Telecom in China
China’s big 3 mobile operators have 9 Million 5G subscribers in advance of the service; Barron’s: China to lead in 5G deployments
According to Beijing News, the three major (state owned) China mobile network operators have already signed up 9 million advance orders for their yet to be launched 5G service. As of October 5th, China Mobile’s 5G subscribers have reached 5.32 million, China Unicom has 1.75 million, China Telecom has 1.76 million, and the total number of committed 5G users is nearly 9 million.
The three China network operators haven’t set a date for the start of service, but will reportedly commence simultaneously, most likely later this month of October. However, there are not many 5G smartphones (only two or three models) and no other endpoints (none announced yet) available from the three major China network operators. The preferential price is between 150 yuan and 550 yuan.
On September 20, Xu Ximing, deputy general manager of the marketing department of China Mobile Group Corporation, said at the China Mobile 5G+ Innovation Cooperation Conference that China Mobile is accelerating the pace of 5G commercialization. The 5G package will be officially released in October, including basic packages and CPE packages. And upgrade plans for old users. Customers will enjoy the “three different fast” login to the 5G network, that is, the 5G terminal does not need to change the card, does not need to change the number, does not need to register, and multi-channel fast order 5G network service.
- The China Unicom prices web page shows that the current campaign supports two mobile phones, Samsung Note 10+5G version offers 500 yuan, and vivo’s iQOO Pro 5G version offers 400 yuan. Telecom’s purchase discounts are 150 yuan for iQOO Pro, 300 yuan for ZTE Axon 10 Pro, and 550 yuan for Samsung Note 10+.
- For China Mobile’s preferential prices, Xiaomi 9 Pro 5G version is offered for 300 yuan, China Mobile’s pioneer X1, Samsung Note 10+ 5G version offer is 500 yuan. China Mobile told the Beijing News that more 5G models will be added in the future.

China Mobile Pioneer X1 is powered by a Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 chipset, a 6.47-inch AMOLED display with a waterdrop notch. The display supports FHD+ resolution and also houses an on-screen fingerprint scanner. Housed inside the waterdrop notch is a powerful 20MP camera.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note: Although Samsung continues phone sales in China, last week the handset maker ceased its mobile phone production operations in China as it closed its last factory in the country, according to Reuters.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China’s 5G network coverage is progressing rapidly and the 5G network is increasingly equipped with a formal commercial foundation. Recently, the official statistics of the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Economics and Information Technology state that the three major network operators have completed more than 8,800 5G base stations in Beijing, covering areas along Chang’an Avenue, the World Expo, CCTV Broadcasting Center, and Shougang Park.
According to a message released by the Beijing Communications Administration, it is expected that by the end of 2019, Beijing will build more than 10,000 5G base stations. According to the current construction progress, the number of 5G base stations in Beijing is expected to reach 12,000 by the end of the year. Among the other three first-tier cities, Shanghai plans to build 10,000 5G base stations in 2019 and 20,000 5G base stations in 2020; Guangzhou proposes to complete no less than 20,000 5G base stations in 2019, and 5G will be built in 2021. The base station is 65,000; the plan for Shenzhen is to build 15,000 5G base stations by the end of 2019.
With the spread of 5G networks, innovative applications in various 5G environments are emerging and even landing. On September 25, Daxing International Airport was officially opened. Eastern Airlines, Beijing Unicom and Huawei jointly released a 5G-based smart travel integrated service system at Daxing International Airport. Under the system, the user does not need to present the ID card and the QR code as usual, and only needs face recognition to complete the travel process such as ticket purchase, check-in, check-in, security check, and boarding.
China’s government is partially subsidizing 5G deployments as we note in several paragraphs below:
- The Shenzhen city government is offering to pay operators RMB10,000 ($1,398) for every standalone 5G base station deployed, with a maximum payout of RMB150 million ($20.9 million). Its 5G plan issued last month promises support for site acquisition and subsidies for base station electricity costs. The tech-dominated Chinese city, home to Huawei, ZTE and Tencent, plans to install 15,000 5G base stations by the end of 2019 and 45,000 by next August (more on this below).
- Almost every Chinese city or provincial government has a 5G development plan. While many are light on specifics, some reveal big ambitions. For example, the government of Zhejiang, the wealthy province near Shanghai, expects to have 30,000 base stations next year. It plans to complete its 5G rollout by 2022, by which time its coverage will “lead the country.”
