Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
According to market research firm Omdia, there were 1.8 billion global 5G subscribers at the end of 2023 with 7.9 billion forecast by 2028. This growth trajectory, while substantial, is subject to various influencing factors such as infrastructure development, spectrum availability, device availability, and consumer demand. Kristin Paulin, Principal Analyst at Omdia, has a cautiously optimistic outlook for 5G. She emphasizes that innovation and cooperation are key to unlocking the full potential of 5G and its transformative impact.
Globally, the number of deployed 5G networks is now comparable to 4G LTE deployments. There are currently 296 commercial 5G networks worldwide, a number expected to grow to 438 by 2025.
In North America, 5G deployment was at 176 million connections as of the third quarter of 2023, a 14% increase from the previous quarter. This represents a 26% market share and a 46% penetration rate. However, there were only two U.S. 5G SA network providers – T-Mobile US and Dish Wireless– as of the end of 2023.
in contrast, Latin America and the Caribbean are still in the early stages of 5G adoption. However, the region shows promise with an expected quadrupling of 5G connections in 2023, reaching 46 million. By 2028, it is anticipated that the region will have 492 million 5G connections.
Jose Otero, Vice President of Caribbean and Latin America for 5G Americas, acknowledges the significance of 4G LTE and 5G as vital mobile communication technologies in Latin America. He anticipates more robust opportunities for 5G in the region, driven by upcoming spectrum auctions and wider access to 5G devices in 2024.
“The global 5G landscape shows positive momentum as innovation and collaboration continue to be the mainstays for long term progress.” said Chris Pearson, President of 5G Americas. “With the World Radio Conference wrapping up, it is important that international co-operation and efforts continue to ensure that spectrum and technology standards continue to propel this growth.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
According to a recent report by Dell’Oro Group, the Mobile Core Network (MCN) market growth rate has been reduced to less than a 1% CAGR (2023-2028).
“This is the fourth consecutive time we reduced the growth rate of the MCN market as the build-out of 5G Standalone (5G SA) networks continues to wane compared to 5G Non-standalone (5G NSA) networks,” said Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “The buildout of 5G SA networks is going slower than anticipated which is restraining growth in the marketplace. To date, we count fifty 5G SA eMBB (enhanced Mobile BroadBand) networks that have been commercially deployed worldwide by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). We counted 18 new 5G SA networks in 2022, but only 12 were launched in 2023. On a positive note, we believe a lot of work has been done in the background, preparing for 5G SA launches by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and we expect 2024 to have more launches than 2022.”
