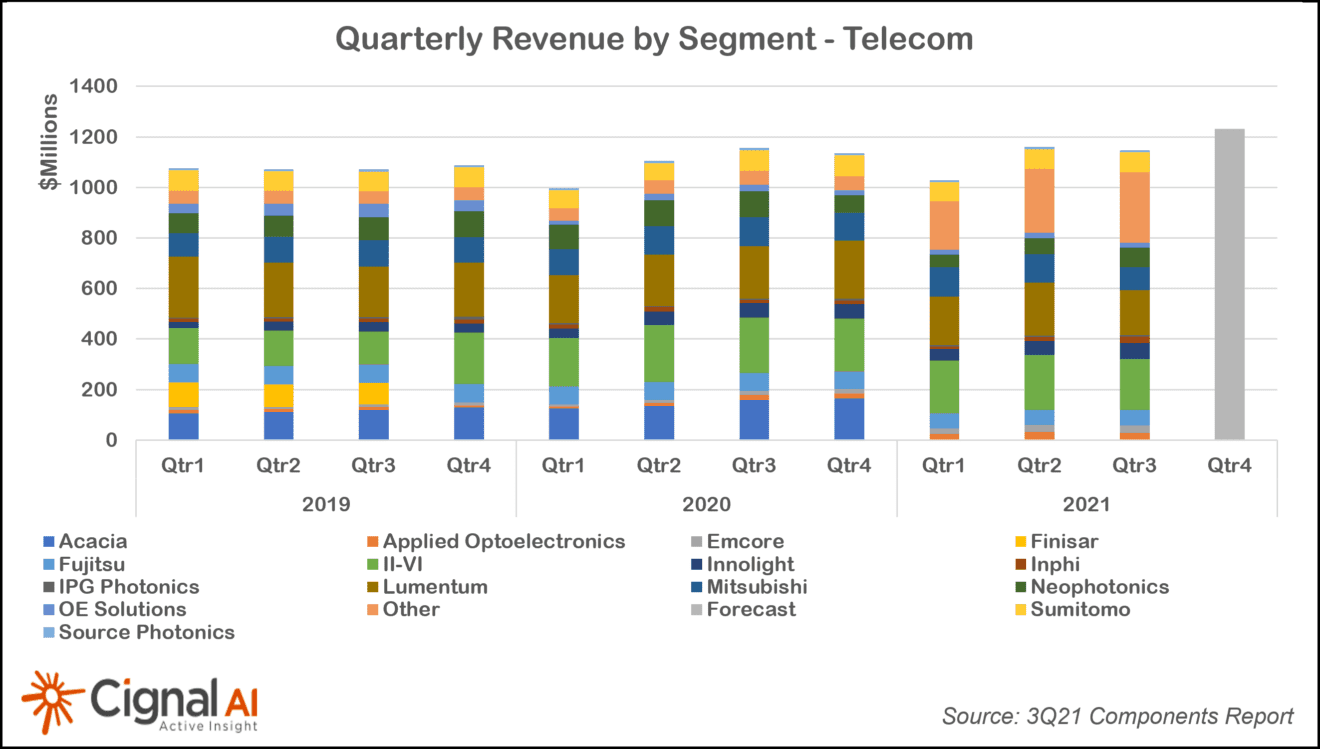
Optical transport equipment deployment faces increasing headwinds as a broad number of network operators embrace IP-over-DWDM in Metro WDM applications, according to the most recent Transport Hardware Report from research firm Cignal AI. The impact of IP-over-DWDM on capex is expected to be moderate until 2023 when implementation of the new approach gathers momentum.
