SON
SNS Telecom & IT: Open RAN Intelligent Controller, xApps & rApps to reach $600 Million by 2025
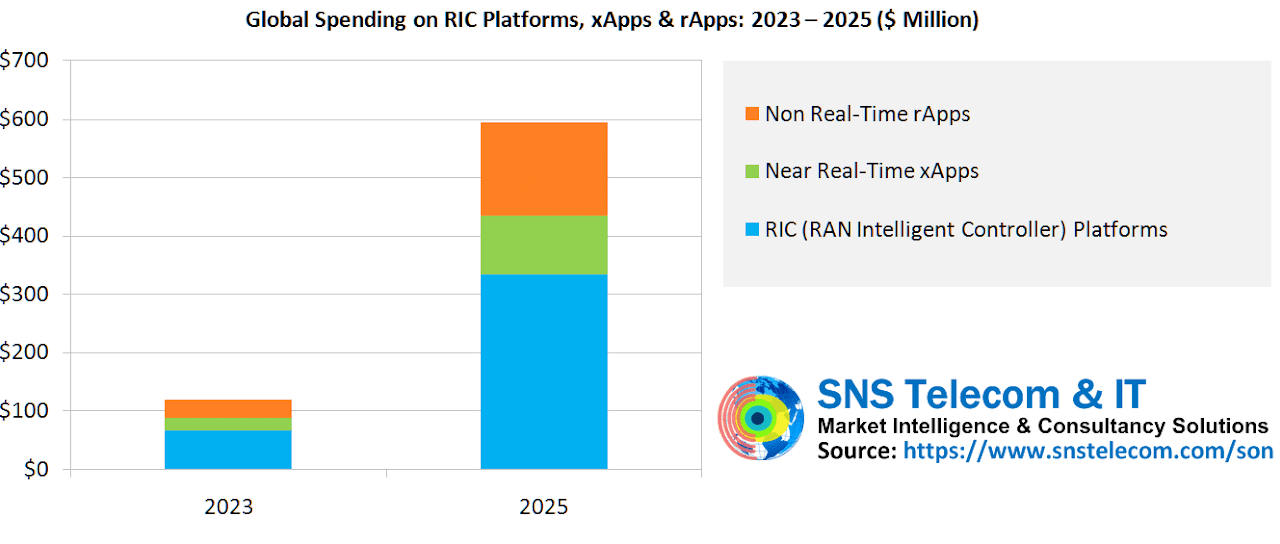
Global spending on Open RAN compliant RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) platforms, xApps and rApps will reach nearly $600 Million by the end of 2025, according to a new report by SNS Telecom & IT. The market research and consulting firm estimates that global spending on RIC platforms, xApps and rApps will reach $120 Million in 2023 as initial implementations move from field trials to production-grade deployments. With commercial maturity, the submarket is further expected to quintuple to nearly $600 Million by the end of 2025.
Annual investments in the wider SON (Self-Organizing Network) [1.] market – which includes licensing of embedded D-SON features, third party C-SON functions and associated OSS platforms, in-house SON capabilities internally developed by mobile operators, and SON-related professional services across the RAN, mobile core and transport domains – are expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 7% during the same period.
Note 1. SONs (Self-Organizing Networks) are radio access networks (RANs) that automatically plan, configure, manage, optimize, and heal themselves. SONs can offer automated functions such as self-configuration, self-optimization, self-healing, and self-protection.technology minimizes the lifecycle cost of running a mobile network by eliminating manual configuration of network elements at the time of deployment right through to dynamic optimization and troubleshooting during operation. Besides improving network performance and customer experience, SON can significantly reduce the cost of mobile operator services, improving the OpEx-to-revenue ratio and deferring avoidable CapEx. SONs strive to make complicated network administration a thing of the past by enabling the creation of a plug-and-play environment for both simple and complex network tasks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- AT&T is among the first mobile operators to invest in the development of Open RAN-aligned RIC functionality and associated applications – particularly xApps for real-time RAN control and optimization. Since 2019, the operator has been collaborating with Nokia and other partners to co-develop an RIC software platform and identify xApp use cases, in alignment with the O-RAN Alliance architecture, to enable RAN programmability for easy integration of new services, as well as AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning)-driven algorithms for automated optimization. At present, the mobile operator is trialing interference management, traffic steering and energy savings-related xApps across a 200-cell site cluster in New Jersey.
