ITU-R report: Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages
At its June 2023 meeting (#44), ITU-R WP 5D has completed its work towards the development of a new report: ITU-R M.[IMT.APPLICATIONS] on Applications of IMT for specific societal, industrial and enterprise usages. WP5D agreed to elevate this PDNR to a Draft New Report (DNR).
Backgrounder:
Enterprises can generally expect reliable and secure network services with IMT (4G LTE and 5G) for fixed and mobile broadband applications across a wide coverage area. While there are subtle differences across different industrial sectors, IMT applications typically involve the following: video surveillance, remote control, autonomous vehicles and robots, automation, and immersive experiences.
The emergence of IMT-2020 “5G RAN” technologies provides manufacturers with the much-needed reliable connectivity solutions, enabling critical communications for wireless control of machines and manufacturing robots, and IoT sensor solutions, which will unlock the full potential of Industry 4.0.
Apart from manufacturing, many other industries are also looking at IMT-2020 technologies as the backbone for their equivalent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The opportunity to address industrial connectivity needs of a range of industries includes diverse segments with diverse needs, such as those in the mining, port, energy and utilities, automotive and transport, public safety, media and entertainment, healthcare, agriculture and education industries, among others.
Some recent trials of IMT-2020 technologies in port operations demonstrated the “3GPP 5G” capabilities for critical communications enablers such as ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to support traffic control, AR/VR headsets and IoT sensors mounted on mobile barges and provided countless possibilities to improve efficiency and sustainability in the complex and changing industrial environments, e.g., ports and mining. Some ports are increasing/accelerating their adoption of digital processes, automation and other technologies to enhance efficiency and resiliency to crises such as a global COVID-19 pandemic.
Similarly, in mining exploration sites, the drilling productivity could be substantially increased through automation of its drills and other technologies. Additional savings from improved efficiency and sustainability could also lead to lower capital expenditures for mines (CapEx) as well as a better safety and working environments for their personnel.
An example of an application in health care that need critical communications supported by the capabilities of IMT-2020 is remote robotic surgery. A latency of one millisecond is critical in providing haptic feedback to a surgeon that is connected through a mobile connection to a surgical robot. A high data rate is needed to transfer high-definition image streams. As an ongoing surgery cannot be interrupted an ultra-reliable communication is needed to keep connection down-time and packet loss very low.
Integration of IMT-2020 networks with industrial communication networks:
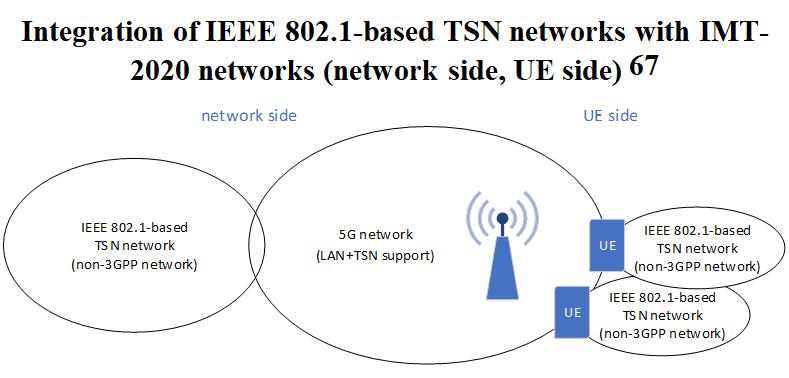
‘Industrial 5G’ networks need to be integrated in existing industrial communication networks. In order to support this, a ‘5G LAN’ interface is necessary, that supports Virtual LANs and Ethernet. Furthermore, support of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and integration of IMT-2020 in industrial TSN networks is of importance. Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is an important functionality of IEEE 802.1-based industrial communication networks in order to provide deterministic, reliable, real-time communication, and the integration of IMT-2020 networks and IEEE 802.1-based TSN networks is very beneficial.
The integration between the IEEE 802.1-based networks and the IMT-2020 networks can be through the ‘5G LAN’ service of the IMT-2020 network on the network side and/or on the UE side (see below Figure).
The integration on the UE side is used, for instance, in use cases where machinery, AGVs, or robots with their own internal network (wired, TSN) are connected to the backhaul part of the industrial communication network through an IMT-2020 link in order to enable mobility or tether less movements.
IEEE 802.1AS-based time synchronization is an important functionality in such industrial TSN communication networks. The accuracy of the time synchronization between the time transmitter (sync master) and any time receiver (sync device) needs to be in the range of 1 µs. The clock synchronization accuracy of the IMT-2020 system needs to be smaller than this value, since IMT-2020 network is only a part in this integrated industrial network.
Depending on the actual physical process, the actual cyber-physical control application, the design of the machinery, AGVs, and robots, and the design of the integrated industrial communication network, different mappings of TSN/time synchronization functionalities to IMT-2020 network elements are possible.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Other important outputs from the June 2023 ITU-R WP 5D meeting:
- A related Draft New Report in the works: ITU-R M.[IMT.MULTIMEDIA] – Capabilities of the terrestrial component of IMT-2020 for multimedia communications.
- SWG IMT 2030 has submitted one draft new Recommendation ITU-R M. [IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND] – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond together with the relevant Liaison Statements.
- The long delayed revision of ITU-R M.1036 Frequency Arrangements for Terrestrial IMT was agreed upon and will be forwarded to ITU-R SG 5 for approval.
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2020/Pages/default.aspx