“IP-over-DWDM is a concept two decades old, but technical compromises, operational challenges, and high cost have prevented its widespread adoption. Gen60C 400ZR/ZR+ pluggable optics can solve these problems with availability well-timed to the 400 Gigabit Ethernet investment cycle,” said Kyle Hollasch, Lead Analyst for Transport Hardware at Cignal AI. “Hyperscale data center interconnect will drive early volumes, but service providers – who are responsible for 75% of optical CAPEX – should get on board in 2023 as the cost savings of IP-over-DWDM becomes impossible to ignore.”
| Cignal AI has cut forecasted spending on standalone optical transport hardware by $1.1B in 2025 as operators introduce pluggable coherent optics into routing and switching equipment to replace standalone traditional and compact modular equipment. This decline will be partially offset by greater sales of IP Routing and Switching hardware, open line systems, and long haul WDM, as well as direct sales of coherent optics to hyperscale operators. Clients can read 400ZR IPoDWDM Market Impact and Forecast for more detail. |
| Additional 3Q21 Transport Hardware Report Findings: |
- Total transport hardware (Optical and IP Switching & Routing) revenue declined -2.5%, with sales in China declining double digits for the second consecutive quarter.
- North American optical revenue grew for the 4th consecutive quarter and registered its first quarter of YoY growth since COVID impacted 2Q20. Fujitsu and Cisco led in revenue growth.
- Sales of optical hardware in EMEA increased YoY as the region registered its 6th consecutive quarter of growth. Regional market leaders Huawei and Nokia declined while ADVA, Infinera, and ZTE grew double digits.
- North American packet transport sales grew 6%, its third straight quarter of growth. Nokia and Cisco led this growth.
- Japanese packet sales continued to grow, up nearly 10% YoY. Cisco increased its lead in the region, with YoY sales growth of 42%.

ONF and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate Fully Disaggregated Open RAN and SD-WAN
Deutsche Telekom is working with the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) and eight vendors to test software-defined radio access networks (SD-RAN) and Open RAN in what it calls a fully disaggregated system. This is the first field trial implementing fully disaggregated open RAN solutions using ONF’s RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) software platform as defined by the O-RAN architecture. This 4G and 5G Standalone (SA) outdoor trial is live at Deutsche Telekom in Berlin, Germany.
In addition, the Facebook-backed Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is taking part by providing hardware and facilities out of the TIP Community Lab in Berlin hosted by Deutsche Telekom.
Carriers are investing in open RAN to enable a new breed of modular and customizable 5G solutions to accelerate innovation and enable the mix-and-match of best-of-breed components from multiple vendors. Open RAN gives operators choice and flexibility to customize and optimize their networks. This SD-RAN trial hosted by DT highlights the promise and flexibility of open RAN by integrating components from eight companies: AirHop, Edgecore, Facebook, Foxconn, Intel, Radisys, Supermicro and Wiwynn. Additionally, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is participating by providing hardware and facilities out of the TIP Community Lab in Berlin hosted by DT. The on-site field trial integration and testing is being coordinated and supported by Highstreet Technologies.
The live trial features horizontally disaggregated hardware (separate RU, DU, and CU units), as well as vertically disaggregated software components including an open source near real-time RIC (nRT-RIC) and xApps coming from the ONF’s SD-RAN project. By integrating proprietary and open source components, including a near real-time RIC and xApps, this ground-breaking trial exemplifies a model for how future open RAN deployments are envisioned to take shape.
The entirety of the trial is operationalized leveraging ONF’s Aether platform, a centrally-managed, multi-cloud, cloud-native platform providing Connectivity-as-a-Service, and highlights network slicing with multiple UPFs running at the edge. The SD-Core component of Aether provides 5G connectivity and the control plane running from the public cloud while SD-Fabric is a fully programmable network fabric optimized for the edge cloud used to instantiate a P4-based 4G/5G UPF in hardware.
Aether hosts the Radisys containerized CU while the Intel® Smart Edge Open (formerly known as OpenNESS) software toolkit hosts the Radisys DU to enable cloud-native deployment of the RAN workload with optimization on the 3rd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor and Intel® vRAN Dedicated Accelerator ACC100. The CU and DU are integrated with ONF’s nRT-RIC, xApps, SD-Core 5G core and Foxconn O-RU.