- As a precursor to rApp capabilities, rival operator Verizon has deployed Qualcomm’s RAN automation platform that uses AI/ML-driven algorithms to automate the optimization of new 5G NR cell sites and simplify the development of custom SON applications for its wireless network.
- New entrant DISH Network Corporation is trialing VMware’s RIC as the platform on top of which RAN applications will run. Through the trial, DISH will specifically evaluate VMware’s RIC on its ability to create custom solutions from a vibrant ecosystem of xApps and rApps, use RAN programmability and intelligence for network automation, and enhance security to monitor and protect RAN traffic at the point it enters the network.
Europe
- In Europe, Vodafone is actively investing in RIC applications within the framework of its wider Open RAN initiative. The mobile operator group – in collaboration with Cohere Technologies, VMware, Capgemini Engineering, Intel Corporation and TIP (Telecom Infra Project) – has successfully completed a multi-vendor PoC (Proof-of-Concept) trial, which demonstrated a two-fold increase in the capacity of a 5G NR cell site using a programmable, AI-based RIC platform supporting a mix of Open RAN components from multiple vendors. As part of the trial, Vodafone used Cohere’s Spectrum Multiplier xApp running on VMware’s distributed RIC to enable more efficient use of spectrum through a novel MU-MIMO (Multi-User MIMO) scheduler.
- In addition, Vodafone is collaborating with Juniper Networks and Parallel Wireless to carry out a multi-vendor RIC trial for tenant-aware admission control use cases using Open RAN standards-compliant interfaces. The trial is initially running in Vodafone’s test labs in Türkiye with plans to move into the mobile operator group’s test infrastructure.
- DT (Deutsche Telekom) is hosting the SD-RAN outdoor field trial in Berlin, Germany, that integrates the ONF’s (Open Networking Foundation) near real-time RIC and end-to-end 5G platform with Open RAN components from various vendors, including xApps for controlling RUs (Radio Units), DUs (Distributed Units) and CUs (Central Units). As part of a separate effort, DT has been collaborating with VMware and Intel Corporation to develop, test and validate an open-standards compliant intelligent vRAN solution, which also features an RIC element.
- Telefónica’s German business unit has connected a Nokia-supplied RIC to a mobile communications cluster – initially spanning 11 RAN nodes supporting 5G NR, LTE and 2G coverage in Berlin’s Hellersdorf district – within its live commercial network. In the initial “learning” phase of operation, the RIC will continuously analyze network data to detect unusual behavior of radio cells. In the second phase, the near-real-time RIC will take AI-driven decisions to dynamically balance the load of the radio cells, selecting optimum parameters from the network data obtained and continuously adjust them in near real-time. Since 2021, Telefónica has also been collaborating with NEC Corporation in validating and implementing cutting-edge Open RAN technologies and various use cases at its lab in Madrid, Spain, including AI-driven RIC applications for RAN optimization.
- BT Group is trialing Nokia’s Open RAN standards-compliant RIC platform across a number of sites in the city of Hull (East Riding of Yorkshire, England), United Kingdom, to optimize network performance for customers of the EE mobile network. French telecommunications giant Orange is also evaluating Open RAN standards-compliant RIC, xApps and rApps provided by various suppliers.
- In Asia, Japan’s Rakuten Mobile is embedding Juniper Networks’ RIC solution into its operating platform to support RAN automation and optimization-related applications.
- NTT DoCoMo is collaborating with NEC Corporation and NEC’s subsidiary Netcracker to jointly develop a RIC platform aimed at improving performance, enhancing customer experience, reducing power consumption and minimizing operational costs.
- Rival Japanese mobile operator KDDI has been collaborating with Samsung to trial various E2E (End-to-End) network slicing-related use cases with an RIC platform in Tokyo, Japan.
- China Mobile has also been working with multiple equipment vendors and third-party suppliers to develop and implement Open RAN standards-compliant RIC, xApps and rApps. Among other engagements, the mobile operator has collaborated with Nokia to carry out a field trial of an AI-powered RAN over its live commercial LTE and 5G NR network infrastructure. Specifically, the trial evaluated AI-based UE traffic prediction in Shanghai and an ML-enabled network anomaly detection solution across more than 10,000 4G/5G cells in Taiyuan.
