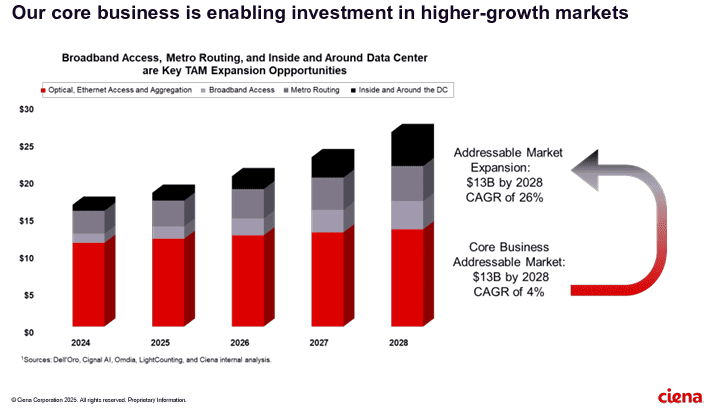
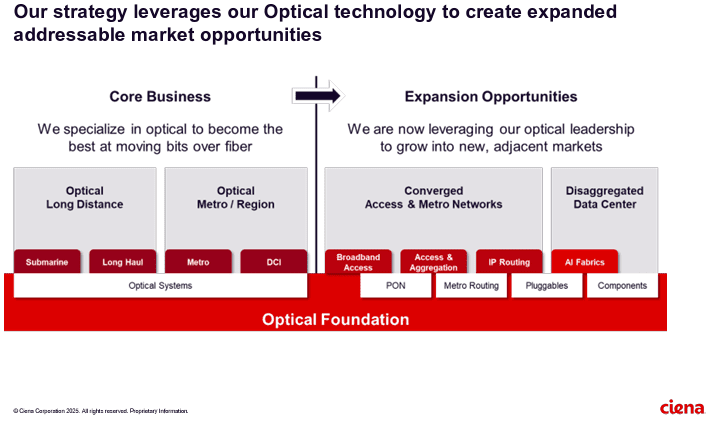
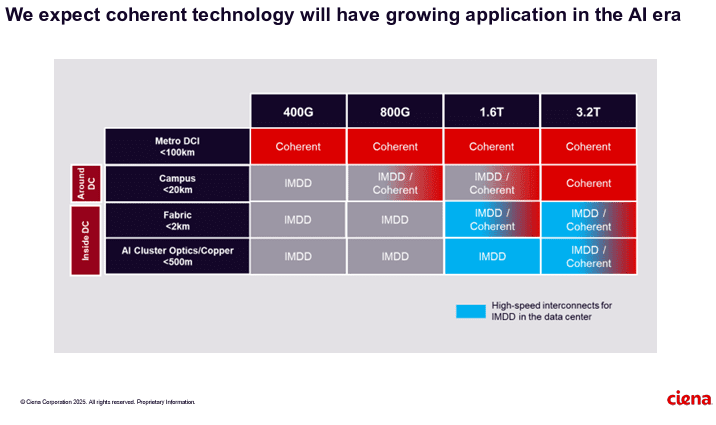
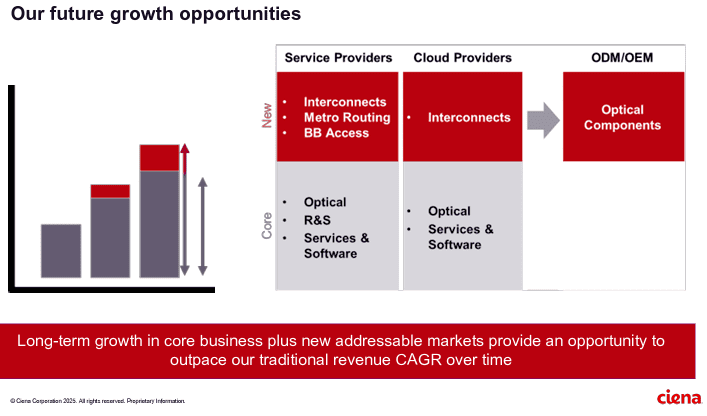
Optical Network Equipment Market
AI infrastructure investments drive demand for Ciena’s products including 800G coherent optics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) infrastructure investments are starting to shift toward networks needed to support the technology, rather than focusing exclusively on computing and power, according to Ciena Chief Executive Gary Smith. The trends helped Ciena swing to a profit and post a 24% jump in sales in the recent quarter.
The company enables high-speed fiber optic connectivity for telecommunications and data centers, helping hyper-scalers such as Amazon and Microsoft support AI initiatives via data center interconnects and intra-data center networking. Currently, the company is ramping up production to meet surging demand fueled by cloud and AI investments.
“There’s no point in investing in these massive amounts of GPUs if we’re going to strand it because we didn’t invest in the network,” Smith said Thursday.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ciena sees a bright future in 800G coherent optics that can accommodate AI traffic. Smith said a global cloud provider has selected Ciena’s coherent 800-gig pluggable modules and Reconfigurable Line System (RLS) photonics for investing in geographically distributed, regional GPU clusters. “With our coherent optical technology ideally suited for this type of connectivity, we expect to see more of these opportunities emerge as cloud providers evolve their data center network architectures to support their AI strategies,” he added.
