Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Introduction:
Despite mounting pressure on venture capital in a difficult economic environment, money is still flowing into generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) startups. Indeed, AI startups have emerged as a bright spot for VC investments this year amid a wider slowdown in funding caused by rising interest rates, a slowing economy and high inflation.
VCs have already poured $10.7 billion into Generative AI [1.] start-ups within the first three months of this year, a thirteen-fold increase from a year earlier, according to PitchBook, which tracks start-ups.
Note 1. Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, synthetic data, images, and audio. The recent buzz around Generative AI has been driven by the simplicity of new user interfaces for creating high-quality content in a matter of seconds.
….………………………………………………………………………………….
Tech giants have poured effort and billions of dollars into what they say is a transformative technology, even amid rising concerns about A.I.’s role in spreading misinformation, killing jobs and one day matching human intelligence. What they don’t publicize is that the results (especially from ChatGPT) may be incorrect or inconclusive.
We take a close look at Generative AI Unicorns with an emphasis on OpenAI (the creator of ChatGPT) and the competition it will face from Google DeepMind.
Generative AI Unicorns and OpenAI:
AI startups make up half of all new unicorns (startups valued at more than $1B) in 2023, says CBInsights.
At Generative AI firms, startups are reaching $1 billion valuations at lightning speed. There are currently 13 Generative AI unicorns (see chart below), according to CBInsights which said they attained their unicorn status nearly twice as fast as the average $1 billion startup.
Across the 13 Generative AI unicorns, the average time to reach unicorn status was 3.6 years but for the unicorn club as a whole the average is 7 years — almost twice as long.
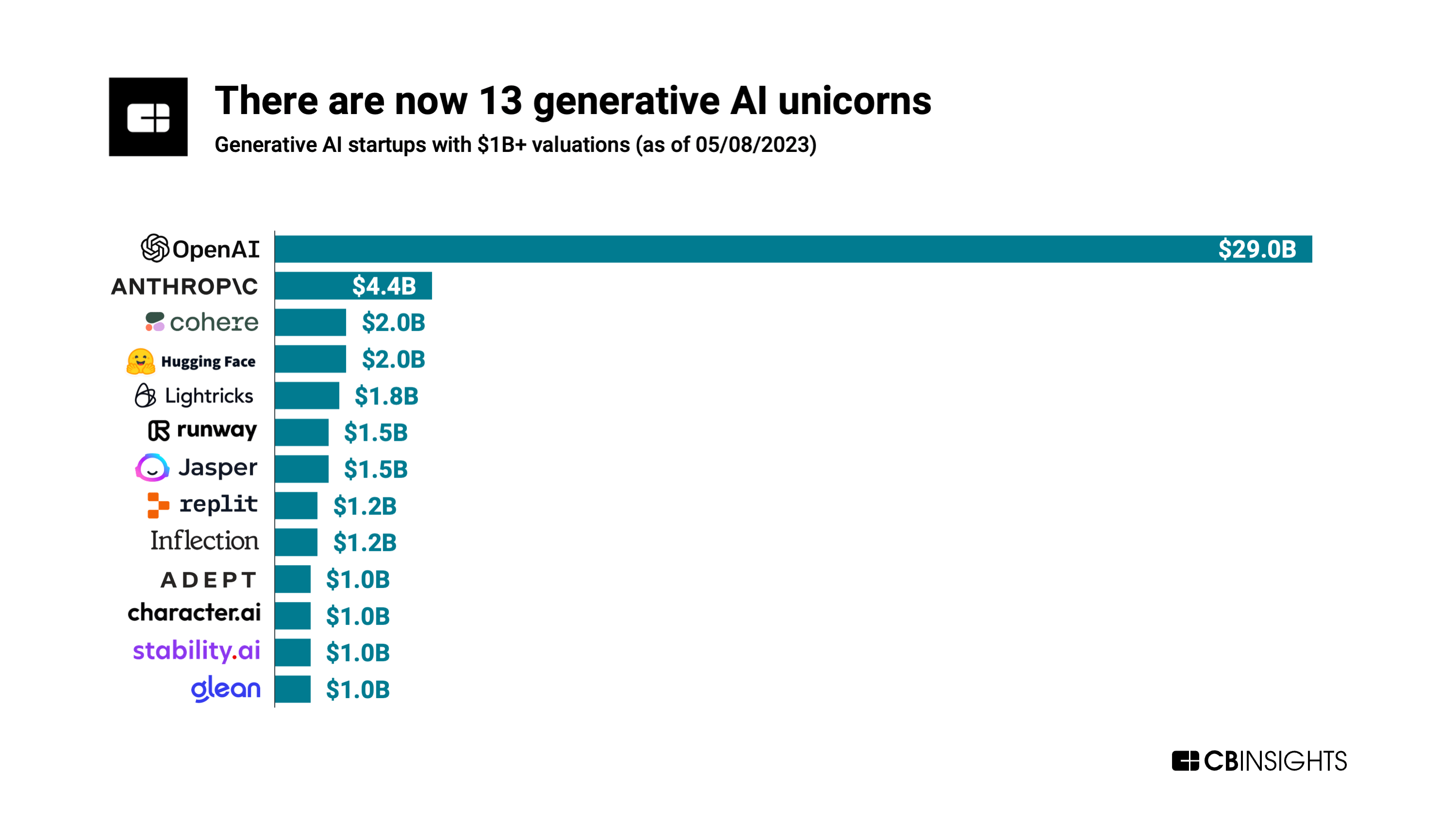
OpenAI, the poster child for Generative AI with its Chat GPT app, tops the list with a valuation of almost $30 billion. Microsoft is the largest investor as it provided OpenAI with a $1 billion investment in 2019 and a $10 billion investment in 2023. Bloomberg reported that the company recently closed an investment fund, exceeding expectations with a value that surpasses $175 million.