The “SON (Self-Organizing Networks) in the 5G & Open RAN Era: 2022 – 2030 – Opportunities, Challenges, Strategies & Forecasts” report presents a detailed assessment of the SON market, including the value chain, market drivers, barriers to uptake, enabling technologies, functional areas, use cases, key trends, future roadmap, standardization, case studies, ecosystem player profiles and strategies. The report also provides global and regional market size forecasts for both SON and conventional mobile network optimization from 2022 till 2030, including submarket projections for three network segments, six SON architecture categories, four access technologies and five regional submarkets.
The report comes with an associated Excel datasheet suite covering quantitative data from all numeric forecasts presented in the report.
The report will be of value to current and future potential investors into the SON and wider mobile network optimization market, as well as SON-x/rApp specialists, OSS and RIC platform providers, wireless network infrastructure suppliers, mobile operators and other ecosystem players who wish to broaden their knowledge of the ecosystem.
For further information concerning the SNS Telecom & IT publication “SON (Self-Organizing Networks) in the 5G & Open RAN Era: 2022 – 2030 – Opportunities, Challenges, Strategies & Forecasts” please visit: https://www.snstelecom.
For a sample of the report please contact: [email protected]
About SNS Telecom & IT:
Part of the SNS Worldwide group, SNS Telecom & IT is a global market intelligence and consulting firm with a primary focus on the telecommunications and information technology industries. Developed by in-house subject matter experts, our market intelligence and research reports provide unique insights on both established and emerging technologies. Our areas of coverage include but are not limited to 5G, LTE, Open RAN, private cellular networks, IoT (Internet of Things), critical communications, big data, smart cities, smart homes, consumer electronics, wearable technologies, and vertical applications.
References:
https://www.snstelecom.com/ric-xrapps
https://www.celona.io/network-architecture/self-organizing-network
SNS Telecom & IT: Shared Spectrum to Boost 5G NR & LTE Small Cell RAN Market
SNS Telecom & IT: Spending on Unlicensed LTE & 5G NR RAN infrastructure at $1.3 Billion by 2023
SNS Telecom: U.S. Network Operators will reap $1B from fixed wireless by late 2019
Facebook to test 5G small cell network with SON features; Combine 5G access with Terragraph wireless backhaul?
The FCC today approved Facebook’s application to test a 5G small cell network across a wide range of mid-band spectrum bands (see below) at its Menlo Park, California headquarters.
Facebook told the FCC in its application:
The experiment involves short-term testing of a 5G over-the-air setup for an outdoor demonstration that is not likely to last more than six months, making an STA (Special Temporary Authority) more appropriate than a conventional experimental license.
The purpose of operation is to demonstrate the self-organizing network (“SON”) features in a 5G over-the-air setup operating in a small cell configuration. Lab testing does not allow feature realization. The outdoor test setup aims at validating the improvements done to 5G cellular networks.
The improvements involve:
(1) Load balancing between the cells in an attempt to optimize the resource utilization, reduce call drops, and create a better user experience by means of improved quality of service; and
(2) Run time selection and updates of the 5G cell physical layer cell identifiers (“PCIs”) to avoid conflict between neighboring cells, thereby avoiding UE drops and reducing network signaling traffic.
The frequency bands to be used are: 2.496-2.690 GHz, 3.3-3.6 GHz, 3.7-3.8 GHz, and 4.8-4.9GHz. A directional antenna will be used to beam the 5G signals.
Facebook did not name the network equipment suppliers for this test nor did they state why they needed to perform these tests. The only hint given was to test “self-organizing network (“SON”) features in a 5G over-the-air setup operating in a small cell configuration.”
One could speculate that Facebook might want to deploy a private 5G network across its sprawling Menlo Park campus. Or they might want to provide 5G access to municipalities using mid-band spectrum.