It’s still early innings for 800G adoption, but demand is climbing due to AI and cloud connectivity. Vertical Systems Group expects to see “a measurable increase” in 800G installations this year. Dell’Oro optical networking analyst Jimmy Yu noted on LinkedIn Ciena’s data center interconnect win is the first he’s heard of that involves connecting GPU clusters across 100+ kilometer spans. “It was a hot topic of discussion for nearly 2 years. It is now going to start,” Yu said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ciena’s future growth opportunities include network service and cloud service providers as well as ODM/OEM sales of optical components.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/earnings/ciena-swings-to-profit-as-ai-investments-drive-demand-0195f30c
https://investor.ciena.com/static-files/d964ccac-74b3-43d9-a73e-ecf67fab6060
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/ciena-now-expects-tariff-costs-10m-quarter
Nokia to acquire Infinera for $2.3 billion, boosting optical network division size by 75%
Nokia has agreed to buy optical networking equipment vendor Infinera in a deal worth $2.3 billion. 70% of the sum will be paid in cash, the remaining 30% in Nokia shares. Nokia said it will accelerate its share buyback program to offset the dilution.
The acquisition will grow the size of its Optical Networks division by 75%, enabling the company to accelerate its product roadmap and increase its exposure to webscale customers, which account for around 30% of Infinera’s revenue.

Nokia and Infinera see a significant opportunity in merging to improve scale and profitability, enabling the combined business to accelerate the development of new products and solutions to benefit customers. The transaction aligns strongly with Nokia’s strategy, as it is expected to strengthen the company’s technology leadership in optical and increase exposure to webscale customers, the fastest growing segment of the market.
- Creates a highly scaled and truly global optical business with increased in-house technology capabilities and vertical integration.
- Strengthens Nokia’s optical position, specifically in North America.
- Accelerates Nokia’s customer diversification strategy, expanding webscale presence.
- Targeted net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million by 2027.
Nokia believes the transaction has compelling financial and strategic merit. The combination with Infinera is projected to accelerate Nokia’s journey to a double-digit operating margin in its Optical Networks business. Nokia targets to achieve EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027. This transaction along with the recently announced sale of Submarine Networks will create a reshaped Network Infrastructure built on three strong pillars of Fixed Networks, IP Networks and Optical Networks. Nokia targets mid-single digit organic growth for the overall Network Infrastructure business and to improve its operating margin to mid-to-high teens level.
The combined Nokia and Infinera will have a global market share of around 20%, broadly equal to Ciena (which acquired Nortel’s optical network division in November 2009 for $769 billion) but lagging behind Huawei’s 31%, according to J.P. Morgan analyst Samik Chatterjee.
“Ciena is less likely to make a competing bid given complexity in integrating competing optical portfolios as well as hurdles in regulatory approval given Ciena’s majority (51%) share of the North America market,” wrote Chatterjee in a research note.
Omdia (Informa) expects optical networking market sales to rise at a compound annual growth rate of 5% between now and 2029. A well-executed takeover may, then, give Nokia a growth story during a period of difficulty for its large mobile business group, responsible for about 44% of total sales last year.
The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable EPS in the first year post close and to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion by 2027*, with a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Pekka Lundmark, President and CEO of Nokia, said:
“In 2021 we increased our organic investment in Optical Networks with a view to improving our competitiveness. That decision has paid off and has delivered improved customer recognition, strong sales growth and increased profitability. We believe now is the right time to take a compelling inorganic step to further expand Nokia’s scale in optical networks. The combined businesses have a strong strategic fit given their highly complementary customer, geographic and technology profiles. With the opportunity to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion, we believe this will create significant value for shareholders.”
Federico Guillén, President of Network Infrastructure at Nokia, said: “Today, Network Infrastructure offers a unique portfolio across the fixed access, optical and IP networks domains built on leading technology innovation and a strong customer focus. This acquisition will further strengthen the optical pillar of our business, expand our growth opportunities across all our target customer segments and improve our operating margin. I am extremely pleased that we are bringing together these two talented and dedicated teams. Separately, we have long respected each other as competitors. Together, we find the logic of combination irresistible.”
David Heard, CEO of Infinera, said: “We are really excited about the value this combination will bring to our global customers. We believe Nokia is an excellent partner and together we will have greater scale and deeper resources to set the pace of innovation and address rapidly changing customer needs at a time when optics are more important than ever – across telecom networks, inter-data center applications, and now inside the data center. This combination will further leverage our vertically integrated optical semiconductor technologies. Furthermore, our stakeholders will have the opportunity to participate in the upside of a global leader in optical networking solutions.”
Compelling strategic benefits for Nokia, Infinera and customers:
- Improving global scale and product roadmap: The combination will increase the scale of Nokia’s Optical Networks business by 75%, enabling it to accelerate its product roadmap timeline and breadth; providing better products for customers and creating a business that can sustainably challenge the competition.
- The combined business will have significant in-house capabilities, including an expanded digital signal processor (DSP) development team, expertise across silicon photonics and indium phosphide-based semiconductor material sciences, and deeper competency in photonic integrated circuit (PIC) technology. The result will be a strong innovative player with a deep and diverse pool of optical networking talent and expertise.
- Gaining scale in North America optical market: The two companies have limited customer overlap, putting the combined business in a strong position in all regions (excluding China). Infinera has built a solid presence in the North America optical market, representing ~60% of its sales, which will improve Nokia’s optical scale in the region and complement Nokia’s strong positions in APAC, EMEA and Latin America.
- Building on Nokia’s commitment to investment in U.S. based manufacturing and advanced testing and packaging capabilities.
- Accelerating Nokia’s expansion into enterprise and particularly webscale: The combination of these two businesses is also expected to accelerate Nokia’s strategic goal of diversifying its customer base and growing in enterprise. Internet content providers (ICP or webscale as Nokia typically calls this segment) make up over 30% of Infinera’s sales. With recent wins in line systems and pluggables, Infinera is well established in this fast-growing market. Infinera has also recently been developing high-speed and low-power optical components for use in intra-data center (ICE-D) applications and which are particularly suited to AI workloads which can become a very attractive long-term growth opportunity. Overall, the acquisition offers an opportunity for a step change in Nokia’s penetration into webscale customers.