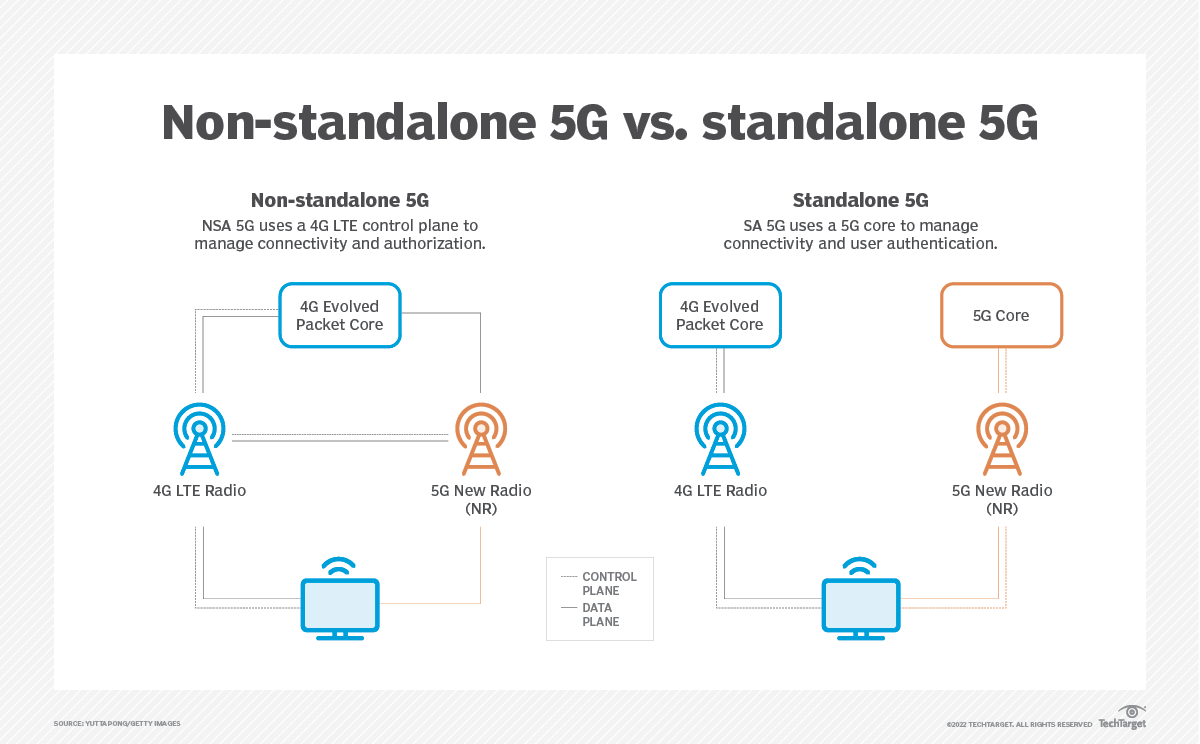
Note 1. Importantly, a 5G SA core network is required to realize 3GPP defined 5G features, like 5G Security, Network Slicing (3GPP’s technical specification (TS) 23.501 defines 5G system architecture with slicing included. TS 22.261 specifies the provisioning of network slices, association of devices to slices, and performance isolation during normal and elastic slice operation).
The 5G SA core network relies on a “Service-Based Architecture” (SBA) framework, where the architecture elements are defined in terms of “Network Functions” (NFs) rather than by “traditional” Network Entities.
5G SA core networks require “cloud-native” hardware and software that has a service-based architecture and decentralized functions. A “cloud-native” 5G core allows for flexible and efficient operation, as well as the effective adoption of new services.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to Verified Market Research, when the full 5G SA feature set is supported, enterprises can realize the following benefits:
- Further improvements to speed and reach, beyond what 5G NSA brings.
- Support for higher-density deployments of devices.
- Support for low-latency and real-time use cases.
- Support for enhanced enterprise site connectivity via network slicing.
- Better security than 5G NSA (which uses 4G LTE security methods and procedures).
- Simplification of the RAN and core compared to 5G NSA since 5G SA supports only 5G and leaves 4G and older standards behind — and even though the 5G SA core alone is more complex than a pure 4G core alone.
GSA claims that more than 121 network operators in 55 countries and territories have invested in public 5G standalone (SA) networks (but they don’t disclose how many of those have been commercially deployed (for example, AT&T and Verizon have been talking up 5G SA for years, but have yet to deploy it!). We trust Dell’Oro’s number of 5G SA eMBB networks deployed.
Findings from the latest GSA update on the 5G SA ecosystem/devices [2.] include:
- There are 2,130 announced devices with claimed support for 5G SA, up 35.7% from 1,569 at the end of 2022.
- Devices with support for 5G SA account for 90.3% of all 5G devices, as of the end of 2023, up from 35.6% in December 2019.
- 93 modems or mobile processors/platform chipsets state support for 5G SA, 90 of which are understood to be commercially available.
Note 2. It’s crucially important to realize that since all 5G SA core networks are different, a 5G SA device that works on one carrier’s network won’t work on any other without a new 5G SA download.
By the end of December 2023, GSA had identified:
• 28 announced form factors • 261 manufacturers with announced available or forthcoming 5G devices
• 2,358 announced devices, including regional variants, but excluding operator-branded devices that are essentially rebadged versions of other phones. Of these, at least 1,964 are understood to be commercially available:
• 1,255 phones, up 34 from November 2023. At least 1,168 of these are now commercially available, up 56 from November 2023
• 308 fixed wireless access customer-premises equipment (CPE) devices for indoor and outdoor uses, at least 209 of which are now commercially available
• 243 modules • 64 tablets • 33 laptops or notebooks • 77 battery-operated hot spots
• 179 industrial or enterprise routers, gateways or modems
• 13 in-vehicle routers, modems or hot spots
• 29 USB terminals, dongles or modems
• 168 other devices, including drones, head-mounted displays, robots, TVs, cameras, femtocells/small cells, repeaters, vehicle on-board units, keypads, a snap-on dongle/adapter, a switch, a vending machine and an encoder
• 1,098 announced devices with declared support for standalone 5G in sub-6 GHz bands, 904 of which are commercially available.
According to Verified Market Research, the market drivers for the 5G Technology Market can be influenced by various factors. These may include:
- Enhanced Data Speed and Capacity: In comparison to its predecessors (4G/LTE), 5G technology offers far faster data rates and more network capacity. Supporting the increasing need for high-bandwidth applications like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and Internet of Things (IoT) devices is imperative.
- Low Latency: The goal of 5G networks is to offer low-latency communication, which shortens the time it takes to send and receive data. This is critical for real-time interactive applications like industrial automation, remote surgery, and driverless cars.
- Growing Need for IoT Devices: One of the main factors driving 5G adoption is the spread of IoT devices across a number of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, and agriculture. 5G is ideally suited for Internet of Things applications due to its low latency and capacity to connect a large number of devices concurrently.
- Rise of Edge Computing: The growth of edge computing is intimately related to 5G networks. Edge computing improves speed and lowers latency by bringing computing resources closer to end users and devices; this makes it a crucial enabler for applications like driverless cars and smart cities.
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: By facilitating effective and dependable communication in smart factories, 5G is anticipated to play a significant role in the fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0. It makes it easier to incorporate technology like automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence into production processes.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure Upgrade: on order to roll out 5G networks, telecommunications service providers are actively spending on infrastructure upgrades. To improve capacity and coverage, new base stations and tiny cells must be installed.
- Government Initiatives and Support: Through legislative frameworks, financial aid, and other means, numerous governments across the globe are actively promoting the rollout of 5G technology. In the global digital landscape, these programmes seek to promote innovation, economic growth, and competitiveness.
- Competitive Environment and Industry Cooperation: Businesses are investing in 5G technology to obtain a competitive advantage due to the highly competitive nature of the telecommunications sector. Furthermore, partnerships between IT firms, telecom service providers, and other relevant parties are quickening the creation and implementation of 5G networks.
Several factors can act as restraints or challenges for the 5G Technology Market. These may include:
- Infrastructure Costs: Given that a large-scale deployment of base stations and small cells is necessary to support 5G, telecom operators may be discouraged by the substantial upfront expenditure necessary for creating and upgrading infrastructure.
- Spectrum Allocation and Availability: The effective operation of 5G networks depends on the allocation and availability of appropriate spectrum bands. Regulatory and geopolitical obstacles can make it difficult to get the necessary spectrum, which can hinder the deployment of 5G services.
- Security Concerns: There are worries about possible cybersecurity attacks due to the vast number of devices connected to 5G networks and the increased connection. Building confidence and promoting wider adoption require overcoming these issues and guaranteeing the security of network infrastructure.
- Interoperability Problems: There are interoperability problems since different generations of cellular technologies coexist. A seamless transition and the prevention of service interruptions depend on the seamless integration of various technologies.
- Regulatory Obstacles: The implementation of 5G networks faces a number of regulatory obstacles, such as spectrum auctions, licence requirements, and local law compliance. Uncertainties surrounding regulations may cause hold-ups and impede the rapid deployment of 5G services.
- Public Health and Safety Concerns: The general public’s reception of 5G networks may be impacted by worries about the possible health impacts of increasing exposure to radiofrequency radiation. Building public trust requires resolving these issues and maintaining clear lines of communication.
- Absence of Killer Applications: The deployment of 5G may be slowed back by the absence of compelling and widely applicable use cases. Creating cutting-edge, impactful apps that take advantage of 5G’s special features is essential to increasing demand.
- Global Economic uncertainty: Businesses’ and operators’ willingness to invest in the rollout of 5G technology can be impacted by economic downturns and uncertainty. Delays in infrastructure upgrades could result from financial considerations and budgetary restrictions.
Charts courtesy of Verified Market Research
References:
5G Continues Robust Momentum Growth and Drives Demand for More Wireless Spectrum
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/5g-system-overview
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/5G-standalone-5G-SA
2 thoughts on “Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices”
Comments are closed.



There has been significant investment in 5G, but 5G is not driving enough revenue growth, and investors are getting restless. Getting the right location for base stations and the associated towers is essential, and many opportunities are emerging to consolidate and refinance the tower infrastructure as part of managing costs. There are opportunities for TowerCos and neutral hosts to acquire and build towers and innovation in the associated energy management systems as well.
The fundamental challenges of bringing remote and rural locations into solid connectivity are still weighing on the industry. Governments are applying pressure and encouraging the sharing of infrastructure that can support mobile broadband and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). The emergence of satellite as a viable option is changing the coverage and service availability equations when considering convergence options.
The ability of the wirelessly connected user to choose from various connectivity options is driving innovation in the approaches to Quality of Experience and this in turn influences the way in which infrastructure is deployed. Our proprietary tools bring insights on the deployment architecture choices as well as the measured or forecasted experiences – Real Wireless is well positioned to help our operator, TowerCo and neutral host clients as they continue to invest and optimise the cost of connectivity.
https://real-wireless.com/challenges-facing-the-wireless-industry-in-2024-and-how-real-wireless-can-help/
Eye Movement Desensitizing and Reprocessing Therapy (EMDR) – Dispelling Common Misunderstandings and Misconceptions:
EMDR therapy features gained extensive recognition because a highly effective treatment with regard to trauma-related issues but false beliefs about its methods as well as efficacy still persist. With this particular forum thread all of us intend for you to debunk some on the common myths as well as misinterpretations surrounding EMDR therapy and provide precise information about its principles in addition to practices.
-Myth #1 and EMDR therapy is just effective intended for treating post-traumatic stress disorder PTSD. Although EMDR therapy is widely used in the treatment regarding PTSD the idea been specifically shown to become effective for a new range regarding other mental health concerns which include anxiety depression phobias and grief.
-Myth #2 and EMDR therapy can be a form of hypnosis or even mind control. EMDR therapies just isn’t hypnosis in addition to doesn’t involve mind control. It truly is a new structured curative approach of which utilizes reciprocal enjoyment techniques to be able to facilitate this processing and integration connected with terrible memories within a new safe in addition to supportive therapeutic environment.
-Myth #3 and EMDR remedy should be only suitable intended for individuals with severe trauma. EMDR therapies could be beneficial pertaining to individuals with a wide range regarding experiences by single-incident traumas to complex childhood traumas. It is not limited to help severe cases in addition to is usually adapted for you to meet the unique needs regarding each individual client.
-Myth #4 and EMDR therapies can be a quick fix as well as miracle cure.
Although some individuals may possibly event significant changes throughout symptoms soon after some sessions of EMDR therapy it truly is not a new quick fix or miracle cure. Healing via trauma takes time and could require ongoing therapy and support. By clarifying these myths and also mistaken beliefs most of us hope for you to promote a new better comprehending connected with EMDR therapy in addition to its potential features intended for individuals searching for relief from the particular effects associated with trauma and also related psychological considerations.