T-Mobile mmWave 5G to be available in six cities on June 28th along with Samsung Galaxy S10 5G smartphone
T-Mobile US has announced it will use millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum to offer up “pre-standard 5G” services in parts of six cities beginning on June 28th. Sales of the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G will commence that same day (see References below). The company published detailed coverage maps showing where subscribers in Atlanta, Cleveland, Dallas, Las Vegas, Los Angeles and New York can expect to access their 5G network.
T-Mobile has said its plan for nationwide coverage hinges on its vast portfolio of 600 MHz spectrum, but the “Un-carrier” also has its own stash of high-band frequencies. Sprint activated its mobile 5G offering using mid-band 2.5 GHz spectrum. The complementary aspects of Sprint’s and T-Mobile’s spectrum is a key piece of the pending $26.5 billion merger, which is awaiting regulatory approval which may be delayed due to several states filing opposition lawsuits.
T-Mobile US CEO John Legere, has been highly critical of AT&T’s and Verizon’s millimeter wave-based 5G deployments (particularly the lack of coverage maps). He wrote in a June 20th blog post that the “New T-Mobile” (merged with Sprint) could deliver the range of spectrum needed for 5G.
“Current 5G networks in the U.S. aren’t anything to write home about. That’s because they’re mostly focused on high-band millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, which doesn’t travel far from the cell site and is blocked by things like trees, windows and doors. It’s a massively important part of 5G, don’t get me wrong, but it’s just that – a PART. We’ve been clear all along… real, game-changing 5G will require a range of spectrum – low, mid and high – and only the New T-Mobile will be able to deliver it.”
Legere stated that the “New T-Mobile” (merged with Sprint) would be better able to deliver 5G because:
- We’ve got the high-band spectrum with mmWave, which delivers massive capacity over a very small footprint.
- Later this year, when compatible smartphones launch, we’ll launch broad 5G on our low-band 600 MHz spectrum, providing the wide area coverage necessary to reach across America.
- If regulators approve our merger with Sprint, we’ll have the crucial mid-band spectrum (2.5 GHz), which provides the balance of coverage and capacity that enables a seamless and meaningful 5G experience. Mid-band spectrum is key to providing an ideal mix of coverage and capacity for 5G networks, and the combination of Sprint’s mid-band and our low-band will allow New T-Mobile to use both spectrum more efficiently, increasing capacity even more.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
T-Mobile said it will use “Multi-band Dual Connectivity” to aggregate “5G in the millimeter wave band and LTE.”
T-Mobile plans to launch a larger 5G network later this year using the low-band 600Mhz 5G spectrum, a technology not supported by the Galaxy S10 5G. 5G smart phones that support both mmWave and the low-band spectrum are expected later this year.
However, critical infrastructure for mmWave 5G will require many more small cells (due to limited range) that will need to be mounted on mainly local (public) government property with fiber backhaul. We wonder why that gating item is hardly ever discussed on line or in the telecom business press? It is probably why T-Mobile’s 5G mmWave coverage is extremely limited as you can see from their coverage maps.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/samsung-galaxy-s10-5g
https://www.tmonews.com/2019/06/t-mobile-galaxy-s10-5g-launch-network-six-cities/
GSA Silicon Summit: Focus on Edge Computing, AI/ML and Vehicle to Everything (V2X) Communications
Introduction:
Many “big picture” technology trends and future requirements were detailed at GSA’s Silicon Summit, held June 18, 2019 in Santa Clara, CA. The conference was a “high level” executive briefing for the entire semiconductor ecosystem- including software, middleware and hardware. Insights on trends, key issues, opportunities and technology challenges (especially related to IoT security) were described and debated in panel sessions. Partnerships and collaboration were deemed necessary, especially for start-ups and small companies, to advance the technology, products and services to be offered in this new age of AI, ML/DL, cloud, IoT, autonomous vehicles, (fake) 5G, etc. Companies involved in the development of next generation Mobility and Edge Intelligence systems architectures and solutions discussed what opportunities, advancements and challenges exist in those key areas.
With the rapid proliferation of smart edge computing devices and applications, the volume of data produced is growing exponentially. Connected, and “intelligent,” devices are predicted to grow to 200 billion by 2020, generating enormous amounts of data every single day. The business potential created by this data comes with huge expectations. Edge devices, edge intelligence, high bandwidth connectivity, high performance computing, machine learning and other technologies are essential to enabling opportunities in markets such as Mobility and Industrial IoT.
This article will focus on Edge Computing, AI moving closer to the endpoint device (at the network edge or actually embedded in the end point device/thing), and vehicle to vehicle/everything communications.
While there were many presentations and panels on security, that is beyond the scope of the IEEE ComSoc Techblog. However, we share Intel’s opinion, expressed during a lunch panel session, that standards for Over The Air (OTA) security software/firmware updates are necessary for almost all smart/intelligent devices that are part of the IoT.
Architectural Implications of Edge Computing, Yogesh Bhatt VP of Products- ML, DL and Cognitive Tech Ericsson – Silicon Valley:
Several emerging application (data flow) patterns are moving intelligence from the cloud to local/metro area to on premises and ultimately to the endpoint devices. These applications include: cloud native apps like content delivery; AI enabled apps like sensing, thinking and acting; immersive apps like media processing/augmentation/distribution.
AI enabled Industrial apps are increasing. They were defined as: The ability to collect and deliver the right data/video/images, at the right velocity and in the right quantities to wide set of well-orchestrated ML-models and provide insights at all levels in the operation. Connectivity and compute are being packaged together and offered as “a service.” One example given was 4K video over (pre-standard) “5G” wireless access at the 2018 U.S. Open. That was intended to be a case study of whether 5G could replace miles of fiber to broadcast live, high definition sports events.

Yogesh Bhatt VP of Products- ML, DL and Cognitive Tech Ericsson – Silicon Valley
Image courtesy of GSA Global
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Required Architecture for Emerging App Patterns: Application Cloud, Management & Monetization Network slices, Mobile Fixed Cloud infrastructure, Distributed Cloud and Transport. The flow of emerging apps requires computing capability to be distributed based on the application pattern and flow. That in turn mandates cross-domain orchestration and automation of services.
Key take-aways:
- Emerging Application patterns will require significant compute capabilities close to the data sources and sinks (end points)
- Current Device-to-Cloud Architecture need to expand to encompass hosting points that provides such processing capabilities
- The processing capabilities at these Edge locations would be anything but like the centralized Cloud Data Centers (DCs)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Heterogeneous Integration for the Edge, Yin Chang Sr. VP, Sales & Marketing ASE Group:
ASE sees the “Empowered Edge” as a key 2019 strategic trend. Edge computing drivers include: latency/determinism, cost of bandwidth, better privacy and security, and higher reliability/availability (connections go down, limited autonomy).
