Ericsson
U.S. Network Operators and Equipment Companies Agree: 5G CAPEX slowing more than expected
We noted in a recent IEEE Techblog post that the 5G spending slowdown in the U.S. is broader than many analysts and executives expected. Well, it’s worse than that! The previously referenced negative comments from the CEO of Crown Castle, were corroborated by American Tower last week:
“The recent pullback was more abrupt than our initial expectations,” said Rod Smith, the CFO for cell tower firm American Tower, during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha. Smith was discussing the reduction in US operator spending on 5G, a situation that is now cutting $40 million out of American Tower’s margin expectations. “The initial burst of 5G activity has slowed down,” agreed the financial analysts at Raymond James in a note to investors following the release of American Tower’s earnings.
Cell tower giant SBA Communications said it too is seeing the broad pullback in spending that has affected its cell tower competitors (i.e. American Tower and Crown Castle). But the company’s management sought to reassure investors with promises of continued growth over the long term. During their earnings call, SBA executives said they expect activity to increase next year as T-Mobile looks to add 3.45GHz and C-band spectrum to its network, and as Dish Network restarts its network buildout.
The two largest 5G network equipment vendors that sell gear in the U.S. are seeing similar CAPEX cutbacks. “We see some recovery in the second half of the year but it will be slower than previously expected,” Nokia CEO Pekka Lundmark said earlier this month during his company’s quarterly conference call, in response to a question about the company’s sales in North America. His comments were transcribed by Seeking Alpha. Ericsson’s CEO, Borje Ekholm, is experiencing similar trends: “We see the buildout pace being moderated,” he said of the North American market, according to a Seeking Alpha transcript
AT&T’s CFO Pascal Desroches confirmed the #1 U.S. network operator is slowing its network spending. “We expect to move past peak capital investment levels as we exit the year,” he said during AT&T’s quarterly conference call, as per a Seeking Alpha transcript. AT&T’s overall CAPEX would be $1 billion lower in the second half of 2023 when compared with the first half of this year due to greatly reduced 5G network build-outs.
“This implies full year capex of ~$23.7 billion, which management believes is consistent with their prior full year 2023 capex guidance of ‘~$24 billion, near consistent with 2022 levels’ and includes vendor financing payments,” wrote the financial analysts at Raymond James in their assessment of AT&T’s second quarter results, citing prior AT&T guidance.
“Although management declined to guide its 2024 outlook, it has suggested that it expects capital investments to come down as it progresses past the peak of its 5G investment and deployments. We believe the trends present largely known CY23 [calendar year 2023] headwinds for direct 5G plays CommScope, Ericsson and Nokia. Opportunities from FWA [fixed wireless access] might provide modest offsets and validate Cambium’s business. AT&T’s focus on meeting its FCF [free cash flow] targets challenge all of its exposed suppliers, which also include Ciena, Infinera and Juniper,” the financial services firm added.
Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg told a Citi investor conference in January that CAPEX would drop to about $17bn in 2024, down from $22bn in 2022″ “We continue to expect 2023 capital spending to be within our guidance of $18.25 billion to $19.25 billion. Our peak capital spend is behind us, and we are now at a business-as-usual run rate for capex, which we expect will continue into 2024,” explained Verizon CFO Tony Skiadas during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha.
“After years of underperformance, perhaps the best argument for Verizon equity is that expectations are very low. They are coming into a phase where capex will fall now that they’ve largely completed their 5G network augmentation. Higher free cash flow will flatter valuations, but it will also, more importantly, lead to de-levering first, and potentially even to share repurchases down the road,” speculated the analysts at MoffettNathanson in a research note to investors following the release of Verizon’s earnings.

T-Mobile USA had previously said its expansive 5G build-out had achieved a high degree of scale and it would reduce its capex sharply starting in 2023.”We expect capex to taper in Q3 and then further in Q4,” said T-Mobile USA’s CFO Peter Osvaldik during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha. He said T-Mobile’s capex for 2023 would total just under $10 billion. T-Mobile hopes to cover around 300 million people with its 2.5GHz midband network by the end of this year. Afterward, it plans to invest in its network only in locations where such investments are necessary.
Similarly, Verizon and AT&T are completing deployments of their midband C-band 5G networks, and will slow spending after doing so. That’s even though neither telco has deployed a 5G SA core network which involves major expenses to build, operate and maintain.
Dish Network managed to meet a federal deadline to cover 70% of the U.S. population with it’s 5G OpenRAN in June. As a result, the company said it would pause its spending until next year at the earliest.
American Tower was a bit more hopeful that CAPEX would pick up in the future:
- “Moderation in carrier spend following the recent historic levels of activity we’ve seen in the industry isn’t unexpected and is consistent with past network generation investment cycles,” explained CFO Rod Smith.
- “The cycles typically progress as there’s a coverage cycle. It’s what we’ve seen in past cycles, including 3G and 4G. It’s an initial multiyear period of elevated coverage capex, and it’s tied to new G spectrum aimed at upgrading the existing infrastructure,” said American Tower’s CEO Tom Bartlett. “And then later in the cycle, it will fill back into a capacity stage where we’ll start to see more densification going on. So I’m hopeful that our investor base doesn’t get spooked by the fact that this is a pullback. It’s very consistent. The cadence is really spot on with what we’ve seen with other technologies.”