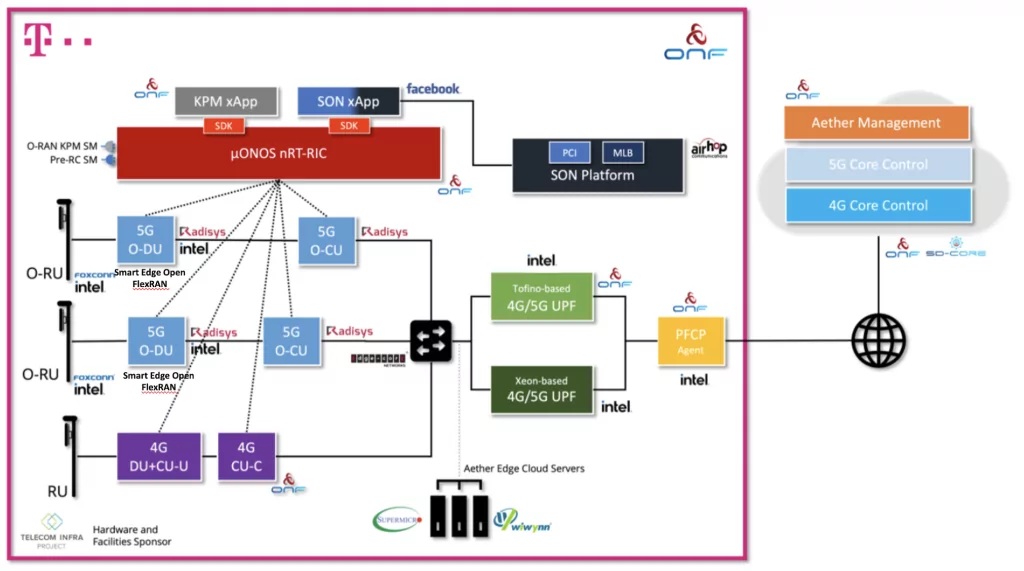
“The Berlin SD-RAN Open RAN Trial, is a momentous step towards realizing the vision of fully disaggregated and intelligent RAN, leveraging ONF’s leading open source RAN Intelligent Controller software platform. In addition to open fronthaul, this trial includes disaggregated RU/DU/CU units, and also vertically disaggregates the RIC and xApps according to SDN principles. Together, we are demonstrating the power of truly open RAN and ecosystem collaboration to accelerate innovation.”
– Alex Choi, Senior Vice President Strategy & Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom and Founding Board Member, O-RAN Alliance
“The SD-RAN Berlin Trial with DT is a significant industry milestone for open RAN. At ONF we are seeing tremendous interest from the mobile community for our open source implementation of the O-RAN architecture, and this trial demonstrates the maturity of the SD-RAN open source RIC and xApp development platform.”
– Guru Parulkar, Executive Director, ONF
“AirHop is thrilled to be participating in this DT SD-RAN trial. We are contributing commercially hardened 5G xApps that work with the complete Open RAN end-to-end solution. The trial demonstrates that commercial xApps can be quickly integrated and deployed using O-RAN defined standard interfaces to deliver automated performance optimization.”
– Yan Hui, CEO, AirHop
“Open systems are the future, and Edgecore is pleased to be leading the charge and to be providing open network hardware that is running software from ONF as part of this DT SD-RAN trial. It has been amazing working with this dynamic community, and a real pleasure to be collaborating with DT on this effort.”
– Jeff Catlin, VP of Technology, Edgecore Networks
“We are excited to see multiple ecosystem partners collaborating to test and trial this disaggregated Open RAN solution. We have made great progress with the RIC-xApp portability paradigm and we look forward to continuing to make contributions to the SD-RAN project.”
– Manish Singh, Head of Wireless Ecosystem Programs, Facebook
“Foxconn has contributed the Radio Units (RUs) that are deployed in the SD-RAN trial. Given that this represents the first deployment of a truly disaggregated RAN solution, we’ve been very pleased with the collaboration and commitment shown by the whole SD-RAN community.”
– Dr. Benjamin Wang, Sr. 5G RD Director, Infrastructure Product Division, Foxconn
“Our long-standing collaboration with ONF and its partners reflects our priority to collaborate with the Open Source community and aligns very well to initiatives such as Intel Smart Edge Open® targeted for open innovation and developer acceleration. It is great to see an entire portfolio of Intel technologies enabling ONF SD-RAN and SD-Core ranging from Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, vRAN accelerators to software offerings such as Intel® FlexRAN and Smart Edge Open® get featured in this trial, paving the way to the next wave of disaggregated and intelligent networks.”