- At the edge (undefined where that is -see my comment below) we might see the following: Collect/Process data, Imaging Device, Image processing, Biometric Sensor, Microphone, Sensors with embedded MCUs, Environmental Sensor.
- At the core (assumed to be somewhere in the cloud/Internet): Compute/Intelligent processing, AI & Machine Learning, Networks/Server Processors, High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), Neuro-engine (future), Quantum computing (future).
Compute capabilities are moving to the edge and endpoints:
- Edge Infrastructure and IoT/Endpoint Systems are growing in compute power per system.
- As the number of IoT/Endpoint systems outgrows other categories, TOTAL Compute will be at the Endpoint.
Challenges at the Edge will require a cost effective integration solution which will need to deal with:
- Cloud connectivity – latency and bandwidth limitations
- Mixed device functionality – sense, compute, connect, power
- Multiple communication protocols
- Form factor constraints
- Battery life
- Security
- Cost High density
ASE advocates Heterogeneous Integration at the Edge— by material, component type, circuit type (IP), node and bonding/ interconnect method. The company has partnered with Cadence to realize System in Package (SiP) intelligent design with “advanced functional integration.” That partnership addresses the design/verification challenges of complex layout of advanced packages, including ultra-complex SiP, Fan-Out and 2.5D packages.
One such SiP design for wireless communications is antenna integration:
- Antenna on/in Package for SiP module integration
- Selective EMI Shielding for non-limited module level FCC certification
- Selective EMI Shielding – partial metal coating process by sputter for FCC EMI certification
- Small Size Antenna Integration – Chip antenna, Printed circuit antenna (under development)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Democratizing AI at the Endpoint, Brian Faith, CEO of QuickLogic:
QuickLogic was described as “a platform company that enables our customers to quickly and easily create intelligent ultra-low power endpoints to build a smarter, more connected world.” The company was founded in 1989, IPO in 1999, and now has a worldwide presence. Brian said they were focused on AI for growth markets including:
▪ Hearable/Wearable
▪ Consumer & Industrial IoT
▪ Smartphone/Tablet
▪ Consumer Electronics
AI and edge computing are coming together such that data analytics is moving from the cloud to the edge to the IoT endpoint (eventually). However, there are trade-offs for where computing should be located which are based on the application type. Some considerations include:
▪Applications latency & power consumption (battery life) requirements
▪Data security can be a factor
▪Local insights are trivial and non-actionable
▪Smart Sensors => rich data => actionable if real-time
▪Network sends insightful data (less bandwidth needed)
▪Cloud focuses on aggregate data insights and actions
AI Adoption Challenges:
1. Resource-Constrained Hardware:
▪ Can’t just run TensorFlow
▪ Limited SRAM, MIPS, FPU / GPU
▪ Mobile or wireless battery/power requirements
2. Resource-Constrained Development Teams:
▪ Embedded coding more complex & fragmented than cloud PaaS
▪ Scarcity of data scientists, DSP, FPGA and firmware engineers
▪ Limited bandwidth to explore new tools / methods
3. Lack of AI Automated Tools:
• Typical process: MATLAB modeling followed by hand coded C/C++
• Available AI tools focus on algorithms, not end-to-end workflows
• Per product algorithm cost: $500k, 6-9 months; often far greater
For Machine Learning (ML) good training is vital as is the data:
• Addresses anticipated sources of variance
• Leverages application domain expertise
• Includes all potentially relevant metadata
• Seeks optimal size for the problem at hand
ML Algorithms should fit within Embedded Computing Constraints:
Endpoint Inference Models:
• Starts with model appropriate to the problem
• Fits within available computing resources with headroom
• Utilizes least expensive features that deliver desired accuracy
SensiML Toolkit:
• Provides numerous different ML and AI algorithms and automates the selection process
• Leverages target hardware capabilities and builds models within its memory and computing limits
• Traverses library of over 80 features to optimize selection to best features to fit the problem
A Predictive Maintenance for a Motor Use Case was cited as an example of AI/ML:
Challenges:
▪Unique model doesn’t scale across similar motors (due to concrete, rubber, loading)
▪ Endpoint AI decreases system bandwidth, latency, power
Monitoring States:
▪ Bearing / shaft faults
▪ Pump cavitation / flow inefficiency
▪ Rotating machinery faults
▪ Seismic / structural health monitoring
▪ Factory predictive maintenance
QuickLogic aims to democratize AI-enabled SoC Design using SiFi templates and a cloud based SoC platform with a goal of a custom SoC in 12 weeks! In 2020 the company plans to have: an AI Software Platform, SoC Architecture, and eFPGA IP Cores. Very impressive indeed, if all that can be realized.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Empowering the Edge Panel Session:
Mike Noonen of Mixed-Com chaired a panel discussion on Empowering the Edge. Two key points made was the edge computing is MORE SECURE than cloud computing (smaller attack surface) and that as intelligence (AI/ML/data processing) moves to the edge, connections will be richer and richer. However, no speaker or panelist or moderator defined where the edge actually is located? Is it on premises, the first network element in the access network, the mobile packet core (for a cellular connection), LPWAN or ISP point of presence? Or any of the above?

Mike Noonen of Mixed-Com leads Panel Discussion
Photo courtesy of GSA Global
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
After the conference, Mike emailed this to me:
“One of the many aspects of the GSA Silicon Summit that I appreciate is the topic/theme (such as edge computing). The speakers and panelists addressing the chosen theme offer a 360 degree perspective ranging from technical, commercial and even social aspects of a technology. I always learn something and gain new insights when this broad perspective is presented.”
I couldn’t agree more with Mike!
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
V2X –Vehicle to Everything connectivity, Paul Sakamoto, COO of Savari:
V2X connectivity technology today is based on two competing standards: DSRC: Dedicated Short Range Communications (based on IEEE 802.11p WiFi) and C-V2X: Cellular Vehicle to Everything (based on LTE). Software can run on either, but the V2X connectivity hardware is based on one of the above standards.
DSRC: Dedicated Short Range Communications:
- Legacy Tech – 20 years of work, Low Latency Performance Range and reliability
- No carrier fees; minimize fixed cost
- Infrastructure needs; how to pay?
