Telecom in China
Huawei’s “resilient” Q1-2020 results and coronavirus commentary
Undaunted by the U.S. campaign to ban its network equipment and smart phones, Huawei reported results for the first quarter 2020 that were in line with expectations, despite the effects of the coronavirus pandemic. The company said its business is continuing to grow, albeit at a slower pace.
Revenue in the first quarter rose by about 1% to 182.2 billion yuan ($25.72 billion), vemart phones, China tech giant rsus a 39% growth posted a year ago. Its net profit margin over the period narrowed to 7.3% from about 8% a year ago. Huawei being a privately owned company did not disclose its net profits.
“The growth rate has slowed, but this is also a resilient performance in the face of both the entity list and the coronavirus we are facing at this moment,” Vice President Victor Zhang said in a statement on Tuesday.
This represents a significant slowdown from the 19 percent sales growth for 2019. The company earlier stated that 2020 would be a very difficult year, its first full year with U.S. sanctions. Along with the effects of the coronavirus outbreak, 2020 “will be the most difficult year” for Huawei, rotating chairman Eric Xu said.

As for the impact from the coronavirus pandemic, Zhang said it was difficult to gauge what that would be in the short or long term, as he presented the results from London rather than Huawei’s Shenzen base to mark 20 years of business in Europe.
The company provided enlightening comments on the coronavirus in its earlier referenced statement:
Networks are a lifeline for people from all walks of life during this public health crisis, so ensuring normal network operations is of paramount importance. Huawei is doing everything in its capabilities to help carriers ensure stable and secure network operations. Together, we are working to meet the network demand created by social distancing as people switch to telecommuting, distance education, and e-commerce for daily necessities.
Since the outbreak, Huawei and its partners have rapidly launched many 5G- and AI-powered medical applications. We are using our expertise in communications technologies to help fight the pandemic and save more lives. The AI-assisted coronavirus diagnosis solution cuts CT scan review times from 12 minutes down to 2, helping doctors improve their diagnostic efficiency. 5G-enabled remote video consultation helps mitigate shortages of frontline experts and increases the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment of critical patients. AI-powered thermal imaging devices can take temperatures, increasing the efficiency of infection prevention and control in public places. In addition, Huawei has been doing its best to get masks, test kits, and other protective supplies to the countries and organizations that need them.
A seed that survives the storm will sprout and then blossom. Even though it is impossible to know when the tides of this pandemic will turn, we at Huawei believe that this challenge will be overcome by standing together.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In March, Huawei reported financial results for 2019, recording a $12 billion revenue shortfall that it attributed to the entity listing, which effectively blacklisted Huawei and numerous affiliates by restricting sales of certain products from U.S. suppliers to the vendor.
Huawei’s consumer segment was particularly hit by the U.S restrictions in the second half of last year. As one of the world’s largest smartphone makers, Huawei was unable to access Google’s proprietary Android operating system and was forced to launch new devices without access to the popular Google Play store.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/press-events/news/2020/4/huawei-announces-q1-2020-business-results
China Mobile says COVID-19 effected Q1 2020 Results: Loss of 4M 4G subs, 31.7M 5G subs
China Mobile’s first quarter 2020 earnings report was somewhat disappointing, save for 5G. Revenues, earnings and profits all decreased for the first quarter as the world’s largest mobile operator felt the impact of the coronavirus outbreak in China.
The state owned telco lost 4 million customers which is < 1/2% of their customer base in the first quarter. There were 946 million total China Mobile subscribers at the end of March 2020.
Revenues fell 2%, to 181.3 billion Chinese yuan (US$25.6 billion), compared with the year-earlier period, while revenue from telecommunications services was RMB168.9 billion, up by 1.8% over the same period last year. Profit attributable to equity shareholders was RMB23.5 billion ($3.3 billion), down by 0.8% over the same period last year.
The company (referred to as “the Group”) addressed the impact of COVID-19 in their Q1 2020 earnings report:
COVID-19 posed an impact on the overall society and economy in the first quarter of 2020. The Group’s business development was no exception. In light of COVID-19, the Group has introduced “three safeguards” which endeavoured to provide reliable communications, maintain service continuity and step up comprehensive prevention and control measures. Leveraging the demand for informatization services brought about by measures to prevent and control COVID-19 and the resumption of work and production, the Group has also accelerated business transformation and upgrade.
The Group’s total number of mobile customers was around 946 million as at 31 March 2020. Among them, the numbers of 4G customers and 5G package customers were 752 million and 31.72 million, respectively. During the first quarter of the year, data traffic business maintained growth momentum with handset data traffic recording a year-on-year increase of 43.4% and handset data DOU (average handset data traffic per user per month) reaching 8.3GB. Total voice usage declined by 16.3% year on-year to 661.4 billion minutes, which was attributable to OTT substitution and COVID-19.
Buoyed by the rapid growth of corporate SMS, total SMS usage rose by 45.4% year-on-year. Mobile ARPU dropped by 6.7% year-on-year to RMB46.9 for the first quarter of the year and the decline rate has moderated compared to that of the previous year. As at 31 March 2020, the total number of wireline broadband customers was 191 million, with a net increase of 4.10 million for the first quarter of the year. Wireline broadband ARPU amounted to RMB31.3.