– Renu Navale, VP & GM in the Network Platforms Group, Intel
“The OCP and ONF have a synergistic relationship, with OCP focused on open hardware and ONF focused on open software that can run on OCP hardware. The SD-RAN trial with DT exemplifies this relationship, demonstrating OCP Inspired™ openEdge servers from Wiwynn, an OCP Certified Solution Provider, running critical components of the SD-RAN solution.”
– Steve Helvie, VP of Channel, Open Compute Project (OCP)
“As a founding member of the SD-RAN initiative with ONF, Radisys is excited to participate in this important SD-RAN trial at DT, demonstrating use cases of RAN optimization and multi-vendor interoperability. We worked closely with the ONF community to develop service models, use cases and in the end-to-end integration of this field trial. This is a significant step towards commercial adoption of O-RAN based solutions by operators.”
– Arun Bhikshesvaran, CEO, Radisys
“Supermicro is excited to have our servers included in the SD-RAN Berlin trial. This trial is a significant step in realizing the potential of open RAN, and it has provided a great opportunity for multi-vendor collaboration and learning. We are a strong supporter of open source and disaggregation, and believe that it is essential for enabling 5G edge, core and cloud networks.”
– Jeff Sharpe, Director, 5G / IoT Edge Solutions, Supermicro
“TIP is pleased to be collaborating to support the SD-RAN Berlin Trial. The RIA sub-group of the TIP OpenRAN project is prioritizing use cases for open RAN that are being highlighted by this effort, so we see terrific synergies working with ONF and the broader SD-RAN community to support this first-of- its-kind trial featuring a multi-vendor mix of RU/DU/CU controlled by an open RIC and xApps.”
– Attilio Zani, Executive Director, Telecom Infra Project
“Wiwynn is pleased to be providing our edge cloud optimized servers as part of the DT SD-RAN trial. These systems are designed for edge and telco applications, and are certified by ONF for the Aether platform used for this DT trial. We are committed to building solutions optimized for open RAN deployments, and we’re very excited to see this DT trial advancing the state-of-the-art for open RAN.”
-Steven Lu, Senior Vice President, Wiwynn
DEUTSCHE TELEKOM SD-RAN TRIAL EVENT:
ONF and DT will be co-hosting a virtual event October 19th offering an in-depth view into the trial and key learnings from the community. Featuring live keynotes and on-demand talks from operator and vendor leaders from across the open RAN movement. Register to hear about lessons learned directly from the experts who have deployed the first trial of its kind! The event is open to anyone.:
Deutsche Telekom SD-RAN Trial – Webinar
October 19th, 2021
5pm CEST, 11am EDT, 8am PDT
REGISTER HERE
References:
ONF and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate Fully Disaggregated Open RAN with Open RIC Platform
Open Networking Foundation spins off Ananki to deliver open source-based Software Defined Private 5G as per Industry 4.0 requirements
Ananki plans to deliver software defined private 5G that is purpose built for the Industry 4.0 revolution, encompasng M2M mobile networks, IoT, and related communication initiatives.
- Private 5G is the key to empowering the machine-to-application communications necessary to complete this vision, according to the ONF.
- Industry 4.0 is a combination of intelligent devices, edge cloud and cloud-based AI/ML which is intended to enable software-based optimization and innovation.

Ananki’s Software-Defined Private 5G+ was said to deliver:
● Optimized 5G+ Experience – Software-defined, automated, AI powered, application optimized connectivity, with enhanced security enabled by a programmable data plane.
● Cloud First – pre-integrated with hyperscaler cloud and edge, delivering private 5G as a SaaS service, creating a continuously improving experience running on any multi-cloud platform.
● Industry 4.0 Ready – Empowering developers to build transformative IoT, IIoT and OT solutions with rich APIs.
