Broadband Status
U.S. Home Internet prices DECLINE amidst fierce competition between wireless carriers and cablecos
Home internet prices in the U.S. are being driven down by fierce competition between mobile carriers offering Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and cable internet companies offering legacy Hybrid Fiber Coax connections. The increased competition has driven down the cost of home internet service, a welcome break for consumers when prices are rising for many other essential products. The price of home internet service fell 3.1% in May from a year earlier, while the overall consumer-price index rose 2.4%, according to the Labor Department.
The WSJ reports that major home-internet service providers including Verizon VZ, Comcast/Xfinity and T-Mobile launched a flurry of price-lock guarantees, promising steady rates for as long as five years. CableCos Charter, which is acquiring Cox, unveiled a three-year deal last year.
Cable companies have struggled to retain broadband internet subscribers since mobile carriers began offering more affordable 5G fixed-wireless access (FWA) internet service in 2018. FWA, which relies on over the air transmission to cell towers instead of HFC access, brought competition into markets where cable companies had long enjoyed being the only game in town. Now both types of providers are growing more aggressive to attract—and keep—customers.
“The cable companies went from gaining subscribers and raising rates every year to declining subscribers and giving people price locks,” said John Hodulik, a UBS analyst. “They’re seeing churn rise in their broadband subscriber base. And they’re trying to nip that in the bud.” Fixed wireless can sometimes cost half as much as a cable-provided internet plan. Though network congestion and other connectivity issues can be an issue for some users, the lower price point has been luring cable customers away.
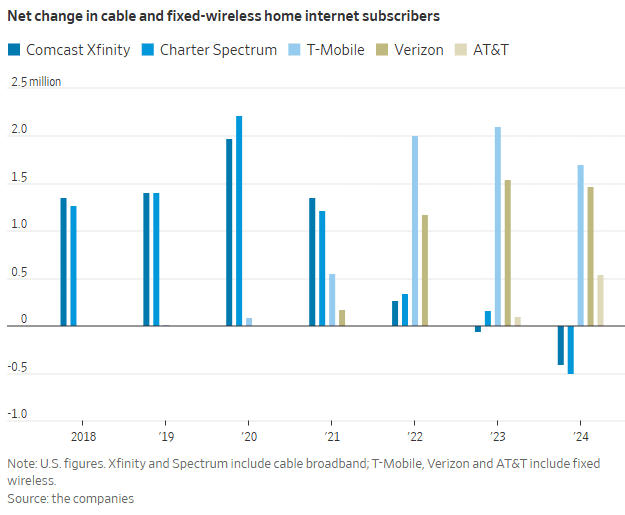
T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T added a combined 3.7 million FWA customers in 2024. In sharp contrast, Comcast’s Xfinity and Charter’s Spectrum lost more than 900,000 home internet subscribers. That’s depicted in this graph:
“Our pricing wasn’t breaking through in the marketplace,” said Steve Croney, chief operating officer for Comcast’s connectivity and platforms business. He said the company’s five-year price lock, introduced in April, competes well against the telecom companies’ offerings.
Frank Boulben, chief revenue officer at Verizon’s consumer group, said his company has been trying to address the “pain points” customers have with cable companies, such as price hikes. That’s why the telco is emphasizing FWA vs its FiOS fiber to the home based service. Boulben said his company would focus on selling fiber service to customers as it becomes available to them.
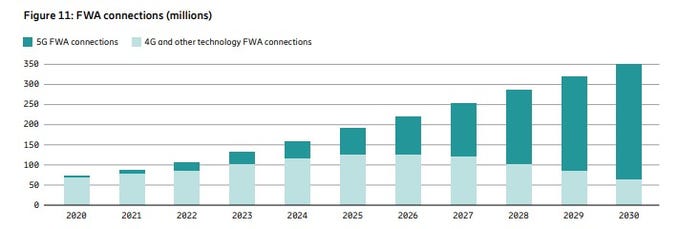
Is FWA the ONLY real killer application for 5G? Even though it was NOT one of the envisioned use cases? Ericsson’s recently released Mobility Report says FWA will account for more than 35% of all new fixed broadband connections, with an expected increase to 350 million by the end of 2030. The report states that more than half of all network service providers (wireless telcos) who offer FWA now do so with “speed-based monetization benefits enhanced by 5G.”