- EU Delegate Act win, but 5GAA is contesting
C-V2X: Cellular Vehicle to Everything:
- Developed from LTE-Big Money Backing
- Cellular communications history; good range and reliability
- Carrier fees required; subsidy for fixed costs
- Mix in with base stations to amortize costs
- China has chosen it as part of the government’s 5G plan
V2X Challenge: Navigate the Next 10 Years:
For mobile use, the main purpose is safety and awareness:
• Tight message security
• Low latency (<1ms)
• Needs client saturation
• Short range
For infrastructure, the main purpose is efficiency and planning:
• Tight message security
• Moderate latency (~100ms)
• Needed where needed
• Longer range
In closing, Paul said V2X is going to be a long raise with many twists and turns. Savari’s strategy is to be ”radio agnostic,” use scalable computing and scalable security elements, have a 7-10 year business plan with a 2-3 year product development cycle, and be ready to pounce at any inflection point (which may mean parallel developments).
May 20, 2020 Update:
ITU-R WP 5D will produce a draft new Report ITU-R M.[IMT.C-V2X] on “Application of the Terrestrial Component of IMT for Cellular-V2X.”
3GPP intends to contribute to the draft new Report and plans to submit relevant material at WP 5D meeting #36. 3GPP looks forward to the continuous collaboration with ITU-R WP 5D for the finalization of Report ITU-R M.[IMT.C-V2X].
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
OpenSignal reports on 5G Speeds and 4G LTE Experience in South Korea & Other Countries
Introduction:
South Korea wireless telcos have all deployed pre-standard versions of “5G,” based on 3GPP Release 15 NR NSA. That relies on a “LTE anchor” for signaling, mobile packet core, etc. Are those “5G” speeds significantly greater than 4G LTE Advanced Pro which AT&T claims is 5GE?
Opensignal has published what it says is the first “real analysis” of 5G download speeds as of June 20, 2019. Their latest report (June 2019) is on the performance of various 4G LTE wireless carriers and devices in South Korea.
5G Speeds in South Korea:
The market research firm reveals that the average 5G download speeds in South Korea (for the Samsung S10 5G and LG Electronics V50 ThinQ 5G) is 111.8 Mbps (see illustrations below), or 48% faster than comparable recent 4G smartphones, and 134% faster than other 4G LTE phones.
While those average 5G speeds outpace what 4G devices obtain, Opensignal’s results show that those averages track well behind the maximum capabilities supported by 5G in South Korea. The vast majority of South Korean 5G smartphone users currently have either the Samsung S10 5G or LG V50 smart phone. Therefore, we compared these 5G users with owners of 4G flagship smartphone from those two brands released in 2018 and 2019, this includes: Samsung S9, S9+, Note 9, S10e, S10, S10+ and LG G7 range, V40, and G8.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Opensignal lists maximum 5G download speeds of 1.2 Gbit/s in the U.S. and 988 Mbit/s in South Korea.
“While 1.2 Gbps is the maximum (download) speed experienced by Opensignal users in real-world conditions, Opensignal has seen speeds as high as 1.5 Gbps in the U.S. using our software but in test conditions that do not reflect the real-world experience.”
Currently, 5G smartphone users connect to both a 4G spectrum band and a (3GPP Release 15) 5G New Radio (NR) band simultaneously in what is called Non-Standalone Access (NSA) mode. Effectively, the system is using 5G for raw download bandwidth, but uses 4G for other network functions. When operators launch services based on Standalone Access, 5G smartphones will be able to connect exclusively to a 5G NR signal and latencies should decrease significantly, improving the experience for consumer applications such as online multiplayer games like Fortnite or PUBG, as well as internet-based voice communication like FaceTime, Tango, WhatsApp, KakaoTalk, LINE, etc. Opensignal expects the experience of 5G users to change during the course of 2019 as 5G’s coverage improves and vendors resolve initial 5G problems.
While there is a significant increase in the average download speeds experienced by 5G smartphone users, both upload speeds and latency — a measure of the responsiveness of the network — are similar between 4G smartphone users and 5G smartphone users. This upload and latency finding is what Opensignal would expect at this early stage of the 5G era because initial 5G technology does not yet seek to improve either characteristic.
As vendors fix 5G teething issues and refine their solutions, peak and average 5G speeds will improve. And, while some 5G frequency bands are not available in particular countries yet – for example 3.5Ghz in the U.S., mmWave in Europe – they will be over the next few years and experience gained from other countries will help carriers improve these later 5G roll outs.
4G LTE Speeds in South Korea and other countries:
South Korea was the only country where smartphone users enjoyed average mobile Download Speeds over 50 Mbps, although Norway was close behind with 48.2 Mbps. Then there was a bit of a drop in speeds to the next two countries, Canada and the Netherlands, where OpenSignal measured Download Speed Experience at just over 42 Mbps. The remaining six of the top 10 markets scored in the 33-40 Mbps range. The global average score of the 87 countries analyzed was 17.6 Mbps — barely a third of the top score.
Canada’s impressive third place is little surprise. Users experienced over 35 Mbps in Download Speed Experience, while speeds of over 60 Mbps weren’t uncommon in the country’s biggest cities.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
4G LTE Mobile Experience in South Korea:
OpenSignal said there was a wide variety of of their metrics in Download Speed Experience, with average speeds ranging from over 50 Mbps to less than 2 Mbps. There were 13 countries with Download Speed Experience scores over 30 Mbps, while 35 of the 87 markets measured fell into the 10-20 Mbps range, and 20 scored under 10 Mbps.
For 4G Availability, LG U+ achieved a near-perfect score. All three South Korean wireless operators were able to deliver a 4G signal to their users more than 95% of the time, putting them among the global elite in 4G reach. LG U+ went further. Its 4G Availability score of 99.5% means that there was practically no instance where our users couldn’t find a 4G connection during our data collection period.
South Korea rates highly in Video Experience. U+ and SK telecom both landed in the Very Good range (65-75 in our 100-point scale) in Video Experience, while KT was less than a point shy of achieving the same rating. That indicates that the consumer Video Experience in South Korea is commendable, exhibiting short load times and little stalling during playback. But South Korea’s operators didn’t score as highly in Video Experience as operators in many other countries, despite their superiority in most of our other metrics. Extremely fast speeds and ubiquitous 4G reach don’t always translate into an Excellent consumer Video Experience.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
Opensignal believes that these early results will improve and change as 5G matures. The firm notes that early 5G networks, like those in South Korea, use the non-standalone 5G spec (3GPP Release 15 NR NSA), which relies on the 5G data plane for downloads, but utilizes 4G LTE for control plane functions.
Opensignal says that average speeds will improve as standalone 5G is deployed and more 5G frequency bands are used.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.opensignal.com/reports/2019/06/southkorea/mobile-network-experience
Verizon CTO Upbeat on 5G Millimeter Wave vs Lack of mid band spectrum?
Millimeter wave spectrum “opens up so many possibilities,” said Verizon Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer Kyle Malady at an investor conference today. Malady made his comments at the Wells Fargo Telecom 5G Forum, which was webcast. “The cloud will go closer and closer and closer,” he said without providing any rationale or support for that statement.