Amidst COVID-19, the Group’s telecommunications services revenue grew by 1.8% year on-year to RMB168.9 billion for the first quarter of 2020. Currently, measures to prevent and control COVID-19 are still underway and some impact may carry over.
The Group will continue to foster business transformation and upgrade and make an all-out effort to promote the coordinated development of the CHBN four major markets. It will also continue to optimize its revenue structure and strive to maintain growth in telecommunications services revenue for the full-year of 2020. The Group’s revenue from the sales of products and others went down by 34.9% year-on year to RMB12.4 billion for the first quarter of the year. The decline was mainly caused by contracted sales of handsets and IoT devices, amongst other products, due to COVID-19.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The figures seem to vindicate arguments that China Mobile will prove fairly resilient to COVID-19 as a critical lifeline to the wider world for people under lockdown/ shelter in place orders. While customer numbers fell in mobile, there was no decline at China Mobile’s fixed-line business, which picked up another 4 million broadband customers to finish March with 191 million in total. On the mobile side, usage of traditional voice services fell from 278 minutes per user each month in the final quarter of 2019 to just 234 minutes in the first quarter of 2020. Mobile data usage, though, rose from 7.1 to 8.3 gigabytes per month over the same period.
Largely due to China government incentives, China Mobile now claims nearly 32 million 5G customers, up from just 2.6 million in December 2019. Sustain that rate of growth and the operator would be on course for almost 120 million 5G customers by the end of this year. That may be difficult once China Mobile has attracted all the early 5G adopters. It will be interesting to see how soon the major improvements brought by 3GPP Release 16 (scheduled to be frozen in early July 2020) will be implemented by the Group’s network equipment vendors- principally Huawei and ZTE.

Key Insights From Bloomberg:
- The carrier, which has more than 940 million subscribers, may benefit in the months ahead as economic activity begins to return toward normal. The expansion of 5G coverage planned this year may also help lure subscribers to higher priced heavy-data plans.
- While the company is spending to expand 5G networks, it has also been maintaining dividend levels and had cash and bank deposits of about 317 billion yuan as of the end of last year.
- Attracting 5G subscribers is a key for growth as those users tend to spend more per month. The company had about 31.7 million 5G subscribers as of the end of March.
- While total subscribers fell in the first quarter, the carrier benefited from a slight rise in average revenue per user from the previous quarter as the introduction of 5G networks made it easier for users to play richer video games and use applications that consume more data.
Iian Morris, International Editor at Lightreading wrote in a blog post:
A challenge for the Group is to meet the investments required for 5G infrastructure. China Mobile has earmarked RMB100 billion ($14.1 billion) for capital expenditure on 5G in 2020, an increase of 317% on what it spent in 2019, according to market-research firm Omdia (owned by market research goliath Informa). Its plan is to add at least 250,000 5G base stations by the end of this year.
Meeting this commitment will be difficult as earnings and cash flow are squeezed by COVID-19. Just-published figures show that earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortization fell nearly 6% in the first quarter, to RMB68.5 billion ($9.7 billion), compared with the year-earlier period. Under government pressure to hit deployment targets, China Mobile may look to reduce costs in other parts of the business to offset the increase in spending on 5G. “The group will continue to develop new sources of revenue and identify ways to curtail expenses, while taking measures to reduce costs and enhance efficiency,” it says in its statement.
Hacking into headcount will be difficult if China Mobile is to avoid disruption to 5G buildout and sales and marketing activities. Nevertheless, the operator may be able to realize some cost savings through pruning of a workforce that numbered as many as 456,239 employees at the end of last year. While major US operators have slashed tens of thousands of roles in recent years, China Mobile seems to have been a lot more cautious on the jobs side: Its staff numbers have fallen less than 1% since the end of 2016.
The latest update on 5G will be a further concern for US officials already worried about falling behind China in the development and rollout of the new network technology. With at least 30 million 5G customers, China already has enough users of the service to spur the development of new commercial applications that might not be feasible in the old 4G world. That is exactly what the US does not want to hear.
References:
China’s big 3 telcos offer 5G Rich Communication Services (RCS)
China’s big three telecom carriers unveiled a new 5G-enabled messaging service on Wednesday, which analysts said is likely to open a new era for social networking.
China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom published a white paper for the 5G messaging service, known as Rich Communication Services, or RCS,. The paper specifies technical details to invite smartphone makers to support the new service.
The 5G RCS messaging service is designed to replace current short messages with a system that is richer, provides phonebook polling, and can transmit in-call multimedia.
5G may facilitate a shift away from basic SMS messaging, ushering in an era of RCS, where mobile messaging can become much more interactive and flexible, more akin to what we now know as iMessaging through platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp. RCS will not only facilitate the sharing of GIFs and high-quality videos, but will also more directly interface with the internet; for example, offering a list of available flights when the user sends a message regarding a holiday.