Ananki’s technological foundation leverages ONF’s open source Aether™, SD-RAN™, SD-Fabric™ and SD-Core™ projects, and melds them together into a commercial offering that is delivered as a SaaS, making private 5G as easy to consume as wifi for enterprises. ONF also incorporates developer APIs to accelerate the creation of more powerful digital transformation solutions. This open platform is hardened and optimized for industrial applications, and introduces developer APIs to empower the creation of more powerful digital transformation solutions.

Other Highlights:
— Ananki delivers slice/device level SLA assurance for mission critical applications.
— Proactively identify network bottlenecks before they impact your application performance.
— Define application priority once and let Ananki (Self healing/optimizing/organizing network) deliver optimal application performance.
— CI/CD lets you dynamically upgrade your service to handle evolving application requirements and security threats.
— Telco grade security and resilience to Enterprise operational networks with AI/Ops fault and detection.
Ananki’s Inception:
When ONF’s Aether was selected for the $30M Pronto Project, DARPA encouraged ONF to commercialize the platform in order to advance the impact of the project’s secure 5G research. To date, ONF has operationalized and deployed Aether at 15 locations operating as a cloud managed service.
To accelerate Aether’s adoption, the ONF board voted unanimously to create a new separate venture backed commercial entity to provide an enhanced, hardened solution so vendors and partners can easily incorporate private 5G into the solutions they then build and deliver to enterprises.
Ananki, has been structured as a Public Benefit Corporation to support and promote open source. Furthermore, Ananki shares common executives with the ONF, ensuring that a consistent vision and mission keeps the two entities well aligned.
Quotes:
Andre Fuetsch, ONF Board Chair and AT&T CTO:
“ONF continues to innovate in ways that magnify the power of open systems and open source across our industry. The ONF board recognizes that the lack of support for open source initiatives from commercial companies remains an inhibiting factor for scaled adoption. To meet this challenge, we have agreed to spin out Ananki as an independent company to pursue commercialization of Aether with a view that this will help accelerate the adoption and impact of open source.”
Guru Parulkar, Executive Director ONF and CEO of Ananki:
“Ananki is broadening the impact of the ONF’s work, and will help ONF’s Aether become much more broadly adopted. By providing a commercially supported option for consuming Aether, many more organizations will be able to easily and economically leverage the benefits of Private 5G for building Industry 4.0 solutions. And in turn, Ananki is committed to contributing back to the ONF open source, helping to advance the Aether platform and broaden the ONF community.”
About Ananki:
Ananki delivers a commercially supported Software-Defined Private 5G as-a-service to help facilitate enterprise digital transformation. As a Public Benefit Corporation, Ananki synergistically builds on Open Networking Foundation (ONF) open source software platforms, and in turn contributes focus, funding, developers and contributions to the ONF projects. With Ananki, companies can now choose a commercially supported option when consuming ONF open source.
About the Open Networking Foundation:
The Open Networking Foundation (ONF) is an operator-led consortium spearheading disruptive network transformation. Now the recognized leader for open source solutions for operators, the ONF first launched in 2011 as the standard bearer for Software-Defined Networking (SDN). Led by its operator partners AT&T, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Google, NTT Group and Türk Telekom, the ONF is driving vast transformation across the operator space. For further information visit http://www.opennetworking.org
For more information, please visit ananki.io and/or register to attend a live keynote on September 28th as part of the Private 5G for Industry 4.0 Spotlight event.
References:
LF Networking 5G Super Blue Print project gets 7 new members
Overview:
LF Networking (LFN), which facilitates collaboration and operational excellence across open source networking projects, today announced seven new member organizations and one associate member have joined the community to collaborate on the 5G Super Blue Print initiative.
The 5G Super Blueprint project covers RAN, Edge, and Core and enables solutions for enterprises and verticals, large institutional organizations, and more. While Networking provides platforms and building blocks across the networking industry that enable rapid interoperability, deployment, and adoption. Participation in this nexus for 5G innovation and integration is open to anyone.

