Telegeography: Strong international bandwidth demand in LatAm; Global Internet traffic and bandwidth increased in 2020
TeleGeography’s latest research on Latin America shows that international bandwidth demand is strong in the region. With an ongoing surge in new submarine cable deployments, content providers are expanding their geographic reach as both owners and anchor customers of new cable systems.
The market research firm reported in August that the average international internet traffic increased 48% in 2020 while internet bandwidth was up 35%, the biggest increase since 2013. In its annual report on submarine networks and capacity, TeleGeography said the global Internet “bent but – for the most part – did not break” during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the market research firm wrote that the spike in bandwidth and traffic growth in 2020 is probably a one-time event and a return to typical rates of growth is likely when the pandemic restrictions end.
International Internet Bandwidth Growth by Region:
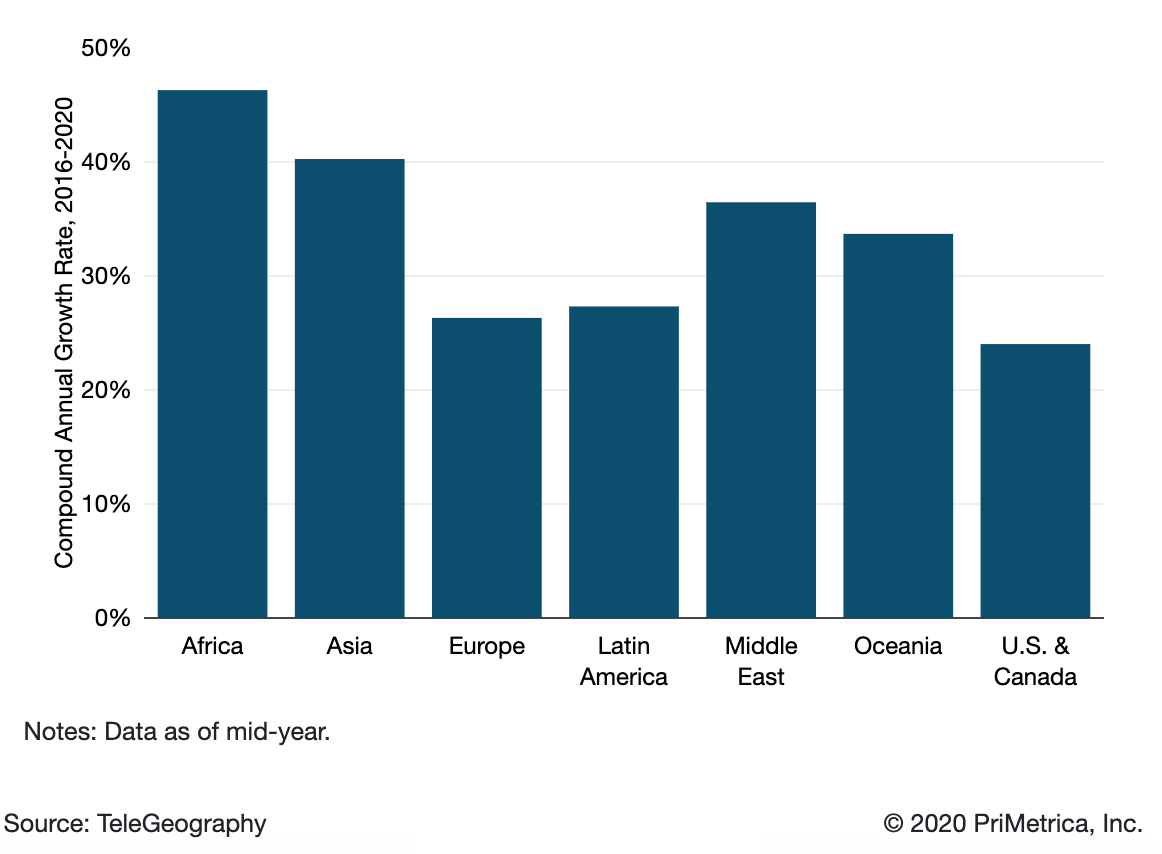
International internet traffic growth largely mirrors that of internet capacity. However, traffic and capacity growth seldom move in perfect tandem. (Network operators will often add capacity in anticipation of traffic growth.). Average and peak international internet traffic increased at a compound annual rate of 30% between 2016 and 2020, comparable to the 29% compound annual growth rate in bandwidth.
Based on discussions with network operators worldwide, TeleGeography believes the trends of recent years will continue. While international Internet bandwidth and traffic growth had been gradually slowing prior to 2020, growth remains brisk. Africa has experienced the most rapid growth in international bandwidth, growing at a compound annual rate of 47% from 2016-2020, with Asia just behind at 40%.
What won’t change is the role of U.S. web giants Google, Microsoft, Facebook and Amazon. They have become far and away the dominant users of international bandwidth, accounting for 64% of all used capacity in 2019. Across six of the world’s seven regions, they added capacity at a compound annual rate of above 70% between 2015 and 2019, compared to a rate of less than 45% for others. Their rapid expansion into subsea capacity has caused a major shift in the global wholesale market, TeleGeography says.
That presence “drives scale to establish new submarine cable systems and lower overall unit costs.” The OTT firms have become a key part of the subsea cable business model. Many of the big cables, invested in by both telcos and Internet players, now rely on the initial capital injection from the Internet content players. This means a share of network capacity or fiber pairs can be allocated to the largest consumers to cover initial costs, with the remaining shares sold as managed wholesale bandwidth.
TeleGeography states that both content players and telcos are trying to cope with massive growth in demand, driven by new applications and greater penetration into emerging markets. “The sheer growth in supply will drive lower unit costs for bandwidth,” it says. “In the face of unrelenting price erosion, the challenge for wholesale operators is to carve out profitable niches where demand trumps competition.” Prices vary enormously even though they are falling sharply. London and Singapore prices have declined 25% since 2017, yet Singapore tariffs are much higher; a 10 GigE port costs roughly three times as much, for example. Thanks to capacity upgrades, the prices for 10 GigE ports in São Paulo and Sydney fell 38% and 22% compounded annually over the past three years. TeleGeography warns that while the unit cost savings from the large cable investments are an incentive to investment for operators, they don’t want to be left with too much excess bandwidth. “It’s often a race to offload wholesale capacity before a new generation of lower-cost supply emerges.”
TeleGeography predicts $8.1 billion worth of new cables will be launched between 2020 and 2022 with the biggest share, $2.3 billion, invested in the trans-Pacific route. But the research firm cautions that the pandemic could disrupt supply. “Temporary cable factory closures combined with delays in permitting and marine installation could hamper the deployment of many planned cables.”
References:
https://blog.telegeography.com/internet-traffic-and-capacity-in-covid-adjusted-terms
https://www2.telegeography.com/covid19-state-of-the-network
One thought on “Telegeography: Strong international bandwidth demand in LatAm; Global Internet traffic and bandwidth increased in 2020”
Comments are closed.



By 2019, wholesale carriers terminated more than two-thirds (71%) of international traffic—up from 59% in 2008.
Traffic to mobile phones in emerging markets has historically spurred expansion of the wholesale market, and that demand continues to drive wholesale’s growth. In 2019, wholesale carriers terminated 86% of traffic to Sub-Saharan Africa and South America, and 83% to Central Asia.
In contrast, only 54% of traffic to western Europe was terminated by wholesale operators. Revenues on calls to sub-Saharan Africa grew 20% between 2012 and 2019, $3.1 billion to $3.7 billion.
https://blog.telegeography.com/wholesale-carriers-terminated-307-billion-minutes-of-traffic-in-2019