Quantum Technologies
AT&T will be “quantum ready” by the year 2025; New fiber network launched in Indiana
AT&T is aiming to become “quantum ready” by the year 2025, said an AT&T quantum security and preparedness team member during this week’s AT&T Security Conference. The tier-one operator has been identifying its cryptographic assets, vetting post-quantum cryptography solutions, and taking trials to identify those solutions, according to Brian Miles, principal member of tech staff at AT&T. “We’ve got AT&T quantum ready on our roadmap by 2025,” Miles said, adding that doesn’t mean the company will be fully quantum secured.
“This just means that we have done all our due diligence. And we have a clear path forward and we have all the solutions identified to target and address some of the different problems posed by quantum computing.”
Editor’s Note:
Quantum technologies function by harnessing the key characteristics of the theory of quantum mechanics, including superposition, entanglement and uncertainty. The resulting technologies are expected to be diverse and far reaching. For example, quantum computers are expected to overcome most “public key encryption” systems, presaging a radical change in cybersecurity. Given its aptitude for navigating complexity, quantum tools are expected to shave years off the time to market for medicines. Secure, efficient communications among drones and other autonomous vehicles will underpin safety and operational effectiveness in the crowded skies of the future. Of course, these nearer terms examples will be joined by applications barely yet imagined as the technology matures.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
That effort should put AT&T in a better position before the cryptographically relevant quantum computer (CRQC) emerges. CRQC is defined as a quantum computer that reaches the compute capability to break an RSA-2048 key using Shor’s algorithm, according to Miles. Shor’s algorithm is a quantum computer algorithm developed in 1994 by American mathematician Peter Shor.
Miles also urges organizations to implement cryptography agility, which is a framework or architecture that allows companies to replace their cryptographic primitives, underlying cryptography, and encryption algorithms with little or no impact on the existing applications.
“In a nutshell, that means you get off board your cryptography, get it out of your applications, get it more centralized, ultimately put automation in place to make the underlying infrastructure [transition] relatively painless,” he explained.
The next significant step is to identify the cryptographic assets and who has the responsibility for that inventory within the company, Miles noted.
“It’s incredibly important to get started on a crypto-agile architecture roadmap within your company quickly,” he said. “The whole crypto-agile architecture at least gives you the tools and the ability to pivot to different cryptography on short notice.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, AT&T is connecting its first customers to its new fiber network in Indiana. The company is investing $29.7 million – on top of $9.9 million contributed by Vanderburgh County, allocated from the American Rescue Plan – to build to 20,000 locations.
In a press release, AT&T calls Vanderburgh a “largely rural community where roughly one-third of homes, farms and businesses did not have access to fixed broadband service before this fiber build.” The network build is expected to be complete in November 2023 and will deliver service up to 5 Gbit/sec.
“We have a once-in-a-generation opportunity to bring high-speed, reliable broadband to communities across the country,” said AT&T CEO John Stankey. “Combining public sector funding and private sector investment is the most cost-effective way to ensure more Americans are able to take advantage of robust connectivity. This type of public-private partnership can serve as a model to help close the digital divide once and for all.”
“If you live in a big city, you probably take your high-speed internet for granted. But it’s a different story in rural parts of the country,” said Cheryl Musgrave, commissioner, Vanderburgh County. “Fortunately, through this collaboration with AT&T, thousands of our rural neighbors will have a new story to tell, because they’ll also have access to fiber-powered broadband.
“I’m truly excited to see the impact this new connectivity will have on our schools and families, and the economic growth of our community,” Musgrave added.
AT&T worked quickly to bring the benefits of fiber to Vanderburgh County residents and businesses, with the network core becoming operational only seven months after the previously announced contract agreement was finalized. That allowed AT&T to connect the first fiber locations earlier than expected. The project will be completed by November 2023.
The new fiber network is capable of delivering speeds up to 5 Gbps on both upload and download. The faster speeds and capacity mean customers can now connect to data intensive online tools and applications, deploy precision agriculture technologies and access vital education resources.
AT&T has extensive experience deploying fiber-optics across Indiana. In fact, hundreds of thousands of locations in the state have access to AT&T Fiber today. AT&T is also currently working with the City of Boonville and the City of Martinsville on public-private partnerships to bring AT&T Fiber to those communities.
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/att-aims-to-be-quantum-ready-by-2025/2022/10/
BT and Toshiba commercial trial of a ‘quantum-secured’ metro network
BT and Toshiba have launched what they say is the world’s first “commercial trial” of a quantum-secured metro network (QSMN).
The QSMN infrastructure will be able to connect numerous customers across London, helping them to secure the transmission of valuable data and information between multiple physical locations over standard fiber optic links using quantum key distribution (QKD).
