Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023
Optical Transceivers:
Optical transceivers save space and reduce the need for additional transmitting and receiving devices because they transmit and receive information all in one device! Additionally, they are an economical, compact tool to enable networks to send information over larger distances, come in a variety of Ethernet speeds from Fast Ethernet to 100 Gigabit Ethernet, and offer great flexibility to grow your network while leveraging existing network devices and infrastructure.
Many newer, high quality Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules have Diagnostic Monitoring Interface (DMI), which automatically monitors SFP operations such as output and input power, temperature, and supply voltage in addition to providing multimode, single mode, and multi-rate SFP options for more flexibility.
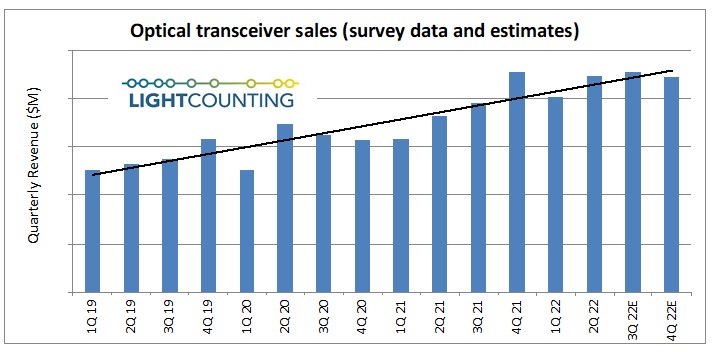
Market Research Future® (MRFR) predicts that the global optical transceiver market will rise to 8 billion in the U.S. by 2023.
Pluggable optics:
400ZR coherent pluggable optics emerged as a connectivity tool for metro-distributed data center connectivity. In 2023, look for three additional innovations to enable even more opportunities for coherent pluggables.
High-performance pluggables with 0 dBm transmit power and low out-of-band noise will enable coherent pluggable transceivers to cover a richer set of use cases, including deployment in metro networks with multiple cascaded ROADMs. This increased transceiver performance will also push some pluggables beyond the 600-km metro threshold and into a portion of the long-haul network.
Advances in intelligent pluggables management, as being defined in the 28-member Open XR Forum and with inputs to other organizations like the OIF, will ease deployment complexity and enable operational support for advanced functionality like remote diagnostics, auto-discovery, spectrum analysis, and streaming telemetry in all types of non-optical hosts, including switches and routers.
A new class of coherent pluggables, such as Infinera’s ICE-XR with digital subcarrier technology, will enable commercial deployment of point-to-multipoint architectures, where a single high-speed (e.g., 400G) hub optic can communicate with multiple lower-speed (e.g., 25G to 100G in 25G increments) optics without requiring intermediate electrical aggregation – thus reducing the amount of equipment, space, and power utilized and the total cost of network ownership by up to 70% over multiple years.
Heavy Reading’s optical networking analyst Sterling Perrin sees “pluggable optics everywhere” being a dominant theme. “This includes the continuing trends in 400ZR and ZR+ but also a big focus on migrating down to small coherent 100G pluggables, pluggables across 5G XHaul networks, and pluggables in PON,” he writes in a note to Light Reading.
Data center transmission:
In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection
Modular data centers, where construction and integration tasks are moved offsite and then shipped and assembled onsite, are becoming mainstream and enabling compute and storage to be quickly and reliably deployed in all types of settings – from just a few racks in a small hut to megawatts of equipment in a multi-story configuration. In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection.
Lisa Huff, Omdia’s senior principal analyst covering optical components will keep an eye out for whether 800G and 1.6T transmission will show up next in data centers. “We are in the middle of 400G deployment inside the data center and, as always, there is much hype around what the next data rate will be,” she writes.
“Omdia expects to see 2x400G and 8x100G solutions start to be deployed inside the data center in 2023, but we will not see high-volume deployment until about 2025 when DR4 and FR4 variants mature and 400G starts to slow down,” she writes. Deployments of 1.6T may start in 2026, but Huff said it might be 2027 or later before we see significant volume.
Coherent routing:
Omdia Senior Principal Analyst Timothy Munks said that with data traffic growing at the network’s edge, network operators are looking for better solutions to collect and move that data into metro and core networks.
“The convergence of IP and optical, or coherent routing, provides cost effective aggregation and transport of diverse traffic streams and offers network operators a pure pay-as-you-grow business model for adding capacity,” he writes.
In this video, Cisco’s Bill Gartner, SVP/GM Optical Systems & Optics, chats with Phil Harvey to discuss their Leading Lights Award and how Routed Optical Networking is transforming infrastructure and the economics of the network.
References:
One thought on “Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023”
Comments are closed.



Great post. I’m encountered some of these issues as well while researching optical networking trends this year. Especially impressed by the growth in pluggable optics and the nascent field of coherent routing being promoted by Cisco. Thanks!