The latest pre-standard 5G technology was designed to support speeds of a gigabit or more, along with lower-latency 9via 3GPP Release 16 not yet completed) and other attributes. However, getting the highest wirelessspeeds requires wide swaths of spectrum that are nearly impossible to come by in frequency bands traditionally used for cellular service. Wide swaths of spectrum are available in high-frequency millimeter wave bands – the downside is that range is not as great as with lower-frequency bands which will require many more small cells in a given geographical area.
5G pioneers AT&T and Verizon used millimeter wave for their initial deployments, but as Sprint and T-Mobile get into the game or make plans to do so, they have touted their ability to quickly cover broad areas by using lower-frequency spectrum, although that didn’t stop T-Mobile from spending more than $842 million to obtain millimeter wave spectrum in the recent auctions. Likewise, AT&T and Verizon have said they expect to deploy 5G in lower-frequency bands as well as in the millimeter wave band.
Verizon 5G Millimeter Wave
Nevertheless, Verizon executives get most fired up when they talk about the millimeter wave band.
Malady offered an interesting data point to support his millimeter wave enthusiasm. Before obtaining millimeter wave spectrum through the acquisition of Straight Path, Verizon had amassed licenses for an average of 160 MHz of spectrum in all bands nationwide. In comparison, the company used four segments, apparently each comprised of 100 MHz, for a total of 400 MHz of millimeter wave spectrum to support its initial mobile 5G launches in Chicago and Minneapolis. And according to Malady, “we’re working on bringing [that] to eight” segments.
Malady didn’t discuss the speeds Verizon is experiencing with mobile service, but he noted that some customers are obtaining gigabit speeds using fixed wireless 5G service in the millimeter wave band, which Verizon has launched in four markets.
AT&T has said it has seen speeds of 1.2 Gbps in mobile 5G trials using a 400 MHz channel over a distance of 150 meters. More on AT&T’s mmWave spectrum holdings here.
Millimeter wave distance limitations are driving a change in network topology, Malady noted. “As the network [becomes] flattened, the antennas [are] smaller and lower,” he explained. “Wireless becomes fiber with antennas hanging off of it.”
As Verizon builds out more fiber to support this model, the fiber also can be used by the company’s other business units, he added.
There may be one additional requirement before 5G can reach its full potential, and Malady discussed that as well. He pointed to the example of police using facial recognition to help find an abducted person by comparing a photo with numerous public cameras, then identifying the closest officer to the abductee’s location. Applications such as that will require processing power located closer to the network edge.
References:
Verizon CTO: 5G Millimeter Wave “Opens Up So Many Possibilities”
https://www.verizon.com/about/our-company/5g/what-millimeter-wave-technology
AT&T owns >630 MHz nationwide of mmWave spectrum + HPE partnership for Edge Networking & Computing
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/verizon-ceo-mmwave-early-days-but-engineering-team-good-it
https://www.lightreading.com/mobile/5g/ve
rizon-mmwave-is-not-a-coverage-spectrum-for-5g/d/d-id/750980
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Meanwhile, carriers and analysts say that a lack of mid-band spectrum is delaying the deployment of wireless services. The Federal Communications Commission has recently proposed allowing carriers to share parts of the Educational Broadband Service spectrum in this range, a plan that a number of educational groups oppose.
The Wall Street Journal (tiered subscription model)
Cignal AI: Japan’s Optical Hardware Growth Soars in 1Q2019; North America Remains Weak
by Scott Wilkinson and Andrew Schmitt of Cignal AI (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Metro Bandwidth Growth Outpaces Long Haul; North America Remains Weak
Japan continued its recent hot streak as 1Q2019 marked the fourth quarter in a row of growth with an extraordinary 82% increase, according to the most recent (1Q2019) Optical Hardware Report from research firm Cignal AI. Japan registered an extraordinary 82% year-over-year increase in optical networking hardware sales in the first quarter of 2019. Prime beneficiaries were domestic suppliers NEC, Mitsubishi and Fujitsu along with Ciena and Nokia, all of which posted significant gains during the quarter.
“The exceptional optical market growth in Japan is the story to watch for 2019,” said Scott Wilkinson, Lead Analyst for Optical Hardware at Cignal AI. “Network operators have begun significant network rebuilds and expansions, and domestic as well as non-Japanese vendors continue to grow sales in the region at remarkable rates.”
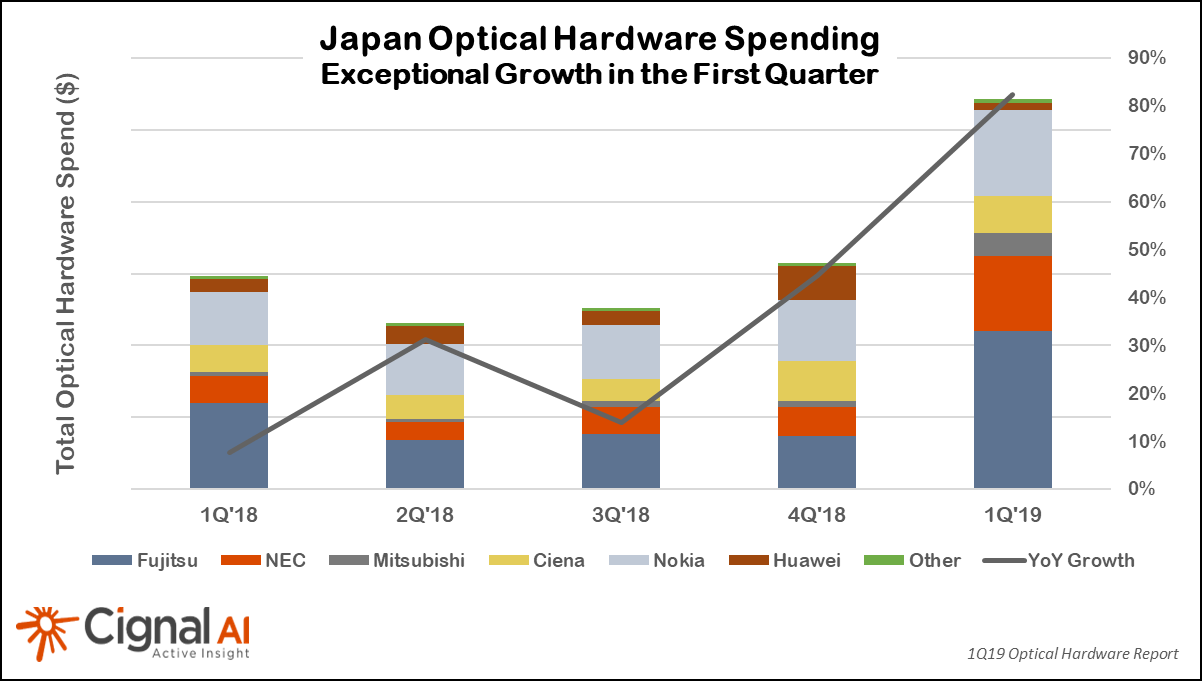
North American growth continued to disappoint as slow optical hardware spending among traditional telco operators obscured growth in sales to cloud and colo operators (e.g. multi-tenant data centers).
