Telegeography
Telegeography: Legacy MPLS networking declines; Direct Internet Access surges
TeleGeography, a global telecommunications market research and consulting firm, has released its 2021 WAN Manager Survey, revealing that Direct Internet Access (DIA) is gaining ground on MPLS, with 42% of average sites running the product in 2021.
At the same time, survey responses show a clear downtrend in MPLS use, from a dominant high of 82% of sites running the product in 2018 down to 46% in 2021. It marks the first time this figure has dropped below half of average sites. This shift to DIA reflects the plans of many WAN managers to reduce their reliance on MPLS in their networks.
Key Findings:
• For the first time, MPLS usage dipped below half of average sites—46% of sites were running MPLS in 2021.
• DIA is hot on the heels of MPLS, with 42% of average sites running the product in 2021.
• MPLS usage at average WAN sites has declined by 5% compounded annually over four years, while DIA and broadband usage has climbed by 3% and 1.5% each year across the same time period.
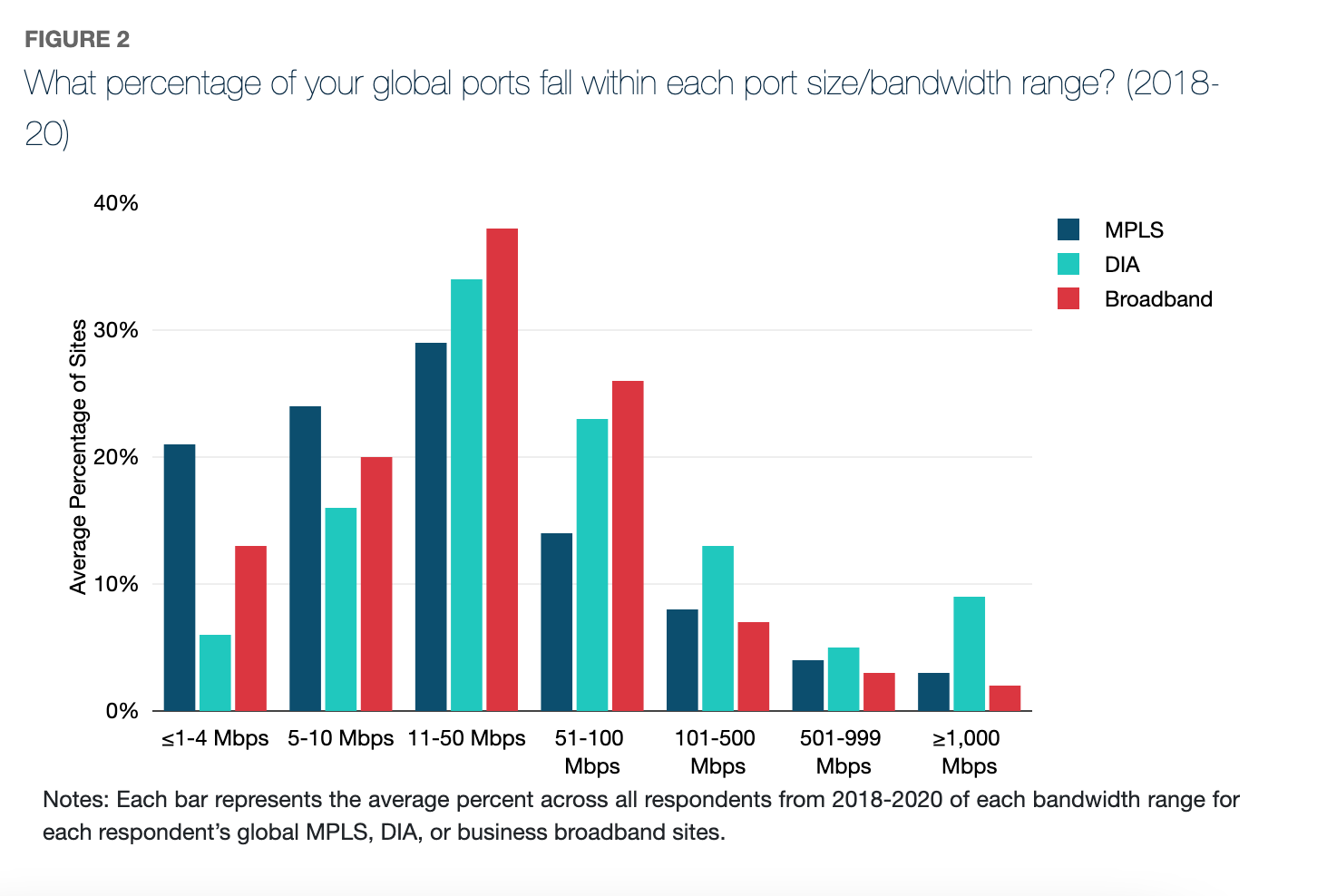
• WAN managers want more bandwidth. Across MPLS, DIA, and broadband, the percentage of large port sizes being procured is growing, while port sizes 50 Mbps and under are declining 1-3% compounded annually.