- Net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million: The combination is expected to deliver EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027*. Approximately one third of the synergies are expected to come from cost of sales due to supply chain efficiencies and the remainder from operating expenses due to portfolio optimization and integration along with reduced product engineering costs and standalone entity costs. Nokia expects one-time integration costs of approximately EUR 200 million related to the transaction.
- Creating value for shareholders: The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable operating profit and EPS in year 1 and to deliver more than 10% comparable EPS accretion in 2027*. Nokia also expects the deal to deliver a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). In addition, Infinera’s investors will have the opportunity to participate in the exciting upside of investing in a global leader in optical networking solutions.
Transaction details:
Under the terms of the definitive agreement, Nokia is acquiring Infinera for $6.65 per share, which equates to an enterprise value of $2.3 billion. For each Infinera share, Infinera shareholders will be able to elect to receive either: 1) $6.65 cash, 2) 1.7896 Nokia shares, or 3) a combination of $4.66 in cash and 0.5355 Nokia shares for each Infinera share. All Nokia shares will be issued in the form of American Depositary Shares. The definitive agreement includes a proration mechanism so that the Nokia shares issued in the transaction do not exceed an amount equal to approximately 30% of the aggregate consideration that may be paid to Infinera shareholders.
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/infinera-stock-price-buy-sell-nokia-ciena-658c7898
https://www.infinera.com/press-release/nokia-to-acquire-infinera/
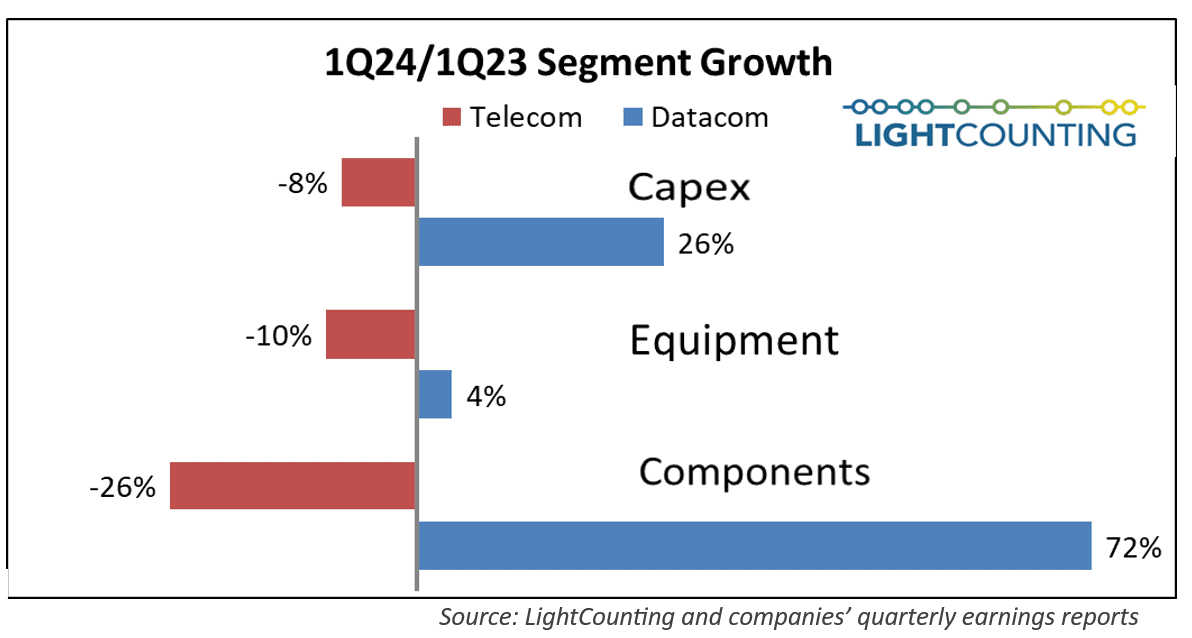
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
Infinera, DZS, and Calnex Successfully Demonstrate 5G Mobile xHaul with Open XR
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
As has been the trend for the past several quarters, Q1 2024 results for the optical communications market were sharply split between very weak sales in the telecom segment (Communications Service Providers or CSPs) and continued strong demand by the hyperscalers (cloud giants). The combined capex of the Top 15 CSPs declined year-over-year for the sixth quarter in a row, while the Top 15 ICPs spending grew for the second quarter in a row, paced by Alphabet (+91%) and Microsoft (+66%). Chinese ICPs spending also increased dramatically, suggesting the AI boom is hitting China too.
Calix and Corning Weigh In: When Will Broadband Wireline Spending Increase?
Broadband wireline network operators (telcos and MSOs/cablecos) have cutback on CAPEX with decreased spending for network equipment. In its latest earnings call, Calix warned that broadband operator spending might not increase until 2025, when BEAD subsidies have been allocated. However, fiber vendor Corning and others suggested spending might increase earlier than that.
Calix specializes in providing optical network access equipment to smaller broadband service providers and has seen significant revenue growth in recent years, but near-term growth will be challenged. Calix management’s guidance was that the 2024 fiscal year will be soft for its business. Despite that softness, the company still believes that it has years of growth ahead for itself starting in 2025 due to BEAD regulatory stimulus that should prove beneficial for the enterprise.