Additional key findings in the 1Q19 Optical Hardware Report:
- Metro Bandwidth Outpaces Long Haul – While long haul spending grew at a higher rate than metro, analysis reveals that metro bandwidth is growing more rapidly.
- Growth in China Decelerates – Growth in China moderated into the single-digits during 1Q19, as 2018’s high spending by Chinese carriers could not continue indefinitely.
- EMEA Posted Solid Gains – Both metro and long haul spending grew during the quarter, with growth led by both traditional and cloud & colo operators.
- CALA Continues Lackluster Performance –Q1 showed no improvement for the region. Relief may be coming, as vendors believe major carriers in the region will return to spending later this year.
Cignal AI’s Optical Hardware Report is issued each quarter and examines optical equipment revenue across all regions and equipment types. The analysis is based on financial results, independent research, and guidance from individual equipment companies. Forecasts are based on overall spending trends for equipment types within the regions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Cignal AI’s interactive Optical Hardware Superdashboard is available to clients of the Optical Hardware Report and provides up-to-date market data for real-time visibility on individual vendors’ results. Users can manipulate data online and see information in a variety of useful ways.
The Cignal AI Optical Hardware Report is published quarterly and includes market share and forecasts for optical transport hardware used in optical networks worldwide. In addition to the interactive tracker, the analysis includes an Excel database as well as PDF and PowerPoint summaries. Subscribers to the Optical Hardware Report also have access to Active Insight, Cignal AI’s real-time news service on current market events.
The report examines revenue for metro WDM, long-haul WDM and submarine (SLTE) equipment in six global regions and includes detailed port shipments by speed. Vendors in the report include Adtran, ADVA, Ciena, Cisco, ECI, Ekinops, Fiberhome, Fujitsu, Huawei, Infinera, Mitsubishi Electric, NEC, Nokia, Padtec, Tejas, Xtera, and ZTE.
Full report details, as well as articles and presentations, are available on the Cignal AI website.
About Cignal AI
Cignal AI provides active and insightful market research for the networking component and equipment market and the market’s end customers. Our work blends expertise from a variety of disciplines to create a uniquely informed perspective on the evolution of networking communications.
Cignal AI: Record Spending on Cloud Operator Optical Networks Drives Growth in 2018
AT&T owns >630 MHz nationwide of mmWave spectrum + HPE partnership for Edge Networking & Computing
Following the close of FCC Auction 102, AT&T won 24 GHz spectrum in 383 Partial Economic Areas (PEAs) for a nationwide average of 254 MHz. All of the licenses won were in the more valuable upper 500 MHz portion of the 24 GHz band, giving AT&T stronger nationwide coverage and additional spectrum depth and capacity in many top markets where demand is often greatest. In the top 10 markets alone, AT&T won nearly 286 MHz on average, including 300 MHz in 8 of those markets.
“We’re leading the nation in mobile 5G deployment and the large, contiguous block of spectrum we won in Auction 102 will be critical to maintaining that leadership,” said Scott Mair, president of AT&T Operations. “We’ve already been recognized for having the nation’s fastest1 and best2wireless network, and by further strengthening our spectrum position, we intend to build on our success. I’d like to congratulate and thank the FCC on the conclusion of another successful auction.”
The licenses it won cover all top 50 PEAs and 99 of the top 100 PEAs. When added to the mmWave spectrum AT&T already holds in the 39 GHz band, AT&T’s average spectrum depth in mmWave increased by two-thirds to more than 630 MHz nationwide.
AT&T will use the spectrum to bolster its mobile 5G strategy. AT&T was the first U.S. wireless carrier to introduce mobile 5G service. The company’s 5G service is currently available in parts of 19 cities – more than any other wireless carrier – with plans to reach parts of 29 cities by the end of 2019. In the first half of 2020, the company expects to have the best combination of mobile 5G, providing high speeds and low latency service over mmWave spectrum and nationwide 5G service over “sub-6” spectrum.
The company spent about $980 million to win an average of 254 MHz of 24 GHz spectrum in 383 out of about 400 total partial economic areas (PEAs) nationwide. The winnings supplement the company’s previous millimeter wave spectrum holdings in the 39 GHz band.
The key appeal of millimeter wave spectrum is that large swaths of it are available, enabling the spectrum to support the highest speeds – although service deployed in the millimeter wave band has less range than service deployed in lower-frequency bands. AT&T’s initial 5G deployments have been in the millimeter wave band, but the company eventually expects to use a combination of millimeter wave and lower frequency spectrum to support 5G.
The average 630 MHz of millimeter wave spectrum that AT&T now holds in key markets would appear to position the company well to support high speeds, as the company previously achieved speeds of 1.2 Gbps in trials using a 400 MHz channel over a distance of 150 meters.
The company also has said that it has seen speeds as high as 400 Mbps on its commercial 5G network, although it cautioned that average speeds are lower.
AT&T also noted in a press release that the licenses it won in the 24 GHz band were in the “valuable” upper 500 MHz of the 24 GHz band and that the licenses cover all top 50 PEAs and 99 of the top 100 PEAs.
Late last year, AT&T was the first U.S. carrier to launch mobile 5G service, although the company did not have a smartphone available for use with the network until last week. Customers initially used 5G-capable Wi-Fi hotspots that work with virtually any smartphone to access the network, which now covers parts of 19 cities. AT&T plans to expand to parts of 10 more cities by the end of 2019 and to launch nationwide service in the first half of 2020.
The company’s initial target for 5G service is business customers – a decision that enabled the company to plan its initial 5G millimeter wave deployments for areas in which key business customers were located. The company also has said that it hopes to command a premium for 5G service in comparison with what it charges for earlier-generation services – a strategy that U.S. wireless carriers have not used previously.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2019/att_enhances_spectrum_position.html
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, AT&T said it will work with Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) to help businesses harness powerful edge capabilities. The two companies have agreed to a go-to-market program to accelerate business adoption of edge connections and edge computing.
