ABI Research: Major contributors to 3GPP; How 3GPP specs become standards
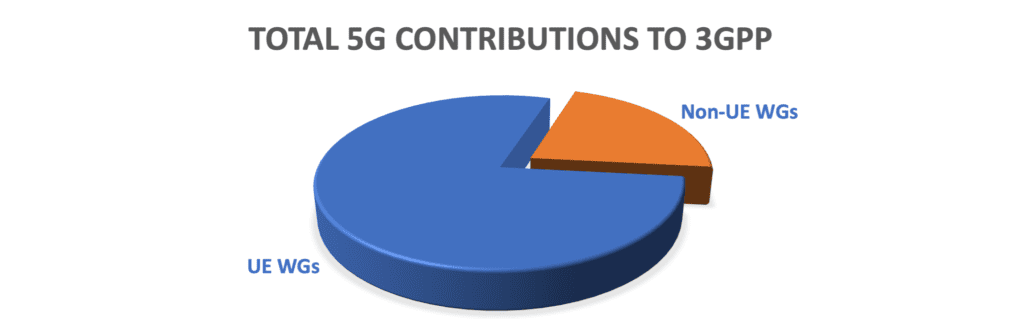
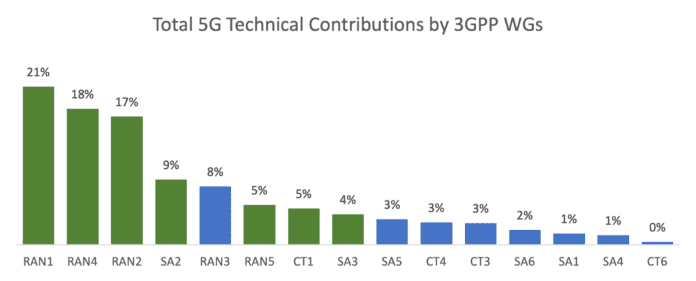
Three large network equipment vendors (Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia) have been leading in both the number of contributions and approved contributions for 5G technologies to The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). This is particularly the case with specifications related to User Equipment (UE) specifications and functionalities that are developed under RAN1, RAN2, RAN4, RAN5, SA2, SA3, and CT1 Working Groups (WGs).
Editor’s Note:
The 3GPP Organizational Partners (OP) are the seven Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs) – from China, Europe, India, Japan, Korea and the United States. The OPs are:
ARIB The Association of Radio Industries and Businesses, Japan
ATIS The Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions, USA
CCSA China Communications Standards Association
ETSI The European Telecommunications Standards Institute
TSDSI Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India
TTA Telecommunications Technology Association, Korea
TTC Telecommunication Technology Committee, Japan
Participation in 3GPP is made possible by companies and organizations becoming Individual Members (IM) of one of the OPs.
- 3GPP specifications are not standards, they have no legal standing. They become “official” standards once one or more of the OPs transposes them, as ETSI has done many times.
- 3GPP specs become ITU-R recommendations when they are submitted to ITU-R WP5D by ATIS, discussed and agreed upon, then sent to WP5 plenary in November for final approval. That procedure was followed to create the ITU-R M.2150 recommendation which features 5G-NR.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The list of the most active companies within 5G 3GPP standards is listed in the table below:
| Top Ranked by Total Contributions | Approved Contributions | Total Contributions | Company Category |
| Huawei | 15,266 | 43,753 | Incumbent Infrastructure Vendor (End-to-End) |
| Ericsson | 11,601 | 36,375 | Incumbent Infrastructure Vendor (End-to-End) |
| Nokia | 7,553 | 23,112 | Incumbent Infrastructure Vendor (End-to-End) |
| Qualcomm | 5,523 | 18,471 | Chipset |
| Samsung | 3,548 | 16,464 | Incumbent Infrastructure Vendor (End-to-End) |
| ZTE | 3,415 | 15,291 | Incumbent Infrastructure Vendor (End-to-End) |
| Intel | 2,151 | 10,770 | Chipset |
| LGE | 1,396 | 10,139 | Handset/UE Vendor |
| CATT | 1,934 | 9,792 | Government/Institution/SDO/Academics |
| vivo | 1,205 | 8,367 | Handset/UE Vendor |
| MediaTek | 1,848 | 7,766 | Chipset |
Source: ABI Research
Key Takeaways:
- Counting contributions alone is insufficient to identify leaders in 3GPP standardization processes. However, it is a crucial step in recognizing active contributors and identifying innovation.
- More than 400 companies from the industry have participated in 3GPP standardization; however, only a handful of companies are consistently active in driving 3GPP 5G standards.
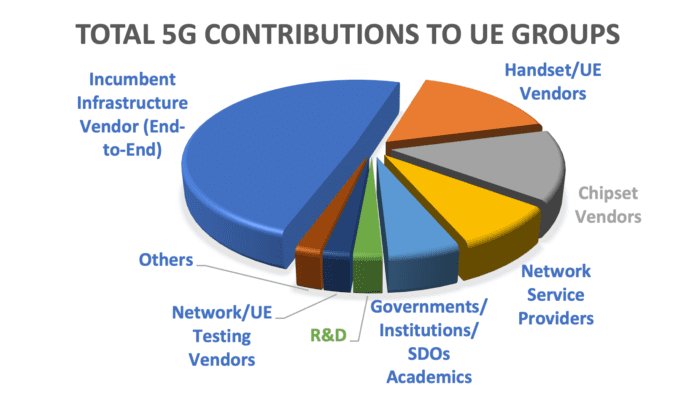
- Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia have, so far, been leading in both the number of total and approved contributions for 5G technologies to 3GPP.
- Network infrastructure vendors are significantly more active than any other company categories, followed by handset vendors, chipset vendors, network service providers, and government research institutions.
- UE-related WGs (i.e., RAN1, RAN2, RAN4, RAN5, SA2, SA3, and CT1) take 80% of total contributions. RAN1, RAN2, RAN4, and SA2 are the most important WGs, impacting the entire mobile industry and receiving massive interest.
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/about-us/partners
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
Busting a Myth: 3GPP Roadmap to true 5G (IMT 2020) vs AT&T “standards-based 5G” in Austin, TX