In April, Dell’Oro Group analyst Stefan Pongratz forecast global telecom capex is projected to decline at a 2% to 3% CAGR over the next 3 years, as positive growth in India will not be enough to offset sharp capex cuts in North America. He also predicted that wireless CAPEX in the North America (NA) region would decline 10% to 20% in 2023 as per this chart:
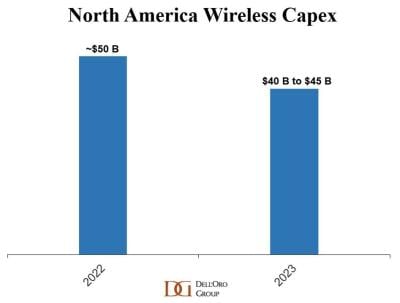
Now, that NA CAPEX decline seems more like 30% this year!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
U.S. 5G spending slowdown continues; RAN revenues set to decline for years!
USA’s 5G capex bubble will burst this year as three main operators cut back
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
Worldwide Telecom Capex to Decline in 2023, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/wireless-capex-north-america-expected-decline-10-20-2023
Dell’Oro: Telecom Capex Growth to Slow in calendar years 2022-2024
BT and Ericsson in partnership to provide commercial 5G private networks in the UK
BT and Ericsson have entered a new multi-million-pound joint partnership to provide commercial 5G private networks for the UK market – the first agreement of its kind. The multi-year contract will enable BT to sell 5G services to businesses and organizations in industries like manufacturing, defense, education, retail, healthcare, transport and logistics. It’s critically important to note that to be effective, a 5G private network requires a 5G Core which facilitates all the 5G features and essentials, e.g. network slicing, automation, MEC, security, etc.
The agreement comes just after BT confirmed it was investing close to £100m over the next three years to accelerate the development of customer solutions which integrate emerging technologies like 5G, IoT, Edge Compute, Cloud and AI.
5G Private Networks provide secure indoor and outdoor 5G cellular coverage, making them suitable for a range of uses – particularly in environments such as factories, education campuses and other large sites where security and ultra-low latency connectivity are important.
New innovative applications and IoT capabilities can be enabled through a private 5G network to improve productivity, optimise operations and drive cost savings, such as asset tracking, predictive maintenance, connected sensors, real-time data processing, automation and robotics.
According to a forecast from MarketResearch.com, 5G Private Networks are predicted to grow at an average rate of 40 per cent a year between 2021 and 2028, by which time the market will be worth $14bn (£10.7bn). Both BT and Ericsson believe there is significant demand from UK businesses looking to take advantage of the benefits the new technology can provide.
From MarketResearch.com:
“Key market players are strategically building partnerships with industry giants to set up a private 5G network to provide high-speed secure connectivity to their customers. For instance, in Feb 2020, Nokia Corporation deployed a private 5G network infrastructure for Lufthansa Technik for virtual inspection of engine parts remotely for its civil aviation clients. Moreover, the rising demand for enhanced bandwidth connectivity for secured enterprise applications is anticipated to fuel the adoption of private 5G services globally.”
Marc Overton, BT’s Managing Director for Division X, Enterprise, said: “This UK-first we have signed with Ericsson is a huge milestone and will play a major role in enabling businesses’ transformation, ushering in a new era of hyper-connected spaces.
“We have combined our skill and expertise at building converged fixed and mobile networks with Ericsson’s leading, sustainable and secure 5G network equipment, to offer a pioneering new proposition that will be attractive to many industries. 5G private networks will also support smart factory processes and the advancement of Industry 4.0 which can realise significant cost savings and efficiencies for manufacturers.
“Unlike a public network, a private 5G network can be configured to a specific business’s needs, as well as by individual site or location. They also provide the foundation to overlay other innovative technologies such as IoT, AI, VR and AR, opening up a multitude of possibilities.”
Katherine Ainley, CEO Ericsson UK & Ireland said: “This ground-breaking agreement with BT means we are together taking a leading role in ensuring 5G has a transformative impact for the UK. The high quality, fast and secure connectivity provided by Ericsson Private 5G can help organisations make all-important efficiency gains that can create safer, more productive, and sustainable business operations and help the country build global leaders in the industries and technologies of the future.”
Case study: BT and Ericsson have already worked together on several major projects incorporating private 5G networks, including Belfast Harbour in Northern Ireland, as they accelerate its ambition to become the world’s best regional smart port.
The partners have installed a 5G private network across 35 acres of operational port. This is helping to drive operational efficiencies and accelerate its digital transformation through optimising processes across transport, logistics, supply chain and shipping, as well as boosting productivity through the smooth-running of the Port’s operations.
Every year more than 1.75 million people and over half a million freight vehicles arrive and depart through the Port every year. While 24 million tonnes of goods are managed and carried by ferries, container ships and cargo vessels.
“With activity on that scale you need smart technology that can really make a difference. And that’s what our standalone private 5G network is enabling at the Port,” added Marc Overton.
“We’re now into phase two of the project and this includes various use cases such as teleoperation of heavy plant machinery, artificial reality (AR) for remote maintenance, as well as enhanced video AI analytics and the use of drones for surveillance and inspections.”
The partnership is also exploring how 5G and other emerging technologies such as AI, IoT and Connected Autonomous Vehicles can be used together to enhance public safety, physical security, and address climate change across the Port and other parts of Belfast City.
Mike Dawson, Corporate Services Director, Belfast Harbour Commissioners, said: “Throughout 2021 and to the end of 2022, we will have completed the implementation of both Public and Private 5G Networks. These are the foundation for several Smart and Green port initiatives, including CCTV cameras, Air Quality Monitors, Drones, MiFi units to maximise operational efficiencies and a Digital Twin. The technologies have supported our data collection on the movement of people and things through our Road Traffic Screens, Wayfinding App and a Community App for Traffic.”
BT Group is the UK’s leading provider of fixed and mobile telecommunications and related secure digital products, solutions and services. We also provide managed telecommunications, security and network and IT infrastructure services to customers across 180 countries.