The U.S. government’s BEAD program promises to funnel a massive $42 billion in subsidies through US states to telecom companies willing to build networks in rural areas. However, allocation of those funds is taking longer than expected, forcing network operators to stall their deployment plans until they have a better sense of how much funding they might get.
“We have seen a significant broadening in the number of customers interested in competing for BEAD [Broadband Equity Access and Deployment program] funds. Today, nearly all our customers are either assembling a BEAD strategy or actively pursuing funds,” Calix CEO Michael Weening said during the company’s quarterly earnings call, according to Seeking Alpha.
“While they do this, they slow their new [network] builds as BEAD money could be used instead of consuming their own capital, and thus, we’ll slow our appliance shipments until decisions are made and funds are awarded,” Weening said. “At that point, the winners will move ahead and those who decided to skip the BEAD program or did not receive BEAD funding, we’ll begin investing to ensure that the winner does not impinge on their market. This represents a delay but also represents a unique opportunity for Calix.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Corning manufactures and sells most of the physical fiber cabling used in U.S. fiber networks. Sales in Corning’s optical business unit – which houses its fiber products – continued to slide in the fourth quarter of 2023.
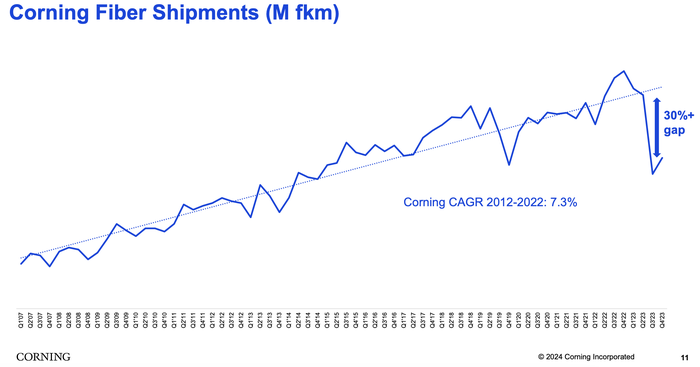
“We anticipate optical communications sales will spring back because we believe and our carrier customers have confirmed that they purchased excess inventory during the pandemic and that they’ve been utilizing this inventory to continue deploying their networks,” said Corning CEO Wendell Weeks during his company’s quarterly earnings call, according to Seeking Alpha.
“We believe these carriers will soon deplete their inventory and execute on the increased broadband deployment plans they’ve communicated to us over the last several months,” Weeks said. “As a result, we expect them to return to their normal purchasing patterns to service their deployments.”
He also noted that operators are waiting for BEAD funding. “We continue to expect BEAD funding really to start to translate into demand, the beginning of it, sort of late this year. They are progressing with awarding the grants and it will just take a bit for those to turn into real programs,” Weeks said.
Weeks suggested that the company is starting to see the glimmer of an uptick in demand from its broadband operator customers, but nothing definite yet. “We’ll know more in the coming months,” he said in his concluding remarks.
Meanwhile, executives at vendor Harmonic said this week they expect sales in the first half of this year to be relatively soft and then accelerate in the second half of the year as operators start to ramp up network upgrades, including moves to DOCSIS 4.0 technologies.
Highlights of LightCounting’s December 2023 Quarterly Market Update on Optical Networking
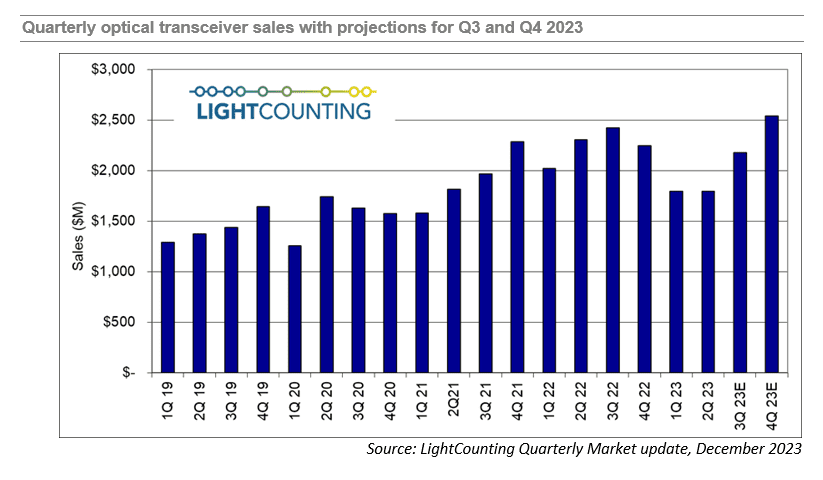
LightCounting’s Quarterly Market Update report [1.] for Q3 2023 revealed that the optical communications industry financial results were disappointing.
Every financial market indicator that the market research firm tracks – ICP (Integrated Communications Provider) and CSP (Communications Service Provider) capex, datacom and networking equipment, and semiconductor (x-Nvidia) and optical components sales – all had negative growth compared to Q3 2022.
Note 1. LightCounting’s Quarter Market Update reports are designed to provide an easy-to-digest snapshot of optical transceiver growth trends, backed up by detailed quarter-by-quarter sales data collected via LightCounting’s proprietary vendor survey. Performance metrics and commentary for top-tier telecom and internet service providers, network and datacom equipment makers, and optical component and semiconductor vendors are also included to provide an understanding of what drives sales trends at the transceiver level.
- Alphabet and Microsoft had record capital expenditures.
- Arista, Broadcom, Calix, Innolight, and Nvidia all reported record revenues.
