Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
There was steady growth in 5G network coverage in 2022, with the number of subscribers reaching almost 1 billion worldwide. Although most of the 5G deployments in 2022 were in the developed economies of the world, Counterpoint Research expects that the bulk of 5G network roll outs in 2023 will be in emerging markets. This will drive the continuing transition from 5G NSA to 5G SA. To date, 42 network operators have deployed 5G SA commercially.
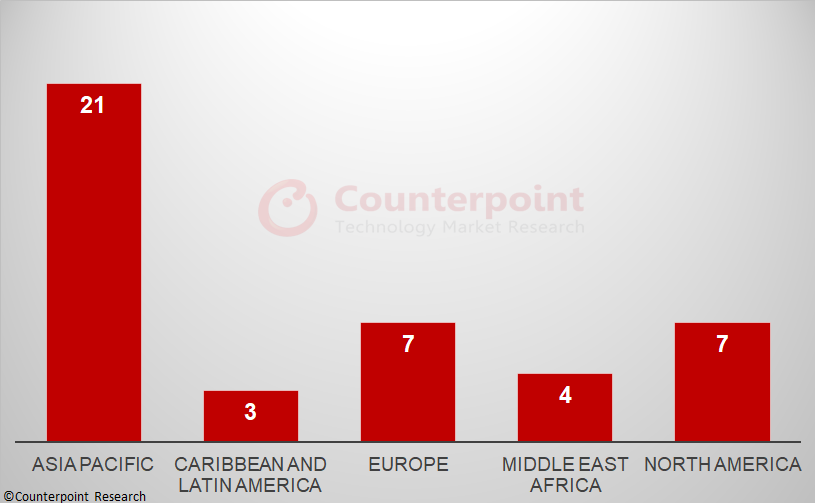
Counterpoint Research ‘s recently published 5G SA Tracker is a culmination of an extensive study of the 5G SA market. It provides details of all operators with 5G SA cores in commercial operation at the end of 2022, with market share by region, vendor and by frequency band. As shown in Exhibit 1, the Asia-Pacific region led the world at the end of 2022, followed by North America and Europe, with the other regions – Middle East and Africa and Latin America – lagging behind.
Key Points:
Key points discussed in the report include:
- Operators – 42 operators have deployed 5G SA commercially [1.] with many more testing and in trials. Most of the deployments are in the developed economies of the world with those in emerging economies lagging. In some markets, operators have adopted a “wait-and-see” approach and are looking for evidence of successful use cases before switching from 5G NSA to SA. The ongoing economic headwinds might also delay commercial deployment of SA particularly during the first half of 2023.
Note 1. By the end of 2022, Dell’Oro Group had identified 39 MNOs that had deployed 5G SA eMMB networks.
- Vendors – Ericsson and Nokia lead the 5G SA Core market globally and are benefiting from the geopolitical sanctions on Chinese vendors Huawei and ZTE in some markets. Asian vendors Samsung and NEC are mainly focused on their respective domestic markets, but and are expanding their reach to Tier-2 operators and emerging markets, while US vendor Mavenir is active across all regions, with multiple deployments due to become live in 2023, including several with Tier-1 operators.
- Spectrum – most operators are deploying 5G in mid-band frequencies, for example, n78, as it provides faster speeds and good coverage. A small number of operators have also launched commercial services in the sub-1GHz and millimetre wave bands. FWA seems to be the most popular use case at present but there is a lot of interest in edge services and network slicing as well.
Report Overview:
Counterpoint Research’s 5G SA Core Tracker, January 2023 tracker provides an overview of the 5G Standalone (SA) market, highlighting the key trends and drivers shaping the market, plus details of commercial launches by vendor, by region and by frequency band. In addition, the tracker provides details about the 5G SA vendor ecosystem split into two categories: public operator and private network markets.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Market Update
- 5G SA Market Deployments
- Commercial Deployment by Operators
- Network Engagements by Region
- Network Engagements by Deployments Status
- Leading 5G Core Vendors
- Mobile Core Vendor Ecosystem
- 5G Core Vendors Market Landscape
- Outlook
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
During its recent Q4 2022 earnings call, Nokia CEO Pekka Lundmark was asked about 5G SA core networks. Lundmark said, “Obviously 5G standalone is now the name of the game because you need 5G standalone in terms of getting the full benefits of 5G. There is going to be a lot of investment in 5G core, and operators will be implementing some critical important services like slicing, which require investment in the 5G core.”
That’s an understatement because 5G SA is needed to realize 3GPP defined 5G features and functions, like security and network slicing. 5G NSA, which is mostly deployed today, is actually 4G with 3GPP 5G-NR for the RAN.
References:
Update on 5G Stand-Alone (SA) Core Networks
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
Global Data: Wireless telcos don’t know how to market 5G SA
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
Why are 5G SA Core networks taking so long to be commercially deployed?
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market driven by 5G SA networks in China
Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Market—A Look into 2023
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks
One thought on “Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments”
Comments are closed.



A 5G SA core, which consists of the user plane, control plane, and shared data layer network functions, allows operators to deliver a more resilient core network and support highly-touted 5G services like network slicing, automation, orchestration, and mobile edge computing.
Nokia as part of a recent deal with Comcast, claims it has more than 80 5G SA core customers, with 25 of the world’s 40 largest communication service providers using its core network products. Nokia late last year began offering its 5G SA core through a software-as-a-service (SaaS) model. This is being offered on-demand through a subscription service managed by Nokia, which removes upfront expenses and the need for an operator or enterprise to manage software maintenance and updates. Comcast explained that its Nokia 5G core is not being offered through this SaaS model.