BT Group consists of four customer-facing units: Consumer serves individuals and families in the UK; Enterprise and Global are our UK and international business-focused units respectively; Openreach is an independently governed, wholly owned subsidiary, which wholesales fixed access infrastructure services to its customers – over 650 communication providers across the UK.
British Telecommunications plc is a wholly-owned subsidiary of BT Group plc and encompasses virtually all businesses and assets of the BT Group. BT Group plc is listed on the London Stock Exchange.
For more information, visit www.bt.com/about
References:
https://www.marketresearch.com/Grand-View-Research-v4060/Private-5G-Network-Size-Share-14553525/
Mavenir at MWC 2022: Nokia and Ericsson are not serious OpenRAN vendors
Andrew Wooden of telecoms.com talked with Mavenir’s SVP of business development John Baker and CMO Stefano Cantarelli to gauge how industry is feeling towards OpenRAN. Here are a few quotes:
“Clearly the (OpenRAN) train has left the station, there’s a lot of buzz about OpenRAN – it’s back to the haves and have nots,” Baker told us. “I see a lot of interest from network operators and a lot of interest from the component suppliers. But on the other side of it, about [Nokia’s recent statement about OpenRAN] – they’re full of it. Because they’re a startup in OpenRAN themselves but are not doing anything. They’re trying to pass on a message that the OpenRAN community is confused, that there are no real OpenRAN players out there, and they’re trying to position themselves as the real OpenRAN player. Digging underneath that, we’re having to call out the Nokia’s and Ericsson’s for confusing the story and trying to keep the confusion running around the marketplace, about the status of OpenRAN.”
“Ericsson has been clear right up front that [they’re] not going to participate in OpenRAN. They name their products as Cloud RAN but you can’t mix and match, so they don’t they don’t meet the OpenRAN requirements. I stand very firm that unless you’ve got two suppliers interworked, then you haven’t got OpenRAN.” Of course, this author agrees 100%!
Regarding Nokia, Baker said: “We’ve been asking for the last two years, every month almost, we’re ready to interwork, when are you ready? And they never get there. So our view is Nokia doesn’t have anything, they’re just trying to protect an old silicon strategy. And that’s their problem. They’ve had two failed attempts, in my opinion, of their silicon strategy – first time they got it completely wrong. Second time they got it too late for the industry because software is now replacing where they are with silicon. I think at the end of the day those two logos are going to disappear in the distance.”
Cantarelli added: “I think Ericsson and Nokia are not stupid. They know OpenRAN is the future, it’s just at the beginning they didn’t think about it, and now they’re a bit late. So they’re protecting their legacy. And they’re waiting for when they’re going to be ready, so it’s purely a delaying technique.”
Some observers think OpenRAN is immediate, and of singular importance, but others don’t think it will be as disruptive as that, at least not right now. This author is in the latter camp. We’ve explained why many times why: without implementation standards there is no interoperability!
References:
Mavenir slams Nokia and Ericsson for confusing the OpenRAN story
Ericsson expresses concerns about O-RAN Alliance and Open RAN performance vs. costs
Vodafone and Mavenir create indoor OpenRAN solution for business customers
https://www.nokia.com/networks/radio-access-networks/open-ran/
Rakuten Communications Platform (RCP) defacto standard for 5G core and OpenRAN?
Strand Consult: Open RAN hype vs reality leaves many questions unanswered
Nokia deploys shared 5G RAN (MORAN) with SoftBank and KDDI in Japan
Nokia today announced that it has been selected by Japanese mobile operators, SoftBank Corp. and KDDI as one of the vendors to deploy Japan’s shared RAN. This deployment will deliver 5G services to both SoftBank and KDDI subscribers in the country. Nokia will install a Multi-Operator Radio Access Network (MORAN) [1.], which will allow both companies to share the RAN while keeping core networks separate. Network sharing helps support efficient RAN deployments as base station sites and infrastructure (equipment) are shared.
Note 1. In MORAN everything in the RAN (antenna, tower, site, power) except the radios are shared between two or more network operators.
The two Japanese telcos announced plans to deploy a shared network, or a Multi-Operator Radio Access Network (MORAN), in June, using equipment from Ericsson and other vendors. We now know that Nokia is one of those other vendors. Ericsson equipment supports network sharing using both TDD (Time Division Duplex) and FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) as well as 4G/LTE and 5G New Radio (NR). The solution consists of Ericsson Radio System products such as RAN Compute (base band) , radio and transport – with the powerful system on a chip, Ericsson Silicon, bringing innovative various solutions such as Ericsson Spectrum Sharing and Ericsson Uplink Booster.
KDDI and SoftBank will particularly focus on quickly building robust 5G network leveraging Ericsson Radio System products and solutions for multiple-bands. Ericsson’s future-proof network-sharing solution will significantly contribute to their nationwide network deployment of 5G and beyond. Ericsson and the service providers have completed verifications and started to deploy the solution commercially.

Under this contract, Nokia will supply its latest AirScale products including baseband and radio platforms. Nokia’s MORAN is triple mode and covers LTE, 5G as well as Dynamic Spectrum Sharing. In particular, Nokia will provide its new generation of ReefShark System-on-Chip based plug-in cards to increase the capacity of the AirScale baseband. The new ReefShark-powered plug-in cards are easily installed and simplify the upgrade and extended operation of all AirScale deployments. They also deliver up to eight times more throughput compared to previous generations. Nokia’s modular AirScale baseband will enable SoftBank and KDDI to scale capacity flexibly and efficiently and as their 5G business evolves.