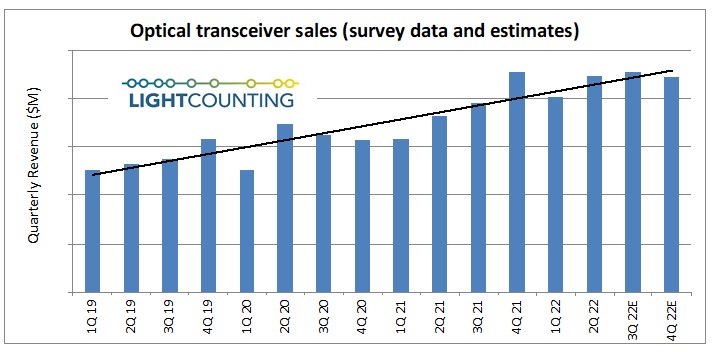
LightCounting is projecting, based on its current analysis, that sales increased in Q3 and will increase further in Q4, to a new record high, as shown in the figure below. This data includes estimates for 400G and 800G transceivers manufactured by Nvidia internally.
The expectation of growth in Q4 carries over to 2024 as well and is consistent with the guidance given by several companies ranging from Alphabet and Amazon to Coherent and Lumentum. The big caveat is that growth in 2024 will be tightly focused on AI-related infrastructure, and growth in demand for those products is expected to far outstrip demand in other segments like traditional telco and enterprise networks. Most of the growth in the optical components and modules market will come from sales of 800G transceivers.
References:
https://www.lightcounting.com/report/december-2023-quarterly-market-update-199
LightCounting: Will Network Transformation resolve telecom’s paradox?
Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023
MTN Group and NEC XON deploy Africa’s first 400G optical transponder using TIP’s Phoenix
Openreach deploys Adtran’s FSP 3000 open optical transport system
Adtran today announced that Openreach, the UK’s largest wholesale broadband network, has deployed its FSP 3000 open optical transport technology to enable its new Optical Spectrum Access 100G Single enterprise service.
Openreach’s new product offers a dedicated fiber link that empowers more UK businesses to harness point-to-point 100Gbit/s data transport. The solution also brings efficiency benefits that reduce capital and operational expenditure. The latest collaboration builds on more than a decade of successful partnership between Adtran and Openreach.
“Corporate cloud applications and other data-intensive tasks such as data center backhaul are fueling a growing demand for bandwidth. Adtran’s scalable optical technology enables us to offer a managed, high-speed service that satisfies that demand at a highly competitive price point,” said Simon Williams, head of optical products at Openreach.
“With no filters or amplifiers required, our Optical Spectrum Access 100G Single service offers secure and always-on optical services that can transport enormous amounts of data. We’re also making dedicated, uncomplicated and customizable access available in a slimmed-down package that’s even easier to manage.”

Adtran’s FSP 3000 technology is helping Openreach deliver managed 100G connectivity to UK businesses. (Photo: Business Wire)
Openreach’s Optical Spectrum Access 100G Single offers a choice of point-to-point Ethernet links at 100Gbit/s or 10 separate channels at 10Gbit/s. Built on Adtran’s scalable, open FSP 3000 optical transport technology, the service empowers Openreach to meet the growing demand for data-intensive cloud-based applications. Engineered for operational simplicity, Adtran’s compact and highly efficient FSP 3000 platform offers a dedicated fiber link ensuring low latency, consistent service quality and unparalleled network reliability for Openreach’s customers.
“Our FSP 3000 technology gives Openreach a powerful optical transport solution that efficiently delivers high-bandwidth services for enterprise customers. Using the Optical Spectrum Access 100G Single service, businesses can now smoothly manage substantial data transfers, even during peak operational hours,” commented Stuart Broome, GM of EMEA sales at Adtran. “We have a great track record of partnering with Openreach to advance digital transformation across the UK. It’s a relationship based on trust and a shared dedication to deliver for customers. Together, we’re providing extra capacity and value for more businesses.”
About Adtran:
ADTRAN Holdings, Inc. (NASDAQ: ADTN and FSE: QH9) is the parent company of Adtran, Inc., a leading global provider of open, disaggregated networking and communications solutions that enable voice, data, video and internet communications across any network infrastructure. From the cloud edge to the subscriber edge, Adtran empowers communications service providers around the world to manage and scale services that connect people, places and things. Adtran solutions are used by service providers, private enterprises, government organizations and millions of individual users worldwide. ADTRAN Holdings, Inc. is also the largest shareholder of Adtran Networks SE, formerly ADVA Optical Networking SE. Find more at Adtran, LinkedIn and Twitter.
References:
BT’s CEO: Openreach Fiber Network is an “unstoppable machine” reaching 9.6M UK premises now; 25M by end of 2026
Adtran showcases coherent innovation at OFC 2023: FSP 3000 open line system & coherent 100ZR
Openreach on benefit of FTTP in UK; Full Fiber rollouts increasing
Analysts: Combined ADTRAN & ADVA will be a “niche player”
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
According to a recent forecast report by Dell’Oro Group, the Optical Transport equipment demand is forecast to increase at a 3 percent compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) for the next five years, reaching $17 billion by 2027. The cumulative revenue during that five year period is expected to be $81 billion.
“We expect annual growth rates to fluctuate in the near term before stabilizing to a more typical 3 percent growth rate,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “There is still a large amount of market uncertainty this year due to the economic backdrop—economists are predicting a high chance of a recession in North America and Europe. However, at the same time, most optical systems equipment manufacturers are reporting record levels of order backlog entering the year, and we expect that most of this backlog could convert to revenue when component supply improves this year,” added Yu.