The new members are:
AQSACOM, a leader in Cyber Intelligence software solutions for communications service providers (CSPs) and law enforcement agencies (LEAs);
Radtronics, which provides secure and powerful private wireless network for Maximum Productivity with new applications and services, through Outcome based and cost efficient solutions enabled by strong innovation;
Turnuium, which enables channel partners to connect people, data, and applications through its turnkey multi-carrier managed SD-WAN;
SEMPRE, which secures 5G for critical infrastructure by moving compute to the edge and leveraging military-grade technology—the only HEMP-hardened 5G gNODEB with Edge; and
Wavelabs, a new-age technology company for the Digital, Cognitive & Industry 4.0 Era have joined LFN at the Silver level. New Associate members include: the Oman government’s Ministry of Transportation, Communications & Information Technology;
ICE Group’s (state telecommunications and energy operator of Costa Rica)
ANTTEC (ICE Group’s main union of technicians and engineers); and
High School Technology Services, which offers coding and technology training to students and adults, have joined as Associate members.
“As the center platform for enabling open source 5G building blocks, collaboration and integration is more important than ever for LFN, amplified by our recent developer event in early June,” said Arpit Joshipura, general manager, Networking, Edge and IoT, the Linux Foundation. “This impressive roster of new members across intelligence, government, enterprise and more are welcome additions to the LFN community. We look forward to continued collaboration that enables rapid interoperability, deployment, and adoption of 5G across the ecosystem.”
Leveraging the convergence of major initiatives in the 5G space, and building on a long-running 5G Cloud Native Network demo work stream, LF Networking is leading a community-driven integration and proof of concept involving multiple open source initiatives in order to show end-to-end use cases demonstrating implementation architectures for end users.
In April, the Linux Foundation and the World Bank launched an online course: 5G and Emerging Technologies for Public Service Delivery & Digital Economy Operations – Fundamentals of 5G Networks: Implications for Practitioners. The course is now available on the World Bank’s Open Learning Campus here. Aimed at decision makers and development practitioners, the course provides an introduction to open source and the critical role it plays in today’s networks.
ONE Summit:
Learn more about the 5G Super Blue Print during the Open Networking & Edge (ONE) Summit, the ONE event for end to end connectivity solutions powered by open source and enables the collaborative development necessary to shape the future of networking and edge computing. Taking place October 11-12, 2021 in Los Angeles, Calif., Registration will open soon.
New Member Support:
“With the dramatic growth of Private Wireless LTE and 5G networks over the coming years, the Open Source community will play a transformational role, which is the reason we’re joining the Linux Foundation Networking,” said Peter Lejon, co-founder of RADTONICS AB. “5G technology will have a huge impact on our future, driving positive changes for all of us. With enterprise and regional operators procuring solutions direct from the solutions providers, initiatives like 5G Super Blueprint and Magma Packet Core will be instrumental in serving a rapidly developing market that will include the next billion users on their journey of capturing value through digitalization. We believe that through Open Source and by working together, we can further accelerate the current pace of innovation and development. Change will never be this slow again,” added Lejon.
Marcus Owenby, SEMPRE’s Global CTO, affirmed “SEMPRE’s support for 5G Super Blueprint will enable enterprise and government organizations to leverage open source technology, while also securing 5G using military-grade technology purpose-built to protect critical infrastructure.”
“Wavelabs.ai is an ardent proponent of the ‘OPEN X’ network vision. We work with the entire ecosystems of clients & partners as an engaged, committed, and collaborative partner to realize 5G open and disaggregated ‘White Box’ network as a reality” said Mansoor Khan, CEO of Wavelabs. “LF Networking open-source 5G initiatives address major opportunities today and tomorrow. We believe this partnership will strengthen Wavelabs mission in accelerating the Journey to Future Connectivity by offering the unique blend of next-generation Digital, Cognitive, and Network technology services and solutions”
Resources
2021 Optical Fiber Conference (OFC) Highlights and Links to Videos
The premier event in optical telecom—the 2021 Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibition (OFC) concluded last week. The virtual event drew over 6,500 registrants from 83 countries.
