GSA: Private Mobile Networks Summary-2022
Introduction:
The demand for private mobile networks based on 4G LTE (and increasingly 5G) technologies is being driven by the spiralling data, security, digitisation and enterprise mobility requirements of modern business and government entities. Organisations of all types are combining connected systems with big data and analytics to transform operations, increase automation and efficiency or deliver new services to their users. Wireless networking with LTE or 5G enables these transformations to take place even in the most dynamic, remote or highly secure environments, while offering the scale benefits of a technology that has already been deployed worldwide.
The arrival of LTE-Advanced systems delivered a step change in network capacity and throughput, while 5G networks have brought improved density (support for larger numbers of users or devices), even greater capacity, as well as dramatic improvements to latency that enable use of mobile technology for time-critical applications.
Private mobile networks are often part of a broader digital transformation programme in an organisation. This could include the introduction or development of cloud networking and other digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, and data analytics. More and more applications of the private mobile network will use these capabilities combined with mobile connectivity.
In addition to companies looking to deploy their own private mobile network for the first time, there is a large group of potential customers that currently operate private networks based on technologies such as TETRA, P25, Digital Mobile Radio, GSM-R and Wi-Fi. Many of these customers are demanding critical broadband services that are simply not available from alternative technologies, so private mobile networks based on LTE and 5G could eventually replace much of this market.
The exact number of existing private mobile network deployments is hard to determine, as details are not often made public. To improve information about this market, GSA is now maintaining a database of private LTE and 5G networks worldwide.
Since the last market update, GSA has been working with Executive Members Ericsson, Huawei and Nokia on harmonising definitions of what counts as a valid private mobile network, and on harmonising sector definitions. That work has led to a restatement of some of GSA’s market statistics.
The definition of a private mobile network used in this report is a 3GPP-based 4G LTE or 5G network intended for the sole use of private entities, such as enterprises, industries and governments. The definition includes MulteFire or Future Railway Mobile Communication System. The network must use spectrum defined in 3GPP, be generally intended for business-critical or mission-critical operational needs, and where it is possible to identify commercial value, the database only includes contracts worth more than €100,000, to filter out small demonstration network deployments.
Private mobile networks are usually not offered to the general public, although GSA’s analysis does include the following: educational institutions that provide mobile broadband to student homes; private fixed wireless access networks deployed by communities for homes and businesses; city or town networks that use local licences to provide wireless services in libraries or public places (possibly offering Wi-Fi with 3GPP wireless backhaul) which are not an extension of the public network.
Non-3GPP networks such as those using Wi-Fi, TETRA, P25, WiMAX, Sigfox, LoRa and proprietary technologies are excluded from the data set. Furthermore, network implementations using solely network slices from public networks or placement of virtual networking functions on a router are also excluded. Where identifiable, extensions of the public network (such as one or two extra sites deployed at a location, as opposed to dedicated private networks), are excluded. These items may be described in the press as a type of private network.
GSA has identified 58 countries and territories with private network deployments based on LTE or 5G, or where private network spectrum licences suitable for LTE or 5G have been assigned. In addition, there are private mobile network installations in various offshore locations serving the oil and gas industries, as well as on ships.
GSA has collated information about 656 organisations known to be deploying LTE or 5G private mobile networks. Since the last update of this report in November 2021, some organisations have been removed from the database and this analysis, owing to a lack of evidence that they met the definition criteria. These examples may be added again in the future.
GSA has counted over 50 equipment vendors that have been involved in the supply of equipment for private mobile networks based on LTE or 5G. Commercial availability of pre-integrated solutions from several equipment providers increased in 2021; these solutions aim to simplify adoption of private networks, which should add market impetus. In addition, GSA has identified more than 70 telecom network operators (counting national operators within the same group as distinct entities) involved with private mobile network projects. Also, global-scale cloud providers (often referred to as “hyperscalers”) are offering private mobile network solutions, sometimes in partnership with mobile operators or network suppliers. Their ability to exploit mass-scale cloud infrastructure and their existing presence in commercial enterprises is likely to drive additional growth in the private mobile network market.
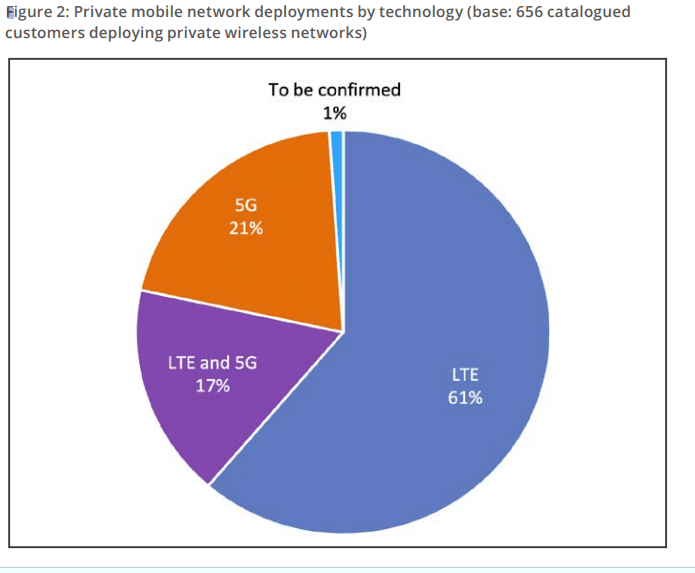
GSA has been able to categorise 656 customers deploying private mobile networks, which as Figure 1 shows, are located all around the world. Where organisations have subsidiaries in different countries or territories deploying their own networks, each subsidiary is counted separately. LTE is used in 78% of the catalogued private mobile network deployments for which GSA has data; 5G is being deployed in 38% of networks.
Dell’Oro Group forecasts a much smaller private wireless market share for 5G. They say LTE is dominating the private market in 2021 and 5G NR still on track to surpass LTE by the outer part of the forecast period, approaching 3 percent to 5 percent of the total 5G private plus public RAN market by 2026.
GSA also tracks the spectrum bands being used for deployments assigned specifically for local or private network purposes. Figure 4 shows that, including known spectrum assignments and deployments, C-band spectrum is the most widely assigned; TDD spectrum at 1.8 GHz comes second and is associated with the greatest number of identified deployments (more than 100 separate metro rail deployments in China). After that comes CBRS spectrum (also technically within the C-band but split out owing to the unusual way it has been assigned in the US).
There are more than 200 CBRS licensees, although they have not all been counted within the licence data, as it is not certain whether the spectrum will be used for public or private networks.
Telecom regulators are also showing signs of making increased allocations of dedicated spectrum available for private mobile networks — typically small tranches in specified locations. This could be acquired directly by organisations instead of by mobile operators, giving industries an alternative deployment model. Dedicated spectrum of this sort has already been allocated in France, the US, Germany and the UK, for example, and GSA expects this trend to be followed in other countries in 2022.
Note that owing to the removal of projects not meeting the new size requirement of at least €100,000, the counts are not directly comparable with those in the previous issue, although the patterns are the same.
GSA will be publishing further statistical updates covering the private mobile sector during 2022.
Acknowledgement: GSA would like to thank its Executive Members Ericsson, Huawei and Nokia for sharing general information about their network deployments to enable this dataset and report to be produced.
References:
https://gsacom.com/paper/private-mobile-networks-summary-february-2022/
One thought on “GSA: Private Mobile Networks Summary-2022”
Comments are closed.



Nice chart.