QKD is an important technology, playing a fundamental role in protecting networks and data against the emerging threat of cyber-attack using quantum computing. The London network represents a critical step towards reaching the UK government’s strategy to become a quantum-enabled economy
The QSMN is a three-node London exchange fiber optic ring using commercially available QKD hardware from Toshiba. BT provided fiber connectivity and “quantum-enabled” local exchanges.
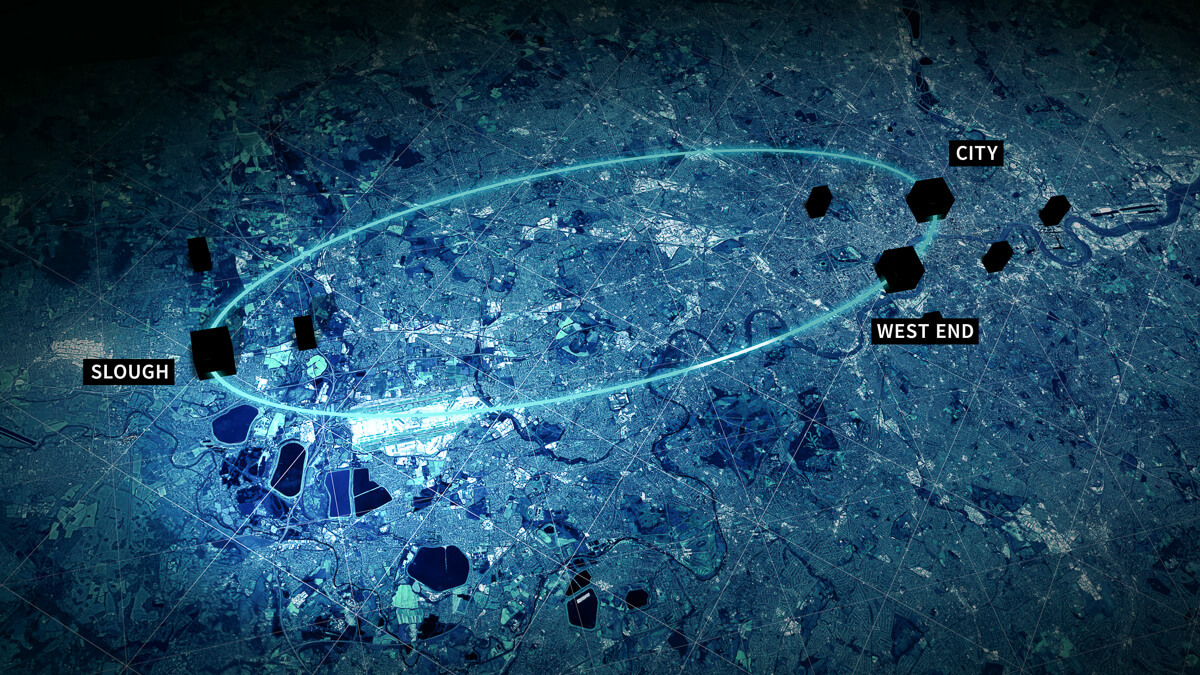
Source: BT
German based optical network vendor ADVA is also involved in the QSMN. For the dedicated QKD “access tails,” BT used a commercially available Optical Spectrum Access Filter Connect (OSA FC) solution from Openreach, the UK incumbent’s infrastructure arm. OSA FC was developed by ADVA.
Financial services firm EY, the network’s first commercial customer, will use the network to connect two of its sites in London, one in Canary Wharf, and one near London Bridge. It will demonstrate how data secured using QKD can move between sites and will showcase the benefits this network brings to its own customers.
BT is working with EY (a non paying customer) and others that want to try QSMN to work out which types of QKD services will be in demand and how the business case might pan out. That initiative will likely be done over a three-year period,
“It’s a commercial trial in the sense that it’s built on commercial kit,” Professor Tim Whitley, managing director at BT’s applied research division, told Light Reading.
“It’s also a commercial trial in the sense that, unlike many trials around, it is effectively integrated in and part of a national operator’s communications infrastructure. It is managed out of our national operations center at Adastral Park.”
BT and Toshiba announced their commitment to creating a trial network in October 2021. BT will operate the network, providing a range of quantum-secured services including dedicated high bandwidth end-to-end encrypted links, delivered over Openreach’s private fibre networks, while Toshiba will provide quantum key distribution hardware and key management software. In the network, QKD keys will be combined with the in-built ethernet security, based on public-key based encryption, which will enable the resultant keys to be used to encrypt the data.
Some recent QKD history:
- BT and Toshiba have been conducting QKD trials since 2013, including a recent collaboration to provide a point-to-point QKD link in Bristol between the National Composites Centre and the Centre for Modelling & Simulation.
- In April 2020, Leo Lehman wrote an article about New ITU-T SG13 Recommendations related to IMT 2020 and Quantum Key Distribution.
- In September 2020, Verizon said it was trialing QKD for encryption over Fiber Optic Links.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….Quotes:
Howard Watson, CTO, BT stated: “Quantum-enabled technologies are expected to have a profound impact on how society and business operates in the future, but they are remarkably complex to understand, develop and build: in particular, ensuring that the end-to-end service designs meet the stringent security requirements of the market. I’m incredibly proud that BT and Toshiba have successfully united to deliver this unique network, and with EY as our first trial customer, we are paving the way for further commercial explorations for quantum technologies and their use in commercial, and societal applications in the future.”
Shunsuke Okada, Corporate Senior Vice President and Chief Digital Officer of Toshiba commented: “Both Toshiba and BT have demonstrated world-class technology development and leadership through decades of innovation and operation. Combining BT’s leadership in networks technologies and Toshiba’s leadership in quantum technologies has brought this network to life, allowing businesses across London to benefit from quantum secured communications for the first time.”
Preparation, technical deployment and testing for the network commenced in late 2021. This included equipment deployment in racks, adding security systems and resilience testing, and finally running and optimising the network. While Tuesday 26th April marked the official launch of the network, it has been running since early April, and will operate for an initial period of up to three years.
Praveen Shankar, EY UK & Ireland Managing Partner for Technology, Media and Telecoms (TMT), commented: “Quantum technology creates new and significant opportunities for business, but presents potential risks. Quantum secure data transmission represents the next major leap forward in protecting data, an essential component of doing business in a digital economy. Our work with two of the world’s leading technology innovators will allow us to demonstrate the power of quantum to both EY and our clients.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The UK Government’s “strategic intent” to develop a quantum-enabled economy was first published in 2020. It sets out a vision for the next 10 years in which quantum technologies will become an integral part of the UK’s digital backbone, unlock innovation to drive growth and help build a thriving and resilient economy, and contribute significant value to the UK’s prosperity and security.
The London network represents an important step to building a national network for quantum secured communications, which will stimulate the growth of a quantum ready economy in the UK.
Howard Watson continued: “This is a significant moment in the UK’s journey towards a quantum-enabled economy, but we’re not there yet. Further investment commitments will be required to broaden the study of quantum technologies that will contribute to this new economy, including quantum computing, quantum cryptography and quantum communications. We look forward to working with our government and industry partners to continue the momentum BT has started and shaping the UK’s quantum strategy.”
The technical collaboration for this network was conducted in BT’s Adastral Park labs in Suffolk, UK, and the Quantum technology Business Division of Toshiba, based in Tokyo, Japan and Cambridge, UK, where the quantum key distribution technology has been developed and is manufactured.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.global.toshiba/ww/news/corporate/2022/04/news-20220427-01.html
Verizon Trials Quantum Key Distribution for Encryption over Fiber Optic Links
New ITU-T SG13 Recommendations related to IMT 2020 and Quantum Key Distribution
Deutsche Telekom’s T-Labs enters research partnership to progress quantum technologies
Deutsche Telekom said it is taking part in the Platform and Ecosystem for Quantum-Assisted Artificial Intelligence project to conduct research into quantum technologies, under the leadership of research and development unit T-Labs. Deutsche Telekom will carry out research activities and tests for potential use cases of quantum technologies, particularly for network operators. A consortium of 15 partners and 33 associated partners are taking part the research projects, funded by the German Federal Ministry of the Economy.
T-Labs will provide specific use cases from the field of telecommunications, including the optimization of communication networks, Industry 4.0 applications or AI-clustering problems for customer segments. Quantum algorithms can provides solutions to the complexity and size of applications. Quantum computers could be used for Deutsche Telekom’s operational business.

Quantum algorithms for telecommunication providers
Quantum computers promise an exponential increase in processing speed for selected problem classes. For example, in combinatorial optimization problems or the training of AI models (AI: artificial intelligence). In communication science, Shor’s algorithm is usually considered the “killer application” of quantum computing. This is because quantum computers can use it to attack today’s security infrastructures.
In the PlanQK project, T-Labs provides some specific use cases from the field of telecommunications. These include the optimization of communication networks, Industry 4.0 applications or AI-clustering problems for customer segments. These applications have a high level of complexity and, if the problem exceeds a critical size, can only be calculated classically with great difficulty. Here, quantum algorithms promise the solution. With growing size, quality and processing speed, quantum computers could find their way into Telekom’s operational business.
The path to a standardized quantum app store
However, the goal is not only to evaluate and demonstrate the applicability of current quantum technology for use at Telekom. The PlanQK project also seeks to prevent the risk of any one company achieving a dominant market position and setting de facto industry standards. This project is targeted at ensuring the development and establishment of a vendor-independent platform and associated ecosystem for quantum-assisted artificial intelligence. Users could then, for example, compile solutions for their company or commission them via the cloud or a quantum app store.
About Deutsche Telekom: Deutsche Telekom at a glance
About T-Systems: T-Systems company profile
References:
New ITU-T SG13 Recommendations related to IMT 2020 and Quantum Key Distribution


