Expose: AI is more than a bubble; it’s a data center debt bomb
We’ve previously described the tremendous debt that AI companies have assumed, expressing serious doubts that it will ever be repaid. This article expands on that by pointing out the huge losses incurred by the AI startup darlings and that AI poster child Open AI won’t have the cash to cover its costs 9which are greater than most analysts assume). Also, we quote from the Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, Barron’s, along with a dire forecast from the Center for Public Enterprise.
In Saturday’s print edition, The Wall Street Journal notes:
OpenAI and Anthropic are the two largest suppliers of generative AI with their chatbots ChatGPT and Claude, respectively, and founders Sam Altman and Dario Amodei have become tech celebrities.
What’s only starting to become clear is that those companies are also sinkholes for AI losses that are the flip side of chunks of the public-company profits.
OpenAI hopes to turn profitable only in 2030, while Anthropic is targeting 2028. Meanwhile, the amounts of money being lost are extraordinary.
It’s impossible to quantify how much cash flowed from OpenAI to big tech companies. But OpenAI’s loss in the quarter equates to 65% of the rise in underlying earnings of Microsoft, Nvidia, Alphabet, Amazon and Meta together. That ignores Anthropic, from which Amazon recorded a profit of $9.5B from its holding in the loss-making company in the quarter.
OpenAI committed to spend $250 billion more on Microsoft’s cloud and has signed a $300 billion deal with Oracle, $22 billion with CoreWeave and $38 billion with Amazon, which is a big investor in rival Anthropic.
OpenAI doesn’t have the income to cover its costs. It expects revenue of $13 billion this year to more than double to $30 billion next year, then to double again in 2027, according to figures provided to shareholders. Costs are expected to rise even faster, and losses are predicted to roughly triple to more than $40 billion by 2027. Things don’t come back into balance even in OpenAI’s own forecasts until total computing costs finally level off in 2029, allowing it to scrape into profit in 2030.
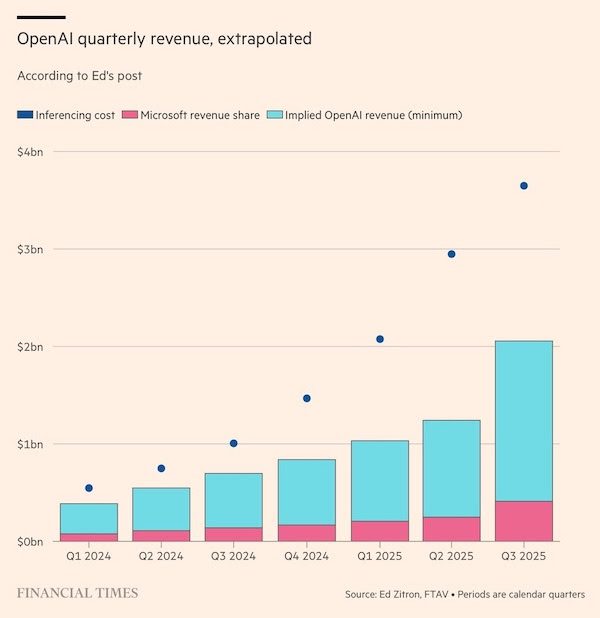
The losses at OpenAI that has helped boost the profits of Big Tech may, in fact, understate the true nature of the problem. According to the Financial Times:
OpenAI’s running costs may be a lot more than previously thought, and that its main backer Microsoft is doing very nicely out of their revenue share agreement.
OpenAI appears to have spent more than $12.4bn at Azure on inference compute alone in the last seven calendar quarters. Its implied revenue for the period was a minimum of $6.8bn. Even allowing for some fudging between annualised run rates and period-end totals, the apparent gap between revenues and running costs is a lot more than has been reported previously.
The apparent gap between revenues and running costs is a lot more than has been reported previously. If the data is accurate, then it would call into question the business model of OpenAI and nearly every other general-purpose LLM vendor.
Also, the financing needed to build out the data centers at the heart of the AI boom is increasingly becoming an exercise in creative accounting. The Wall Street Journal reports:
The Hyperion deal is a Frankenstein financing that combines elements of private-equity, project finance and investment-grade bonds. Meta needed such financial wizardry because it already issued a $30B bond in October that roughly doubled its debt load overnight.