- The north-west province of Shanxi — not known for its advanced tech industries — has also made 5G a top priority. It has bench marked its 5G rollout against other provinces and, like Zhejiang, has set a target of 30,000 base stations by 2022. And the city is also offering subsidies for base station power costs and help in site selection.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From an article titled, “The Real 5G Winner Could Be China,” in the October 7, 2019 print edition of Barron’s:
Multiple Wall Street analysts are getting more optimistic about China’s 5G build out. For instance, Rosenblatt Securities notes that local governments in the Asian country are providing subsidies to “speed up 5G network deployments.” As a result, Rosenblatt says, more than 300 cities in China will have 5G networks by the end of next year. Even Hall, the Goldman Sachs 5G skeptic, expects 120 million 5G smartphones to ship next year, largely because of China’s aggressive build out.
In a report this past week, Piper Jaffray analyst Harsh Kumar cited a Chinese think tank that sees China-based companies spending $411 billion on 5G networks from 2020 to 2030. Of the 600,000 5G base stations expected to be rolled out worldwide next year, Kumar says half will be deployed in China: “We expect 2020 global [5G] deployments to largely be driven by the Chinese market.”
5G may come together slowly in the U.S. market, but China is serious about winning the race.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://tech.sina.com.cn/t/2019-10-06/doc-iicezzrr0343842.shtml
https://www.lightreading.com/asia-pacific/china-telcos-rack-up-9m-5g-advance-subs/d/d-id/754643?
https://www.barrons.com/articles/the-real-5g-winner-could-be-china-51570228459
https://www.wsj.com/articles/in-the-race-to-dominate-5g-china-has-an-edge-11567828888
Conflicting reports: Huawei and China Mobile may buy Brazil carrier Oi
The O Globo website reported on Saturday that Huawei is joining forces with China Mobile to buy struggling Brazilian carrier Oi, in an attempt to boost their footprint in Latin America’s largest market. The two Chinese companies anticipate a significant growth in business once Brazil starts deploying its 5G network. Oi’s 360,000 kilometers of fiber infrastructure is seen as an attractive asset.
Oi declined to comment on the matter, while Huawei and China Mobile did not immediately respond to Reuters’ requests for comment.
However, on Sunday Huawei told Reuters it was not interested in acquiring struggling Oi or any other Brazilian carrier.
“Huawei has no plan or interest in acquiring Oi or any other Brazilian carrier. In Brazil for more than 20 years, the company is working with all major Brazilian carriers supplying the best products and solutions to support digital transformation in Brazil,” the company said in an emailed statement to Reuters.
It would be very strange for Huawei to invest in a telecom carrier which is traditionally its bread and butter customer!
Brazil’s largest fixed-line carrier has been struggling to turnaround its business since it filed for bankruptcy protection in June 2016 to restructure approximately 65 billion reais of debt. Oi is also negotiating its network with Spain’s Telefonica and Telecom Italia, AT&T and another (unnamed) Chinese company.
Speculation of the bid comes as Brazil’s Senate approved a bill to update the country’s obsolete framework for telecommunications, paving the way for Oi to implement a plan to sell up to $2 billion in non-core assets. Earlier this week, Suno Notícias reported that China Mobile has filed a request to operate in Brazil and eventually acquire Oi. The country’s telecom regulatory agency Anatel said Sept. 17th it didn’t have any official information regarding the request.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum: Huawei launches new ‘Vision TV’ with 4K quantum dot color, which comes in 55″/65″/75″ sizes. Media paying attention to the fact that Huawei is adopting QD technology, which until now has been a key technology for Samsung’s TV (QLED) strategy. (ZDNet)
http://www.zdnet.co.kr/view/?no=20190920082939
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
China Wireless Carriers Consider 5G Partnership Amidst 5G Budget Constraints in 2019
Chinese mobile operators may be soon working together to build 5G networks in order to limit the costs, the Nikkei Asian Review reports. And why not- all three are state owned!
China’s second- and third-ranked mobile carriers, China Telecom and China Unicom area already close to an agreement. Number one China Mobile hasn’t commented yet. Please see China Mobile chairman’s statement in the last paragraph below.
China Telecom Chairman and CEO Ke Ruiwen said that his company is in “deep consideration” to jointly build a 5G network with China Unicom. He confirmed that top management on both sides have already reached a “high level of consensus” on the matter and “substantial progress” has been made toward a final deal.
“Co-building and co-sharing would bring great savings in capital expenditure, operating expenditure, as well as improve resource utilization,” Ke said, without revealing any numbers that might quantify the cost savings.
The 5G partnership was hinted at by China Unicom Chairman and CEO Wang Xiaochu earlier. During the company’s first-half earnings briefing, Wang floated the idea of a “co-built, co-shared” 5G infrastructure. Wang left the door open to cooperating with China Mobile and China Broadcasting Network, which were granted 5G licenses in June, but said China Unicom was “mutually complementary” with China Telecom, noting their strengths in different regions of the country.

The Chinese government hopes that developing a 5G network will help buoy the economy, but the three major mobile carriers are concerned about expenses and profits. © AP ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China Telecom’s Ke also mentioned these advantages at the operator’s first-half results presentation. Although Ke dodged questions from reporters in Hong Kong about the savings on investment and when an official agreement would be signed, he confirmed that top management on both sides have already reached a “high level of consensus” on the matter and “substantial progress” has been made toward a final deal.
Both mobile carriers are limiting their 5G investment budgets this year. China Telecom is keeping its budget unchanged from the beginning of the year at 9 billion yuan ($1.27 billion), while China Unicom is holding within the previously committed range of 8 billion yuan.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The chief uncertainty about such a 5G mobile carrier partnership is about exactly what facilities the operators would share? Making use of the same cell towers, poles and other “passive” infrastructure would be no great leap. Through China Tower-a jointly owned telecom infrastructure business- all three mobile network operators have already pooled mobile towers to reduce costs.
China Tower is a joint venture of the three major Chinese mobile carriers. Chairman Tong Jilu told reporters on Aug. 7 that the cell-tower builder has not changed its annual capital expenditure budget of 30 billion yuan since the beginning of the year. Tong stressed that his company’s investment “is up to the telecom operators,” adding the annual investment “would not likely exceed the budget.”
China Tower said earlier this month that it had received client demands to install 65,000 5G base stations to date, a number that it expects to rise to 100,000 by the end of the year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
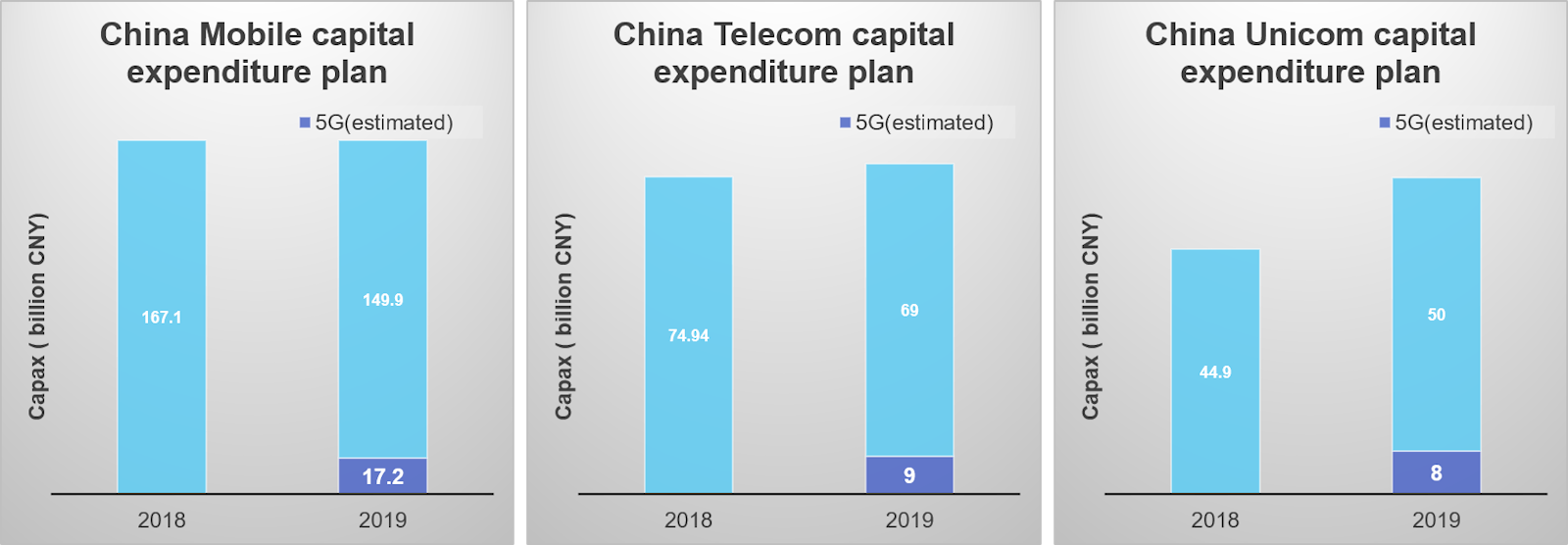
Market leader China Mobile has pledged to allocate CNY 24 billion to 5G this year, above the CNY 17 billion suggested in March. Chairman Yang Jie said that its total capital expenditure for 2019 will be under CNY 166 billion, below last year’s CNY 167.1 billion. The company’s 5G investment this year is much smaller than the 38.7 billion yuan reported by Chinese media when 5G licenses were granted in early June. The government aims to spur job creation and support embattled equipment suppliers like Huawei and ZTE as the trade conflict with the U.S. drags on, but the carriers seem to have their own agenda.