However, OpenAI may have a formidable competitor in Google DeepMind (more details in DeepMind section below).
….……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Anthropic is #2 with a valuation of $4.4B. It’s an AI safety and research company based in San Francisco, CA. The company says they “develop large-scale AI systems so that we can study their safety properties at the technological frontier, where new problems are most likely to arise. We use these insights to create safer, steerable, and more reliable models, and to generate systems that we deploy externally, like Claude (to be used with Slack).”
In Q1-2023, Generative AI companies accounted for three of the entrants to the unicorn club with Anthropic, Adept, and Character.AI all gaining valuations of $1B or above.
New Generative AI Unicorns in May:
Ten companies joined the Crunchbase Unicorn Board in May 2023 — double the count for April 2023. Among them were several AI startups:
- Toronto-basedCohere, a generative AI large language model developer for enterprises, raised $270 million in its Series C funding. The funding was led by Inovia Capital valuing the 4-year-old company at $2.2 billion.
- Generative video AI company Runway, based out of New York, raised a $100 million Series D led by Google. The funding valued the 5-year-old company at $1.5 billion.
- Synthesia, a UK-based artificial intelligence (AI) startup, has raised about $90 million at a valuation of $1 billion from a funding round led by venture capital firms Accel and Nvidia-owned NVentures. “While we weren’t actively looking for new investment, Accel and NVIDIA share our vision for transforming traditional video production into a digital workflow,” said Victor Riparbelli, co-founder and CEO of Synthesia.
….…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Google DeepMind:
Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai said in a blog post, “we’ve been an AI-first company since 2016, because we see AI as the most significant way to deliver on our mission.”
In April, Alphabet Inc. created “Google DeepMind,” in order to bring together two leading research groups in the AI field: the Brain team from Google Research, and DeepMind (the AI startup Google acquired in 2014). Their collective accomplishments in AI over the last decade span AlphaGo, Transformers, word2vec, WaveNet, AlphaFold, sequence to sequence models, distillation, deep reinforcement learning, and distributed systems and software frameworks like TensorFlow and JAX for expressing, training and deploying large scale Machine Learning (ML) models.
By launching DeepMind as Google’s Generative AI solution, there could be a new battle front opening in quantum computing, machine learning perception, gaming and mobile systems, NLP and human-computer interaction and visualization.
A recent DeepMind paper says the Alphabet unit has extended AI capabilities with faster sorting algorithms to create ordered lists. Their paper says it shows “how artificial intelligence can go beyond the current state of the art,” because ultimately AlphaDev’s sorts use fewer lines of code for sorting sequences with between three elements and eight elements — for every number of elements except four. And these shorter algorithms “do indeed lead to lower latency,” the paper points out, “as the algorithm length and latency are correlated.”
Their researchers created a program based on DeepMind’s AlphaZero program, which beat the world’s best players in chess and Go. That program trained solely by playing games against itself, getting better and better using a kind of massively automated trial-and-error that eventually determines the most optimal approach.
DeepMind’s researchers modified into a new coding-oriented program called AlphaDev, calling this an important next step. “With AlphaDev, we show how this model can transfer from games to scientific challenges, and from simulations to real-world applications,” they wrote on the DeepMind blog. The newly-discovered sorting algorithms “contain new sequences of instructions that save a single instruction each time they’re applied. AlphaDev skips over a step to connect items in a way that looks like a mistake, but is actually a shortcut.”
….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
While many luminaries, such as Henry Kissinger, Eric Schmidt and Daniel Huttenlocher, have lauded Generative AI as the greatest invention since the printing press, the technology has yet to prove itself worthy of the enormous praise. Their central thesis, that a computer program could “transform the human cognitive process” in a way tantamount to the Enlightenment, is a huge stretch.
Gary Marcus, a well-known professor and frequent critic of A.I. technology, said that OpenAI hasn’t been transparent about the data its uses to develop its systems. He expressed doubt in CEO Sam Altman’s prediction that new jobs will replace those killed off by A.I.
“We have unprecedented opportunities here but we are also facing a perfect storm of corporate irresponsibility, widespread deployment, lack of adequate regulation and inherent unreliability,” Dr. Marcus said.
The promise and potential of Generative AI will not be realized for many years. Think of it as a “research work in progress” with many twists and turns along the way.
….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/generative-ai-unicorns-valuations-revenues-headcount/
https://pitchbook.com/news/articles/Amazon-Bedrock-generative-ai-q1-2023-vc-deals
Curmudgeon/Sperandeo: Impact of Generative AI on Jobs and Workers
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
4 thoughts on “Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight”
Comments are closed.



From ChatGPT:
Generative AI, also known as generative modeling, refers to a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques that involve generating new content, such as images, text, or even music, based on patterns and data it has learned from. Generative models are designed to learn the underlying distribution of the training data and then use that knowledge to generate new, similar examples.
One popular approach to generative AI is generative adversarial networks (GANs). GANs consist of two components: a generator and a discriminator. The generator learns to create new samples, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between real and generated samples. Through an iterative process, the generator and discriminator improve their abilities, leading to the generation of increasingly realistic and high-quality content.
Another approach is the use of autoencoders, which are neural networks designed to encode input data into a lower-dimensional representation and then decode it back to its original form. By training an autoencoder on a specific dataset, it can learn to generate new examples that resemble the input data.
Generative AI has found applications in various domains, including image synthesis, text generation, music composition, and even video generation. It has both practical and creative implications, offering opportunities for generating new content, data augmentation, simulation, and more. However, it is important to note that generative AI models also raise ethical concerns, such as potential misuse and generating misleading or harmful content.
Impact of Generative AI on Jobs and Workers, the Curmudgeon with Victor Sperandeo
More than 75% of companies are looking to adopt AI tech in the next five years, according to the Future of Jobs report from the World Economic Forum published in May, which surveyed 803 companies across the world.
AI innovators including OpenAI, the company behind the ChatGPT chatbot [see Q &A below], have been trying to walk a fine line on the impact of their technology on jobs and workers. “Every large company has an army of people that read and review contracts for revenue recognition purposes, for example,” said Brad Lightcap, chief operating officer of OpenAI, at a Wall Street Journal event in Cannes, France. “You may not have that job. That may not be a job of the future,” he added.
Generative AI could potentially create some jobs as well as eliminate others. OpenAI’s Lightcap said that a company which uses AI to double the amount of computer code it writes will need more employees for other things. “There’s more people that need to be brought in to do product design,” Lightcap said. “There’s more people that need to be brought in to do distribution, operations, sales and marketing.”
Lightcap added that while AI models are good at jobs, they need to be told what tasks they should be doing, and their work must be checked and verified. “People will become more orchestrators,” he said.
http://www.fiendbear.com/Curmudgeon517.htm
Reuters: US-based generative AI job postings up 20% in May, Indeed data show
The May figure, at 204 per million job postings, was also more than double the 2021 level and underscored the buzz around AI, sparked by the runaway success of OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Data scientist roles made up 5% of the AI job postings on Indeed’s U.S. platform, while roles such as software engineer, machine learning engineer and data engineer were also in demand.
“There has been a notable increase in job seeker interest in AI-related jobs, especially since the introduction of ChatGPT,” said Nick Bunker, director of economic research at Indeed.
The jump comes at a time when the broader tech job market is under pressure from mass layoffs at companies such as Meta Platforms and Amazon.com Inc, which are tightening their belts to cope with an uncertain economy.
Overall, tech jobs are down 43.6% in the United States from June last year, Indeed said, adding the number of available AI jobs was not keeping up with the interest from job seekers.
https://www.reuters.com/technology/us-based-generative-ai-job-postings-up-20-may-data-2023-06-22/
“Generative artificial intelligence” is set to add up to $4.4 trillion of value to the global economy annually, according to a report from McKinsey Global Institute, in what is one of the rosier predictions about the economic effects of the rapidly evolving technology.
Generative A.I., which includes chatbots such as ChatGPT that can generate text in response to prompts, can potentially boost productivity by saving 60 to 70 percent of workers’ time through automation of their work, according to the 68-page report, which was published early Wednesday. Half of all work will be automated between 2030 and 2060, the report said.
McKinsey had previously predicted that A.I. would automate half of all work between 2035 and 2075, but the power of generative A.I. tools — which exploded onto the tech scene late last year — accelerated the company’s forecast.
“Generative A.I. has the potential to change the anatomy of work, augmenting the capabilities of individual workers by automating some of their individual activities,” the report said.
McKinsey’s report is one of the few so far to quantify the long-term impact of generative A.I. on the economy. The report arrives as Silicon Valley has been gripped by a fervor over generative A.I. tools like ChatGPT and Google’s Bard, with tech companies and venture capitalists investing billions of dollars in the technology.
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/06/14/technology/generative-ai-global-economy.html