Editor’s Note:
RCS has been talked about and in development for many years, with very little commercial market acceptance to date. RCS’ biggest problem has been that it requires consensus across a large and complex industry. Contrast that with an OTT messaging startup with a dozen staff can create a viral global app overnight. It remains to be see if the collaboration between China’s big three telecom operators will make 5G RCS successful in China.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
With the new 5G RCS message service, consumers won’t have to download a variety of mobile apps. They can directly buy train tickets and book flights by sending messages.
Ma Jihua, an independent telecom analyst, said the new 5G-powered messaging service, if properly promoted, will usher in a new era of social networking, and erode the social networking business of Tencent Holdings Ltd.

A pedestrian walks past a 5G promotion board in Nanjing, capital of Jiangsu province. [Photo by Su Yang/For China Daily]
………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Telecom Vice President Wang Guoquan said the new 5G messaging services would enhance 5G innovation and help turn 5G from “the biggest variable affecting the telecom industry” into the biggest vehicle for growth.
He said China Telecom would work with industry partners “to build a new ecosystem and promote the rapid development of rich media information.”
Besides the three operators, 11 device vendors including Huawei, Xiaomi, Vivo, Oppo and Samsung endorsed the new messaging service and promised early support on their handsets. Huawei stated that it would have an RCS-capable phone this June, while Xiaomi has confirmed that all of its new 5G phones will also run the new messaging service.
“Together with ecosystem partners, we will start a new chapter in 5G messaging and further promote RCS applications in China,” said a statement from the three operators releasing the paper.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
GSMA says the key development has been the creation of the universal profile (UP), an industry-agreed set of features intended to simplify RCS product development and deployment.
The Chinese players can also take heart from the positive numbers out of the first two years of the RCS-based +Message service in Japan, supported by all three operators.
User numbers rose 35% to 17.5 million in 2019 and are forecast to hit 40 million in 2021, according to a GSMA-commissioned study.
The number of business messages sent over the platform is expected to reach more than 150 million in 2021 and 1.2 billion in 2023.
What’s more, users appear responsive to the marketing messages. The open rate is 85% in Japan and 75% globally, compared to 3% for direct mail.
Says the GSMA: “+Message also allows Japanese consumers to communicate directly with a range of brands and services, for example allowing them to engage with virtual assistants to book flights, buy goods and make restaurant reservations.”
Worldwide, the GSMA says 88 operators have launched RCS, attracting 403 million users.
Messaging research firm MobileSquared has predicted that RCS will be the world’s biggest business messaging platform by 2021, with 2 billion users. The firm notes that while WhatsApp (owned by Facebook) has 1.5 billion users, it may be difficult to monetize it as a marketing channel because users are required to opt in.
References:
http://global.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202004/08/WS5e8d67aea310aeaeeed50c6a.html
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/china-operators-to-offer-rcs-based-5g-messaging/d/d-id/758762?
https://www.totaltele.com/505475/Chinese-operators-back-RCS-in-new-white-paper
China’s CBN to use 700MHz for 5G network but needs a telco partner
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced that it has repurposed the country’s frequency use plan for 700MHz spectrum in order to accelerate the development of 5G technology and to promote the effective use of spectrum resources.
Under the new plan, MIIT will abandon the current usage – 702MHz-to-798MHz for TV and radio and broadcasting – in favor of 703MHz-743MHz/758MHz-798MHz for FDD mobile communication systems. In its notification, the MIIT ruled that mobile systems operating in this band must not interfere with broadcasting or other services operating in the same or adjacent frequency bands. Further, to avoid interference, frequency migration, site relocation and equipment mediation of existing legal radio stations must be carried out. The costs of that will charged to the user(s) of the 700MHz mobile spectrum.
The spectrum in question is currently held by radio and TV broadcaster China Broadcasting Network (CBN), which is also known as China Radio and Television. It plans to use the airwaves in conjunction with its 4.9GHz spectrum to provide a suite of interactive TV services in the short term, and mobile communication (4G and 5G?) plus IoT services in the future.

CBN was a surprise new entrant to mobile when the MIIT issued 5G licenses in June 2019. The company, owned by the National Radio and Television Administration (NRTA), was set up just five years ago. It had total revenues last year of RMB78 billion (US$10.9 billion) — around a third of China Unicom’s and a fifth of China Telecom’s.
CBN began its first wireless network trial last October– a standalone 5G pilot network in central Shanghai, announced last week by the Shanghai city government.
According to broadcast industry website DVBCN, CBN is planning to build pilot networks in 15 or so major cities, such as Beijing, Tianjin and Nanjing.
May 21, 2020 Update:
China Broadcasting Network Corporation (CBN) and China Mobile said they would jointly build and share a 5G network and also collaborate in content and platform sharing.
For China Mobile and CBN, joint network investment and construction at a 1:1 ratio is just one part of their arrangement, which will continue until 2031.
They will jointly own and share the capacity, but China Mobile has committed to wholesaling capacity on its 2.6GHz 5G network to its smaller partner. In areas where the 700MHz band is not yet commercially available, it will open up its 2G and 4G networks.