Edge computing marks a giant leap forward in providing faster processing and potentially enhanced security for business applications. AT&T Multi-access Edge Compute (MEC) Services enable businesses to take advantage of AT&T cellular coverage – including 5G as it becomes available – as well as new capabilities to manage cellular traffic through virtual network functions. HPE Edgeline Converged Edge Systems help create use cases where applications can reside on premises for lower latency processing.
“AT&T’s software-defined network, including our 5G network, combined with HPE’s intelligent edge infrastructure can give businesses a flexible tool to better analyze data and process low-latency, high-bandwidth applications,” said Mo Katibeh, Chief Marketing Officer, AT&T Business. “Bringing compute power closer to our network helps businesses push the boundaries of what is possible and create innovative new solutions.”
Enabling edge computing is a core tenet in AT&T’s strategy to help businesses get the most out of 5G. This is an important step in bringing these technologies to scale, so businesses can continue to transform how they will use networks in the 5G era.
“HPE believes that the enterprise of the future will need to be edge-centric, cloud-enabled and data-driven to turn all of its data into action and value,” said Jim Jackson, Chief Marketing Officer, HPE. “Our go-to-market alliance with AT&T, using HPE Edgeline Converged Edge Systems, will help deliver AT&T MEC services at scale to help our customers more quickly convert data into actionable intelligence, enabling unique digital experiences and smarter operations.”
https://about.att.com/story/2019/att_and_hpe.html
Ericsson announces 5G standalone NR software and 2 new Massive MIMO radios
Ericsson released a software update to its cellular base station hardware that the vendor says will markedly improve 5G network performance by increasing its capacity and coverage, especially indoors and in hard-to-reach areas. The upgrade will support a 3GPP Release 15 specification of Standalone 5G New Radio (NR) which, unlike NSA (Non Stand Alone), does not need 4G LTE infrastructure such as signalling, mobile packet core and network management.
Ericsson says its 5G standalone NR software makes for a new network architecture, delivering key benefits such as ultra-low latency and even better coverage (says the company).
Ericsson also announced what it calls inter-band NR carrier aggregation, which is software that extends the coverage and capacity of NR on mid bands and high bands when combined with NR on low bands. Ericsson claims the software can help improve speeds in areas with poor coverage and in indoor environments.
Ericsson says it is evolving its cloud solution with an offering optimized for edge computing to meet user demand. This will enable service providers to offer new consumer and enterprise 5G services such as augmented reality and content distribution at low cost, low latency, and high accuracy.
Fredrik Jejdling, Executive Vice President and Head of Business Area Networks, Ericsson, says: “We continue to focus our efforts on helping our customers succeed with 5G. These new solutions will allow them to follow the 5G evolution path that fits their ambitions in the simplest and most efficient way.”
The new standalone 5G NR software can be installed on existing Ericsson Radio System hardware. Coupled with Ericsson’s 5G dual-mode Cloud Core solutions, the new products are aimed at opening new business opportunities for service providers – especially having established an architecture that facilitates agility, provides advanced support for network slicing and enables the speedy creation of new services.
Most pre-standard “5G” network operators have deployed NSA (Non Stand Alone) using LTE infrastructure. Once the 5G coverage has been established, they can now also deploy standalone.
Low bands will play a key role in cost-efficiently extending the coverage provided by 5G deployments to date. Ericsson has also launched Inter-band NR Carrier Aggregation – a new software feature that extends the coverage and capacity of NR on mid- and high bands when combined with NR on low bands. This will improve speeds indoors and in areas with poor coverage.
Two new Massive MIMO radios have also been added to the Ericsson Radio System mid-band portfolio, allowing service providers to build 5G with precision: AIR 1636 for wider coverage which provides optimized performance on longer inter-site distances; and AIR 1623 for easy site build with minimal total cost of ownership.
 Ericsson’s 5G hardware is now being used in networks all over the world. Image courtesy of Ericsson
Ericsson’s 5G hardware is now being used in networks all over the world. Image courtesy of Ericsson
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5G (with low latency as per 3GPP Release 16 and later- IMT 2020) will enable augmented reality, content distribution and gaming, and other applications that require low latency and high bandwidth to perform with accuracy. To help service providers meet these requirements and offer new consumer and enterprise services, Ericsson is evolving its cloud solution with the launch of Ericsson Edge NFVI (Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure), optimized for the network edge.
A compact and highly efficient solution, Ericsson Edge NFVI is part of the end-to-end managed and orchestrated distributed cloud architecture, which makes it possible to distribute workloads, optimize the network and enable new services in the cloud.
Ericsson is also launching the Ericsson partner VNF Certification Service, a partner certification program for virtual network functions (VNF). The service is open to all VNF vendors and grants a certification on the Ericsson NFVI platform using Ericsson Labs. This will create an ecosystem with a shorter time-to-market for working with partners and applications.
Industry Analyst Hugh Ujhazy, Vice President, IOT & Telecommunications at International Data Corporation (IDC), Asia Pacific, says: “Ericsson’s latest 5G offerings equip service providers with an even broader 5G portfolio by adding the Standalone NR option. The series of solutions being added to the Ericsson 5G platform will allow service providers to deploy 5G sensibly and address new business opportunities with full flexibility. What you get is faster, cheaper, makes better use of existing assets and with fewer truck rolls. That’s pretty cool.”
Dana Cooperson, Research Director, Analysis Mason, says: “Improved E2E 4G/5G network architecture flexibility and new 5G use cases require distribution to the edge. To be successful in providing new services it is essential to have a cost-efficient platform for distributed workloads. Ericsson’s initiative with the Edge NFVI solution and distributed cloud architecture will contribute to service providers’ success in 5G.”
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/2019/6/ericsson-launches-enhanced-5g-deployment-options
AT&T to Focus new WarnerMedia Innovation Lab on 5G Experiences
AT&T’s WarnerMedia Innovation Lab in New York City will serve as a testing ground for leveraging 5G to provide innovative storytelling through advertising, according to company executives. The 20,000 square foot lab is being built in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan (this author’s home town) and is scheduled to open in early 2020. The WarnerMedia lab will also draw consumer insights and technology from AT&T’s Xandr ad sales unit.
“By working across AT&T, we’re able to combine the latest in 5G technology with immersive content experiences and cutting-edge advertising capabilities,” said David Christopher, president of AT&T Mobility and Entertainment. “The WarnerMedia Innovation Lab will be a space where developers, creators and visitors will be inspired to push the boundaries of entertainment, all powered by the company that first introduced the U.S. to the power of mobile 5G.”
“Storytelling is in our company’s DNA and part of that experience is how the content is enjoyed, including advertising. The Lab is a critical part of our testing and learning on the new experiences in advertising that we will be rolling out to market,” said Dan Reiss, head of advanced advertising and branded content at WarnerMedia Ad Sales.
