GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
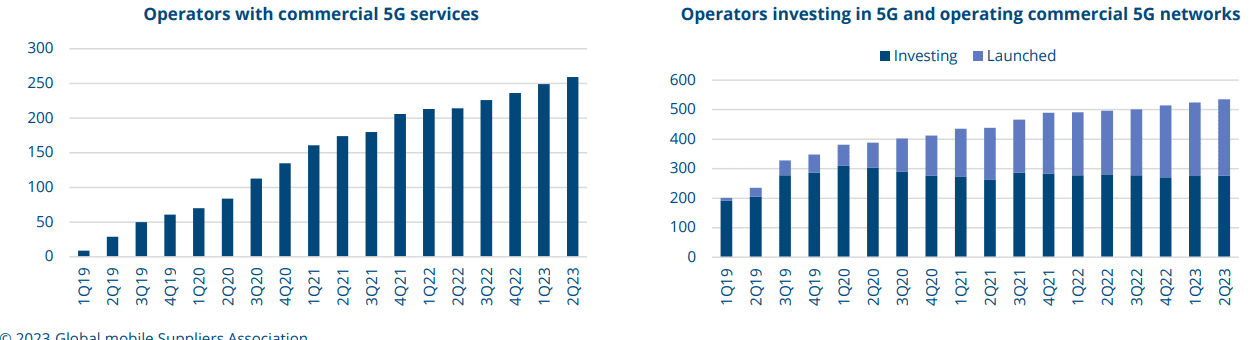
By the end of June 2023, GSA had identified 535 network operators in 162 countries and territories were investing in 5G, including trials, acquisition of licences, planning, network deployment and launches.
This number excludes nearly 200 additional companies awarded priority access licences in the U.S. auction of CBRS spectrum, which could potentially be used for 5G
Of those, a total of 259 operators in 102 countries and territories had launched one or more 3GPP-compliant 5G services 252 operators in 100 countries and territories had launched 5G mobile services 113 operators in 62 countries and territories had launched 3GPP-compliant 5G fixed wireless access services (just over 43% of those with launched 5G services)
13 operators had announced soft launches of their 5G networks that are not counted in the above launch figures 115 operators are identified as investing in 5G standalone (including those evaluating/testing, piloting, planning and deploying, as well as those that have launched 5G standalone networks).
GSA has catalogued 41 operators as having deployed or launched 5G standalone (SA) in public networks.
115 network operators are identified as investing in standalone 5G (including those evaluating, testing, piloting, planning and deploying as well as those that have launched standalone 5G networks).
GSA has catalogued 2,039 announced 5G devices, up by more than 62% from 1,257 at the start of 2022 GSA has identified 1,083 announced 5G phones, up more than 76% from 613 at the start of 2022
There are at least 1,650 commercially available 5G devices, up more than 66% annually from 990
References:
GSA: 5G Device Ecosystem June 2023 Summary
GSA FWA Report: 38 commercially launched 5G FWA networks in the EU; Speeds revealed
One thought on “GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)”
Comments are closed.



T-Mobile has been building on its early move to 5G SA with other services ranging from carrier aggregation to private networks. At the same time, T-Mobile has been working to streamline its core network architecture
T-Mobile this week announced that software developers can use network slicing on its standalone (SA) 5G network to build video calling applications with more consistent uplink and downlink speeds and lower latency. The result, the company said, could be more reliable video calls that may not freeze or skip.
T-Mobile noted that companies like Dialpad Ai, Google, Webex by Cisco, Zoom and others have signed up to test out its new capability.
Analysts generally cheered the move.
“This is another important step in making sure 5G lives up to the promise of delivering new and user-centric services for consumer and business users,” wrote analyst Jack Gold on LinkedIn. “While some have questioned the promise of 5G improvements over current systems as functional improvements have been slow to appear, this move shows that forward-looking providers can achieve breakthroughs that advance the capabilities and usefulness of 5G for both businesses and consumers.”
The launch “is a big deal,” added Recon Analytics Founder Roger Entner on X (formerly Twitter).
https://www.lightreading.com/service-provider-cloud/programmable-5g-gets-little-more-real/a/d-id/785926?