Enter Morgan Stanley, with a plan to have someone else borrow the money for Hyperion. Blue Owl invested about $3 billion for an 80% private-equity stake in the data center, while Meta retained 20% for the $1.3 billion it had already spent. The joint venture, named Beignet Investor after the New Orleans pastry, got another $27 billion by issuing bonds that pay off in 2049, $18 billion of which Pimco purchased. That debt is on Beignet’s balance sheet, not Meta’s.
Dan Fuss, vice chairman of Loomis Sayles told Barrons: “We are good at taking credit risk,” Dan said, cheerfully admitting to having the scars to show for it. That is, he added, if they know the credit. But that’s become less clear with the recent spate of mind-bendingly complex megadeals, with myriad entities funding multibillion-dollar data centers. Fuss thinks current data-center deals are too speculative. The risk is too great and future revenue too uncertain. And yields aren’t enough to compensate, he concluded.
Increased wariness about monster hyper-scaler borrowings has sent the cost of insuring their debt against default soaring. Credit default swaps (CDS) more than doubled for Oracle since September, after it issued $18 billion in public bonds and took out a $38 billion private loan. CoreWeave’s CDS gapped higher this past week, mirroring the slide of the data-center company’s stock.
According to the Bank Credit Analyst (BCA), capex busts weigh on the economy, which further hits asset prices, the firm says. Following the dot-com bust, a housing bubble grew, which burst in the 2008-09 financial crisis. “It is far from certain that a new bubble will emerge (after the AI bubble bursts) this time around, in which case the resulting recession could be more severe than the one in 2001,” BCA notes.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The widening gap between the expenditures needed to build out AI data centers and the cash flows generated by the products they enable creates a colossal risk which could crash asset values of AI companies. The Center for Public Enterprise reports that it’s “Bubble or Nothing.”

Should economic conditions in the tech sector sour, the burgeoning artificial intelligence (AI) boom may evaporate—and, with it, the economic activity associated with the boom in data center development.
Circular financing, or “roundabouting,” among so-called hyperscaler tenants—the leading tech companies and AI service providers—create an interlocking liability structure across the sector. These tenants comprise an incredibly large share of the market and are financing each others’ expansion, creating concentration risks for lenders and shareholders.
Debt is playing an increasingly large role in the financing of data centers. While debt is a quotidian aspect of project finance, and while it seems like hyperscaler tech companies can self-finance their growth through equity and cash, the lack of transparency in some recent debt-financed transactions and the interlocked liability structure of the sector are cause for concern.
If there is a sudden stop in new lending to data centers, Ponzi finance units ‘with cash flow shortfalls will be forced to try to make position by selling out position’—in other words to force a fire sale—which is ‘likely to lead to a collapse of asset values.’
The fact that the data center boom is threatened by, at its core, a lack of consumer demand and the resulting unstable investment pathways, is itself an ironic miniature of the U.S. economy as a whole. Just as stable investment demand is the linchpin of sectoral planning, stable aggregate demand is the keystone in national economic planning. Without it, capital investment crumbles.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Postscript (November 23, 2025):
In addition to cloud/hyperscaler AI spending, AI start-ups (especially OpenAI) and newer IT infrastructure companies (like Oracle) play a prominent role. It’s often a “scratch my back and I’ll scratch yours” type of deal. Let’s look at the “circular financing” arrangement between Nvidia and OpenAI where capital flows from Nvidia to OpenAI and then back to Nvidia. That ensures Nvidia a massive, long-term customer and providing OpenAI with the necessary capital and guaranteed access to critical, high-demand hardware. Here’s the scoop:
- Nvidia has agreed to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI over time. This investment will be in cash, likely for non-voting equity shares, and will be made in stages as specific data center deployment milestones are met.
- OpenAIhas committed to building and deploying at least 10 gigawatts of AI data center capacity using Nvidia’s silicon and equipment, which will involve purchasing millions of Nvidia expensive GPU chips.
Here’s the Circular Flow of this deal:
- Nvidia provides a cash investment to OpenAI.