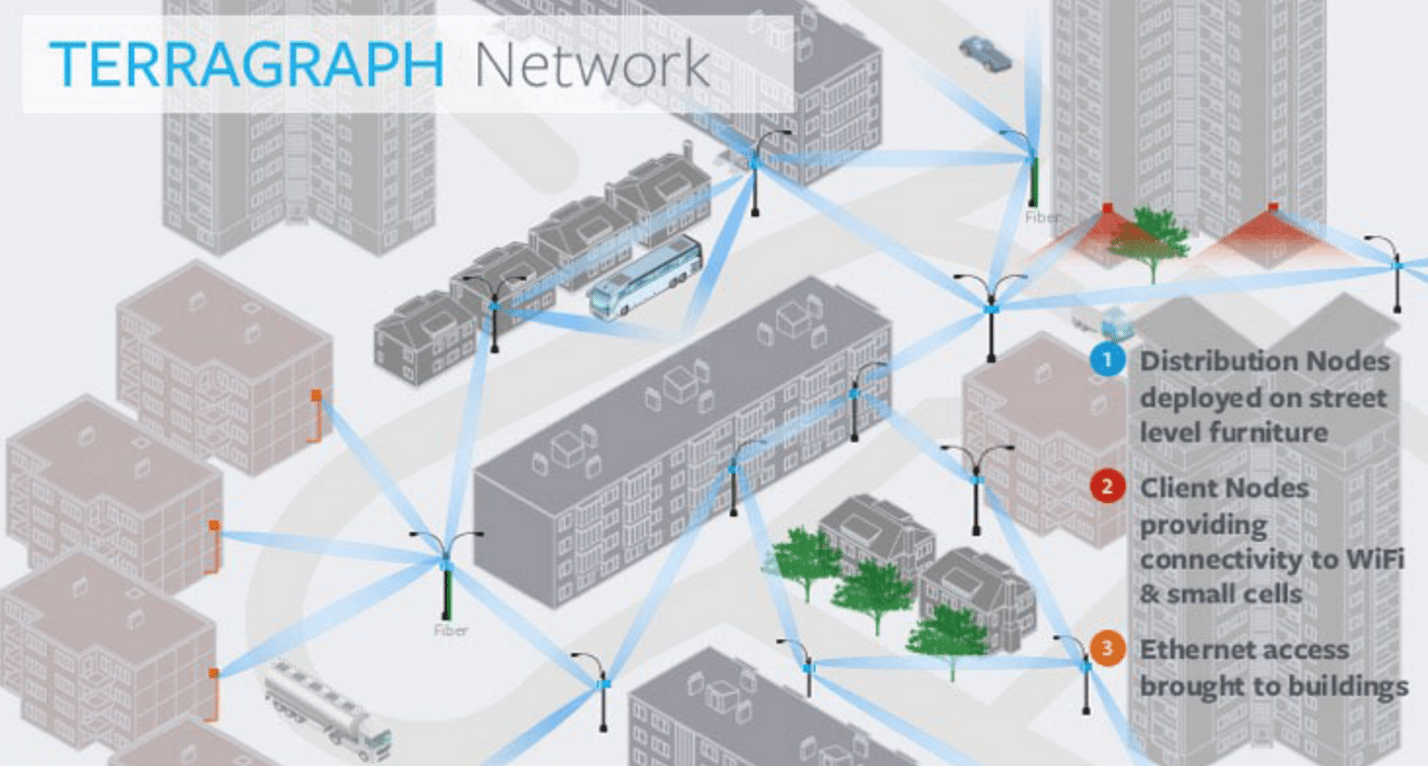
The company does have some recent experience designing and deploying millimeter wave wireless distribution networks (based on Terragraph) which could be combined with a 5G access network.
- Facebook’s Terragraph wireless backhaul technology is being used by Cambium Networks in their 60 GHz cnWave solution. Terragraph is a high-bandwidth, low-cost wireless solution to connect cities. Rapidly deployed on street poles or rooftops to create a mmWave wireless distribution network, Terragraph is capable of delivering fiber-like connectivity at a lower cost than fiber, making it ideally suited for applications such as fixed wireless access and Wi-Fi backhaul.
- In June 2018, Magyar Telekom, subsidiary of Deutsche Telekom, deployed their first Terragraph network in Mikebuda, Hungary. Terragraph improved local network speeds from 5M bps to 650M bps.
- Common Networks, a California based Internet Service Provider, deployed a Terragraph network to serve customers in Alameda, CA. Local businesses and customers of Common Networks saw an immediate improvement in internet speeds. Common Networks presented their approach at a 2018 IEEE ComSoc SCV technical meeting in Santa Clara, CA.
References:
https://apps.fcc.gov/oetcf/els/reports/STA_Print.cfm?mode=current&application_seq=106515
https://apps.fcc.gov/oetcf/els/reports/GetApplicationInfo.cfm?id_file_num=0482-EX-ST-2021
https://connectivity.fb.com/terragraph/
Facebook’s Terragraph gains momentum with operator, vendor buy-in