Cignal AI: NA Optical Network Spending to Accelerate; IEEE 802.3ct; NeoPhotonics 400G Multi-Rate Transceiver
|
||
 |
Additional 2Q21 Transport Hardware Report Findings:
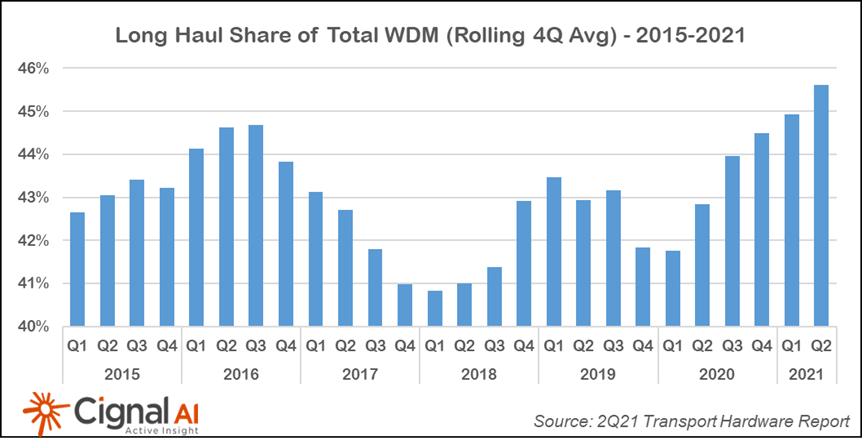
- The spending mix between long-haul and metro WDM reached a record level following 5 quarters of investment in advanced coherent and line system technology. Carriers may be deferring metro expenditures considering the imminent availability of transport system upgrades utilizing 400G coherent pluggables.
- Chinese optical and packet hardware spending collapsed, resulting in the largest single quarterly decline on record and the first instance of consecutive quarters with YoY declines.
- Sales of optical hardware in EMEA were up significantly YoY as the region continues to produce steady single-digit growth. Despite strategic wins by Nokia and observations of increasing replacement activity from Ciena, Huawei’s footprint in EMEA shows no noticeable impact from geopolitical factors.
- North American packet transport sales were up slightly, with market leader Cisco realizing gains in Core as its 8000 series routers ramp.
- Component shortages weighed on smaller equipment manufacturers as constrained global semiconductor production increased lead times. ADVA and Infinera quantified the effect on sales (10% and 6% of revenue, respectively), though larger vendors reported minimal impact on their sales. Vendors do not anticipate resolution of these issues until 2022.
Editor’s Note: IEEE 802.3ct and 100GBASE‑ZR
It will be interesting to see if optical packet transport will evolve from to Ethernet MAC frames directly over DWDM systems. IEEE 802.3ct “Physical Layers and Management Parameters for 100 Gb/s Operation over DWDM Systems” standard was approved in June 2021 for that purpose.
Extended reach (i.e., 80 km ~50 miles or longer) optical Ethernet solutions primarily support television distribution (e.g., cable and direct-broadcast satellite) and mobile/cellular backhaul aggregation networks. A need was identified to not only support 100 Gb/s extended reach operation for these applications, but also to support up to 48 multiplexed 100 Gb/s channels over a single lane of single-mode optical fiber cabling. This amendment defines one Physical Layer (PHY) specification and management parameter for extended reach 100 Gb/s operation.
The new PHY specification is 100GBASE-ZR: A Physical layer specification supporting 100 Gb/s operation on a single wavelength capable of at least 80 km over a DWDM system. Specifically, 100 Gb/s transmission using 2‑level pulse amplitude modulation and dual polarization differential quadrature phase shift keying (DP-DQPSK) modulation over single‑mode fiber (2 fibers total), with reach up to at least 80 km.
In addition, 100GBASE-ZR is specified as part of a Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) system. In this system, up to 48 100GBASE‑ZR optical signals, transmitting between the 1528.77 nm and 1566.31 nm wavelengths, can be multiplexed for operation over 2‑fiber single‑mode optical cabling referred to as a “black link”. Black link refers to a link where only the input and output link and transfer characteristics (e.g., chromatic dispersion, optical return loss, and inter-channel crosstalk) are specified, with interoperability ensured at these locations. The amendment does not specify how the black link is designed, constructed, configured, or operated. DWDM network elements inside the black link may include an optical multiplexer, an optical de‑multiplexer, and one or more optical amplifiers and no assurance of interoperability at these multichannel points is provided.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, NeoPhotonics Corporation, a leading developer of silicon photonics and advanced hybrid photonic integrated circuit-based lasers, modules and subsystems for bandwidth-intensive, high speed communications networks, today announced a new, high output power version of its 400G Multi-Rate CFP2-DCO coherent pluggable transceiver with 0 dBm output power and designed to operate in metro, regional and long haul ROADM based optical networks.
“Our newest CFP2-DCO coherent pluggable module, with high output power, robust ROADM filtering tolerance and demonstrated transmission over 1500 km, allows customers to use one coherent pluggable solution to cover essentially all metro ROADM use cases, simplifying network design, enabling disaggregation, and lowering inventory costs.” said Tim Jenks, Chairman and CEO of NeoPhotonics. “The key to achieving line card equivalent performance in a pluggable module, but with significantly lower power than a line card, is the vertical integration of our optical solution and Nano tunable laser,” concluded Mr. Jenks.
References:
https://www.neophotonics.com/press-releases/?newsId=12741