- OpenAI uses that capital (and potentially raises additional debt using the commitment as collateral) to build new data centers.
- OpenAI then uses the funds to purchase Nvidia GPUs and other data center infrastructure.
- The revenue from these massive sales flows back to Nvidia, helping to justify its soaring stock price and funding further investments.
What’s wrong with such an arrangement you ask? Anyone remember the dot-com/fiber optic boom and bust? Critics have drawn parallels to the “vendor financing” practices of the dot-com era, arguing these interconnected deals could create a “mirage of growth” and potentially an AI bubble, as the actual organic demand for the products is difficult to assess when companies are essentially funding their own sales.
However, supporters note that, unlike the dot-com bubble, these deals involve the creation of tangible physical assets (data centers and chips) and reflect genuine, booming demand for AI compute capacity although it’s not at all certain how they’ll be paid for.
There’s a similar cozy relationship with the $1B Nvidia invested in Nokia with the Finnish company now planning to ditch Marvell’s silicon and replace it by buying the more expensive, power hungry Nvidia GPUs for its wireless network equipment. Nokia, has only now become a strong supporter of Nvidia’s AI RAN (Radio Access Network), which has many telco skeptics.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/big-techs-soaring-profits-have-an-ugly-underside-openais-losses-fe7e3184
https://www.ft.com/content/fce77ba4-6231-4920-9e99-693a6c38e7d5
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/three-ai-megadeals-are-breaking-new-ground-on-wall-street-896e0023
Can the debt fueling the new wave of AI infrastructure buildouts ever be repaid?
AI Data Center Boom Carries Huge Default and Demand Risks
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
Gartner: AI spending >$2 trillion in 2026 driven by hyperscalers data center investments
Amazon’s Jeff Bezos at Italian Tech Week: “AI is a kind of industrial bubble”
FT: Scale of AI private company valuations dwarfs dot-com boom




Laura Chambers, CEO of Mozilla—maker of the Firefox browser—sees the situation as a classic, straightforward bubble. Funding is abundant, it is easier than ever to make low-grade products, and most AI companies are running at a loss, she says. “Yes. It’s really easy to build a whole bunch of stuff, and so people are building a whole bunch of stuff, but not all of that will have traction. So the amount of stuff coming out versus the amount of stuff that’s going to [be sustainable] is probably higher than it’s ever been. I mean, I can build an app in four hours now. That would have taken me six months to do before. So there’s a lot of junk being built very, very quickly, and only a part of that will come through. So that’s one piece of the bubble,” she said.
“I think the most interesting piece is monetization, though. All the AI companies, all these AI browsers, are running at a massive loss. At some point that isn’t sustainable, and so they’re going to have to figure out how to monetize.”
Babak Hodjat, chief AI officer at Cognizant, said he believed diminishing returns were setting in to large language models. The DeepSeek launch from earlier this year—in which a Chinese company released an LLM comparable to ChatGPT for a fraction of the cost—was a good example of this. Building AI was once a huge, expensive, and difficult undertaking. But today, many AI use-cases (such as custom-built, task-specific AI agents) don’t need huge models underpinning them, he said.
“The bulk of the money that you see—and people talk about a bubble—is going into commercial companies that are actually building large language models. I think that technology is starting to be commoditized. You don’t really need to use that big of a large language model, but those guys are taking money because they need a lot of compute capacity. They need a lot of data. And their valuation is based on, you know, bigger is better. Which is not necessarily the case,” he told Fortune.
https://www.aol.com/finance/tech-execs-admit-ai-bubble-141038315.html
Postscript: November 23, 2025:
In this new AI era, consumers and workers are not what drives the economy anymore. Instead, it’s spending on all things AI, mostly with borrowed money or circular financing deals.
BofA Research noted that Meta and Oracle issued $75 billion in bonds and loans in September and October 2025 alone to fund AI data center build outs, an amount more than double the annual average over the past decade. They warned that “The AI boom is hitting a money wall” as capital expenditures consume a large portion of free cash flow. Separately, a recent Bank of America Global Fund Manager Survey found that 53% of participating fund managers felt that AI stocks had reached bubble proportions. This marked a slight decrease from a record 54% in the prior month’s survey, but the concern has grown over time, with the “AI bubble” cited as the top “tail risk” by 45% of respondents in the November 2025 poll.