• The most common strategy for backing up MPLS is using an alternative connectivity service like DIA or broadband.
• Zero Trust Security adoption is on the rise, growing from just 8% of respondents in 2019 to 35% in 2021, and the knowledge gap is narrowing.
• Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign on (SSO) are the top ZTS features implemented.
• Increased remote work is the top factor driving companies towards ZTS solutions.
• Top network infrastructure security vendors in hardware–Palo Alto, Cisco, and Fortinet–also lead in the software-based security vertical.
TeleGeography’s WAN Manager Survey features analysis based on the experiences of WAN managers from 185 companies with a median revenue of $10 billion USD. The 2021 focuses on IT managers whose day-to-day role covers designing, sourcing, and managing U.S. national, regional, and global corporate wide area computer networks. It also includes 60 new responses across various industries.
TeleGeography’s report highlights how the extension of COVID-related remote work has accelerated many ongoing WAN trends like migration to the cloud, SD-WAN adoption, and incorporation of alternative access technologies into the underlay. To that effect, the team found that DIA and business broadband usage have been on the rise, with DIA experiencing a four-year CAGR increase of 3% and broadband logging an increase of 1.5%.
“Through our survey, we can see that enterprise companies are embracing hybrid networks more and more. MPLS usage in our respondents’ WAN has been declining steadily, and in 2021 we saw a near-equal ratio of MPLS and DIA in the average network. Given these rates, we’ll have an eye on DIA usage to perhaps overtake MPLS in future surveys,” said Elizabeth Thorne, Senior Analyst at TeleGeography.
TeleGeography’s new survey also reveals WAN managers’ views on zero trust security (ZTS) and secure access service edge (SASE) adoption. ZTS adoption is on the rise, growing from just 8% of respondents in 2019 to 35% in 2021, a significant increase in just two years.
Telegeography asked WAN managers how far along they were in implementing ZTS (Zero Trust Security) or SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) security policies on their network. Here are the results:
• Implementation of one or more elements of ZTS/SASE on at least some of the respondent’s network jumped from just 8% in 2019 to 35% in 2021, a significant increase in just two years.
• There’s been a narrowing of the knowledge gap. Just 8% of respondents were unfamiliar with ZTS in 2021, compared to one in five in 2019.
• Overall we saw a shift down the deployment pipeline, with reductions in the percentage of respondents who either had not started, or were just beginning their implementation journey.
• In 2021 we introduced the option “Waiting on SD-WAN,” as in past interviews many respondents indicated that their adoption of zero trust policies was incumbent on their SD-WAN deployment. That is reflected in the results, as it was the second most common–28%–stage respondents were in.
Other findings:
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) represents a small percent of average WAN sites, often used as backups or temporary connectivity.
- Satellite had the lowest reported average usage, and has maintained its reputation as an expensive connectivity option of last resort.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
End Quote:
“Enterprise networking is evolving, in part due to an increase in remote working. Network managers are facing the challenge of accommodating a remote-friendly, work-from-anywhere environment and many will likely be moving toward internet-first networks and further away from MPLS in the coming years,” said Greg Bryan, Senior Manager at TeleGeography.
References:
https://www2.telegeography.com/download-the-wan-manager-survey-executive-summary
Telegeography: Strong international bandwidth demand in LatAm; Global Internet traffic and bandwidth increased in 2020
TeleGeography’s latest research on Latin America shows that international bandwidth demand is strong in the region. With an ongoing surge in new submarine cable deployments, content providers are expanding their geographic reach as both owners and anchor customers of new cable systems.
The market research firm reported in August that the average international internet traffic increased 48% in 2020 while internet bandwidth was up 35%, the biggest increase since 2013. In its annual report on submarine networks and capacity, TeleGeography said the global Internet “bent but – for the most part – did not break” during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the market research firm wrote that the spike in bandwidth and traffic growth in 2020 is probably a one-time event and a return to typical rates of growth is likely when the pandemic restrictions end.