MORAN is a way for mobile operators to share radio access network infrastructure, reduce their costs, expand the coverage of their networks and achieve an efficient and effective roll-out of new technologies. The RAN uses dedicated radio frequencies assigned to each service provider ensuring they maintain independent control of their resources. Nokia supports a range of network sharing solutions suiting all operating scenarios. Nokia’s flexible MORAN solution can also be utilized by mobile operators and enterprises for private networks, as well as public networks or industrial campuses.
MORAN should help Softbank and KDDI roll out 5G faster and cheaper. Costs will decrease and subscriber coverage will be quicker. They are also working together on a shared rural coverage project announced 18 months ago, that will see them share base station assets to build out 5G more quickly in rural areas.
Tomohiro Sekiwa, Senior Vice President and CNO, SoftBank, said: “In order to deliver the best 5G experience to customers nationwide as quickly as possible, SoftBank is working with KDDI to develop a shared 5G network. In this effort, a Multi-Operator Radio Access Network is a key technology that will bring various efficiencies and we look forward to the high performance of Nokia’s products in this regard.”
Tatsuo Sato, Vice President and Managing Officer, Technology Planning, KDDI, said: “We are pleased to work closely with both Nokia and SoftBank to accelerate 5G network deployment across Japan. With this Multi-Operator Radio Access Network, we anticipate delivering the superior unique experiences of 5G to customers faster.”
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks at Nokia, said: “Nokia has been at the forefront of network sharing around the world since the deployment of the world’s first commercial shared network. We have a long-standing partnership with both SoftBank and KDDI and are excited to work collaboratively with them on this project. Our latest AirScale solutions will be utilized, including the new baseband plug-in cards to add capacity where it is needed and deliver best-in-class 5G connectivity to their customers.”
It will be interesting to see the impact that this network gear sharing deal has on SoftBank and KDDI’s respective 5G businesses in the coming months and years.
Resources:
Activate massive 5G capacity with Nokia AirScale
AirScale baseband | Nokia
AirScale Active Antennas | Nokia
AirScale Radio | Nokia
Network Sharing
References:
https://telecoms.com/511728/kddi-and-softbank-add-nokia-to-shared-5g-ran-ticket
https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/2021/6/ericsson-sets-up-japans-first-multi-operator-ran-with-kddi-and-softbank
Network Infrastructure Sharing and the MORAN Concept:
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-s/opb/itujnl/S-ITUJNL-JFETF.V1I1-2020-P10-PDF-E.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlzuxMR2xQ4
Ericsson & MediaTek near 500 Mbps upload in mmWave carrier aggregation tests
Ericsson announced a new upload speed record with 5G on mmWave spectrum – double the current upload speeds and the fastest recorded to date.
In a four-component carrier uplink aggregation tests with MediaTek, a peak throughput rate of 495 Mbps was achieved. This included 425 Mbps on 5G New Radio (5G RAN) test and a 70 Mbps on 4G-LTE test.
The demo performed in June used pre-commercial software on a device containing a MediaTek M80 5G chipset. The lab tests used Ericsson RAN Compute baseband 6648 with the AIR 5331 millimeter wave radio. Four carriers of 100 MHz each in the 39 GHz band were used for non-standalone 5G, along with 20 MHz in the 1,900 MHz band for LTE (more in Tech Details below).
Ericsson said the test of uplink carrier aggregation is the first of its kind, as the industry previously focused more on boosting download speeds. The increased adoption in the past year of home working and schooling has driven the use of applications like videoconferencing that require also fast upload speeds.
Upload speed dictates how quickly data is sent from the computer or handheld device to the internet. This includes uploading files, such as photos and videos to social media or collaborative worksites. Upload speeds are also crucial to the image and sound quality of video conferencing. Strong uplink means less or even none of those frozen screens, or broken audio, when using apps like Skype or Microsoft Teams. Similarly, faster uplink improves voice over internet protocol (VoIP) calls and online gaming experience.
Hannes Ekström, Head of Product Line 5G RAN at Ericsson, said: “We continue to build on our previous successes, breaking our own record in upload speed. With a peak rate of close to 500 Mbps, we’ve demonstrated in this latest milestone with MediaTek how unprecedented data speeds can be delivered in uplink using mmWave and carrier aggregation. This means our customers can enhance their 5G offerings with higher uplink data rates, vastly improving user experience.”
JS Pan, General Manager of Wireless Communication System and Partnership at MediaTek, said: “This world’s first demonstration of an industry-leading mmWave uplink technology in partnership with Ericsson, shows MediaTek is again establishing 5G milestones and pushing the envelope of its capabilities. 5G mmWave connectivity helps boost network coverage and capacity, faster performance, and introduces more diverse use cases.”
This latest technology milestone follows a single user multiple input multiple output (SU-MIMO demo in April 2021 when Ericsson delivered a single user uplink data rate of 315 Mbps, 15-20 times faster than current typical uplink speed.
Tech details:
Ericsson and MediaTek integrated four component carrier, each of 100 MHz, in the uplink using non-standalone architecture (aggregating 8x100MHz in the downlink and 4×100 MHz in the uplink). The integration carried out in a lab setting resulted in a throughput of 495 Mbps (425 Mbps in 5G plus 70 Mbps in 4G), doubling the current uplink speed on the market.
The test was done using the 39 GHz spectrum of NR (400 MHz) and combining it with a single carrier of LTE 1900 MHz spectrum (20 MHz). The whole bandwidth was then aggregated using the LTE and NR links, realizing a total throughput of close to 500 Mbps.