JP Morgan Chase estimates up to $7 trillion of AI spending will be with borrowed money. “The question is not ‘which market will finance the AI-boom?’ Rather, the question is ‘how will financings be structured to access every capital market?’ according to strategists at the bank led by Tarek Hamid.
As an example of AI debt financing, Meta did a $27 billion bond offering. It wasn’t on their balance sheet. They paid 100 basis points over what it would cost to put it on their balance sheet. Special purpose vehicles happen at the tail end of the cycle, not the early part of the cycle, notes Rajiv Jain of GQG Partners.
Fears of an AI bubble fueled volatility in recent weeks as big tech valuations stretched and Wall Street’s top executives warned of a market correction. Global AI-related investments are projected to exceed $4 trillion by 2030, reflecting investor zeal to capitalize on a technology that surged in popularity after ChatGPT was launched three years ago. Record spending by big tech persists despite skepticism about a near-term payoff as many organizations report zero measurable return from billions in capital investment. Tech sector valuations have soared to dot-com era levels – and, based on price-to-sales ratios, well beyond them. Some of AI’s biggest proponents acknowledge the fact that valuations are overinflated, including OpenAI chairman Bret Taylor:
AI will transform the economy… and create huge amounts of economic value in the future,” Taylor told The Verge. “I think we’re also in a bubble, and a lot of people will lose a lot of money.”
Alphabet’s (GOOG) (GOOGL) Sundar Pichai sees “elements of irrationality” in the current scale of AI investing, not unlike the excessive investment during the dot-com boom. If the AI bubble bursts, Pichai added, no company will be immune, including Alphabet, despite its breakthrough technology, Gemini, fueling gains.
Big tech and AI start-ups like OpenAI and Anthropic are leaning heavily on circular deals and heavy debt to finance AI spending has raised eyebrows on Wall Street.
The top five hyperscalers have raised a record $108B worth of debt in 2025 – more than 3x the average over the past nine years, according to data compiled by Bloomberg Intelligence. Moreover, some firms are turning to off-balance-sheet entities, including special-purpose vehicles (SPVs) – structures with a checkered history going back to Enron, D.A. Davidson analyst Gil Luria observed. A slowdown in AI demand could render the debt tied to these SPVs “worthless,” Luria warned, potentially triggering another financial crisis.
AI’s rapid expansion has masked some underlying economic issues. As US investment in AI-related industries surged over the past five years, non-AI investment remained stagnant, a Deutsche Bank research report revealed. And, outside of data centers, economic demand has been weak. In fact, the US would be close to a recession this year without technology-related spending, the report added. Meanwhile, a front-loading of chip orders has helped offset some of the tariff-driven constraints on global trade.
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4848572-5-top-stocks-for-ai-fatigue?
In 2025, investment in tech equipment and software had reached 4.4% of GDP, nearly as high as at the peak of the dotcom bubble (Chart 1). The five hyperscalers – Amazon, Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Oracle – had plans to add about $2 trillion of AI-related assets to their balance sheets by 2030. Given that AI assets typically depreciate at a rate of around 20% per year, this implied that the hyperscalers were facing an annual depreciation expense of $400 billion – more than their combined profits in 2025. These capex plans still do not capture the full extent of the AI build-out. OpenAI alone had intended to spend $1.4 trillion on data centers, alongside the billions that Anthropic and xAI planned to undertake, and the additional billions in AI-related assets targeted by the emerging “neoclouds” – CoreWeave, Nebius, IREN, Lambda, and Crusoe.
https://www.bcaresearch.com/sites/default/files/2026-01/GIS_SO_2025_12_11_Sample_Report.pdf
Yann LeCun left his role as Meta’s chief AI scientist in late 2025, arguing that the capabilities of LLMs were limited. In his estimation, LLMs were great at regurgitating old knowledge but not so great at coming up with new knowledge. Supporting LeCun’s perspective, a study by METR found that experienced programmers who had access to AI took 19% longer to finish their tasks than those who did not