“OFC 2021 saw technology announcements and technical presentations spanning the optical communications ecosystem, including advancements in optoelectronic devices, packaging and digital signal processing that are all rapidly evolving to achieve 800G and beyond, as well as those in architectures and algorithms towards more intelligent optical networking,” said Jun-ichi Kani, OFC General Chair, NTT, Japan. “OFC is the only event where attendees can access the full spectrum of trends shaping the industry and the way we connect across the globe.”
Speakers presented breakthroughs in many areas, including 400/ZR+, 800G, co-packaged optics, embedded optics, next-gen optical access, silicon photonics, space-division multiplexing, data center networks, automation and intelligence in networks and more. Sessions on quantum science and technologies, sensor applications and free space optics appealed to a large audience and enriched the OFC experience. Recorded sessions are available to registrants as on-demand content for 60 days following the close of the event.
“OFC is the go-to event for the optics industry,” said Jimmy Yu, vice president, Dell’Oro Group. “From the thought-provoking panel discussions to the product announcements, OFC has always been the place where I learn about emerging technologies.”

Technology experts from global leaders II-VI, Broadcom, Ciena, Cisco, Corning, Innolight, Intel, Juniper Networks, Lumentum, NeoPhotonics, Nokia and Ribbon discussed developments in hardware and software-based networking solutions in daily briefings with leading analysts, Sterling Perrin, Heavy Reading; Ian Redpath, OMDIA; Andrew Schmitt, Cignal AI; Jimmy Yu, Dell’Oro Group and Vladimir Kozlov, LightCounting. The videos can be viewed here.
The TIP sub-group said multi-vendor integration and services operations “were achieved through open standard models and APIs supported by the Optical SDN Controller, including Transport-API, OpenConfig and Open REST.”
“This proof of concept is an important milestone in the journey to fully open and disaggregated optical networking. It offers new levels of visibility and a way to manage the entire multi-vendor environment,” commented Christoph Glingener, CTO at ADVA.
Technology Showcases from 3M, AIM Photonics, Corning, EFFECT Photonics, Infinera, Jabil, Juniper Networks, Keysight Technologies, Lumentum, Luna Innovations, Murata, Nokia, Pi, Renesas, Ribbon, Samtec, Sicoya, Synopsys, Tektronix, Telescent and Xilinx gave deep dives into their cutting-edge products.
OFC 2021 exhibitor news announcements are posted to the OFC Newsroom.
Innovations in Optics
Leading researchers from around the world presented technical peer-reviewed papers, including:
- Trans-Atlantic Real-Time Field Trial Using Super-Gaussian Constellation-Shaping to Enable 30 Tb/s+ Capacity — A team of researchers from Infinera Corporation, USA and Facebook demonstrated a record-breaking transatlantic transmission across MAREA.
- A Latency-Aware Real-Time Video Surveillance Demo: Network Slicing for Improving Public Safety — Researchers presented a latency-aware optical metro network having sophisticated monitoring and data analytics capabilities and discussed the network architecture and enabling technologies, as well as a video surveillance case of the system.
- Demonstration of 100Gbit/s Real-Time Ultra High Definition Video Transmission Over Free Space Optical Communication Links — A team of researchers discussed how they achieved real-time FSO transmission of an ultrahigh-definition video stream between two buildings in Beijing.
- 224-Gb/s PAM4 Uncooled Operation of Lumped-electrode EA-DFB Lasers with 2-km Transmission for 800GbE Application — Researchers at Lumentum showed how they developed an optical solution that uses four 200 Gbps wavelength lanes to reach 800 GbE.
Post Deadline Papers looked to the future with developments in high-speed individual LEDs, modulated lasers, record low loss in hollow core fibers for applications in power delivery and sensing and other topic areas important to industry.
Analysts also revealed their recent findings around the sector to coincide with the event. For instance, Cignal AI suggested there have been strong gains in switching and routing spending by operators in the first quarter of the year, but these were offset by the slightly weaker deployment of optical transport gear.
Scott Wilkinson, lead analyst for transport hardware at Cignal AI, noted that “Chinese spending on optical hardware has plateaued as major 5G network builds mature and new projects have not been initiated.” He added that the country’s “extraordinary growth during 2015 to 2018 could not continue long term due to the impracticality of expanding upon the enormous amounts that had been spent in the region.”