Additional highlights from the Optical Transport 5-Year January 2023 Forecast Report:
- Optical Transport market expected to increase in 2023 due to improving component supply.
- WDM Metro market growth rates in next five years are projected to be lower than historic averages due to the growing use of IP-over-DWDM.
- DWDM Long Haul market is forecast to grow at a five-year CAGR of 5 percent.
- Coherent wavelength shipments on WDM systems forecast to grow at 11 percent CAGR, reaching 1.2 million annual shipments by 2027.
- Installation of 400 Gbps wavelengths expected to dominate for most of forecast period.
About the Report
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport 5-Year Forecast Report offers a complete overview of the Optical Transport industry with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments, wavelength shipments (by speed up to 1.2+ Tbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers, optical switch, Disaggregated WDM, DCI, and ZR Optics.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Lumen Technologies is expanding its 400G wavelength network across North America. Lumen said it has now deployed the network in 70 markets. More than 240 data centers have access to Lumen’s 400G Wavelength Services, and the network has over 800 Tbit/s of capacity.
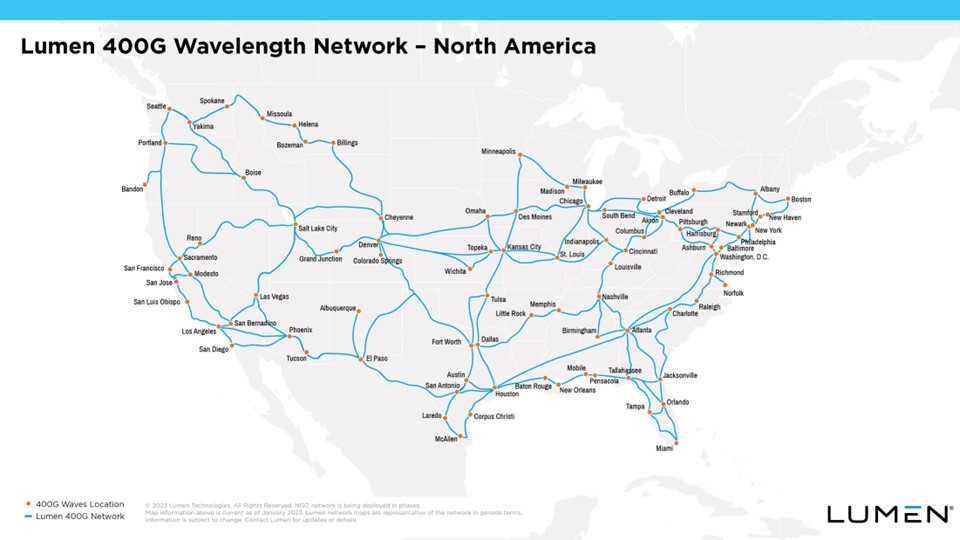
Lumen said it plans to continue its intercity 400G expansion this year, pushing the network “deeper into the metro edge.” The company noted that wavelength services will assist customers in moving workloads to the cloud, and provide private, dedicated connections.
Enterprise customers can also examine network options, plan out their wavelengths and get cost estimates with Lumen’s Topology Viewer.
References:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/lumen-kicks-up-its-400g-offering-across-the-us-301730126.html
Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023
Optical Transceivers:
Optical transceivers save space and reduce the need for additional transmitting and receiving devices because they transmit and receive information all in one device! Additionally, they are an economical, compact tool to enable networks to send information over larger distances, come in a variety of Ethernet speeds from Fast Ethernet to 100 Gigabit Ethernet, and offer great flexibility to grow your network while leveraging existing network devices and infrastructure.
Many newer, high quality Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules have Diagnostic Monitoring Interface (DMI), which automatically monitors SFP operations such as output and input power, temperature, and supply voltage in addition to providing multimode, single mode, and multi-rate SFP options for more flexibility.
Market Research Future® (MRFR) predicts that the global optical transceiver market will rise to 8 billion in the U.S. by 2023.
Pluggable optics:
400ZR coherent pluggable optics emerged as a connectivity tool for metro-distributed data center connectivity. In 2023, look for three additional innovations to enable even more opportunities for coherent pluggables.
High-performance pluggables with 0 dBm transmit power and low out-of-band noise will enable coherent pluggable transceivers to cover a richer set of use cases, including deployment in metro networks with multiple cascaded ROADMs. This increased transceiver performance will also push some pluggables beyond the 600-km metro threshold and into a portion of the long-haul network.
Advances in intelligent pluggables management, as being defined in the 28-member Open XR Forum and with inputs to other organizations like the OIF, will ease deployment complexity and enable operational support for advanced functionality like remote diagnostics, auto-discovery, spectrum analysis, and streaming telemetry in all types of non-optical hosts, including switches and routers.
A new class of coherent pluggables, such as Infinera’s ICE-XR with digital subcarrier technology, will enable commercial deployment of point-to-multipoint architectures, where a single high-speed (e.g., 400G) hub optic can communicate with multiple lower-speed (e.g., 25G to 100G in 25G increments) optics without requiring intermediate electrical aggregation – thus reducing the amount of equipment, space, and power utilized and the total cost of network ownership by up to 70% over multiple years.
Heavy Reading’s optical networking analyst Sterling Perrin sees “pluggable optics everywhere” being a dominant theme. “This includes the continuing trends in 400ZR and ZR+ but also a big focus on migrating down to small coherent 100G pluggables, pluggables across 5G XHaul networks, and pluggables in PON,” he writes in a note to Light Reading.