China Mobile’s statement said while the two partners would retain their own brands, they would explore further joint efforts in areas such as products, operations and content and even in “channels and customer services.”
For China Mobile, which already has 260MHz of 5G spectrum in the 2.6GHz and 4.9GHz bands, the partnership adds to its spectrum inventory and in particular access to precious low-band frequencies.
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2020/0520/2020052000370.pdf
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
As in Shanghai, these will be standalone 5G networks in the 4.9GHz band. The company expects to deploy 200 basestations in each city at an estimated total cost of RMB2-3 billion ($279-419 million).
Table 1. China 5G spectrum allocation
| Operator | Assigned spectrum | Total | Shared spectrum |
| China Mobile | 2515-2675MHz | 160MHz | |
| China Mobile | 4800-4900MHz | 100MHz | |
| China Telecom | 3400-3500MHz | 100MHz | 3300-3400MHz (indoor) |
| China Unicom | 3500-3600MHz | 100MHz | 3300-3400 MHz (indoor) |
| China Broadcast Network | 703-798MHz | 80MHz | 3300-3400 MHz (indoor) |
| China Broadcast Network | 4.9GHz (trial) | TBD | |
| Source: MIIT | |||
Local China news outlet C114 writes that the new network operator (CBN) still needs to clear the spectrum and migrate existing radio and TV services to other frequencies, the cost of which was estimated to run to more than CNY10 billion (USD1.41 billion).
CBN, with income of around $11 billion from cable TV services, lacks the financial scale to build a national network and compete against three big telco incumbents.
CBN has business partners such as Alibaba and financial group Citic, but a partnership with a telco (like China Mobile) is needed to build out the network. The new network rollout cost is estimated to be at least 60 billion yuan (US$8.5 billion).
CBN may be able to reduce that expense through cooperation with cellular providers, though, with a senior China Mobile official quoted as saying that the two providers had communicated ‘to discuss the possibility of co-construction.’
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/china-releases-700mhz-for-5g/d/d-id/758667?
China Telcos Lose Subscribers; 5G “Co-build and Co-share” agreement to accelerate
Decrease in China’s Mobile Subscribers:
China’s wireless carriers are reporting substantial drops in subscribers as the coronavirus crisis reduces business activity.
China Mobile Ltd., the world’s largest wireless carrier, reported its first net decline since starting to report monthly data in 2000. China Mobile subscriptions fell by more than 8 million over January and February, data on the company’s website show.
China Telecom Corp. said it lost 5.6 million users in February, while China Unicom Hong Kong Ltd. subscribers fell by 1.2 million in January.
The across the board China subscriber slump indicates that the coronavirus pandemic crisis, which first emerged in China late last year, is crimping growth, even at businesses that provide essential services and earn monthly revenue. ARPU will likely also decline, according to analysts.
Chris Lane, an analyst at Sanford C. Bernstein & Co said that part of the decrease in wireless subscribers could be due to migrant workers — who often have one subscription for where they work and another for their home region — canceling their work-region account after the virus prevented them from returning to work after the Lunar New Year holidays which began in late January.
While the drop in users is unusual, the total is small relative to total wireless subscriptions, which have risen to a combined 1.6 billion for the three carriers. Things may improve starting this month as work in factories and other businesses in China resumes, Lane said.
Net income fell 9.5% last year at China Mobile, partly on government mandates to cut prices and improve service, but also due to a spike in financing costs – up from RMB144 million ($20.2 million) to RMB3.25 billion ($460 million).
The company, which reported earnings last week, told analysts revenue would remain stable this year, a sign management was not worried about the fall in subscribers.
China Unicom overcame flat revenue growth to post an 11.1% increase in net earnings for 2019. The state-owned telco slashed opex by 22% and marketing cost by 5% to record a 11.3 billion yuan ($1.6 billion) full-year profit.
“In 2019, the domestic telecommunications industry development experienced a short-term pain with weak revenue growth and pressure on industry value,” Chairman and CEO Wang Xiaochu said.

………………………………………………………………………………………..
Co-build and Co-share Agreement:
In September 2019, China Unicom entered into a cooperation agreement with China Telecom to jointly build one 5G access network across the country. China Unicom would be doubling it’s own 5G network coverage, bandwidth, capacity and transmission speed, providing users with better experience.
China Unicom said it will actively step up the “co-build and co-share” with China Telecom in areas such as 4G indoor distributed antenna systems, server rooms, optical fiber and pipelines to further enhance network advantages and corporate value.
References:
https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/china-s-mobile-carriers-lose-15-million-users-as-virus-bites-1.1410626
https://www.telecomlead.com/5g/china-unicom-reveals-5g-network-capex-plans-94530
China Mobile has 15.4 million 5G customers; 5G+ is primary focus area
China Mobile today published its 2019 annual financial report, stating that the company’s operating revenue reached CNY745.9 billion -a year-on-year increase of 1.2% – and its net profit was CNY106.6 billion ($15 billion) – a year-on-year decrease of 9.5%.
The fall in net profits was largely due to a spike in financing costs – up from RMB144 million ($20.2 million) to RMB3.25 billion ($460 million).