International Internet Bandwidth Growth by Region:
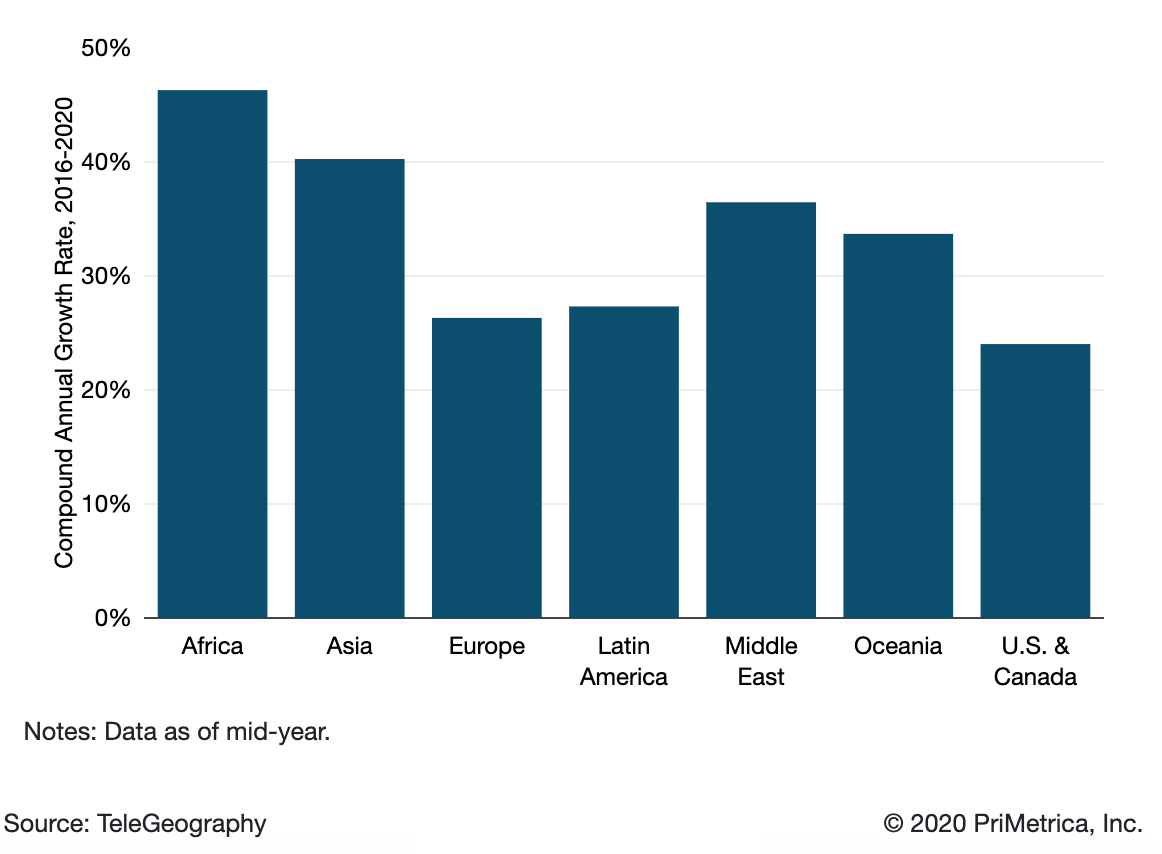
International internet traffic growth largely mirrors that of internet capacity. However, traffic and capacity growth seldom move in perfect tandem. (Network operators will often add capacity in anticipation of traffic growth.). Average and peak international internet traffic increased at a compound annual rate of 30% between 2016 and 2020, comparable to the 29% compound annual growth rate in bandwidth.
Based on discussions with network operators worldwide, TeleGeography believes the trends of recent years will continue. While international Internet bandwidth and traffic growth had been gradually slowing prior to 2020, growth remains brisk. Africa has experienced the most rapid growth in international bandwidth, growing at a compound annual rate of 47% from 2016-2020, with Asia just behind at 40%.
What won’t change is the role of U.S. web giants Google, Microsoft, Facebook and Amazon. They have become far and away the dominant users of international bandwidth, accounting for 64% of all used capacity in 2019. Across six of the world’s seven regions, they added capacity at a compound annual rate of above 70% between 2015 and 2019, compared to a rate of less than 45% for others. Their rapid expansion into subsea capacity has caused a major shift in the global wholesale market, TeleGeography says.
That presence “drives scale to establish new submarine cable systems and lower overall unit costs.” The OTT firms have become a key part of the subsea cable business model. Many of the big cables, invested in by both telcos and Internet players, now rely on the initial capital injection from the Internet content players. This means a share of network capacity or fiber pairs can be allocated to the largest consumers to cover initial costs, with the remaining shares sold as managed wholesale bandwidth.
TeleGeography states that both content players and telcos are trying to cope with massive growth in demand, driven by new applications and greater penetration into emerging markets. “The sheer growth in supply will drive lower unit costs for bandwidth,” it says. “In the face of unrelenting price erosion, the challenge for wholesale operators is to carve out profitable niches where demand trumps competition.” Prices vary enormously even though they are falling sharply. London and Singapore prices have declined 25% since 2017, yet Singapore tariffs are much higher; a 10 GigE port costs roughly three times as much, for example. Thanks to capacity upgrades, the prices for 10 GigE ports in São Paulo and Sydney fell 38% and 22% compounded annually over the past three years. TeleGeography warns that while the unit cost savings from the large cable investments are an incentive to investment for operators, they don’t want to be left with too much excess bandwidth. “It’s often a race to offload wholesale capacity before a new generation of lower-cost supply emerges.”
TeleGeography predicts $8.1 billion worth of new cables will be launched between 2020 and 2022 with the biggest share, $2.3 billion, invested in the trans-Pacific route. But the research firm cautions that the pandemic could disrupt supply. “Temporary cable factory closures combined with delays in permitting and marine installation could hamper the deployment of many planned cables.”
References:
https://blog.telegeography.com/internet-traffic-and-capacity-in-covid-adjusted-terms
https://www2.telegeography.com/covid19-state-of-the-network