RELATED LINKS
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2021/7/ericsson-and-mediatek-achieve-mmwave-uplink-record
Dell’ Oro: Huawei still top telecom equipment supplier; optical transport market +1% in 2020
Huawei has increased its lead as the#1 global telecoms network equipment vendor, boosting its revenue share by a three percentage points last year, according to Dell’Oro Group. Nokia lost one percentage point of revenue share year-on-year, as did Cisco, the latter falling to 6%. Ericsson gained one percentage point to match Nokia at 15% of the market and ZTE also saw a 1% uptick to 10% of the global telecom market. (Please refer to chart below).
Dell’Oro Group’s preliminary estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market – Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network, SP Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch (CES) – advanced 7% year-over-year (Y/Y) for the full year 2020, growing at the fastest pace since 2011.
The telecom and networking market research firm suggests revenue rankings remained stable between 2019 and 2020, with Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Cisco, Ciena, and Samsung ranked as the top seven suppliers, accounting for 80% to 85% of the total market. At the same time, revenue shares continued to be impacted by the state of the 5G rollouts in highly concentrated markets. While both Ericsson and Nokia improved their RAN positions outside of China, initial estimates suggest Huawei’s global telecom equipment market share, including China, improved by two to three percentage points for the full year 2020.
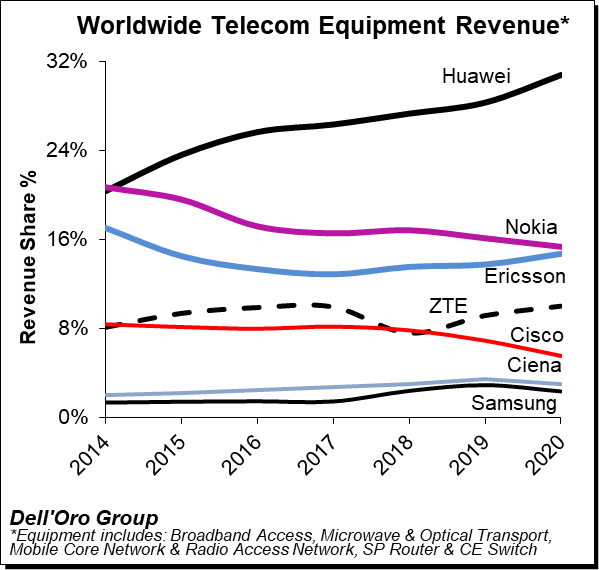
Dell’Oro now estimates the following revenue shares for the top seven suppliers:
| Top 7 Suppliers | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| Huawei | 28% | 31% |
| Nokia | 16% | 15% |
| Ericsson | 14% | 15% |
| ZTE | 9% | 10% |
| Cisco | 7% | 6% |
| Ciena | 3% | 3% |
| Samsung | 3% | 2% |
Additional key takeaways from the 4Q2020 reporting period:
- Preliminary estimates suggest that the positive momentum that has characterized the overall telecom market since 1Q-2020 extended into the fourth quarter, underpinned by strong growth in multiple wireless segments, including RAN and Mobile Core Networks, and modest growth in Broadband Access and CES.
- Helping to drive this output acceleration for the full year 2020 is faster growth in Mobile Core Networks and RAN, both of which increased above expectations.
- Covid-19 related supply chain disruptions that impacted some of the telco segments in the early part of the year had for the most part been alleviated towards the end of the year.
- Not surprisingly, network traffic surges resulting from shifting usage patterns impacted the telecom equipment market differently, resulting in strong demand for capacity upgrades with some technologies/regions while the pandemic did not lead to significant incremental capacity in other cases.
- With investments in China outpacing the overall market, we estimate Huawei and ZTE collectively gained around 3 to 4 percentage points of revenue share between 2019 and 2020, together comprising more than 40% of the global telecom equipment market.
- Even with the higher baseline, the Dell’Oro analyst team remains optimistic about 2021 and projects the overall telecom equipment market to advance 3% to 5%.
Dell’Oro Group telecommunication infrastructure research programs consist of the following: Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Mobile Core Networks, Mobile Radio Access Network, Optical Transport, and Service Provider (SP) Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last week, Dell’Oro Group reported that the optical transport equipment revenue increased 1% in 2020 reaching $16 billion. In this period, all regions grew with the exception of North America and Latin America.
“Between concerns on starting new optical builds during the start of the pandemic and aggressive plans on 5G deployments that required a larger share of a service provider’s capital budget, the spending on optical transport dramatically slowed by the end of 2020,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group.
“It was a really dramatic drop in optical equipment purchases in the fourth quarter. While we anticipated a slowdown near the end of the year due to concerns around COVID-19, we were surprised by a 29 percent year-over-year decline in WDM purchases in North America as well as a 12 percent decline in China. That said, there was good growth in the other parts of the world, especially Japan,” continued Yu.
| Optical Transport Equipment Market | |
| Regions | Growth Rate in 2020 |
| North America | -6% |
| Europe, Middle East and Africa | 2% |
| China | 1% |
| Asia Pacific excluding China | 13% |
| Caribbean and Latin America | -14% |
| Worldwide | 1% |
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments (by speed including 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps, and 800 Gbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), optical switch, optical packet platforms, data center interconnect (metro and long haul), and disaggregated WDM. To purchase this report, please email [email protected].
References:
Extended-range 5G NR data call over mmWave completed; Ericsson & Qualcomm test 5G SA Carrier Aggregation
Qualcomm Technologies, Casa Systems and Ericsson announced that the companies successfully completed what they call the world’s first extended-range 5G NR data call over mmWave. The extended range data call was completed in Regional Victoria, Australia on 20 June, achieving a farthest-ever connection of 3.8 kilometers (km).
This so called “breakthrough” from Qualcomm Technologies, Casa Systems and Ericsson provides global network operators and ISPs with the reach and performance to offer fixed broadband wireless as a “last mile” access technology. Of course, line of sight communications (i.e. no trees, walls or other blockages permitted). With the increased range demonstrated for mmWave, that technology may be suitable for fixed wireless access (FWA) as well as for 5G mobile service in suburban or even rural areas that won’t require as many small cells or high density cell towers.
Network operators will have the potential to use their existing mobile network assets to deliver fixed wireless services and expand their service with ease to new areas, from urban to rural, while delivering 5G’s multi-gigabit speeds and ultra-low latency to a wider customer base within their coverage footprint. In addition, this milestone will proliferate the roll-out of FWA customer-premises equipment (CPE) devices to areas that are often too difficult to reach with traditional broadband, including rural and suburban areas, empowering more customers across the globe to access superior connectivity at fiber optic-like speeds.
The extended-range data call was achieved by applying extended-range software to commercial Ericsson hardware – including Air5121 and Baseband 6630 – and a 5G CPE device powered by the Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 5G Modem-RF System with the Qualcomm QTM527 mmWave antenna module.

“With the introduction of the Qualcomm QTM527 mmWave antenna module as part of the Snapdragon X55 5G Modem-RF System, we are empowering operators and OEMs to offer high-performance, extended-range multi-gigabit 5G broadband to their customers – which is both flexible and cost-effective, as they can leverage existing 5G network infrastructure,” said Gautam Sheoran, senior director, product management, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. “With this major milestone being the first step in utilizing mmWave for an extended-range 5G data transfer, our collaboration with Casa Systems and Ericsson is paving the way to implement fixed broadband services for broad coverage in urban, suburban and rural environments.”
“As operators look to close the digital divide and expand broadband services throughout rural, suburban and urban communities, the technology in this data connection underscores the critical role mmWave will play in the global proliferation of 5G networks,” said Steve Collins, senior vice president, access devices, Casa Systems. “This collaboration with Qualcomm Technologies and Ericsson is an industry milestone that makes it possible for operators to offer multi-gigabit broadband services wirelessly as a new broadband alternative solution using mmWave spectrum, and we look forward to delivering innovative CPE devices that further empowers the global broadband delivery ecosystem.”
“Ericsson has a long history of working with extended range across generations of mobile technologies, pioneering with 3G, then 4G and now with 5G. By collaborating with leading industry partners like Qualcomm Technologies and Casa Systems, we are able to ensure that everyone can access the transformative benefits of 5G connectivity. This achievement will open up opportunities for communications service providers around the world and how they can use mmWave spectrum for long-range use cases,” said Per Narvinger, head of product area networks, Ericsson.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
5G SA Carrier Aggregation from Qualcomm & Ericsson:
Today’s announcement comes just three days after Qualcomm and Ericsson announced that they completed interoperability tests for 5G standalone (SA) carrier aggregation. Carrier aggregation allows operators to use multiple sub-6 GHz spectrum channels simultaneously to transfer data between base stations and a 5G mobile device.
The test was completed at Ericsson’s labs in Beijing, China. The connection reached 2.5 Gb/s peak speeds by aggregating 100 MHz and 60 MHz within the 2.5 GHz (n41) TDD band in a 70% downlink configuration and using 4×4 multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology. In Sweden, the two companies established a successful 5G SA carrier aggregation data call by combining 20 MHz in the 600 MHz (n71) FDD band with 100 MHz of spectrum in the 2.5 GHz (n41) TDD band.
Implementation of 5G carrier aggregation delivers enhanced network capacity along with improved 5G speeds and reliability in challenging wireless conditions, allowing consumers to experience smoother video streaming and enjoy faster downloads. This key 5G capability is expected to be widely deployed by operators around the world in 2021, according to Ericsson.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Qualcomm
Qualcomm is the world’s leading wireless technology innovator and the driving force behind the development, launch, and expansion of 5G. When we connected the phone to the internet, the mobile revolution was born. Today, our foundational technologies enable the mobile ecosystem and are found in every 3G, 4G and 5G smartphone. We bring the benefits of mobile to new industries, including automotive, the internet of things, and computing, and are leading the way to a world where everything and everyone can communicate and interact seamlessly.
Qualcomm Incorporated includes our licensing business, QTL, and the vast majority of our patent portfolio. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a subsidiary of Qualcomm Incorporated, operates, along with its subsidiaries, substantially all of our engineering, research and development functions, and substantially all of our products and services businesses, including our QCT semiconductor business.
About Casa Systems, Inc.
Casa Systems, Inc. is delivering physical, virtual and cloud-native 5G infrastructure and customer premise networking for high-speed data and multi-service communications networks. Our core and edge convergence technology enables public and private networks for both communications service providers and enterprises. Casa Systems’ products deliver higher performance, improved network flexibility and scalability, increased operational efficiency and lower total cost of ownership (TCO). Commercially deployed in more than 70 countries, Casa serves over 475 Tier 1 and regional service providers worldwide. For more information, visit http://www.casa-systems.com.
About Ericsson
Ericsson enables communications service providers to capture the full value of connectivity. The company’s portfolio spans Networks, Digital Services, Managed Services, and Emerging Business and is designed to help our customers go digital, increase efficiency and find new revenue streams. Ericsson’s investments in innovation have delivered the benefits of telephony and mobile broadband to billions of people around the world. The Ericsson stock is listed on Nasdaq Stockholm and on Nasdaq New York. www.ericsson.com
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2020/8/5g-carrier-aggregation
Ericsson deploys 25,000 base stations in Russia; 100 5G deployment agreements top Huawei & Nokia
Sebastian Tolstoy, Head of Ericsson in Russia, said:
“Our development enables Tele2’s subscribers the opportunity to use mobile internet services in high quality. As all our network equipment in Russia supports an upgrade to 5G technologies through remote software installation, operators in Russia are able to launch new services as soon as they get the appropriate licenses.
Ericsson’s 5G Innovation Hub in Moscow gives Russian service providers the opportunity to test innovations on live 5G and IoT networks. The Ericsson Academy, our training center co-located at the Innovation Hub, trains more than 1,000 specialists from Russian service providers and students each year.”
The pace of deployment from Ericsson is truly impressive, especially in the context of the ongoing pandemic. If the current pace is maintained, the five-year deal will be completed in two years.
Aleksey Telkov, CTO of Tele2 Russia, comments:
“In the Moscow region, from the very start, we installed 5G-ready base stations. We deployed a pilot 5G network in the center of Russia’s capital, and together with Ericsson, we are carrying out a large-scale network modernization across the country.
This allows us to say that Tele2 is technologically ready for 5G.”

The 5G Zone uses the 28 GHz band in non-Standalone (NSA) mode and the frequency band for anchor LTE band is Band 7 (2600MHz). 5G pocket routers supporting 28 GHz were used as end-user devices for mobile broadband services with ultra-high speeds.
Ericsson and Tele2’s 5G Zone was used to demonstrate the opportunities 5G presents, including immersive VR entertainment, smart buildings, and other consumer and industrial use cases.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ericsson announced it had 100 telco 5G agreements following the announcement of a 5G deal with Telekom Slovenije yesterday. That’s a lot of progress made in a relatively short time. Just under a year ago, Ericsson had publicly announced 24 5G contracts with equipment live in 15 networks. As of today, 58 contracts have been publicly announced and Ericsson’s gear is being used in 56 live 5G networks.
Börje Ekholm, President and CEO, Ericsson, said:
“Our customers’ needs have been central to the development and evolution of Ericsson’s 5G technology across our portfolio from the very beginning. We are proud that this commitment has resulted in 100 unique communications service providers globally selecting our technology to drive their 5G success ambitions.
We continue to put our customers center stage to help them deliver the benefits of 5G to their subscribers, industry, society and countries as a critical national infrastructure.”
Ericsson has been able to capitalize on the uncertainty surrounding Huawei’s future in many Western countries due to security concerns. Even prior to the UK’s decision to ban Huawei’s equipment, many operators in Britain were moving away from the Chinese vendor. India is now moving in that same direction.
In April, Howard Watson, BT’s chief technology and information officer, said:
“Having evaluated different 5G core vendors, we have selected Ericsson as the best option on the basis of both lab performance and future roadmap. We are looking forward to working together as we build out our converged 4G and 5G core network across the UK.”
For comparison, Nokia says it has 85 commercial 5G deals and equipment live in 33 5G networks. In February 2020, Huawei aid it had secured more than 90 commercial 5G contracts worldwide, an increase of nearly 30 from last year despite the relentless pressure from U.S. authorities and being banned in the UK.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Ericsson deploys 25,000 base stations in Russia to support Tele2’s 5G rollout
https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/China-tech/Huawei-claims-over-90-contracts-for-5G-leading-Ericsson
Ericsson: U.K. Telecom Rules May Hinder Country’s 5G Opportunity
Bloomberg reports that the U.K. risks missing the benefits of fifth-generation (5G) wireless networks, because of policies that could lead to an expensive and inefficient roll-out, according to Swedish telecommunications equipment giant Ericsson AB.
“Decisive action is needed — uncertainty is not good for business and it could delay the roll-out of the U.K.’s 5G network, putting the country’s long-term competitiveness at risk. The U.K. was late in adopting 4G and largely missed the economic opportunity that came with it. There is a real possibility of history repeating itself.” said Arun Bansal, head of the wireless equipment supplier’s European and Latin American operations.
Bansal identified several concerns with U.K. policy. He said there’s a risk the airwaves (frequency spectrum) owned by different carriers could be fragmented and inefficient. International cooperation is required so the same frequency bands are used within the country.
NOTE: It is the job of ITU-R WP5D to update ITU-R M.1036 Frequency arrangements for implementation of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) in the bands identified for IMT in the Radio Regulations. WP 5D gets spectrum recommendations inputs from WRC 19 meeting outputs from last Fall. A new version of M.1036 must be completed before IMT 2020 (5G) RIT/SRIT specs are approved.
The telecom regulator in each country is then responsible for assigning frequencies to each IMT service, e.g. 4G and 5G within their country. The U.K. telecom regulator is OFCOM. In the U.S. it’s the FCC.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Bansal also noted the country’s required planning approvals are slowing engineers’ work and making it more expensive, Bloomberg reported He urged the government could do a better job at supporting 5G as a potential replacement for landline broadband, the report said.
Britain’s government rejected the criticisms and said reforms have made network deployment cheaper and easier.
In a statement, the U.K. Department for Digital, Culture, Media & Sport told Bloomberg that the country’s campaign to roll out gigabit-capable broadband nationwide “is technology neutral, and we would be happy to meet with the supplier to discuss the role of 5G.”
Ericsson has been positioning itself to supply British carriers with billions of pounds’ worth of 5G equipment. With U.K. officials now looking to curtail the role of its Chinese rival Huawei Technologies Co. amid growing tensions with Beijing, that potential opportunity has grown — as long as Ericsson can show it’s able to match Huawei’s technological edge.
Bansal didn’t mention Huawei by name. However, he denied claims that Ericsson was technologically behind any other player, and said it’s ready for whatever approach Britain chooses. “We ship enough 5G-ready radios to cover the greater London area every single day,” he said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Bansal’s allegations comes one week after O2, the London-based telecommunications services provider owned by Telefónica, selected Ericsson to deploy its 5G across the UK and upgrade the existing 2G/3G/4G sites as part of a major network modernization program.
In April, BT said it would use Ericsson equipment for the core of its 5G network. Ericsson would provide a “cloud native, containerized” core for 4G, non-standalone 5G, and eventually 5G standalone services, which will become a converged IP network.
NOTE that there are no standards or specifications for such a core network. The only 5G core spec we know of is 3GPP Release 16 specification TS.23501 5G Systems Architecture-V16.4.0 (27 March, 2020) which does not specify how to build a cloud native containerized core network.
“The containerization of core network functions will enable BT to benefit from greater industry innovation in many areas, including automation, orchestration, network resilience, security, and faster upgrade techniques,” Ericsson said at that time. “This means increasing overall network availability for customers and services while being cost-effective.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Last month, PYMTS reported COVID-19 has prompted Ericsson to update its forecast for worldwide 5G subscriptions to 2.8 billion by 2025 from 2.6 billion, the company said in a webinar.
“We’re witnessing transformative changes just in the last two months,” Patrik Cerwall, Ericsson’s head of strategic marketing, said in the “Unboxed Office” event that was broadcast live on Periscope.
Amy McCune, Ericsson North America’s vice president and chief operations officer, told PYMNTS in May that shifts in lifestyle, work and healthcare are accelerating the demand for the next generation of wireless communications technologies.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Ericsson Says UK Telecom Rules Are Slowing 5G Installs And Driving Up Costs
Sweden Telecom Operators Announce 5G Network Launches and Details
Three major telecom companies in Sweden –Tele 2, Telia, and Tre Sweden– have announced their upcoming 5G network launches and areas covered. Sections of Stockholm, the nation’s capital, already have 5G service, with many more being added to the list as the year goes on, as well as other cities and towns in Sweden.
On May 24th, Tele 2 switched its network to 5G, with availability opening up to customers as of June 24 in Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. The Tele2 network will offer service at more than 1 Gbps through 80 MHz bandwidth on the C-band.
Customers with a Tele2 Unlimited subscription and a compatible handset from Samsung’s Galaxy S20 series will get free access to Tele2’s 5G network from 24 June. Other offers and cooperations with other phone manufacturers will be presented later, and Tele2 will gradually phase in 5G throughout Sweden.
Telia inaugurated its first major 5G commercial network in Stockholm today (May 25th) even though it had already been up and running for a few weeks. It has 15 base stations that are already in place, and 60 more will be built in June hand in hand with Ericsson, who will be powering the network for Telia. Initial services on the 700Mhz band will cover most of central Stockholm by mid-June, including the Norrmalm, Östermalm and Vasastan districts (more below).
Tre Sweden is jumping on the 5G board by bringing its network in the centers of Malmö, Lund, Helsingborg, Vasteras, Uppsala, and western parts of Stockholm in June. Tre said that it would activate 5G in Stockholm city centre after the summer. The earlier start in western Stockholm will include Kungsholmen, Bromma and parts of Solna. This will be an expansion of its already-launched 5G network back in December 2019, when it announced testing.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Telia takes center stage to promote 5G:
Telia aims to enhance and supplement its low-band 5G commercial services with additional nationwide 5G coverage, including mid- and high-bands, following the auction of the related spectrum by the Swedish government later this year. For this launch Telia is using its existing 700MHz spectrum, boosted by LTE and New Radio (NR) carrier aggregation.

Fredrik Jejdling Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, Ericsson; Allison Kirkby, CEO, Telia Company; Anders Ygeman, Sweden’s Minister of Energy and Digital Development, at the Telia Company 5G launch in Stockholm.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Having already partnered successfully on 5G in Sweden – including enabling the country’s first live 5G network at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology and partnering with Volvo to operate Sweden’s first industrial 5G network – Telia selected Ericsson as its 5G partner for the launch network. Ericsson President and CEO, Börje Ekholm, said 5G will transform Swedish life, society and business for the better.
Earlier this month Telia’s sister company Telia Norway also launched its first commercial 5G services, with Ericsson as its sole 5G RAN supplier.
Allison Kirkby, CEO of Telia, said in a press release: “Our networks have never been more important to lives and livelihoods, than now. Telia’s 5G launch lays the foundations for the next phase of digital transformation, with innovation, sustainability, and security as three critical pillars, and we are proud to be doing this launch in partnership with Ericsson.”
Kirkby continued “As we roll-out 5G across Sweden, we will open up new user experiences and accelerated innovation in areas such as entertainment, healthcare, manufacturing, and transport, that will collectively strengthen and protect everyone living and working in Sweden, and Swedish competitiveness in the world.”
Telia’s 5G network is due to power most of Stockholm’s city center by June 21, and its private customers that are within range and have a 5G-ready smartphone and Jobbmobil contract will be able to enable the new 5G network. Moreover, its network is run 100% on renewable energy certified by the Swedish Society for Nature Conservation.
5G launches are scheduled for later in the year in other major cities in Sweden including Gothenburg and Malmö.
References:
https://interestingengineering.com/sweden-sets-up-first-5g-network-with-its-major-telecom-companies
https://www.tele2.com/about/who-we-are/tele2-5g
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/tele2-telia-and-3-sweden-announce-5g-networks-launches–1339788
https://www.teliacompany.com/en/news/news-articles/2018/swedens-first-5g-network-goes-live/