Operating revenue was just 1.2% higher, at RMB745.9 billion ($104.8 billion), while telecom services revenue improved by a meager 0.5%.
A few highlights:
- The largest China telecom network provider acquired 15.4 million 5G customers in the first three months after launch.
- In 2019, China Mobile’s mobile users increased by 25.21 million, reaching a total of 950 million. Its mobile Internet data traffic increased by 90.3% year-on-year and its mobile Internet DOU reached 6.7GB.
- Wireline broadband customers grew by 30.35 million to a total of 187 million.
- China Mobile’s family broadband users reached 172 million, an increase of 17.1% year-on-year. Its family broadband comprehensive ARPU reached CNY35.3.
- At the end of 2019, China Mobile’s government and corporate clients reached 10.28 million, a year-on-year increase of 43.2%. The company’s international business revenue saw a year-on-year increase of 31.4%.
Mr. Yang Jie, China Mobile’s Chairman of the Board said in the press release:
“We were faced with a challenging and complicated operating environment in 2019 where the upside of data traffic was rapidly diminishing and competition within the telecommunications industry and from cross-sector players was becoming ever more intense. Coupled with this was the impact of government policies, including the continued implementation of the “speed upgrade and tariff reduction.”
Against this backdrop, all of us at China Mobile joined together to overcome these hurdles and work towards our ultimate goal of becoming a world-class enterprise by building a dynamic “Powerhouse”. This was centred on the key strategy of high-quality development, supported by a value-driven operating system that leverages our advantages of scale to drive further convergence, integration and digitization across the board.
We structured our organization to enable effective and synergetic capability building and collaborative growth, while nurturing internal vitality. In addition, we further implemented our “5G+” plan to spearhead the development of “four growth engines”, comprising the “customer,” “home,” “business” and “new” markets. These measures have helped us obtain positive momentum in overall operating results, which was a hard-earned achievement for us in a tough year.”
Yang noted that the COVID-19 epidemic had driven more and more businesses and consumers online and encouraged greater takeup of digital and cloud-based services. “We will leverage these opportunities, as well as the 5G network, to further develop the information and communications services market.”
Business Market:
The “business” market was China Mobile’s new growth engine and we strove to nurture new growth points by fully leveraging our cloud and network convergence advantages, building on our DICT (data, information and communications technology) infrastructure comprising IDC, ICT, Mobile Cloud, big data and other corporate applications and information services. Buoyed by active promotion of our “Network + Cloud + DICT” smart services, customers and revenue recorded rapid growth.
As of the end of 2019, the number of corporate customers increased to 10.28 million, representing year-on-year growth of 43.2%.
Focusing on key sectors such as industry, agriculture, education, public administration, healthcare, transportation and finance, the company deepened go-to-market resources to promote DICT solutions that cater to sector-specific scenarios. This strategy has boosted DICT revenue to RMB26.1 billion, or growth of 48.3% year-on-year, contributing a larger portion of our overall revenue.
“5G+” Achieved a Good Start:
China Mobile sped up the development of 5G and have been fully implementing its “5G+” plan since June 2019, when we were granted the 5G licence. These initiatives have shown good initial results.
The company actively participated in setting international standards for 5G to drive technological development. It led 61 key projects in relation to 5G international standards setting and own more than 2,000 5G patents. It also helped to continuously strengthen the Standalone 5G (within 3GPP Release 15 and 16).
Its “six international standards (3GPP specifications are not standards) on 5G system architecture” and “38 international standards including 5G NR (New Radio) terminals and base station radio frequency” scooped all the top prizes in the 2019 Science and Technology Awards presented by the China Communications Standards Association, demonstrating our leadership in 5G communications standards.
At the same time, the company accelerated the implementation of “5G+” by formulating well- coordinated development of 5G and 4G. It constructed and began operating more than 50,000 5G base stations and launched 5G commercial services in 50 cities. Emerging technologies such as AI, IoT (Internet of Things), cloud computing, big data and edge computing were assimilated into 5G (5G+AICDE) and developed more than 200 critical capabilities, while making breakthroughs in over 100 5G joint projects.
In terms of 5G+Eco, we aimed to develop the ecosystem with other industry players. Through its 5G Innovation Centre and 5G Industry Digital Alliance, more than 1,900 partners were attracted.
The 5G Device Forerunner Initiative, guiding manufacturers to launch 32 5G devices, was established. The level of maturity was basically the same between the 2.6 GHz and 3.5 GHz industry chains. Benefiting from forward-looking planning and effective execution, we expanded 5G+X, where “X” stands for the wider application of 5G, in applications that have been adopted by a plethora of industry sectors, as well as the mass market. For the latter, we launched exclusive plans for 5G customers and feature services such as ultra-high definition videos, cloud-based games and full-screen video connecting tones. As of the end of February 2020, our 5G plans attracted 15.40 million package customers – maintaining an industry-leading position.
In terms of vertical sector, China Mobile explored the possibility of combining 5G with AICDE capabilities, extending collaboration in the industry and deep-diving into classic manufacturing scenarios to develop our leadership in 5G smart manufacturing, 5G remote medical services and 5G automated mining, among other sectors. A total of 50 group-level demo application projects were implemented.