About 80% of the global network operators sampled by Ericsson currently offer FWA, with the most rapid area of growth among CSPs (communications service providers) offering 5G-enabled speed-based tariff plans. These opportunities are about the ability to offer a range of subscriber packages with different downlink and uplink data options with 5G FWA. As with fiber deals, “increasing monetization opportunities for CSPs compared to earlier generations of FWA.” 51% of operators with FWA offerings now include these speed-based options, which is up from 40% on the same period in June 2024 and represents a 27.5% increase. The June 2024 number had grown 50% on the June 2023 equivalent.
Source: Ericsson Mobility Report
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“We are at an inflection point, where 5G and the ecosystem are set to unleash a wave of innovation,” said Erik Ekudden, Ericsson Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer. “The recent advancements in 5G standalone (SA) networks, coupled with the progress in 5G-enabled devices, have led to an ecosystem poised to unlock transformative opportunities for connected creativity. Service providers have recognized this potential of 5G and are beginning to monetize it through innovative service offerings that extend beyond merely selling data plans. To fully realize the potential of 5G, it is essential to continue deploying 5G SA and to further build out mid-band sites. 5G SA capabilities serve as a catalyst for driving new business growth opportunities.”
Fixed-wireless doesn’t work everywhere. Besides congestion weak signals can make coverage spotty. If your cell phone doesn’t pick up 5G coverage smoothly, fixed-wireless from the same company probably won’t work either.
Verizon, AT&T and T-Mobile are winning converts to FWA at a faster pace than many anticipated, said Jonathan Chaplin, a managing partner at equity research firm New Street Research. Charter agreed to buy Cox last month for $21.9 billion in equity and assume $12 billion of its outstanding debt, in part to acquire scale to better compete with fixed wireless access. However, fixed-wireless growth can’t last indefinitely. The wireless networks on which they run will eventually hit capacity, limiting how many subscribers they can add. Chaplin estimates the networks can support around 19 million total fixed-wireless subscribers—which he predicts they will reach in about five years, accounting for planned network expansions that the companies have announced. When that limit is reached, cable companies may regain the upper hand and keep growing their fiber customer base, Chaplin said.
The big three wireless carriers (AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile) have all been investing in fiber-based wired networks via build-outs and acquisitions. AT&T is bringing new customers in via FWA, with the long-term goal to convert them to fiber-based service, said Erin Scarborough, who runs that company’s broadband and connectivity initiatives.
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/ericsson-says-fwa-is-boosting-telco-monetization-opportunities
https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report
https://www.consumeraffairs.com/news/cable-vs-wireless-war-is-driving-prices-down-062525.html
Dell’Oro: 4G and 5G FWA revenue grew 7% in 2024; MRFR: FWA worth $182.27B by 2032
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
5G Advanced offers opportunities for new revenue streams; 3GPP specs for 5G FWA?
FWA a bright spot in otherwise gloomy Internet access market
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
The U.S. The Commerce Department is examining changes to the NTIA’s $42.5 billion broadband funding bill (Broadband Equity Access and Deployment- BEAD), which endeavors to expand internet access in underserved/unserved areas. [BEAD was part of the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) during the Biden administration] The proposed new rules will make it much easier for Elon Musk owned Starlink satellite-internet service, to tap in to rural broadband funding, according to the Wall Street Journal. [Starlink is owned by SpaceX which is majority owned by Elon Musk).
Commerce Department Secretary Howard Lutnick said that BEAD will be revamped “to take a tech-neutral approach that is rigorously driven by outcomes, so states can provide internet access for the lowest cost.” The department is also “exploring ways to cut government red tape that slows down infrastructure construction. We will work with states and territories to quickly get rid of the delays and the waste. Thereafter, we will move quickly to implementation in order to get households connected. All Americans will receive the benefit of the bargain that Congress intended for BEAD. We’re going to deliver high-speed internet access, and we will do it efficiently and effectively at the lowest cost to taxpayers.”
By making the broadband the grant program “technology-neutral,” it will free up states to award more funds to satellite-internet providers such as Starlink, rather than mainly to companies that lay fiber-optic cables which connect the millions of U.S. households that lack high-speed internet service.
The potential new rules could greatly increase the share of funding available to Starlink. Under the BEAD program’s original rules, Starlink was expected to get up to $4.1 billion, said people familiar with the matter. With Commerce’s overhaul, Starlink, a unit of Musk’s SpaceX, could receive $10 billion to $20 billion.
“The Trump administration is committed to slashing government bureaucracy and harnessing cutting-edge technology to deliver real results for the American people, especially rural Americans who were left behind” under the Biden administration, White House spokesman Kush Desai said.
“Leave it alone; let the states do what they’ve done,” Missouri State Rep. Louis Riggs, a Republican, said in a recent interview. “The feds could not do what the states have done. In 10 or 15 years, all they basically did, they walked in and screwed everything up. God love them, they just keep throwing money at the problem, which is okay when you give it to the states and let us do our jobs, but trying to claw that funding back and stand up a new grant round is the worst idea I’ve heard in a very long time, and that’s saying a lot coming out of D.C.”
The overhaul could be announced as soon as this week, possibly without some details in place, the people said. Following any changes, states might have to rewrite their plans for how to spend their funding from the program, which could delay the implementation.
Lutnick told Commerce staff he plans to do away with other BEAD program rules, including some related to climate impact and sustainability, as well as provisions that encouraged states to fund companies with a racially diverse workforce or union participation, the people said. The program requires internet-service providers that receive funding to offer affordable plans for lower-income customers. Lutnick saids he is considering reducing those obligations.
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick at the White House last month. Photo: Francis Chung/Pool/Cnp/ZUMA Press
Many broadband providers worried the Musk-led Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) would eliminate or reduce the program’s funding. Is that not a conflict of interest considering that Musk owns Starlink/SpaceX?
Given the overhaul, fiber broadband providers may not benefit from it as much as they expected because non-fiber technologies are poised to receive more funding than before.
Fiber Broadband Association CEO Gary Bolton said in a statement that all “Americans deserve fiber for their critical broadband infrastructure. Fiber provides significantly better performance on every metric, such as broadband speeds, capacity, lowest latency and jitter, highest resiliency, sustainability and provides the maximum benefit for economic development and is required for AI, Quantum Networking, smart grid modernization, public safety, 5G and the future of mobile wireless communications. We urge our policymakers to do what’s right for people and to not penalize Americans for where they live or their current income levels.”
Telecommunications and broadband consultant John Greene wrote that states that have started the sub-grantee selection process, such as Louisiana, “might be forced to rethink their process in light of potential new rules.” Other “states, like Texas, might be better served to pause their process until after Commerce has completed their review and made any necessary changes,” he said.
References:
Nokia will manufacture broadband network electronics in U.S. for BEAD program
New FCC Chairman Carr Seen Clarifying Space Rules and Streamlining Approvals Process
Highlights of FiberConnect 2024: PON-related products dominate
2021 U.S. Broadband Infrastructure law has been a colossal failure – who’s to blame?
The 2021 U.S. Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), AKA the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law was signed into law November 15, 2021. It included $42.5 billion for states to expand broadband to “unserved,” mostly rural, communities. The White House said it would “Ensure every American has access to high-speed internet…. The Bipartisan Infrastructure Deal will deliver $65 billion to help ensure that every American has access to reliable high-speed internet through a historic investment in broadband infrastructure deployment. The legislation will also help lower prices for internet service and help close the digital divide, so that more Americans can afford internet access.”
In his speech at the Democratic National Convention, President Joe Biden trumpeted his broadband program in historic terms, calling it a national build-out “not unlike what Roosevelt did with electricity.” Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris helped create and promote the program as vice president, and on the campaign trail it could offer a way to show how the White House has delivered for rural Americans.
Yet almost three years later, ground hasn’t been broken on a single project! The Biden-Harris Administration recently said construction won’t start until next year at the earliest, meaning many projects won’t be up and running until the end of the decade. Who’s to blame?
- NTIA was expected to play a major role in the endeavor to connect every American to high-speed, affordable broadband. They intended to work closely with all stakeholders, including State and local governments, Tribal governments, industry, and community leaders, as well as across the Federal government to ensure that this bold investment is targeted to those who need it most. But they haven’t helped a bit!
- States must submit plans to the U.S. Commerce Department about how they’ll use the funds and their bidding process for providers. The Commerce Dept. has piled on mandates that are nowhere in the law and has rejected state plans that don’t advance progressive goals. Commerce hoped to spread the cash to small rural cooperatives, but the main beneficiaries will be large providers that can better manage the regulatory burden. Bigger businesses always win from bigger government.
- Commerce is all but refusing to fund anything other than fiber broadband, though satellite services like SpaceX’s Starlink and wireless carriers 5G FWA can expand coverage at lower cost. Extending 5G to rural communities costs a couple thousand dollars per connection. Building out fiber runs into the tens of thousands. Fiber networks will require more permits, which delay construction. But fiber will require more union labor to build. Commerce wants grant recipients to pay union-scale wages and not oppose union organizing.
- The Administration has also stipulated hiring preferences for “underrepresented” groups, including “aging individuals,” prisoners, racial, religious and ethnic minorities, “Indigenous and Native American persons,” “LGBTQI+ persons,” and “persons otherwise adversely affected by persistent poverty or inequality.”
- In Virginia, that leaves thousands of mostly rural residents stuck in a long-outdated version of the internet. According to the official state count, there are more than 100,000 homes and offices across Virginia with connection speeds slow enough to qualify for the $1.48 billion in funding. “People need to see it,” said Lynlee Thorne, a political director for Democratic campaign group Rural Ground Ggame, which helps lead campaigns for Virginia state seats. “It’s got to be a lot more concrete. We’re past the point of being able to earn people’s votes based on the status quo or just hope.”
- Last week, Cox Communications last week sued Rhode Island over the state’s plan to “build taxpayer-subsidized and duplicative high-speed broadband internet in affluent areas of Rhode Island like the Breakers Mansion in Newport and affluent areas of Westerly,” where Taylor Swift owns a $17 million vacation home. Cox says there are better ways to spend taxpayer dollars. According to the Federal Communications Commission, 99.97% of U.S. households already have access to high-speed internet.
References:
https://www.politico.com/news/2024/09/04/biden-broadband-program-swing-state-frustrations-00175845
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Apparently, there’s no place to hide in any telecom or datacom market? We all know the RAN market has been in a severe decline, but recent Dell’Oro Group reports indicate that Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network and Cable CPE shipments have also declined sharply in the 1st Quarter of 2024.
Here are a few selected quotes from Dell’Oro analysts:
“The North American broadband market is in the midst of a fundamental shift in the competitive landscape, which is having a significant impact on broadband equipment purchases,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President with Dell’Oro Group. “In particular, cable operators are trying to navigate mounting, but predictable, broadband subscriber losses with the need to invest in their networks to keep pace with further encroachment by fiber and fixed wireless providers,” explained Heynen.