In general, analysts reported subdued activity by Chinese operators across all product categories after last year’s strong growth, while most other territories showed a rebound this quarter.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
OFC 2022 will be held 06 – 10 March at the San Diego Convention Center, San Diego, CA.
For more information contact: [email protected]
References:
https://www.ofcconference.org/en-us/home/
https://www.eetindia.co.in/ofc-highlights-open-optical-nets/
Deutsche Telekom: Access 4.0 in Production Leveraging ONF VOLTHA and SEBA open source software
Deutsche Telekom (DT) recently announced its Access 4.0 (A4) platform began providing services to customers in Stuttgart in December 2020. This marks a major milestone in DT’s efforts building a state-of-the-art disaggregated broadband solution that blends open source and vendor proprietary components into a production-grade highly optimized solution for providing FTTx services.
Deutsche Telekom’s Access 4.0 is the next generation of software-defined access networking. The program constitutes a true paradigm shift, not only in terms of technology but also ecosystem, collaboration, and agility. By leveraging an edge cloud approach, we create a cost-efficient, lean-to-operate, and scalable access platform to deliver gigabit products. It works in our labs and in an early field trial.

A key foundational building block of A4 is ONF’s Virtual OLT Hardware Abstraction (VOLTHA) open source software controlled by the ONF’s ONOS SDN Controller and a set of ONOS Apps. This VOLTHA stack enables operators to extend software defined programming to the fixed access network, and makes it possible to embrace a best-of-breed approach to selection of white box network equipment. In addition to this open source stack, ONF’s SDN-Enabled Broadband Access (SEBA) Reference Design documents the architecture and framework used to assemble open solutions such as DT’s.
VOLTHA™ is an open source project to create a hardware abstraction for broadband access equipment. It supports the principle of multi-vendor, disaggregated, “any broadband access as a service” for the Central Office. VOLTHA currently provides a common, vendor agnostic, GPON control and management system, for a set of white-box and vendor-specific PON hardware devices. With the upcoming introduction of access Technology Profiles, VOLTHA will support other access technologies like EPON, NG-PON2 and G.Fast as well.
VOLTHA, operational in the A4 network, has been developed as a joint effort between ONF, ONF operator partners (particularly AT&T, Deutsche Telekom and Turk Telekom), and additional members and vendors in the VOLTHA ecosystem. The role of the operators is key in shaping the architecture and requirements for VOLTHA and SEBA with their sharing of insight learned in field trials and early commercial deployments. This collaboration has helped to improve, harden and scale VOLTHA and SEBA.
SEBA™ is a lightweight platform based on a variant of R-CORD. It supports a multitude of virtualized access technologies at the edge of the carrier network, including PON, G.Fast, and eventually DOCSIS and more. SEBA supports both residential access and wireless backhaul and is optimized such that traffic can run ‘fastpath’ straight through to the backbone without requiring VNF processing on a server.
- Kubernetes based
- High Speed
- Operationalized with FCAPS and OSS Integration
“Deutsche Telekom is reaching an important milestone in its transformation into a software-based telecommunications provider,” explains Walter Goldenits, CTO Telekom Deutschland, adding, “We are thus consistently shaping the path taken by the industry toward solutions based on open and disaggregated components in the fixed network area as well.”
Abdurazak Mudesir, head of Services & Platforms and Access Disaggregation at Deutsche Telekom Technik, adds: “Disaggregation is now a reality. For the first time we’re producing a BNG on Whitebox hardware and are using software-defined networking technology to control that gateway. That’s a hugely important step toward our broadband network’s future structure. With the software-defined approach of Access 4.0 we’re driving forward automation and can implement lean processes ourselves in combination with our OSS platforms.”
Access 4.0 is primarily tailored to Deutsche Telekom’s broadband internet access for FTTH/B. This use case marks, however, just the start of the transformation. The underlying A4 platform technology should in future be able to support other applications at the network edge, especially in the 5G and Open RAN environment. The next step will see the project team focus on honing the platform for rollout in other regions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telekom.com/en/company/details/access-4-0-563612