“The Lab is more than a technology incubator, but also a dream factory for us to create the wonderment that fans have come to love and expect from WarnerMedia,” said Jesse Redniss, GM for WarnerMedia Innovation Lab, in a statement. He described the location as a place where WarnerMedia will “flex the best of [its] creative storytelling capabilities combined with cutting edge technology from AT&T and our partners to deliver experiences that will be talked about for a lifetime.”
“Every day, Xandr looks for new innovative ways to help marketers and create a better viewing experience for consumers,” said Kirk McDonald, CMO, Xandr. “Working with our colleagues at AT&T Communications and WarnerMedia, we are uniquely positioned to develop new advertising innovations that engage consumers and provide integral feedback for marketers and brands. The WarnerMedia Innovation Lab will accelerate the adoption of new advertising formats and provide an environment to showcase our collaborative work.”

Image Courtesy of WarnerMedia
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T stated the new lab will be “[unveiling] a new balance in the relationship between advertising, technology and content” and said that its work would include mixed reality and/or virtual reality applications, “5G uses that enhance new advertising capabilities,” and better user experiences related to advertising.
Architectural firm Design Republic will head the design of the project, with work beginning this summer with completion scheduled for early 2020.
References:
https://www.broadcastingcable.com/news/at-t-focuses-innovation-lab-on-5g-experiences
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20190617/5g/warnermedia-lab-to-be-outfitted-with-att-5g
https://www.fiercevideo.com/tech/at-t-details-new-5g-equipped-warnermedia-innovation-lab
Paul Budde: What Does ‘Peak Telecom’ Mean for 5G? Asian Telecoms Maturity Index
By Paul Budde, edited by Alan J Weissberger
Peak Telecom and 5G:
“Peak telecom” is described as the maximum point of expansion reached by the traditional telecommunications industry before the internet commoditized the industry to a utility (dumb) pipe.
I thought of this when I read the recent outcomes of the famous Ericsson Consumer Lab survey. The company used the results of the survey to counteract market criticism regarding the viability of the telco business models in the deployment of 5G.
It will come as no surprise that Ericsson, as a manufacturer of 5G gear, has given the report a positive spin. However, I remain skeptical about the short-term business models for the deployment of 5G (so does the editor). Once full deployment happens over the coming decade, I certainly can see long-term opportunities. These will revolve around content and apps as well as areas such as IoT in smart homes, cities and energy. However, the question is, will this lead to new financial opportunities for the telcos? Peak telecom questions such an outcome.
What exactly do these broader 5G opportunities mean for the telecommunications operators — the companies who have to build the infrastructure? It is here that we can see that we have reached peak telecom. For several years now, we have seen that growth in the telecom industry is rather stagnant. Profits are still being made but mostly generated by lowering costs. For example, new telecom access speeds are provided at no extra cost to the users. Basically, consumers are getting more for the same price.
There has continuously been the promise of new revenues that could be generated through a range of new telecoms development (internet, broadband, smartphones). The telcos have, however, largely failed to move into the content/app market where the new profits are occurring. Companies such as Amazon, Facebook, Google, Alibaba, Tencent and Netflix have been the primary commercial beneficiaries of these developments.
The Ericsson report mentions that mobile access in congested areas and in mega-cities is becoming a problem and that 5G will assist here. I agree, but will customers pay extra for it?
It also mentions opportunities for 5G to be an alternative to fixed broadband and for it to become a key technology in fixed wireless networks. There certainly will be niche market opportunities here, but this is a highly price-sensitive market. The economics of mass fixed infrastructure favors it over mobile infrastructure. Any gains here will basically be a substitution of a fixed service they already provide, so the overall net gain for the industry will be neglectable.
The report indicates that 20% of smartphone users are prepared to pay a premium for 5G. The current commercial 5G service in South Korea is charging a meager 10% premium. No doubt, in coming years, through competition even that premium will disappear.
The report indicates that consumers expect new innovation such as foldable phones, VR glasses, AI, 360-degree camera, robotics and so on. All true but it all depends how affordable these products and service will be and again who will develop these next “must-have” products? Here, also, the telcos will most likely be missing out.
I fully agree with the report’s assessment that we have to look at 5G over the more extended period. As mentioned, there are good reasons to believe that once full deployment exists, it will open up many new business opportunities.
However, will this promise be enough for telcos to make the substantial upfront investments that are needed? This without a clear indication if they can extract any significant new revenues from 5G? The more likely scenario is that the digital giants are going to be the ones that will reap the real profits of those innovations.
I stick to my argument that the key reason for the telcos to move into 5G is because of network efficiencies, which lead to lower costs.
–>This is absolutely critical in this peak telecom market.
To end on a more positive note for the industry, there is the first mover advantage with short term premium price opportunities for those who can tap into the early adopters’ market. There is always a group of users who simply do want to have the newest of the newest, whatever the price. The size of this market varies — depending on how “hot” the new product is seen by this market segment — and could be anywhere between 10% and 25%.
This is certainly attractive for the telcos as it allows them to recoup some of the initial investment rapidly. In relation to mobile products and services, this mainly relates to “must have” gadgets and, in particular, the smartphone. The current price (in Korea) of a 5G phone is approximately US$1,500 (AU$2,153), without any outstanding features.
The lack of attractive smartphones could be another negative for some of the early adopters. Time will tell.
Asia Telecoms Maturity Index:
This index, created by Paul Budde, analyzes the Broadband, Mobile and Fixed Line markets of a specific country as well as a range of parameters to help you evaluate the economic development of a country.
BuddeComm’s Telecoms Maturity Index measures and ranks the maturity of a country’s telecoms industry on a scale of 1 to 100. All countries are placed into one of three categories: ‘Market Leaders’, ‘Market Challengers’ and ‘Market Laggards’, according to their Market Index score.