Looking ahead, 5G presents infinite possibilities. China Mobile will continue to take a systematic approach to planning and steadily implementing our “5G+” initiatives. The company will speed up technology, network, application, operations and ecosystem upgrades, accelerate industry transformation by converging technologies, integrate data to strengthen information transmission in society, and introduce digitized management to build the foundation for digital society development. By doing so, China Mobile will seek more extensive 5G deployment, covering more sectors and creating greater efficiency and social value.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.chinamobileltd.com/en/file/view.php?id=226450
https://www.chinatechnews.com/2020/03/19/26442-china-mobile-net-profit-down-9-5-in-2019
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/china-mobile-reports-154m-5g-customers/d/d-id/758329?
China has more than 1.6 billion mobile subscribers (> China’s entire population!)
China has a little more than 1.6 billion mobile subscribers as of year end 2019. That’s remarkable, considering China 2019 population is estimated at 1,433,783,686 people at mid year 2019 according to UN data.
- China Mobile gained more than 3.73 million new customers in December 2019, up from 2.95 new additions in November.
- China Telecom added 1.18 million new subscribers.
- China Unicom lost 2.7 million users in December.
China Mobile remains by far the largest Chinese cellular operator, with 950.2 million customers, of which 758 million are 4G users.
China Telecom, which has been growing steadily in the past year, has moved into second place with 335.57 million mobile customers, compared to 318.4 million at Unicom.
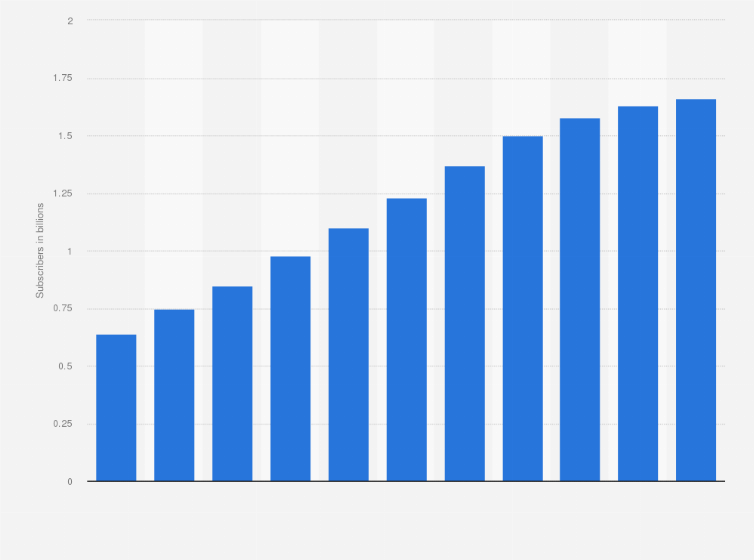
Number of mobile phone subscribers in China from 2008 to 2018 (Source: Statista.com)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China Mobile is also biggest in the fixed broadband market, ending 2019 with a total of 187.04 million users. However, in December 2019, it lost 609,000 fixed broadband customers, compared to a net addition of 694,000 in November and more than 1.9 million customer adds in October. China Telecom saw its fixed broadband subscriber base drop by 0.62 million in the month to 153.13 million, and Unicom lost 975,000 for a total of 83.47 million fixed broadband subscribers.
On November 1, 2019, Chinese operators China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom announced the rollout of 5G mobile phone services to customers. The three operators started by offering 5G plans for CNY 128 per month.
While the rollout of 4G in China took 46 months, 5G is expected to be available within ten months. China Mobile, the biggest of the three operators, already has 10 million customers interested in 5G, who are the first to access the services at launch. China Mobile earlier announced it expects to end 2019 with 5G coverage of 50 cities, and add another 340 cities in 2020, covering a population of 600-700 million people.
References:
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/china-ends-2019-with-more-than-16-billion-mobile-customers–1323638
China Internet penetration reached 61.2% in 1st half 2019; 99.1% access Internet via mobile phones!
2019 World 5G Convention in Beijing: China has built 113,000 5G base stations; 130,000 by the end of 2019
China secured 870,000 5G mobile subscribers in just 20 days after the country kicked off commercialization of the (pre-IMT 2020 standard) 5G mobile technology on October 31st. About 113,000 5G base stations have already entered service and the number will hit 130,000 by the end of this year, marking China one of the world’s largest 5G deployments, the ministry said.
As China continues to expand its 5G market, it has never set limits on what percentage of the domestic market can be supplied and equipped by foreign tech brands, the nation’s top industry regulator said on Thursday, November 21st. Miao Wei, minister of industry and information technology, said the world is at a tipping point for large-scale 5G network construction, and it is wrong for any country to use the excuse of cybersecurity risks to practice trade protectionism.