Data center transmission:
In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection
Modular data centers, where construction and integration tasks are moved offsite and then shipped and assembled onsite, are becoming mainstream and enabling compute and storage to be quickly and reliably deployed in all types of settings – from just a few racks in a small hut to megawatts of equipment in a multi-story configuration. In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection.
Lisa Huff, Omdia’s senior principal analyst covering optical components will keep an eye out for whether 800G and 1.6T transmission will show up next in data centers. “We are in the middle of 400G deployment inside the data center and, as always, there is much hype around what the next data rate will be,” she writes.
“Omdia expects to see 2x400G and 8x100G solutions start to be deployed inside the data center in 2023, but we will not see high-volume deployment until about 2025 when DR4 and FR4 variants mature and 400G starts to slow down,” she writes. Deployments of 1.6T may start in 2026, but Huff said it might be 2027 or later before we see significant volume.
Coherent routing:
Omdia Senior Principal Analyst Timothy Munks said that with data traffic growing at the network’s edge, network operators are looking for better solutions to collect and move that data into metro and core networks.
“The convergence of IP and optical, or coherent routing, provides cost effective aggregation and transport of diverse traffic streams and offers network operators a pure pay-as-you-grow business model for adding capacity,” he writes.
In this video, Cisco’s Bill Gartner, SVP/GM Optical Systems & Optics, chats with Phil Harvey to discuss their Leading Lights Award and how Routed Optical Networking is transforming infrastructure and the economics of the network.
References:
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
Cisco’s Restructuring Plan:
Cisco plans to lay off over 4,100 employees or 5% of its workforce, the company announced yesterday. That move is part of a restructuring plan to realign its workforce over the coming months to strengthen its optical networking, security and platform offerings. Cisco noted in financial filings it expects to spend a total of $600 million, with half of that outlay coming in the current quarter. The company will also reduce its real estate portfolio to reflect an increase in hybrid work.
In a transcript of Cisco’s Q1 2023 Earnings Call on November 17th, Cisco Chief Financial Officer Scott Herren characterized the move as a “rebalancing.” On that call, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Chuck Robbins said the company was “rightsizing certain businesses.”
Herren and CEO Chuck Robbins said the company is looking to put more resources behind its enterprise networking, platform, security and cloud-based products. In the long run, analysts expect Cisco margins to improve as more revenue comes from security and software products.
By inference Cisco is de-emphasizing sales of routers to service providers who are moving towards white boxes/bare metal switches and/or designing their own switch/routers.
A Cisco representative told Fierce Telecom:
“This decision was not taken lightly, and we will do all we can to offer support to those impacted, including generous severance packages, job placement services and other benefits wherever possible. The job placement assistance will include doing “everything we can do” to help affected employees step into other open positions at the company.”
Cisco implemented a similar restructuring plan in mid-2020 which included a substantial number of layoffs.

Growth through Acquisitions:
Much of Cisco’s revenue growth over the years has come from acquisitions. The acquisitions included Ethernet switch companies like Crescendo Communications. Kalpana and Grand Junction from 1993-1995. Prior to those acquisitions, Cisco had not developed its own LAN switches and was primarily a company selling routers to enterprises, telcos and ISPs.
Here are a few of Cisco’s acquisitions over the last five years:
- In 2017, Cisco acquired software maker AppDynamics for $3.7 billion. It bought BroadSoft for $1.9 billion in late 2017.
- In July 2019, Cisco acquired Duo Security for $2.35 billion, marking its biggest cybersecurity acquisition since its purchase of Sourcefire in 2013. Acquiring Duo Security bolstered Cisco in an emerging category called zero trust cybersecurity.
- In late 2019, Cisco agreed to buy U.K.-based IMImobile, which sells cloud communications software, in a deal valued at $730 million.
- In May 2020, Cisco acquired ThousandEyes, a networking intelligence company, for about $1 billion.
Aside from acquisitions, new accounting rules have been a plus for revenue recognition. The rules known as ASC 606 require upfront recognition of multiyear software licenses.
One bright spot for Cisco have been sales of the Catalyst 9000 Ethernet switches. The company claims they are the first purpose-built platform designed for complete access control using the Cisco DNA architecture and software-defined SD access. This means that this series of switches simplifies the design, provision and maintenance of security across the entire access network to the network core.
There is also an opportunity for Cisco in data center upgrades. The so-called “internet cloud” is made up of warehouse-sized data centers. They’re packed with racks of computer servers, data storage systems and networking gear. Most cloud computing data centers now use 100 gigabit-per-second communications gear. A data center upgrade cycle to 400G technology has been delayed.
Routed Optical Networking:
Cisco in 2019 agreed to buy optical components maker Acacia Communications for $2.6 billion in cash. China’s government delayed approval of the deal. In January 2021, Cisco upped its offer for Acacia to $4.5 billion and the deal finally closed on March 1, 2021. Acacia designs, manufactures, and sells a complete portfolio of high-speed optical interconnect technologies addressing a range of applications across datacenter, metro, regional, long-haul, and undersea networks.
Acacia’s Bright 400ZR+ pluggable coherent optical modules can plug into Cisco routers, enabling service providers to deploy simpler and more scalable architectures consisting of Routed Optical Networking, combining innovations in silicon, optics and routing systems.
Routed Optical Networking works by merging IP and private line services onto a single layer where all the switching is done at Layer 3. Routers are connected with standardized 400G ZR/ZR+ coherent pluggable optics.
With a single service layer based upon IP, flexible management tools can leverage telemetry and model-driven programmability to streamline lifecycle operations. This simplified architecture integrates open data models and standard APIs, enabling a provider to focus on automation initiatives for a simpler topology. It may be a big winner for Cisco in the near future as service providers move to 400G transport.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/cisco-plans-cut-5-workforce-under-600m-restructuring-plan
https://www.cisco.com/site/us/en/products/networking/switches/catalyst-9000-switches/index.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/corporate-strategy-office/acquisitions/acacia.html
Heavy Reading: Coherent Optics for 400G transport and 100G metro edge
Telecom Infra Project introduces Open FAN to promote multi-vendor interoperability
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) has announced a new initiative for “open fixed access networks (FAN)” at the FYUZ conference in in Madrid, Spain. The Open FAN initiative is being led by Telefónica, Telecom Italia, and Vodafone. As in the mobile radio access network, the goal is to ensure products from competing vendors can be combined in the same fixed access network. That is the essence of true interoperability.
The work will focus on improving interoperability and diversity in the access network, accelerating innovation and boosting capacity in the last mile through the transition from GPON to XGS-PON. Specifically, Open FAN is targeting the link between optical line terminals (OLTs) and optical network terminals (ONTs), the boxes that sit at either end of a fiber connection. Integration with SDN controllers, the traffic cops of the network, is another priority. Open FAN has just become the latest TIP sub-group, part of the fixed access project group.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
TIPs Fixed Broadband Project Group is developing a new generation of open and disaggregated technologies that help operators increase the availability of fast and reliable broadband services across the world. The goal of the TIP fixed access sub-group is to build access networks capable of delivering high speed connectivity over the last mile. The primary objective for this group is to achieve a high degree of interoperability in the access domain, including:
- East-west interworking and integration between network elements
- Northbound integrations to OSS and network management systems
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Participants are currently drawing up technical requirements for a so-called “pizza box” OLT that can be delivered to the local telco. They will issue a request for information later this year as they assess the technical capabilities of vendors and their “readiness” for open FAN.
“The disaggregation of OLTs represents a valuable opportunity to broaden the telecom supply chain, which we’ve seen has become more important than ever during recent times,” said Paolo Pellegrini, TIM’s access innovation project manager, in telling remarks. “TIM is excited about the opportunities to work with a new generation of hardware and software suppliers who can bring innovative solutions that will help us build more cost-effective and efficient networks.”
Data from Omdia, owned by Informa, shows that just three vendors controlled 85% of the market for OLTs last year. Two of them, Huawei and ZTE, are Chinese, leaving Nokia as the only other supplier. The lack of alternatives explains why the UK government was less restrictive in fixed than it was in mobile when clamping down on Chinese vendors.
TIP probably hopes interoperability will boost competition in a market for passive optical network (PON) products worth about $8 billion in sales last year. If operators could more easily buy OLTs separately from ONTs, developers could focus resources on one area. An OLT specialist would not require an ONT capability to compete.
Today, mixing FAN products from different vendors is problematic, said a source at TIP, and Nokia seems to agree.
“It is not easy to do, but it is something that we do,” said Federico Guillén, the head of Nokia’s network infrastructure business group, during an interview at the recent Network X event in Amsterdam. “If you do this, you have to put in some rules for how the OLT and the ONT communicate and set a lower denominator, which means you are missing some features. Interoperability doesn’t come for free.”
Telecom already has an interface for connecting OLTs to ONTs, called OMCI (for ONT management control interface). But when it comes to multi-vendor interoperability, this does not seem to have delivered. “It was perfectly standardized, and everyone was implementing and following, but they were choosing different options,” said Stefaan Vanhastel, the chief technology officer for Nokia’s fixed network unit.
Nokia served about 24% of the global PON market last year, according to Omdia’s data, but has increased its presence in OLTs, according to Guillén. A backlash against Huawei in many countries outside China has probably helped. “Our market share is growing, especially where we want it to grow, which is the OLT side,” he told Light Reading. “The ONT side is a very crowded space.”
Specialists may find that challenging Nokia in the FAN is just as hard as it is in the RAN. Last year it pumped €4.2 billion (US$4.2 billion) into research and development, including investments in the silicon platforms that support higher-speed broadband services. At Network X, it announced a new OLT, branded Lightspan MF-14, that provides an upgrade path to 100G-capable networks. “Operators have a solution that will be reusable as line cards are upgraded over time,” said Julie Kunstler, chief analyst with Omdia. “This has lots of capacity and ONTs will be upgraded as needed.”
The new TIP Open FAN subgroup expects to issue an RFI to establish the technical capabilities and readiness of suppliers to deliver such a solution later in the year, with test and validation to follow.However, there was no mention of network equipment vendor support for open FAN in the TIP’s statement and without that it could struggle. If enough operators urge change, those vendors may have to budge – but the wariness of Ericsson and Nokia about open RAN illustrates just how difficult that could be. Open FAN also appears to lack an equivalent of the O-RAN Alliance, the group developing open RAN specifications. TIP has previously distanced itself from specifications development. If an alternative to OMCI is needed, who takes the lead?
Whether open FAN becomes as big a deal as open RAN is doubtful. For one thing, operators spent about $37 billion less on FAN products last year than on RAN kit, according to Omdia’s numbers. Most of their fixed-line capex goes into civil engineering, and no amount of interoperability or virtualization will save money there.
Despite the muscle of Huawei, Nokia and ZTE, the market was also growing more competitive before open FAN was a thing, according to Omdia’s Kunstler. Ciena, an optical equipment vendor based in the US, and Sterlite, an Indian firm that sells fiber-optic cable, are just two examples of companies moving into a PON market forecast to generate nearly $16 billion in annual sales by 2027.
References:
https://telecominfraproject.com/wp-content/uploads/Fixed-Access-UCD_v1.0_20220628.pdf