The Telecoms maturity index is used to fuel regional analysis, it provides a unique approach and allows a comprehensive country vs region comparison. 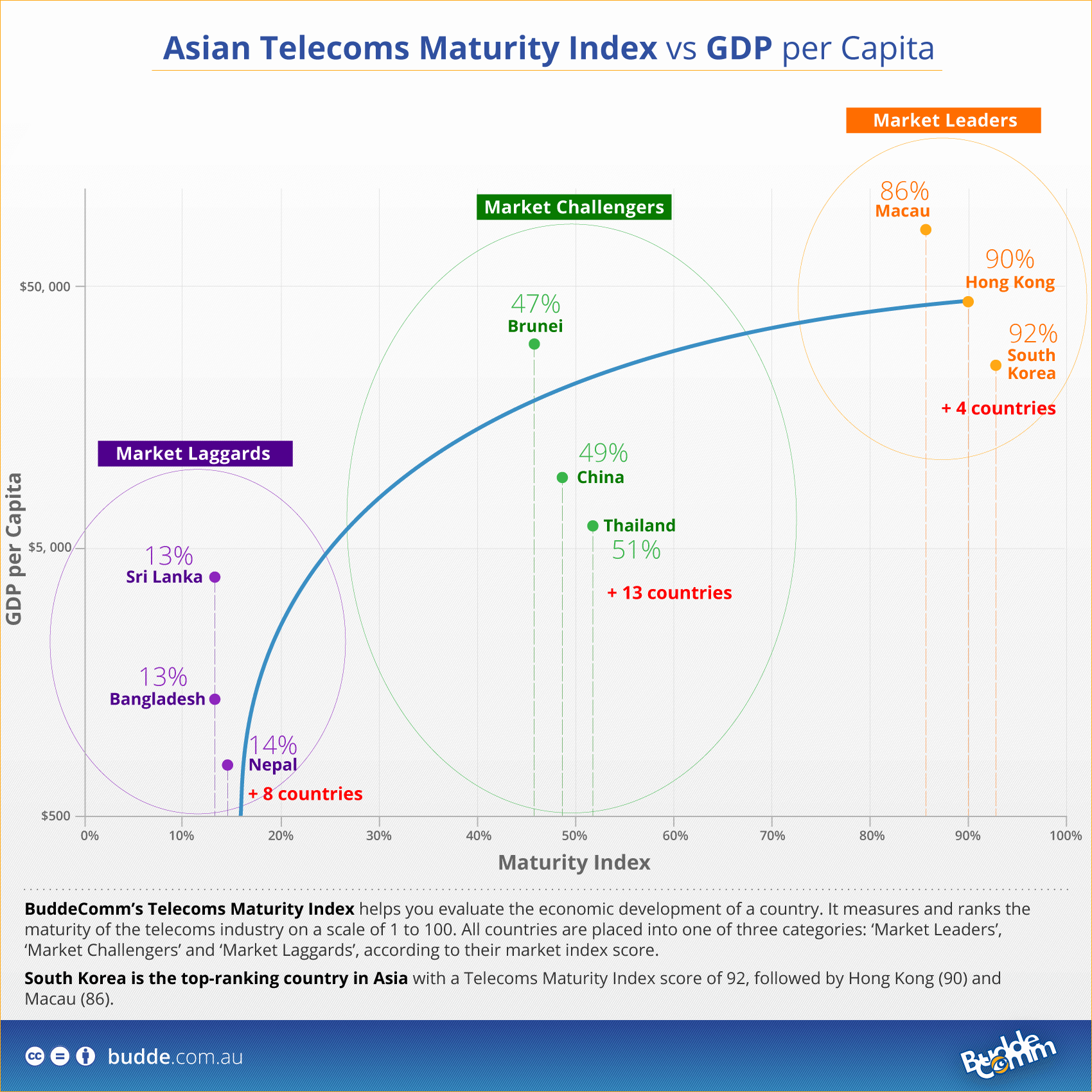
Asia – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
Asian countries in the Market Leaders category have fixed broadband penetrations in the range of 25% and 42% and mobile broadband penetrations in the range of 98% and 135%. South Korea is the top-ranking country in Asia with a Telecoms Maturity Index score of 92, followed by Hong Kong (90) and Macau (86).
Find more information on the Asian telecoms market or Contact Us.
For more information on BuddeComm’s Telecoms Maturity Index, see:
- Africa – Fixed Broadband Market – Statistics and Analyses
- Africa – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
- Asia – Fixed Broadband Market – Statistics and Analyses
- Asia – Mobile Infrastructure and Mobile Broadband
- Asia – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
- Asia – Telecom Forecasts
- Europe – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
- Latin America – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
- Middle East – Mobile Infrastructure and Mobile Broadband
- Middle East – Mobile Network Operators and MVNOs
https://www.budde.com.au/Research/Buddecomm-Telecoms-Maturity-Index
Who Stole 5G Technology? Huawei ban has huge impact on semiconductor industry
NOTE: There are no U.S. cellular equipment manufacturers. The only two in the west are Ericcson and Nokia- both based in Europe. However, U.S. based Qualcomm has been developing 5G silicon and is the only 5G (fabless) semiconductor vendor in the U.S. They will likely have an IMT 2020 compliant chip set as the company regularly attends ITU-R WP 5D meetings. The only other 5G merchant market semiconductor company we know of is Taiwan based MediaTek. Samsung and Huawei have developed 5G silicon but are using it ONLY for their own devices- not sold to merchant semiconductor market.
The only U.S. semiconductor companies that we know of that make their own chips are Intel and Micron.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IHS Markit says Huawei fall- out on memory market is huge:
Huawei in recent years has carved out prominent positions in the global smartphone and mobile infrastructure markets (not to mention fiber optics infrastructure and IT markets). In 2018, Huawei rose to take second place in the smartphone business, with 206.1 million shipments, according to the IHS Markit Smartphone Intelligence Service. This put it just slightly ahead of Apple, at 204.7 million.
In 2017, the company became the leader in the worldwide mobile infrastructure equipment market, surpassing Ericsson. Huawei has retained the top position and rose to account for nearly one-third of the market, with a 31 percent share of global revenue in 2018, as reported by the IHS Markit Mobile Infrastructure Intelligence Service.
Huawei’s market position has translated directly into purchasing power, with the company ranking as the world’s fourth-largest OEM semiconductor buyer in 2018. Huawei spent $15.9 billion on semiconductors in 2018, according to the IHS Markit OEM Semiconductor Spending & Design Activity Intelligence Service. Memory represents a considerable slice of that spending, with the company buying $1.7 billion worth of DRAM and $1.1 billion worth of NAND flash memory for the year.
In the memory business, the wireless communications market was the second-largest global market for DRAM in 2018, following computer platforms, with revenue of $21.3 billion. Wireless was also the second largest market for NAND flash memory after computers, with revenue of $14.6 billion in 2018. HDD and solid-state drive (SSD) products enjoy major usage in the enterprise segment where Huawei operates. The enterprise market generated 72.8 million HDD unit shipments in 2018, while SDD demand amounted to 34 million, according to the IHS Markit HDD and SDD Storage Intelligence Service. For Micron and Western Digital, the revenue lost because of the ban is not likely to be replaced easily or quickly.
IHS-Markit says No Winners:
While the ban was ostensibly designed to penalize Huawei and benefit the U.S. tech industry, the reality is the pain will be felt by companies on both sides of the Pacific, affecting key U.S. suppliers along with Huawei.