“No country should ban a company in its 5G network rollout based on unproved allegations of cybersecurity risks,” Miao said at the opening ceremony of the 2019 World 5G Convention in Beijing. The event runs through Saturday. China highly values cybersecurity and deeply understands that ensuring cybersecurity is a prerequisite for better growth of new-generation wireless technology, he added. “China sticks to transparent, equal and fair principles when purchasing 5G telecom equipment. We never preset market shares for domestic and foreign enterprises,” Miao said. “China welcomes global companies and research institutions to jointly build a 5G network and share the benefits of its development,” he added.
As the top industry regulator, the ministry will oversee Chinese telecom carriers’ bidding processes, and it encourages competition, Miao said, adding that delivering quality 5G products and services is the only way for companies to increase their market share in China.
The minister also called for international cooperation to accelerate the global rollout of 5G, highlighting the need to establish an international mechanism for recognizing 5G-related patents in a bid to build unified global standards.

Ke Ruiwen, chairman of China Telecom, said the telecom operator has established close ties with foreign companies and international associations to promote maturity of the 5G industry chain.
Foreign telecom equipment makers including Nokia and Ericsson as well as US chip giants such as Intel and Qualcomm have actively participated in China’s 5G testing and trial operations. Now they are scrambling to tap into opportunities in the country, which has built the world’s largest 4G network and is eager to do the same in the 5G era.
Frank Meng, chairman of Qualcomm China, said the company is pleased to join hands with industry partners to accelerate development of 5G in China.
Qualcomm has partnered with Chinese smartphone makers to bring affordable and quality 5G handsets to the global market. Xiaomi Corp, for instance, said it will unveil at least 10 5G smartphones next year.
Nokia China President Markus Borchert said earlier this year that cooperation with multinational companies is highly regarded by the Chinese government. This makes the Finnish company more confident in the healthy, steady and sustainable development of China’s 5G industry, Borchert added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
China is set to become the world’s largest 5G market by 2025, with 460 million 5G users, according to the Global System for Mobile Communications Association.
The number of 5G users in China is expected to be higher than that in Europe (205 million) and the United States (187 million) combined by that time, the association said.
Raymond Wang, partner with global consultancy firm Roland Berger, highlighted China’s commitment to further deepen opening-up and said Chinese companies have the confidence to compete with their foreign counterparts on the global stage.
References:
http://www.china.org.cn/business/2019-11/22/content_75434545.htm
China’s big 3 mobile operators have 9 Million 5G subscribers in advance of the service; Barron’s: China to lead in 5G deployments
According to Beijing News, the three major (state owned) China mobile network operators have already signed up 9 million advance orders for their yet to be launched 5G service. As of October 5th, China Mobile’s 5G subscribers have reached 5.32 million, China Unicom has 1.75 million, China Telecom has 1.76 million, and the total number of committed 5G users is nearly 9 million.
The three China network operators haven’t set a date for the start of service, but will reportedly commence simultaneously, most likely later this month of October. However, there are not many 5G smartphones (only two or three models) and no other endpoints (none announced yet) available from the three major China network operators. The preferential price is between 150 yuan and 550 yuan.
On September 20, Xu Ximing, deputy general manager of the marketing department of China Mobile Group Corporation, said at the China Mobile 5G+ Innovation Cooperation Conference that China Mobile is accelerating the pace of 5G commercialization. The 5G package will be officially released in October, including basic packages and CPE packages. And upgrade plans for old users. Customers will enjoy the “three different fast” login to the 5G network, that is, the 5G terminal does not need to change the card, does not need to change the number, does not need to register, and multi-channel fast order 5G network service.
- The China Unicom prices web page shows that the current campaign supports two mobile phones, Samsung Note 10+5G version offers 500 yuan, and vivo’s iQOO Pro 5G version offers 400 yuan. Telecom’s purchase discounts are 150 yuan for iQOO Pro, 300 yuan for ZTE Axon 10 Pro, and 550 yuan for Samsung Note 10+.
- For China Mobile’s preferential prices, Xiaomi 9 Pro 5G version is offered for 300 yuan, China Mobile’s pioneer X1, Samsung Note 10+ 5G version offer is 500 yuan. China Mobile told the Beijing News that more 5G models will be added in the future.

China Mobile Pioneer X1 is powered by a Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 chipset, a 6.47-inch AMOLED display with a waterdrop notch. The display supports FHD+ resolution and also houses an on-screen fingerprint scanner. Housed inside the waterdrop notch is a powerful 20MP camera.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Note: Although Samsung continues phone sales in China, last week the handset maker ceased its mobile phone production operations in China as it closed its last factory in the country, according to Reuters.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China’s 5G network coverage is progressing rapidly and the 5G network is increasingly equipped with a formal commercial foundation. Recently, the official statistics of the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Economics and Information Technology state that the three major network operators have completed more than 8,800 5G base stations in Beijing, covering areas along Chang’an Avenue, the World Expo, CCTV Broadcasting Center, and Shougang Park.
According to a message released by the Beijing Communications Administration, it is expected that by the end of 2019, Beijing will build more than 10,000 5G base stations. According to the current construction progress, the number of 5G base stations in Beijing is expected to reach 12,000 by the end of the year. Among the other three first-tier cities, Shanghai plans to build 10,000 5G base stations in 2019 and 20,000 5G base stations in 2020; Guangzhou proposes to complete no less than 20,000 5G base stations in 2019, and 5G will be built in 2021. The base station is 65,000; the plan for Shenzhen is to build 15,000 5G base stations by the end of 2019.
