Telecom Regulation
Vodafone Spain (Zegona), MasOrange and Telefonica in possible RANco joint venture
In an interview with Expansion published on January 26, 2026, Zegona [1.] CEO Eamonn O’Hare revealed that Vodafone Spain, MasOrange and Telefonica have been holding talks on the possibility of joining their mobile networks together since late last year. “We are talking with Orange and Telefónica to create a RANco,” he said.
Note 1. Zegona owns 100% of Vodafone Spain.
However, Zegona was unable to give the potential joint venture its full attention due to demands of its ongoing fiber projects. Telefonica and Vodafone created their Fiberpass joint venture (JV) in 2025 and agreed to sell a 40% stake to AXA in November. Meanwhile, Vodafone and MasOrange brought in GIC as an investor in their PremiumFiber JV last summer.

Eamonn O’Hare, president and CEO of Zegona
“The whole team was so involved in the fibercos that we didn’t have the time or energy to thoroughly develop the project,” O’Hare told the Expansion. Instead, his staff focused on tying up the fiber optic projects and then took a break over the Christmas period, he explained. “And now we’re back with more energy.”
Why a JV rather than a merger of telcos: “Mergers and acquisitions are not a priority in Spain and the regulatory risk is very high,” he said. Zegona has a greater motivation to make the RANco a reality. “Today there are three companies…that manage three national mobile networks with exactly the same fixed costs, but Orange and Telefónica have twice as many customers as us,” O’Hare explained. “Therefore, our national mobile network is inefficient. Just as our fixed infrastructure was inefficient and unprofitable, [and] that’s why we powered the fibercos.”
“It would be easier to broker a deal with MasOrange to share the network in certain areas, so the synergies would be in urban areas. But we don’t have anything with Telefónica, so there it would all be synergies.” Telefonica already has a mobile network sharing deal in place with Vodafone in sparsely populated areas, and was rumoured to be in talks with the telco on a broader RANco arrangement this time last year.
As a result, a partnership with Telefonica would bring greater synergies as there are no existing arrangements in place in the mobile space, but any deal would be a more difficult deal to hammer out and it would be trickier to bring in an investor, O’Hare added. Zegona has three priorities in Spain: to align its valuation with those of its competitors; to boost its cash flow to €1 billion; and to develop a RANco. “As long as we are in the middle of that transformation, we have no interest in mergers and acquisitions,” he said. And in addition, “the regulatory obstacle is…too big.”
“Historically, these small businesses have grown and then tried to sell themselves to MásMóvil. But MásMóvil no longer buys. Neither do we or Telefónica,” O’Hare said. “No one is buying. So they… will just be devoured by us and by Digi, as in the Pac-Man game.”
Would Huawei network equipment be used in the proposed Spanish RanCo? Vodafone is the mobile operator with the largest network provided by Huawei. Orange is reducing its share, and Telefónica only uses Huawei in part of its core network in Spain and not at all in its radio network. If the Brussels Cybersecurity Act mandates the replacement of this Chinese equipment, what will Vodafone Spain (Zegona) do?
“If Europe is more aggressive on the Huawei issue , I suppose we should accelerate efforts to reduce the amount of Huawei equipment in the network… should we accelerate RANco for this reason? Officially, the answer is no.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.expansion.com/empresas/tecnologia/2026/01/26/6973ab17468aebd1418b4590.html
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G Market Nears Mainstream With $5 Billion Surge
España hit with major telecom blackout after power outage April 28th
Orange Spain & Ericsson to build 5G Infrastructure for 3 High-Speed Rail Lines
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
Telefónica – Nokia alliance for private mobile networks to accelerate digital transformation for enterprises in Latin America
Ericsson and O2 Telefónica demo Europe’s 1st Cloud RAN 5G mmWave FWA use case
Telecom and AI Status in the EU
GSMAi: key telecom developments in 2025; major trends to watch in 2026
Introduction:
During a recent GSMA Intelligence (GSMAi) webinar, key developments in the 2025 telecom sector were identified. They include satellite communications expansion/partnerships, eSIM proliferation, and industry consolidation.
Projections for 2026 suggest that 6G evolution (in 3GPP and ITU-R WP 5D) and artificial intelligence (AI) will have the greatest impact within the telecom space.
Mergers & Acquisitions:
Radhika Gupta, GSMAi’s Head of Data Acquisition, asserted that 2025 marked a pivotal shift, signaling that “ice finally broke on consolidation” within the telecommunications sector. The completion of the Vodafone UK and Three UK merger is cited as primary evidence, reducing the UK market from four major competitors to three.
“This particular event is important because Europe historically had been very particular about not approving such mergers that shrink a market from four players to three players for competition reasons. Even in the UK, back in 2016, Three and O2 [now Virgin Media O2] attempted to merge, which was not approved by the European Commission on competition reasons only.”
- A mandatory £11bn joint network investment plan over eight years for infrastructure upgrades.
- Capped consumer tariffs for three years to mitigate price escalation.
- Pre-set wholesale prices for three years, ensuring fair access for Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs).
“While I don’t think we will see satellite providers overtaking terrestrial services, as some have speculated, it shows that direct-to-device is a formidable trend right now… operators representing almost 70% of [the global mobile] market share has at least one satellite partnership with companies like Starlink,” Hatt added.
Editor’s Note: AST SpaceMobile, Iridium and Skylo and other satellite network operators are also making similar partnerships with cellular network operators to offer direct-to-device (D2D) satellite connectivity. The use cases are emergency texting and future voice/data, aiming to eliminate mobile dead zones by connecting standard smartphones to LEO satellites. These collaborations leverage existing mobile networks and spectrum to provide ubiquitous coverage, with AT&T and Verizon focusing on AST SpaceMobile and T-Mobile partnering with Starlink for expanded services.
 Image Credit: European Space Agency
Image Credit: European Space Agency
Accelerating eSIM Adoption and OEM Strategy:
GSMA, ETSI, IEEE, ITU & TM Forum: AI Telco Troubleshooting Challenge + TelecomGPT: a dedicated LLM for telecom applications
GSMA Vision 2040 study identifies spectrum needs during the peak 6G era of 2035–2040
Gartner: Gen AI nearing trough of disillusionment; GSMA survey of network operator use of AI
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
Highlights of GSMA study: Mobile Net Zero 2024, State of the Industry on Climate Action
Omdia: Regulatory activity to impact telecom in 2022; Global 5G status
According to market research dynamo Omdia, 2022 will be rife with regulatory activity that will impact the telecommunications market for years to come.
“As technology evolves, regulation will become more important than ever in the TMT industry,” said Sarah McBride, senior analyst for regulation at Omdia.
Omdia identified several trends it says will be “at the heart of regulatory activity” next year, including spectrum licensing, fiber networks, the digital divide and 6G (even though 5G spectrum has not been standardized by ITU-R in a revision to M.1036).
Regarding the digital divide (between the broadband haves and have nots), Omdia says “governments should learn from the pandemic and recognize the need for these broadband services to be affordable to all.”
The Omdia analysts say that governments must define a “comprehensive national digital strategy that includes providing state-aid tools to improve broadband availability and affordability.”
Such a strategy should go beyond deployment to “ensure citizens can use connectivity transformatively to bring about innovation and growth.” Doing so will encourage more deployment and investment, writes Omdia.
However, to avoid too much government intervention, Omdia also stresses the need for cooperation by service providers.
“Experience shows that market-led development, not a reliance on government intervention, is the most effective model for effective allocation of resources. However, economic viability is lower in some rural and sparsely populated areas than in populous areas,” Omdia said. The firm recommends that network operators collaborate by sharing infrastructure to reduce deployment costs and create shared wireless networks to “remove the need for regulators to set ambitious coverage obligations as part of spectrum licenses or universal service obligations.”
According to Omdia’s tracker for 5G networks, more than 150 5G networks have been launched around the world to date, which the research firm says will continue to drive demand for more spectrum.
“5G will profoundly affect society because of its ultrafast speeds, low latency, and high reliability, which enable digital transformation and support new use cases,” writes Omdia.
Regulators need to effectively manage spectrum allocation, “allowing access to the right amount of internationally harmonized spectrum (e.g., 700MHz, 3.6GHz, and 26GHz bands in the EU) in a timely manner to keep costs down.”
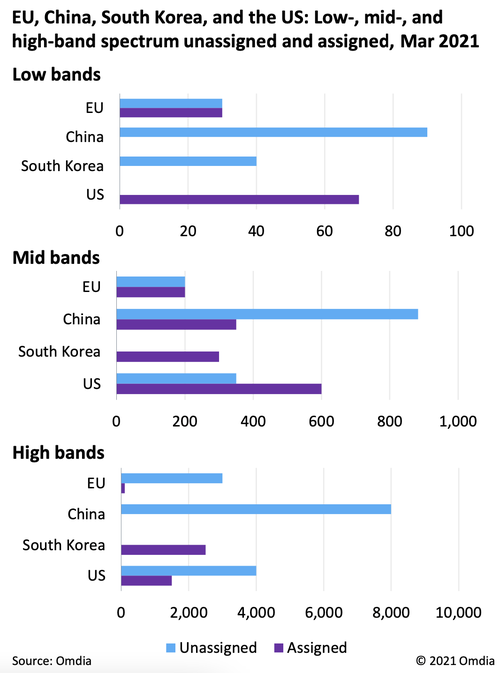
As operators continue to build out their 5G networks, Omdia tells policymakers it’s important to plan ahead on 6G standards, given the role these networks will play in the digital economy and the danger posed by a lack of cohesion.
Specifically, the firm warns against further splintering the telecom and Internet ecosystem, or what it calls “the splinternet.”
“It is especially important that regulators and policymakers prepare for future network generations by ensuring agreement is reached on 6G standards. A fragmentation of standards must be avoided to prevent any further separation of the telecoms and internet ecosystem, a ‘splinternet’,” writes Omdia.
Acknowledging that plans for 6G are in their infancy, Omdia further tells policymakers to begin identifying appropriate spectrum bands, though it notes that such plans “will need to be balanced with the need to release spectrum for 5G.”
Part of the rush to deploy high-speed internet everywhere includes a migration to fiber, whether through new builds or upgrades of existing cable networks. Omdia says that as network operators migrate to fiber, regulators should focus on promoting competition, pricing strategies and raising awareness amongst consumers about fiber access.
The firm further states that regulators should include fiber access in wholesale obligations, “once sufficient fiber coverage is reached.”
It’s important for network operators to collaborate with regulators on network upgrade plans and give wholesale customers advance warning to avoid disruption.
“Operators need to give their wholesale customers a sufficient notice period when withdrawing copper networks. This includes providing formal notifications that outline the timeframes involved, the replacement products on offer, and the new price terms,” writes Omdia.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
In a separate report titled, 2022 Trends to Watch: Global 5G, Omdia says that 5G network rollouts are still in the early stages, especially in developing regions.
“But there are compelling reasons for telcos to commit to 5G so they can differentiate around an improved network experience, as well as realize network efficiencies and lower operating costs. Moreover, 5G’s enhancements over 4G – most noticeably speed and latency – will come to be appreciated by consumers more next year as an increasing number of data-intensive services and applications become popular in the mass market,” the research firm said.
“A surprise to many next year may be the rapid emergence of satellite to augment telcos’ terrestrial network coverage,” Omdia observed.
“A key driver for hybrid satellite-cellular deployments is the need for ubiquitous high-speed data coverage, something which telcos can greatly benefit from if their rivals’ 5G network coverage remains patchy.”
Major telcos including BT, Deutsche Telekom, Telecom Italia and Verizon signed significant deals with satellite internet providers in 2021 to offer a hybrid approach to targeted residential, enterprise and industrial markets.
Omdia believes that the likely success of these satellite internet initiatives could jump-start a flurry of new activity in this area in 2022.
“Although most end users aren’t rushing to buy 5G, the quality of their network experience in terms of reliability, speed, and coverage is increasingly important to them. As such, 5G offers telcos a better opportunity than 4G to differentiate, especially for ones that can claim they offer the best-in-market network experience,” Omdia said.
Omdia thinks that partnership strategies will be even more important for telco 5G success in 2022.
“How good telcos are at partnering, whether for content, service, or technology development, will increasingly define how successful they are in consumer, enterprise, and industrial markets. Because of its enhanced capabilities over 4G, 5G enables telcos to offer much more, and they will have to partner effectively to capitalize on this.”
“Except for 5G MEC (really ?), the ecosystem and markets for advanced 5G technologies are still in their infancy. However, 5G front-runners are already launching them, placing them in a strong position to gain a first-mover advantage when the market is ready to adopt them,” Omdia said.
References:
https://www.broadbandworldnews.com/document.asp?doc_id=774240&
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/12/18/etsi-mec-standard-explained-part-ii/