Despite the government’s push for swift deployment of a network, Yang said “the peak period of 5G investment will be between 2020 and 2022.” This author completing agrees with that comment with the real investment not starting till 2021 after IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT standard has been completed by ITU-R.
………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/china-telecom-unicom-consider-5g-network-partnership–1305741
https://www.lightreading.com/mobile/5g/chinas-5g-market-has-teething-trouble/d/d-id/753657
IDTechEx: China’s 5G investments may be slowing, but it’s still the 5G market to watch
China is certain to be one of the world’s largest 5G markets and has been spending heavily to gain an early lead in 5G adoption, yet there are signs that 5G momentum is slowing down in the market. That was one of the conclusions of a new report from IDTechEx Research on the 5G technology market forecast for the next 10 years.
The report found that China’s big three operators China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom have all announced 5G capex budgets that are lower than expected.
China Unicom plans to spend between 6 billion yuan ($893.3 million) and 8 billion yuan on 5G in 2019, while China Telecom has allocated 9 billion yuan. While market leader China Mobile has not disclosed its projected 5G spending, the report forecasts that its spending will be in the region of 17 billion yuan. The total 5G capex budget allocated in China (34 billion yuan) for 2019 is therefore significantly lower than the projected 50 billion to 100 billion yuan.
Factors behind the lower than expected spending include: greater activity to upgrade 3G networks to 4G, falling per-subscriber revenue and the uncertainty over whether 5G investments will generate returns, the market research firm said. The CEO from Huawei, the top one telecom infrastructure supplier and number two smartphone provider in the world, has publicly expressed a similar concern on the payback from 5G.
Based on slower than expected 5G deployment schedules, the total contribution of 5G for the telecoms sector could be reduced from the projected $200 billion by 2029 to $160 billion. Network operators are forecast to invest around $200 billion to $350 billion for 5G development from 2020 to 2030.
Source: IDTechEx Research
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
IDTechEx Research predicts that by 2030 the direct 5G revenue in China will be 6.3 trillion CNY (about $930 bn) and the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) in the coming ten years will be 29%. 5G will create 8 million jobs and contribute around 5.8% GDP growth in China by 2030. The indirect revenue generated by 5G will be 10.6 trillion CNY (about $1,579 bn), with CAGR of 24%. Among them, the direct revenue for telecoms will be over $200 bn by 2029.
As the current 5G deployment plan is slower than expected, these numbers might be overestimated. The new IDTechEx Research report 5G Technology, Market and Forecast 2019-2029 forecasts a moderated revenue of $160 bn for telecoms in China by 2029. Nonetheless, China is still the main market to watch. It is likely that the telecoms in China will invest at least $200-350 bn from 2020-2030 for 5G development, with the key focus on automotive, industry, healthcare and energy.
References:
https://www.idtechex.com/research/articles/is-5g-slowing-down-in-china-00016958.asp
More information can be found from 5G Technology, Market and Forecast 2019-2029 – contact [email protected] or visit www.IDTechEx.com/5g.
China Broadcasting Network Corp. to launch mobile network; already provides cable TV, Internet and Telecom services in China
As China state-owned telecom carriers (Unicom, China Mobile, China Telecom) prepeare for launch of 5G services, Beijing is supporting the creation of a new full-service telco by upgrading the nation’s cable network giant, China Broadcasting Network Corp. This is evident from the flurry of initiatives from the state-owned cable TV network operator to enhance its infrastructure and emerge as a stronger entity that can join the Big Three telecom firms in their own game.
Last month, China Broadcasting, an entity set up to run the nation’s cable TV system before being awarded, in 2016, a license to operate internet and telecom services, announced strategic partnerships with CITIC Group and Alibaba Group to help speed up efforts for network upgrades.
Under the cooperation agreements, China Broadcasting, which was founded by what is currently known as the National Radio and Television Administration (NRTA), will receive assistance from CITIC and Alibaba “for integrated development and upgrading of the nation’s cable TV networks as well as related product development and management,” state news agency Xinhua reported.
China aims to make its national cable TV networks smarter and create new generation radio and TV technology infrastructure by integrating cable TV networks and letting 4K, 5G, IPv6, big data, artificial intelligence and quantum communications technologies play their roles, Nie Chenxi, the head of the NRTA, said at the signing ceremony.
China Broadcasting’s plans comes as the traditional cable TV business faces a tough challenge in the era of internet TV and streaming services, throwing up the need for operators to upgrade themselves and expand their services via two-way interactive high speed broadband infrastructure.
Currently, telecom operators like China Telecom and China Mobile are offering fiber-to-the-home or fiber-to-the-building broadband networks to provide dedicated bandwidth for each broadband line, while cable network can only adopt a share-bandwidth approach. That has made it difficult for cable networks to compete with the fiber broadband operators.
China has seen cable TV subscribers falling in number after hitting a peak in 2016. Last year, subscribers were estimated at 223 million, down 8.75 percent from a year ago. The industry has seen its profitability get constrained and profit margins decline amid the weak subscriber figures. Meanwhile, IPTV and OTT video platforms had around 150 million users in 2018.
As the industry gets reshaped, CITIC is emerging as a key player in the reform of China’s cable network. The group, as a matter of fact, is not new to telecom network deployment. It owns CITIC Guoan network in Beijing, which is expanding its cable network operation across the nation. The conglomerate is also exploring new business models by teaming up with local cable operators to operate smart community service platforms for citizens.
Such experience puts CITIC in a good position to help integrate China’s state-owned nationwide cable network into a single valuable backbone network to deliver high definition content to TV as well as mobile devices.
CITIC Group can also help ease the financial burden of the government on network capital expenditure. Though there isn’t an equity deal, CITIC’s partnership with China Broadcasting can help the latter catch up with the three big state-owned telecom carriers through a market-driven approach.
In November last year, mainland media quoted Chinese authorities as saying that they have allowed China Broadcasting to build 5G networks, a move that will allow the market to transform into a four-player battleground. China Daily cited sources close to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology as saying that China Broadcasting, which was formed in 2014 by combining several regional cable TV operators, was officially applying for a 5G license. That will help boost competition in the industry that has long been dominated by three players — China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom.
In China, traditional cable TV service has been facing keen competition from online media services such as IPTV, OTT video as well as Internet video. Telecom operators are using fiber broadband to provide IPTV services to their broadband users, while OTT players like Youku and Tencent also dominate the screen time of Chinese users.
Amid this situation, cable TV network operators need to invest not only on the content but also the network technology to provide triple or even quad play in the market to catch up with the telecom carriers.
China Broadcasting is preparing to launch a mobile network using the 700MHz spectrum band. The spectrum is currently being used for domestic analogue television broadcasting. Now, China Broadcasting and CITIC have formed a joint venture, China Broadcasting Network Mobile, to operate a mobile business on 700Mhz band. The joint venture is expected to receive a mobile license from the Chinese government so that they can build a network across the nation to challenge the dominance of the Big Three operators.
As the low-band 700MHz spectrum can have better network coverage compared with other frequency bands, the joint venture will be in a good position to provide better coverage for high speed mobile internet using 5G technology. Once the 5G war kicks off, apart from China Broadcasting, CITIC Group could also effectively become a major player in the China telecom market.
References:
http://www.ejinsight.com/20190409-china-cable-network-reform-what-it-means-for-telecom-industry/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telecommunications_industry_in_China
http://english.cctv.com/2016/05/06/VIDElPgPCFpnb3m4hk1XC3Gq160506.shtml