With the spread of 5G networks, innovative applications in various 5G environments are emerging and even landing. On September 25, Daxing International Airport was officially opened. Eastern Airlines, Beijing Unicom and Huawei jointly released a 5G-based smart travel integrated service system at Daxing International Airport. Under the system, the user does not need to present the ID card and the QR code as usual, and only needs face recognition to complete the travel process such as ticket purchase, check-in, check-in, security check, and boarding.
China’s government is partially subsidizing 5G deployments as we note in several paragraphs below:
- The Shenzhen city government is offering to pay operators RMB10,000 ($1,398) for every standalone 5G base station deployed, with a maximum payout of RMB150 million ($20.9 million). Its 5G plan issued last month promises support for site acquisition and subsidies for base station electricity costs. The tech-dominated Chinese city, home to Huawei, ZTE and Tencent, plans to install 15,000 5G base stations by the end of 2019 and 45,000 by next August (more on this below).
- Almost every Chinese city or provincial government has a 5G development plan. While many are light on specifics, some reveal big ambitions. For example, the government of Zhejiang, the wealthy province near Shanghai, expects to have 30,000 base stations next year. It plans to complete its 5G rollout by 2022, by which time its coverage will “lead the country.”
- The north-west province of Shanxi — not known for its advanced tech industries — has also made 5G a top priority. It has bench marked its 5G rollout against other provinces and, like Zhejiang, has set a target of 30,000 base stations by 2022. And the city is also offering subsidies for base station power costs and help in site selection.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From an article titled, “The Real 5G Winner Could Be China,” in the October 7, 2019 print edition of Barron’s:
Multiple Wall Street analysts are getting more optimistic about China’s 5G build out. For instance, Rosenblatt Securities notes that local governments in the Asian country are providing subsidies to “speed up 5G network deployments.” As a result, Rosenblatt says, more than 300 cities in China will have 5G networks by the end of next year. Even Hall, the Goldman Sachs 5G skeptic, expects 120 million 5G smartphones to ship next year, largely because of China’s aggressive build out.
In a report this past week, Piper Jaffray analyst Harsh Kumar cited a Chinese think tank that sees China-based companies spending $411 billion on 5G networks from 2020 to 2030. Of the 600,000 5G base stations expected to be rolled out worldwide next year, Kumar says half will be deployed in China: “We expect 2020 global [5G] deployments to largely be driven by the Chinese market.”
5G may come together slowly in the U.S. market, but China is serious about winning the race.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://tech.sina.com.cn/t/2019-10-06/doc-iicezzrr0343842.shtml
https://www.lightreading.com/asia-pacific/china-telcos-rack-up-9m-5g-advance-subs/d/d-id/754643?
https://www.barrons.com/articles/the-real-5g-winner-could-be-china-51570228459
https://www.wsj.com/articles/in-the-race-to-dominate-5g-china-has-an-edge-11567828888
Conflicting reports: Huawei and China Mobile may buy Brazil carrier Oi
The O Globo website reported on Saturday that Huawei is joining forces with China Mobile to buy struggling Brazilian carrier Oi, in an attempt to boost their footprint in Latin America’s largest market. The two Chinese companies anticipate a significant growth in business once Brazil starts deploying its 5G network. Oi’s 360,000 kilometers of fiber infrastructure is seen as an attractive asset.
Oi declined to comment on the matter, while Huawei and China Mobile did not immediately respond to Reuters’ requests for comment.
However, on Sunday Huawei told Reuters it was not interested in acquiring struggling Oi or any other Brazilian carrier.
“Huawei has no plan or interest in acquiring Oi or any other Brazilian carrier. In Brazil for more than 20 years, the company is working with all major Brazilian carriers supplying the best products and solutions to support digital transformation in Brazil,” the company said in an emailed statement to Reuters.
It would be very strange for Huawei to invest in a telecom carrier which is traditionally its bread and butter customer!
Brazil’s largest fixed-line carrier has been struggling to turnaround its business since it filed for bankruptcy protection in June 2016 to restructure approximately 65 billion reais of debt. Oi is also negotiating its network with Spain’s Telefonica and Telecom Italia, AT&T and another (unnamed) Chinese company.
Speculation of the bid comes as Brazil’s Senate approved a bill to update the country’s obsolete framework for telecommunications, paving the way for Oi to implement a plan to sell up to $2 billion in non-core assets. Earlier this week, Suno Notícias reported that China Mobile has filed a request to operate in Brazil and eventually acquire Oi. The country’s telecom regulatory agency Anatel said Sept. 17th it didn’t have any official information regarding the request.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum: Huawei launches new ‘Vision TV’ with 4K quantum dot color, which comes in 55″/65″/75″ sizes. Media paying attention to the fact that Huawei is adopting QD technology, which until now has been a key technology for Samsung’s TV (QLED) strategy. (ZDNet)
http://www.zdnet.co.kr/view/?no=20190920082939
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:



