India’s 5G Conundrum: Mass Adoption not seen till 2023-2024!
by Hetal Gandhi (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
The writer is a Director at CRISIL Research
As the noise around India’s upcoming 5G spectrum auction rise, one must remember that ecosystem development is crucial to the success of next-generation technology. India is yet to complete the transition from 2G and 3G to 4G-LTE. But the march towards 5G is inexorable and necessitates giga-buck spending. Telcos have already invested more than Rs 3 lakh crore (India money) over the past three years, and a large portion of that money has been used to roll out 4G-LTE networks across the country, and we are still counting.
The implementation of any paradigm-shifting technology spawns manifold ecosystem changes such as spectrum usage, network infrastructure and devices. While newer bands will be made available for 5G services in India, the reserve price for the spectrum bands, recommended by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) at around $0.23/MHz/pop (for metros), is almost twice compared to $0.12/MHz/pop auctioned in the UK in June 2018.
At TRAI’s pricing, owning a block of 20 MHz spectrum across circles in the 3.3-3.6 GHz band will cost a staggering Rs 98,000 crore or so. Also, high-frequency bands such as these will require more investments in cell sites because of their low-propagation characteristics. Even though a combination of sub-1 GHz and 3.3-3.6 GHz is ideal for the 5G rollout, prices in the 700 MHz band remain very high while the rest of the sub-1 GHz bands will be mostly utiliszd for 2G (voice) and 4G-LTE services.
The government seems ready to conduct the 5G auction towards the end of 2019, but it is imperative for telcos to check the readiness of their ecosystems before plonking down truckloads of money to buy spectrum. On the other hand, if the US and China successfully adopt 5G by 2020 as expected, subsequent adopters will have the benefit of lower network equipment and device costs, thus making the ecosystem transition smoother.
An important 5G ecosystem prerequisite, essential to building use cases, is optic fibre networks. But India lags far behind with lower than 30 per cent use of fibre as on date compared to more than 70 per cent in the US and China. CRISIL Research estimates that India needs to lay another 10 lakh fibre km to be 5G-ready. That will require an investment of over Rs 1 lakh crore.
Nearly three-fourths of this cost will occur to get right-of-way (RoW) approvals, which can be as high as Rs 1 crore per km in metros. We believe it will take three-four years for telcos to reach the required fibre levels, given delays in RoW and other permissions.
For telcos, getting RoW approvals has been as much an issue as making investments and RoW issues may delay fibre deployment. However, leasing of fibre can significantly reduce the investments required, depending on sharing modalities, and it will also make India 5G-ready sooner.
Furthermore, the Indian telecom industry is struggling under a massive debt load of Rs 4 lakh crore (as of March 31, 2018). In the recent past, a combination of asset and stake sales and sponsor support have helped telcos maintain their debt levels. But bundling of voice with data amid a price war, coupled with high investments, has resulted in low returns. We now see low single-digit returns on the capital employed in the industry compared to more than 15 per cent three-four years ago. So, telcos need to explore areas of revenue generation to make such investments viable.
While 5G-enabled devices are expected to enter India in late 2019 or early 2020, it may take another three-four years before mass adoption of affordable versions takes place. With the number of interconnected devices rising, the Internet of things will unfold newer revenue streams across domains such as healthcare, education and transportation. A lot is in store for Indian telcos, but things will not take a clear shape before fiscal 2023.
Copyright 2019. Living Media India Ltd
Sprint’s Earnings Report + Update on LTE Wireless Network and 5G Launch
Sprint Corp.’s third quarter earnings report showed the company’s effort to produce rapid growth and cut costs, while awaiting approval of its proposed $26.5 billion merger with T-Mobile US Inc.
On Thursday January 31th, the Overland Park-based wireless carrier reported its second consecutive quarter of year-over-year growth in wireless service revenue and its sixth consecutive quarter of postpaid net additions. The company also reported its 12th consecutive quarter of operating income.
Sprint reported 309,000 postpaid net additions in the quarter that ended Dec. 31, an improvement of 53,000 compared to the previous year, as the carrier focused on growing revenue per customer with wearables and other services.

“Sprint’s strategy of balancing growth and profitability while we work toward regulatory approval of our T-Mobile merger is reflected in our fiscal third-quarter results,” Sprint CEO Michel Combes said in a press release. “We delivered solid financials, increased network investments as we prepare for our mobile 5G launch, and continued the digital transformation of the company.”
For the full fiscal year, the company expects to cut costs by more than $1 billion for the fifth consecutive year, with net reductions of less than $500 million after reinvestments. Sprint more than doubled its quarterly network investments, or cash capital expenditures excluding leased devices, to $1.4 billion, and increased by approximately $150 million compared to the previous quarter as the company moved toward launching its 5G service. The company reports it now has 2.5 GHz spectrum deployed on approximately 75 percent of its macro sites, and has 27,000 small cells deployed — both key factors in deploying 5G service.
Sprint reported a net loss of $141 million in the quarter compared to a net income of $7.2 billion in the year-ago period.
https://www.bizjournals.com/kansascity/news/2019/01/31/sprint-third-quarter-earnings-report.html
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Highlights of Sprint’s Earnings Call:
Sprint CEO Michel Combes:
Atlanta is one of our Massive MIMO markets preparing for 5G launch in the coming months. That means fans in town for the Superbowl will see exceptional network performance in the highest traffic locations, whether they are inside or outside the stadium, to a nearby museum or hotel, or traveling around the city to one of the many special events planned this weekend.
We’re also preparing to launch our mobile 5G network in the first half of 2019. Our Massive MIMO radio are software upgradable to 5G NR as you know, allowing us to fully utilize our spectrum for both LTE and 5G simultaneously while we enhance capacity even further with 5G and begin to support new 5G use cases.
We celebrated an important milestone earlier this month on our path towards launching mobile 5G service in the first half of this year, when we completed the world’s first over-the-air 5G data transition using 2.5 and Massive MIMO on Sprint’s live commercial network.
We’ve also announced three 5G devices including smartphones from both LG and Samsung as well as a feature-rich mobile hotspot from HTC. The other carriers are not standing still, but our significant work investments, spectrum resources and cutting-edge technologies will help us continue to improve our network and we expect to deliver robust 5G experience in major metro areas.
Nevertheless, we’re hopeful to complete our merger with T-Mobile which is the only path to deliverings of breadth and depth of spectrum which will allow us to provide a truly consistent national-wide 5G experience to Americans.
As a stand-alone company, we love to scale to keep pace with the bigger carriers, AT&T and Verizon, in sustained capital investments and without additional low-band spectrum we will face challenges to provide customers with coverage comparable to that of the big two carriers.
Sprint CTO John Saw:
We expect to be substantially done with adding 2.5 GHz to where we needed it in another quarter, towards spring this year. And like we have said, we have made significant progress. A year ago, we were only at 50% of our sites having 2.5 GHz.
Small cells, again, a lot of momentum recently, 27,000 small cells. A year ago, we only had 3,000. So the permits are starting to come in. Some of our infrastructure that we are leveraging, especially with the cable companies, is making it easier for us to deploy small cells faster.
LTE Advanced has rolled out in more than 270 cities, and this is why we’re starting to make an impression even in the big markets where our customer experience speeds have improved significantly because of LTE Advanced.
We expect the LTE Advanced upgrades to complete around spring this year as well. Small cells will continue to be a focus for us because we need to continue to densify our networks even with 5G. A network is never done, Brett, so we are also rapidly transitioning to focusing on 5G as well. As you know, a lot of our radios that we’re deploying today with Massive MIMO allows us to simultaneously support LTE and 5G, and that is going to be the main focus for the rest of this year for 5G.
Closing remarks by Michel Combes:
We are aggressively executing our Next-Gen Network deployment to deliver a network build for unlimited with building the foundation for our mobile 5G network that will launch commercially in the coming months. We continue to enhance our value proposition and continue to transform our cost structure and customer experience with digital, artificial intelligence, advanced analytics and automation.
References:
Sprint’s Next-Gen Network and Massive MIMO as “linchpin for 5G”
NGNM Alliance conference with ITU on 5G and IoT licensing; RAN/Core Network report with WBA
The Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGNM) Alliance and ITU organized and successfully held a multi-stakeholder conference on licensing practices in the emerging, pre-standard 5G industry and the Internet of Things (IoT). The conference, held in Geneva, Switzerland, attracted representatives from network operators including NTT Docomo, vendors including Ericsson, Nokia and Microsoft, and licensing and standards bodies such as ETSI and the Japanese and European Patent Offices.
Also participating were representatives from vertical industries set to benefit from the introduction of 5G – including automotive, consumer electronics and semiconductors – as well as patent tool administrators.

A host of insightful sessions took place igniting an inclusive exchange on:
- Patent licensing practices with interactive discussions that focused on issues stakeholders need to be aware of.
- Sharing licensors’, licensees’ and pool administrators’ requirements on patent pools/platforms.
- Identifying proposed practices and conducts for paent licensors and licensees.
- Listing requirements for increasing transparency and assessing essentiality of Standard Essential Patents declared to Standards Developing Organisations.
“It’s great to notice that our joint ITU-NGMN conference has been such a success. Obviously, the 5G ecosystem is different. New use cases beyond mobile broadband – like massive IoT as well as highly demanding requirements from vertical industries on low latency, ultra-high reliability and security – are causing substantial network transformation,” NGMN CEO Dr. Peter Meissner said. All these challenges have implications on the intellectual property of mobile network operators and across the different industry segments. Conferences like this are key in identifying IPR issues and exploring solutions for the enlarged ecosystem,” he added.
On a related matter, NGMN will be hosting a Press & Industry Briefing on 5G use cases beyond mobile broadband on 26thFebruary 2019, from 11am – noon at Mobile World Congressin Barcelona, Spain. If you are interested in attending or speaking to an NGMN representative, please contact: ngmn(at)proactive-pr.com.
AT&T’s 5G Use Cases at NGNM Conference on Licensing Practices in 5G Industry Segments
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
NGMN and Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) have published the first results of their collaboration to drive the convergence of multi-technology RANs and core networks. The joint report identifies a number of emerging opportunities and use cases that the industry can benefit from through the convergence of 3GPP’s 5G and Wi-Fi, driven by the ever-enhancing capabilities of licenced and unlicensed technologies. It also highlights the key challenges, which must first be addressed in order to realise convergence over 3GPP Access and Wi-Fi – including tighter integration of Wi-Fi access in 5G networks, network manageability and policy control, and the enablement of Wi-Fi-only devices.
The convergence opportunity
Wi-Fi and cellular ecosystems have traditionally followed their own development paths. The latest versions of each technology have greatly enhanced capability compared with early offerings, with Wi-Fi 6 and 3GPP’s 5G, encompassing New Radio (NR) and LTE from Release 15 onwards, as well as the 3GPP 5G Core. However, as society increasingly depends on fast reliable data connectivity, NGMN and WBA believe an important capability for the industry is the convergence at a network level between 5G and Wi-Fi, so that the unique and complementary capabilities of both RANs can be leveraged to provide seamless network services. Bearing in mind that a significant amount of data traffic from smartphones use a Wi-Fi access, this will lead to a better user experience and create new business opportunities for both Wi-Fi and cellular providers.
New resource requirements
The report identifies a number of use cases and verticals that may require combined resources from both 5G and Wi-Fi networks in providing cost effective solutions that meet diverse sets of requirements on throughput, latency, connection density, coverage, availability and reliability. For example, enterprise services on cellular networks, and in particular, those that the 5G Core enables, may require a new look at the use of an access neutral mechanism for a number of reasons. These include gaps in coverage, the proliferation of indoor and outdoor Wi-Fi deployments, and potential for multi-site enterprise environments.
“Convergence of 5G and Wi-Fi can potentially bring major benefits to cellular operators, enterprise Wi-Fi and public Wi-Fi solution providers, giving access to 5G and enterprise services from both Wi-Fi and 5G access networks.” said Dr. Peter Meissner, CEO of the NGMN Alliance. “However, in order to realise service and network convergence, we have worked with the WBA to identify a number of requirements that must first be satisfied. This is particularly true in the enterprise and Public Wi-Fi space, where there is a demand from cellular operators for a standardised solution for improved visibility and control in the configuration and management of Wi-Fi access networks.”
5G/Wi-Fi Interworking
A number of industry developments and specifications address the interworking of 5G and Wi-Fi from a technical standpoint:
- 3GPP has already developed specifications to ensure tight integration of 3GPP and non-3GPP radio technologies, such as Wi-Fi. In order to better serve customers and provide the full 5G experience the tight integration of non-3GPP technologies needs to be ensured also within the 5G Core Network. Solutions enabling some of these objectives have already been adopted by 3GPP and Wi-Fi 6, such as the EAP authentication framework similar to Wi-Fi, to accommodate different wireless service subscription-types (e.g. mobile, wireless or fixed broadband) and their native authentication methods.
- 3GPP Release 15 provides some support for interworking between 5G and Wi-Fi. In particular, 3GPP Release 15 provides support for untrusted non-3GPP access (such as Wi-Fi) to the 5G core via Non-3GPP Interworking Function (N3IWF), with secure transport of Control-Plane/User-Plane (CP/UP) messages over an IKEv2/IPSec tunnels between the terminal devices and the N3IWF
- 3GPP Release 16 is continuing the work by enhancing capabilities for Wi-Fi integration, including trusted Wi-Fi support and access traffic steering, switching and splitting.
However, challenges and needs remain – including the enablement of Wi-Fi only devices to connect to the 5G core, further study to ensure the tight integration between 5G and Wi-Fi networks, an interface to enable certain level of network manageability and policy control between 5G core and Wi-Fi networks, and the ability of a client to route traffic over one or more accesses, making optimal use of the available connectivity. As a next step, the WBA and NGMN are undergoing further study on these challenges in order to uncover potential solutions. This will culminate in the recommendation of a future strategy for Converged RAN deployment, ensuring the best user experience making use of both Wi-Fi and Cellular access.
Tiago Rodrigues, General Manager of WBA said: “Wi-Fi 6 introduces new capabilities for carriers, cities and enterprises to cost effectively provide additional coverage and capacity, mainly indoor, to address the 5G use case requirements. Now it’s time to fully capitalize on these capabilities by delivering a clear strategic path for converged RAN deployments. This is a priority. We will continue to work closely with NGMN and its members to review, develop and test potential solutions, as identified in our recent 5G White Paper.”
https://www.ngmn.org/fileadmin/ngmn/content/downloads/Technical/2019/RAN_Convergence_Paper_V2.pdf
AT&T Extends Fiber Footprint, Grows Wireless Network; Identifies 2019 Strategic Initiatives
AT&T’s fiber footprint continues to grow. On yesterdays 4Q2018 earnings call, AT&T CFO John Stephens said: “We now passed more than 1 million customer locations with fiber and are on our way to hit the 40 million locations later this year. This will extend our fiber network to 22 million locations when include business. Subscribers on our fiber network increased by more than 1 million last year, driving the number of total broadband customers in our fiber footprint to substantially more than 3 million, and the longer we have fiber in the market the higher our penetration rates go.,,This performance is helping drive broadband revenue growth.”
AT&T CEO Randal Stephenson added: “We also accelerated our fiber deployment and we now reach a 11 million customer locations in addition to 8 million business locations. As a result, our broadband business grew by over 6% in the quarter and it’s really important to note that this fiber deployment is foundational to our 5G network.”
During the Q&A session, Stephenson said: “we will finish the lion share of the fiber build by mid-year. We’ll be at 14 million locations passed with our fiber footprint. You’re seeing now the impact as we move our customers into the fiber footprint. You’re not seeing the overall broadband subscribers grow, but as people migrate to fiber you’re seeing a significant lift in ARPU. We had 6% broadband growth in the fourth quarter with no overall subscriber growth. We added about 250,000 fiber customers roughly.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
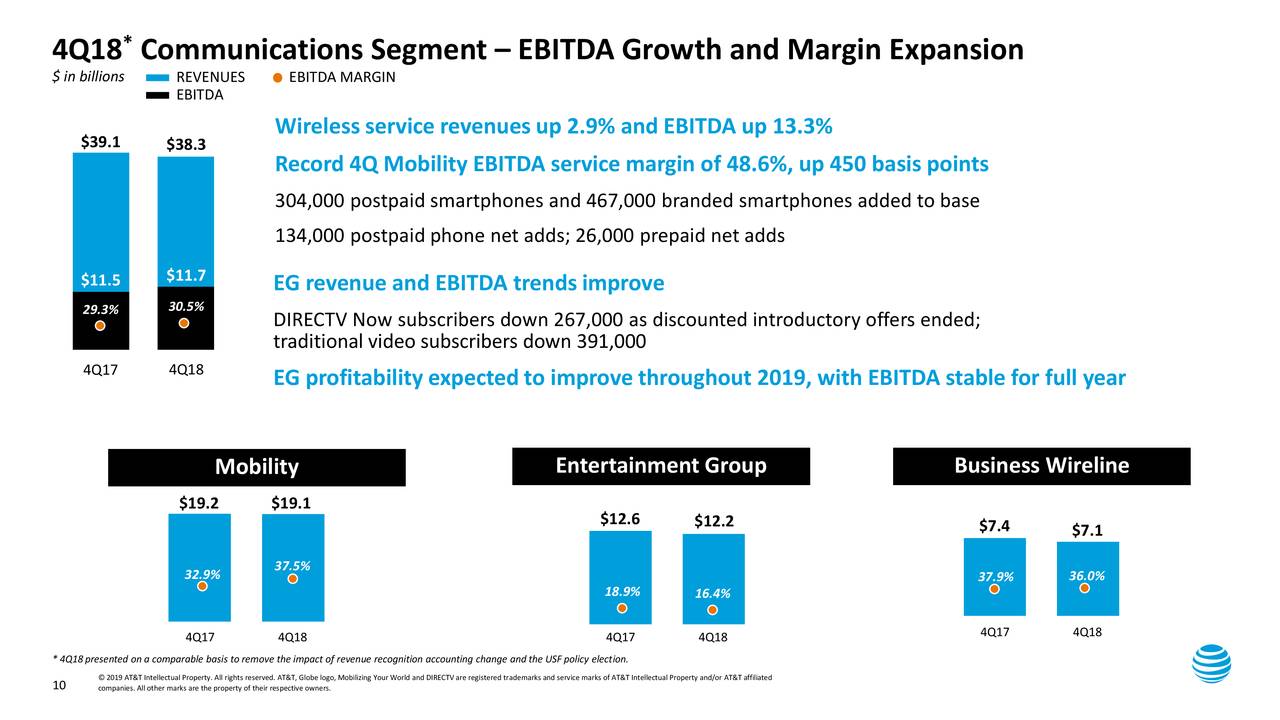
In the communications segment, AT&T’s largest business, the carrier and media giant gained a net 134,000 phone subscribers who pay a monthly bill, falling far short of analysts’ estimates of 208,000, according to research firm FactSet. AT&T has 153 million total phone subscribers. Churn, or the rate of customer defections, was 1 percent during the fourth quarter, up from 0.89 percent the previous year.
Stephenson played up AT&T’s wireless network when he said: “In terms of our networks, our quality and performance are on a very strong trajectory. GWS named us the best network and the most comprehensive study that’s been conducted. We introduced the first standards based mobile 5G network in parts of 12 cities last month and our first net deployments finished the year well ahead of schedule.”
During the Q&A, he added: “I will say over time three to five year time horizon unequivocally 5G will serve as a fixed broadband replacement product. I am very convicted that that will be the case. We are obviously on a standards-based path. We want a standards-based path that is mobile (5G) first, but just like every other product evolution and mobility this will play out the same.”
“Will you have enough capacity with 5G to have a good broadband product that serves as a streaming service for all of your DIRECTV NOW, your Netflix, etc? I absolutely am convinced that we will have that capacity, particularly as we turn up millimeter wave spectrum. That’s where the capacity and the performance comes from and that’s where you’ll begin to see a broad – a true replacement opportunity for fixed line broadband. So I have little doubt that in the three to five year time horizon you’ll start to see substitution of wireless for fixed line broadband.”
With respect to AT&T’s 5G Evolution (which is really 4G+), Stephens said: “We also made significant strides in our (5G, but really 4G+) network of evolution in the fourth quarter. Randall told you about our network leadership (referred ti as “standards based 5G;” yet the IMT 2020 standard won’t be completed till late 2020 at the earliest) in 5G introduction. With the additional spectrum we’re adding, carrier aggregation and other network improvements, 5G evolution is producing better speeds for our customers today when compared to standard LTE. Our first net deployment is reaching critical mass and providing a tailwind for our results.”
During the Q&A session Stephens added: “We’re seeing the effects of 5G evolution be real and in customers hands today which is making a difference. We do have about 450,000 FirstNet qualified customers from about 5000 organizations or departments that have signed up for it. A significant amount of those early adopters were migrations, so maybe close to two thirds or 60% or so, but we are now getting a lot of new ads. And as this build out gets passed the existing 40% in the 50%, 60% and 70% so to speak as we continue make that progress, I think you’ll see us begin to grow that new customer share and numbers significantly.
So we really do view that as a tailwind for the whole business as it improves existing customers quality, speed, throughput, but it also gives us visibility which we’ve been successful at, our teams had a good job with gaining new customers.”

Here are AT&T’s strategic goals for 2019: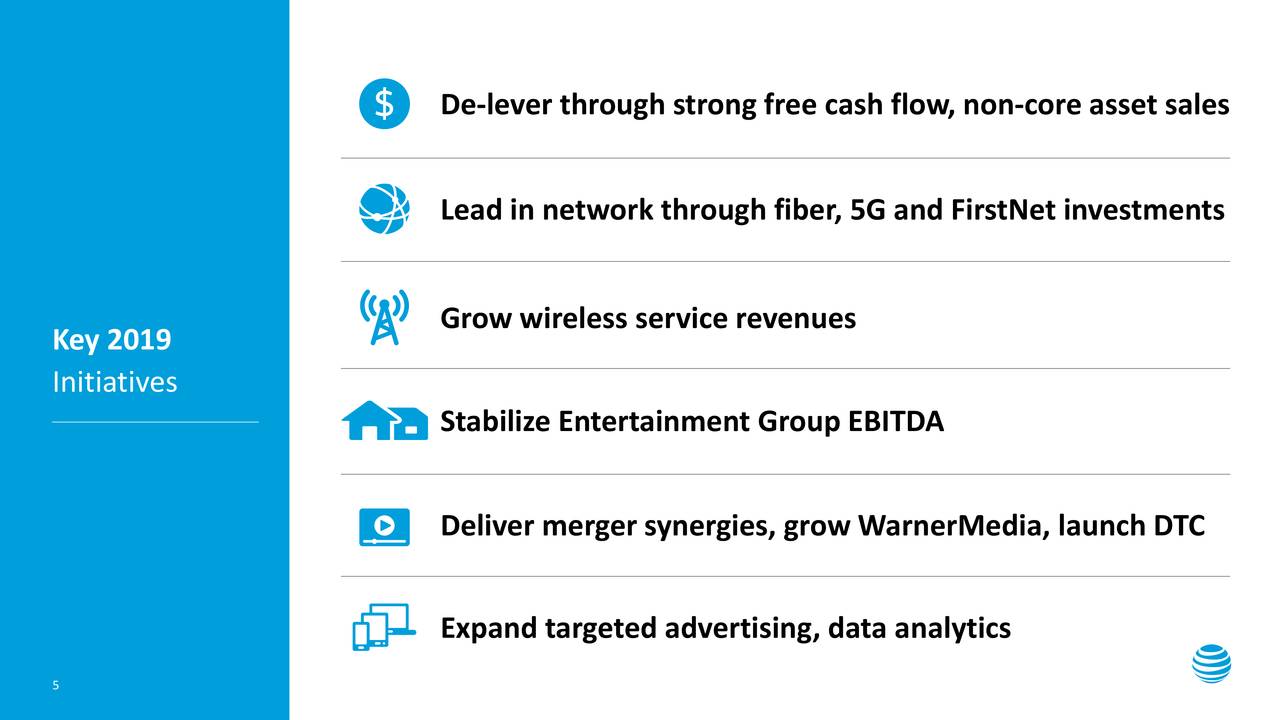
Here are the 4Q2018 Results of AT&T’s Communications business:
Analyst Opinions:
AT&T’s revenue of $47.99 billion missed estimates of $48.5 billion. AT&T also reported net additions of 134,000 phone subscribers, below analyst estimates of 308,000. The company also lost 403,000 satellite TV subscribers and 14 percent of its DirecTV Now streaming subscribers in the quarter.
Bank of America analyst David Barden said that, despite the quarter’s shortcomings, AT&T is moving in the right direction. “Within the wireless business, which accounts for 50% of total EBITDA, service revenue grew, net adds were positive, and EBITDA beat by a material amount as the handset upgrade rate was much lower than expected,” Barden wrote.
Raymond James analyst Frank Louthan said AT&T is prioritizing deleveraging its balance sheet in 2019 and should be able to hit its 2.5 times target by the end of the year. “We believe the video sub trends will be offset as marketing packages with mobility and FirstNet take hold and drive improved profitability per sub, but this could take time for investors to see the signs,” Louthan wrote.
Morgan Stanley analyst Simon Flannery said there were some encouraging signs for investors in the fourth quarter, but AT&T has limited near-term financial visibility as it digests its Time Warner acquisition.
IHS Markit 5G Smartphone Whitepaper; Analysts on Samsung’s Feb. 20 Galaxy 10 Launch?
IHS Markit 5G Smartphone Whitepaper:
In a new complimentary white paper, “Substance behind the Hype: 5G Smartphones Primed and Ready for Fast Rollout,” IHS Markit explores how the global 5G transition is poised to take place at a faster pace than for any previous wireless generation transition. “It is easy to paint the current momentum behind 5G as the usual pre-launch hype drummed up by vested stakeholders,” said Wayne Lam, principle analyst for IHS Markit and lead author of the white paper. “However, the mobile industry is fundamentally better prepared and more aligned with a common standard than at any previous technology transition.”
Industry uncertainly adds friction to development and discourages firms from making big bets when the outcome is less than certain. While past wireless technology upgrades had competing standards vying for industry attention, there is no doubt about the air interface standard that will be used for 5G. “The 5G electronic ecosystem is significantly more mature, at this point, compared to the same time during the LTE transition,” Lam said. “Key 5G chipsets have been tested, proven and designed into devices, and the industry is now poised to deliver their first 5G smartphone in early 2019.”
“As telecom companies embark on the start of another wireless generation transition, they are doing so with a robust and coordinated ecosystem of carriers, handset makers and component suppliers,” Lam said. “By and large, the industry is finding itself with an unprecedented opportunity to execute a wireless transition in the best position possible.”
To download the complimentary “Substance behind the Hype: 5G Smartphones Primed and Ready for Fast Rollout” white paper from IHS Markit, visit https://cdn.ihs.com/www/pdf/0119/IHSMarkit-Whitepaper_5G-Smartphone_Jan2019.pdf.
Update: Global smartphone market ends 2018 on downturn
By Gerrit Schneemann, smartphones senior research analyst, IHS Markit; Wayne Lam, mobile devices and networks director, IHS Markit; and Jusy Hong, mobile handset devices director, IHS Markit
Global smartphone shipments recorded a negative year-over-year growth rate in the fourth quarter (Q4) of 2018, for a third consecutive quarter. According to IHS Markit preliminary smartphone data, global smartphone shipments reached 365.2 million units in Q4 2018, which is a 5.7 percent y/y decline. For the 2018 calendar year, shipments declined 2.4 percent compared to the previous year, from 1.44 billion units in 2017 to 1.41 billion units in 2018.
Following is an overview of the smartphone market leaders in 2018, based on unit shipments:
Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics maintained its shipment-volume lead, shipping 70.2 million units in Q4 2018. Samsung’s negative growth rate in 2018 continued, as shipments declined 5.5 percent compared to the same quarter of 2017. As a result, its market share fell to 19.2 percent in Q4 2018, which is flat compared to the previous year. Severe competition from Chinese rivals in many regions continued to impact Samsung’s business – and has led to Samsung changing its strategy for how new technologies are deployed in the company’s product range. For example, the first triple-camera Samsung device was a Galaxy A phone and, instead of a Galaxy S device, Samsung released the world’s first quad-camera smartphone – the Galaxy A9 — last year.
Overall Samsung smartphone shipment volume declined 8 percent, falling from 316 million units in 2017 to 290 million units in 2018. This is the first time Samsung shipped fewer than 300 million units in any year since 2014.
Huawei
Huawei shipped 60.5 million units in Q4 2018, rising 47.7 percent, year over year. The company continued its double-digit y/y growth for the fourth consecutive quarter, growing in most of regions, except North America where Huawei has little exposure. Fast growing markets for Huawei include Europe, Middle East and Africa. In 2018, Huawei was able to exceed Apple in unit-based shipments for three consecutive quarters, propelling the Chinese brand to second-ranked position in the market, unseating Apple from its perch. However, the network infrastructure side of Huawei has faced increased scrutiny from the United States and other governments around the world, due to potential security concerns in to roll out of 5G networks.
Apple
Apple shipped 64.3 million units in Q4 2018, down 16.9 percent from 77.3 million units in Q4 2017. The company’s performance faced significant challenges in China and in the overall global smartphone market in Q4 2018. Furthermore, Apple’s super-premium handset pricing seems to have stunted its unit growth potential in the quarter. Importantly, there is no quick fix for Apple to change fortunes in China or India. In China, local competition is fierce; while in India, Apple’s products are ill-equipped to fit into the country’s price-cautious market.
Xiaomi
The recent trend of high double-digit growth halted for Xiaomi in Q4 2018. The company shipped 24.8 million units, down 12.1 percent from 28.2 million units in Q4 2017.
Oppo and Vivo
Oppo and Vivo shipped 26.4 and 25.2 million units, respectively. Oppo shipments declined 3.6 percent, while Vivo shipments grew 7.2 percent.
Conclusions
Xiaomi, Oppo and Vivo were adversely affected by the continued negative growth of the smartphone market in China. On the other hand, Huawei strengthened its market leadership in China. Tension between the US and China stimulated a feeling of patriotism in China, leading smartphone users to choose Huawei over other brands. Moreover, Huawei boasts significant international business – which other brands are still working to establish – enabling the company to achieve tremendous success in the fourth quarter.
The combined market concentration on the top six companies continued to intensify in Q4 2018, accounting for 75 percent of global smartphone shipments. Most of the rest brands saw their shipments and market shares fall in the quarter.
Meanwhile, Nokia increased its shipments to 15 million units in 2018, up from 5 million units in the previous year. Finland-based HMD Global is operating its Nokia-branded smartphone business, by focusing on mid-range and low-end smartphones in Europe, Asia and Africa. The company will soon expand into North America.
Quarterly Global Smartphone Shipments (Millions of Units)
| Q4-18 | Q3-18 | Q4-17 | QoQ | YoY | |||||
| Rank | Shipments | M/S | Shipments | M/S | Shipments | M/S | |||
| 1 | Samsung |
70.2 |
19% |
70.9 |
20% |
74.3 |
19% |
-1% |
-6% |
| 2 | Apple |
64.3 |
18% |
46.9 |
13% |
77.3 |
20% |
37% |
-17% |
| 3 | Huawei |
60.5 |
17% |
52.0 |
15% |
41.0 |
11% |
16% |
48% |
| 4 | Oppo |
26.4 |
7% |
31.2 |
9% |
27.4 |
7% |
-15% |
-4% |
| 5 | vivo |
25.2 |
7% |
28.9 |
8% |
23.5 |
6% |
-13% |
7% |
| 6 | Xiaomi |
24.8 |
7% |
33.3 |
9% |
28.2 |
7% |
-26% |
-12% |
| 7 | LG |
11.1 |
3% |
11.6 |
3% |
13.9 |
4% |
-4% |
-20% |
| 8 | Motorola |
10.1 |
3% |
10.7 |
3% |
11.4 |
3% |
-6% |
-11% |
| 9 | TCL-Alcatel |
4.5 |
1% |
5.7 |
2% |
4.8 |
1% |
-21% |
-5% |
| 10 | Nokia |
4.2 |
1% |
4.5 |
1% |
4.4 |
1% |
-7% |
-5% |
| Others |
63.3 |
18% |
59.9 |
17% |
81.3 |
21% |
6% |
-22% |
|
| Total |
365.2 |
|
355.6 |
|
387.4 |
|
3% |
-6% |
|
Source: IHS Markit – Smartphone Intelligence Service
© 2019 IHS Markit
Global Smartphone Shipments (Millions of Units)
| Rank | Company | 2018 | 2017 | YoY |
| 1 | Samsung | 290 | 316 | -8% |
| 2 | Huawei | 206 | 153 | 35% |
| 3 | Apple | 205 | 216 | -5% |
| 4 | Xiaomi | 120 | 92 | 30% |
| 5 | Oppo | 115 | 118 | -2% |
| 6 | vivo | 104 | 95 | 9% |
| 7 | LG | 45 | 56 | -19% |
| 8 | Motorola | 39 | 38 | 3% |
| 9 | TCL-Alcatel | 17 | 21 | -18% |
| 10 | Nokia | 15 | 5 | 175% |
| Others | 254 | 334 | -24% | |
| Total | 1,410 | 1,444 | -2% |
Source: IHS Markit – Smartphone Intelligence Service
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About IHS Markit (www.ihsmarkit.com)
IHS Markit (Nasdaq: INFO) is a world leader in critical information, analytics and solutions for the major industries and markets that drive economies worldwide. The company delivers next-generation information, analytics and solutions to customers in business, finance and government, improving their operational efficiency and providing deep insights that lead to well-informed, confident decisions. IHS Markit has more than 50,000 business and government customers, including 80 percent of the Fortune Global 500 and the world’s leading financial institutions. Headquartered in London, IHS Markit is committed to sustainable, profitable growth.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Analysts Weigh-in on Samsung’s Feb. 20 Galaxy 10 Launch?
Avi Greengart, a mobile device analyst with GlobalData, said a big challenge with every new phone model release for Samsung and other vendors is that as phones have matured, users are holding onto their phones longer.
“As much as Samsung needs to compete with Apple, it needs to compete with the phone consumers already have – the S10 needs to be a phone that entices existing Android phone owners to upgrade,” Greengart told eWEEK. “We know what phones are and what they do – no single new feature is likely to be groundbreaking. However, design is definitely an area of focus; Samsung was actually the first vendor with an edge-to-edge display, but now that’s not enough.”
The new phones will almost certainly include 5G capabilities for each of the major mobile carriers’ networks as they come online, but more will be needed to make a sales impact, he said.
“There is a tricky balance that Samsung must hit – it needs radical designs and bleeding edge technologies like folding displays and 5G that push the envelope for early adopters, but it also must make more traditional 4G phones exciting enough to entice mainstream consumers to upgrade as well,” Greengart said. “It’s not enough to just cram massive amounts of technology into the phone for the wealthiest consumers. In the U.S., the competition really is focused around Apple and Samsung, but in Europe and Asia, Chinese brands like Honor and Xiaomi are attacking Samsung with premium phones at lower price points.”
Charles King, principal analyst with Pund-IT, agreed. “At this point, Samsung is one of the two to three phone makers that can and do fight Apple to a draw,” King told eWEEK. “With phones like Samsung’s [current] Galaxy S9, it really comes down to the buyer’s operating system and applications preferences. That’s a significant contributor to Apple’s overall slowdown in iPhone sales growth over the last few months.”
For buyers, solid and noticeable improvements in cameras and displays in newer phones can help Samsung inspire more sales of its latest handsets, while a larger issue for many customers are the high prices of the devices, King said. “I believe the emergence of $1,000 handsets last year clarified the ceiling of what the vast majority or consumers will pay for a smartphone. So it’s important for Samsung to either deliver significant, compelling new features or performance capabilities, or to show greater flexibility in pricing.”
Tuong Nguyen, an analyst with Gartner, said a big issue that Samsung and other handset makers have to deal with when releasing new models nowadays is that for buyers, it’s tough to differentiate because all the major vendors have large screens, plenty of storage and all the rest.
For Samsung and other smartphone makers, there are no current “must-have” features that can be included in a handset to assure huge resulting sales of the phones, he said. “I think there are numerous features that are compelling, but they need to improve and come together in a way that increases the value proposition of smartphones in a significant way.”
What could boost sales for a phone would be the ability to use a smartphone as a hub or centralized device so users could control different aspects of their tech lives without having to open multiple apps or make other adjustments, Nguyen said. “I would categorize all this under learn, predict, surprise and anticipate. This is the type of step change we need to drastically attract users,” Nguyen said.
Another analyst, Rob Enderle, principal of Enderle Group, told eWEEK he expects the new Samsung flagship devices to include 5G, a bump in performance and features such as battery life and camera quality, as well as enhancements in wireless charging–including a rumored feature that enables the phone to charge another device wirelessly at the same time. What Samsung will have to try to overcome, though, is that because wide deployments of 5G is still more than a year away many users may be satisfied to hang on to their existing handsets for now, Enderle said.
“Smartphones have been really good for years now, and the natural need to replace them has dropped sharply over time,” said Enderle. “In the current period, this behavior is likely more directly related to a reduction in effective demand-generation.”
https://www.eweek.com/mobile/can-we-expect-5g-at-samsung-s-feb.-20-galaxy-10-launch
Huawei launches 5G multi-mode chipset and 5G CPE Pro Smartphone
Huawei officially launched its 5G multi-mode chipset Balong 5000 — along with the first commercial 5G device powered by it, the Huawei 5G CPE Pro. The Chinese tech giant claims that together, these two new products provide the world’s fastest wireless connections for one’s smartphone, home, at the office and on-the-go. We don’t doubt that.
Balong 5000 officially unlocks the 5G era, according to Huawei. This chipset supports a broad range of 5G products in addition to smartphones, including home broadband devices, vehicle-mounted devices and 5G modules.

Photo courtesy of Huawei. Huawei’s 5G CPE Pro achieves a high speed of 3.2 Gbps in live network tests.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“The Balong 5000 will open up a whole new world to consumers,” said CEO of Huawei’s Consumer Business Group Richard Yu. “It will enable everything to sense, and will provide the high-speed connections needed for pervasive intelligence. Powered by the Balong 5000, the Huawei 5G CPE Pro enables consumers to access networks more freely and enjoy an incredibly fast connected experience. Huawei has an integrated set of capabilities across chips, devices, cloud services and networks. Building on these strengths, as the leader of the 5G era, we will bring an inspired, intelligent experience to global consumers in every aspect of their lives.”
Balong 5000 supports 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G on a single chip. It reduces latency and power consumption when exchanging data between different modes, and will significantly enhance user experience in the early stages of commercial 5G deployment.
“Balong 5000 is the first chipset to perform to industry benchmarks for peak 5G download speeds. At sub-6 GHz (low-frequency bands, the main spectrum used for 5G), Balong 5000 can achieve download speeds up to 4.6 Gbps. On mmWave spectrum (high-frequency bands used as extended spectrum for 5G), Balong 5000 can achieve download speeds up to 6.5 Gbps — 10 times faster than top 4G LTE speeds on the market today,” Huawei said.
On a 5G network, a 1-GB HD video clip can be downloaded within three seconds, and 8K video can be streamed smoothly without lag. This sets a new benchmark for home CPEs. In addition to homes, the Huawei 5G CPE Pro can also be used by small and medium-sized enterprises for super-fast broadband access.
Adopting new Wi-Fi 6 (IEEE 802.11ax) technology, the Huawei 5G CPE Pro delivers speeds of up to 4.8 Gbps. It is the first 5G CPE that supports HUAWEI HiLink protocols, bringing smart homes into the 5G era.
As a 5G pioneer, Huawei began research and development in 5G as early as 2009, and is currently the industry’s only vendor that can provide end-to-end 5G systems. Huawei has more than 5700 engineers dedicated to 5G R&D, including over 500 5G experts. In total, Huawei has established 11 joint innovation centers for 5G solutions worldwide
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The NY Times reported that in 2018, Huawei edged out Apple as the second-biggest provider of cellphones around the world. Richard Yu, who heads the company’s consumer business, said in Beijing several days ago that “even without the U.S. market we will be No. 1 in the world,” by the end of this year or sometime in 2020.
Last year, AT&T and Verizon stopped selling Huawei phones in their stores after Huawei began equipping the devices with its own sets of computer chips — rather than relying on American or European manufacturers. The National Security Agency quietly raised alarms that with Huawei supplying its own parts, the Chinese company would control every major element of its networks. The N.S.A. feared it would no longer be able to rely on American and European providers to warn of any evidence of malware, spying or other covert action.
For months, the White House has been drafting an executive order, expected in the coming weeks, that would effectively ban United States companies from using Chinese-origin equipment in critical telecommunications networks. That goes far beyond the existing rules, which ban such equipment only from government networks. “China’s 2017 National Intelligence Law requires Chinese companies to support, provide assistance and cooperate in China’s national intelligence work, wherever they operate.”
The White House’s focus on Huawei coincides with the Trump administration’s broader crackdown on China, which has involved sweeping tariffs on Chinese goods, investment restrictions and the indictments of several Chinese nationals accused of hacking and cyberespionage. President Trump has accused China of “ripping off our country” and plotting to grow stronger at America’s expense.
References:
https://consumer.huawei.com/en/press/news/2019/huawei-launches-5g-multi-mode-chipset-and-5g-cpe-pro/
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/28/us/politics/meng-wanzhou-huawei-iran.html
IHS Markit: SDN deployed by 78% of global service providers at end of 2018
By Michael Howard, senior research director, carrier networks, IHS Markit
Highlights
- All of the 23 service providers surveyed reported that they will deploy SDN at some point. More than three-quarters (78 percent) of those providers will deploy or evaluate the architecture by the end of this year, growing to 87 percent by the end of 2019.
- Software-defined wide-area networks (SD-WANs) leads the list of SDN-based services expected to generate new revenue, with 78 percent of respondents identifying it as a key deployment goal, while nearly half (48 percent) plan to implement network slicing for IoT.
- Automation and reduction of capex and operating-expenditure (opex) are among the goals for the top domains for SDN deployments. By the end of 2019, 74 percent of respondents will use SDN to automate the delivery of new services, followed by operations and management at 65 percent.
Our analysis
Service providers are in the early stages of a long-term transition to software-defined networks (SDN), according to the sixth annual “Carrier SDN Strategies Service Provider Survey” in 2018 from IHS Markit. Various barriers and drivers have become more prominent, as operators get closer to commercial deployment, although the barriers remain. These barriers include the problem of products that are not carrier grade and difficulty with integration into existing networks.
Service providers around the globe – representing 44 percent of worldwide telecom capital expenditure (capex) and 44 percent of revenue – are investing in software defined networks (SDNs) as part of a larger move to automate their networks and transform their internal processes, operations, and the way they offer services to their customers. Providers view SDN as a key technology underpinning the fundamental changes in telecom network architecture that delivers benefits in new service agility, quicker time to revenue, automation, operational efficiency, and capex savings.
Many operators have some parts of their networks running under SDN control. The rest are moving from their proof-of-concept (PoC) investigations and evaluations for SDN toward commercial deployments in the tail end of 2018 and 2019.
The top two reasons service providers are investing in and deploying network SDN are the following:
- Simplification and automation of service provisioning, leading to service agility and quicker time to revenue
- End-to-end network management and control as part of increased automation
The majority of service providers are investing in SDN in order to simplify and automate the provisioning of their networks for end-to-end network and service management and control—with the goal of having a global view of network conditions across the various vendors’ equipment, network layers, and technologies. SDN figures in provider plans to generate revenue, with multi-cloud and network slicing for applications and IoT figuring more prominently this year.
Still, carriers will learn that some avenues are not as fruitful as expected, and telecom equipment manufacturers and software suppliers may well invent new approaches that open up new applications.
Carrier SDN Strategies Service Provider Survey – 2018
This sixth annual survey of global service providers explores plans and strategies of 23 operators for evaluating and deploying SDNs. The study identifies the drivers for this fundamental change in service provider network architecture and explores use cases, development stages, barriers, applications, target network areas, and timing of deployment plans.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Note:
But what SDN model or version was implemented by these service providers? That is not stated in Michael Howard’s report.
There’s the classical SDN/Open Flow model from ONF, the overlay or virtual network model, the evolutionary model, hybrid model, DevOps management model, VMWare’s two NSX versions, etc
Also, most versions of SDN use a centralized controller and NOT segment or hop by hop routing. Yet Cisco and Juniper routers can handle segment-routing traffic. Their versions of SDN are ready for segment routing, as well. Moreover, Linux has an open source implementation of segment routing, and Cumulus Networks’ Linux-based network OS also supports it.
With so many different versions of SDN, it appears that network equipment and software built for one SDN based network will not work on ANY other service provider’s SDN unless multiple SDN versions/models are supported in the same equipment/software.
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20170811/three-different-sdn-models-tag27-tag99
https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/tip/Three-models-of-SDN-explained
https://searchvmware.techtarget.com/opinion/VMwares-two-NSX-versions-are-the-future-of-SDN
OpenVault: Broadband Internet Usage Accelerated in 2018
Executive Summary:
U.S. households consumed an average of 268.7 gigabytes (GB) of data in 2018, up from 201.6 GB for 2017, according to a new report about U.S. household broadband data consumption from OpenVault, a provider of data consumption and analytics software. Median usage was 145.2 GB per household in 2018, up from 103.6 GB in 2017. The increase in average consumption was 33.3% and the increase in median consumption was 40%.
Open Vault attributed the different growth rates to growing consumption across service providers’ entire subscriber bases, rather than growth only among heavy users. Their year end 2018 data showed that:
U.S. Household Broadband Data Consumption:
- Average usage for households with flat-rate pricing was 282.1 GB per household, which was more than 9% higher than the 258.2GB average usage for households on usage-based billing (UBB) plans. Average usage for all households was 268.7GB/HH in 2018, up from 226.4GB/HH at the end of June 2018 and a 33.3% increase over the YE 2017 average of 201.6GB/HH.
- Median usage was 145.2GB/HH in 2018, up from 116.4GB/HH in June 2018 and a 40% increase over the YE 2017 median of 103.6GB/HH.
- The percentage of flat-rate (non-UBB) households exceeding 1 terabyte (TB) of usage was 4.82%, a full percentage point higher than the 3.81% of UBB households that exceeded the 1 TB threshold.
- The percentage of households using 1TB or more almost doubled in 2018, rising to 4.12% of all households from 2.11% in 2017, while the percentage of households exceeding 250 GB rose to 36.4% from 28.4% during the same time frame.
In addition to analyzing trends in broadband consumption, OpenVault also tracked expansion within the US consumer device landscape, observing a 5.3% increase in connected devices when comparing the week after Christmas with the week before Christmas. While Amazon, Samsung and Apple collectively accounted for the majority of the growth, the 15.6% rate of increase for Amazon devices was significantly higher than the rates of growth for Samsung (4.1%) and Apple (2.9%).
“As connected devices, streaming services and broadband speeds increase, service providers need an alternative to infrastructure upgrades that would enable them to keep up with demand,” said Josh Barstow, Open Vault executive vice president of corporate strategy and business development, in a prepared statement about the U.S. household broadband data consumption research. “Our analysis makes it clear that usage-based billing is among the most effective tools the industry has in managing consumption and reducing the need for massive capital expenditures.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
3GPP RAN WG meeting in Taiwan: January 21 – 25, 2019: NTT DOCOMO’s URLLC Use Cases
3GPP RAN WG meeting in Taiwan: January 21 – 25, 2019:
A five-day working group meeting of the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) RAN WG opened in Taiwan on Monday January 21, 2019, with 459 registered delegates attending. The goal of the meeting is to progress 3GPP Release 16 which will include an important IMT 2020 Use Case: Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC). I counted over a dozen contributions on the URLLC topic at this 3GPP meeting’s document list which can be accessed here.
Services for latency sensitive devices for applications like factory automation, autonomous driving, and remote surgery. These applications require sub-millisecond latency with error rates that are lower than 1 packet loss in 10⁵ packets [ITU-R M.2410.0]. New techniques need to be devised to meet the stringent latency and reliability requirements for URLLC.
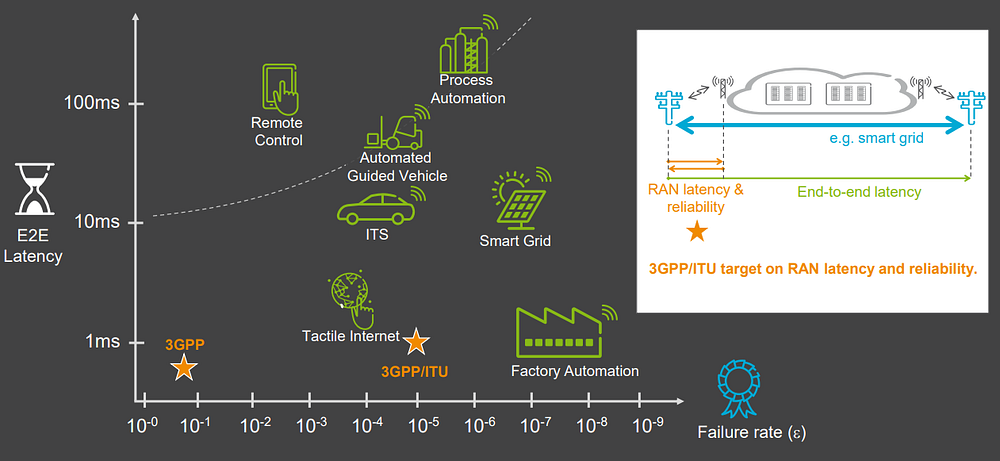
An interesting 3GPP RAN meeting contribution on Views and evaluations for URLLC scenarios by Kazuaki Takeda of NTT DOCOMO will be presented this week. In that contribution, NTT DOCOMO selected the following cases for evaluation:
| Case | Use-case | Reliability | Latency | Data packet size and traffic model | Description |
| 1 | Factory automation
@ 30GHz |
99.9999 (%) | 2ms for end-to-end
1ms for air-interface |
DL & UL: 32 bytes
Periodic and deterministic traffic model with data arrival interval 2ms |
Motion control |
| 2 | Factory automation
@ 4GHz |
99.9999 (%) | 2ms for end-to-end
1ms for air-interface |
DL & UL: 32 bytes
Periodic and deterministic traffic model with data arrival interval 2ms |
Motion control |
| 3 | Rel.15 enabled use-case in indoor hotspot
@ 4GHz |
99.9 (%) | 7ms for air-interface | DL & UL: 4096 bytes
FTP model 3 |
AR/VR |
| 4 | Rel.15 enabled use-case in urban macro
@ 4GHz |
99.999 (%) | 1ms for air-interface | DL & UL: 32 bytes
FTP model 3 |
Sporadic traffic |
| 5 | Power distribution
@ 700MHz |
– | – | – | UL/DL SINR CDF only |
There are high interests on supporting industrial IoT type of services at local area using carrier frequencies of around 4GHz and 30GHz [2]. It would be possible to evaluate NR performance in this type of scenario by simulating case 1, case 2, and case 3. For AR/VR type of services in a specific local area, it is not sure whether all the packets should be delivered as URLLC packets, or some specific type of packets (e.g., control packet) for AR/VR service should only be delivered as URLLC packets (i.e., other types of packets for AR/VR service can be delivered as eMBB). The simple way is to treat all the packets as URLLC packets as the evaluation assumption. Case 3 can be viewed as representing such situation. For emergency type of services in wide area, it can be represented by case 4. As the case 5, we partly evaluate the wide area performance at 700MHz.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Taiwan 5G Commercialization Summit
In conjunction with the referenced 3GPP working group meeting, the Taiwan 5G Commercialization Summit organized by Taiwanese entities was also held in Taipei on Monday, January 21st. The organizers of the Taiwan 5G summit were: MediaTek, Chunghwa Telecom, the Taiwan Association of Information and Communications Standards, and the 5G Office of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA). Tung Tzu-hsien (童子賢), the head of iPhone assembler Pegatron Corp and a private sector group advising the government’s national innovation/new economy task force, said 5G technology is expected to drive sophisticated applications of the future such as smart medical care and the Internet of Vehicles. Many of those new applications will require URLLC.
Mr. Tung urged the Taiwan government to update regulations to meet the needs of a fast-changing telecom environment and prevent Taiwan from lagging behind other countries in 5G development. As long as Taiwan is successful in 5G development, it will create major commercial opportunities for the local Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector, he added.
Since January 2018, Chunghwa Telecom has teamed up with the MOEA’s 5G Office, and the government-sponsored Institute for Information Industry (III) and Industrial Technology Research Institute in a 5G development alliance.
ZTE makes prototype smartphone call on China Unicom’s trial 5G network vs Huawei’s 5G NR @ 2.6GHz?
ZTE, which recently completed the 3rd phase of CMIIT IMT-2020 5G core network tests, just announced it made the a 5G mobile call using its 5G prototype smartphone on the Guangdong branch of China Unicom’s trial 5G network in Shenzhen, China. The trial was conducted in collaboration with China Unicom and involved placing a 3GPP Release 15 compliant New Radio (NR) non-standalone (NSA) mobile call using the prototype smartphone. It used ZTE’s 5G end-to-end solution, including radio access network, core network, transport network and prototype device. In addition to demonstrating a 5G call, the test verified key 5G technologies including Massive MIMO, 5G NR, non-standalone (NSA) dual connectivity, FlexE transport technology and 5G common core architecture (defined by who?).

ZTE says “the future 5G system should be a unified network adaptable to different scenarios.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“ZTE’s 5G solution has passed the end-to-end test in the three months after the release of the 3GPP Rel-15,” ZTE said in a statement. “It showcases ZTE’s strong competency in 5G R&D and commercialization, demonstrating ZTE’s role as a reliable partner to global 5G operators and a key player in the 5G industry.”
Last year, ZTE announced a series of new-generation 5G base stations. The Chinese telecom and mobile phone vendor said that the new generation of 5G high/low frequency Active Antenna Unit (AAU) base stations support 3GPP release 15 “5G NR” NSA specification for the data plane. The latest ZTE base stations combine the radio and antenna parts. It is capable of integrating multiple frequency bands, which create what is known as the “AAU solution.” AAU supports 5G functions such as Massive MIMO and Beamforming.
Meanwhile, Huawei says it completed a 5G New Radio (NR) trial in the 2.6 GHz spectrum band. Huawei said 2.6 GHz is one of the “excellent choices for operators to deploy 5G NSA/SA commercial network.” The company noted that 2.6 GHz is an “abundant spectrum resource around the world, but not fully used in many areas.” Huawei’s tests in the 2.6 GHz band follows earlier trials in the 3.5 GHz and 4.9 GHz bands.
The two Chinese telecom vendors are vying to take the lead in 5G testing under the jurisdiction of China’s IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group, which was established in 2013 as China’s platform to promote 5G research in that country. The 5G R&D trial established three separate phases for verifying a 5G solution: key technologies, technical solutions, and system networking.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/press-center/news/201901/20190118
https://www.zte.com.cn/china/topics/zte-5g-en/index.html
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/huawei-takes-5g-supremacy-shot-at-zte/2019/01/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/tag/chinas-imt-2020-promotion-group/