Omdia, owned by the ADVA, expects cable access equipment spending to grow later in 2024 and peak in 2026 at just over $1 billion, then drop off to $700 million in 2029.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Customer’s excess inventory of DWDM systems continued to be at the center stage of the Optical Transport market decline in the first quarter of 2024,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “However, we think the steeper-than-expected drop in optical transport revenue in 1Q 2024 may have been driven by communication service providers becoming increasingly cautious about the macroeconomic conditions, causing them to delay projects into future quarters,” added Yu.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Inflation has impacted the ability of some Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to raise capital, and it has also impacted subscribers when it comes to upgrading their phones to 5G. Many MNOs have lowered their CAPEX plans and announced that they have fewer than expected 5G subscribers on their networks; which limits MNOs’ growth plans. As a result, we are lowering our expectations for 2024 from a positive growth rate to a negative one,” by Research Director Dave Bolan.
- As of 1Q 2024, 51 MNOs have commercially deployed 5G SA (Stand Alone) eMBB networks with two additional MNOS launching in 1Q 2024.
References:
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
U.S. broadband subscriber growth slowed in 1Q-2024 after net adds in 2023
The pace of U.S. broadband subscriber growth slowed considerably in the first quarter of 2024 as fiber, fixed wireless access (FWA) and cable broadband service providers collectively turned in results that were worse than what they posted in the year-ago period.
Total industry net additions, including or excluding FWA and geosynchronous (GEO) satellite broadband providers, decelerated noticeably in Q1 2024. The total market’s growth rate decreased to just 2.3% year-over-year, the slowest since the COVID-19 pandemic, analysts at MoffettNathanson estimated in its latest broadband industry trends report (paid subscription required). When FWA and GEO satellite categories were excluded, the growth rate was much worse: -0.7%.
The overall number of U.S. broadband market subscribers decelerated by 299,000 net adds versus the year-ago quarter. “That was the most abrupt since Q2 2022,” said MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett. “The bottom line is that penetration of home broadband stalled, and perhaps even declined in the quarter, particularly if one adjusts for the growth in homes passed in rural areas under RDOF [Rural Digital Opportunity Fund] subsidies and unsubsidized edgeouts,” Moffett wrote.
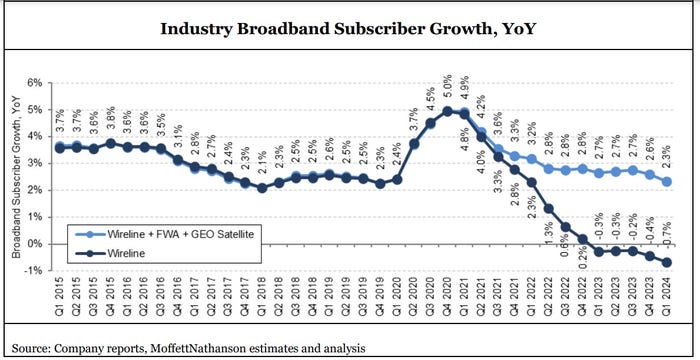
Here’s a breakdown of U.S. broadband subscribers by access type:
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) providers added 879,000 subs in Q1 2024, down from a gain of 925,000 in the year-ago period.
- Fiber net adds also slowed – from 487,000 in Q1 2024 versus a gain of 517,000 in the year-ago quarter.
- DSL losses of 560,000 in Q1 were similar to a year-ago loss of 571,000.
- MSO/cable network operators shed 169,000 broadband subs in Q1, much worse than a year-ago gain of about 71,000 subs.
“The culprit for cable’s weaker broadband net additions was a slower market growth rate,” though lower new household formation and cessation of ACP enrollments in the quarter also played a role, Moffett noted.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to Statista, the total number of broadband subscribers in the U.S. stood at 114.7 million at the end of 2023, This was an increase of over four million subscribers compared to the previous year.
Source: Statista
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In March 2024, Leitman Research found that the largest cable and wireline phone providers and fixed wireless services in the U.S. – representing about 96% of the market – acquired about 3,520,000 net additional broadband Internet subscribers in 2023, similar to a pro forma gain of 3,530,000 subscribers in 2022.
Leitman Research findings for 2023:
- The top cable companies lost about 65,000 subscribers in 2023 – compared to about 530,000 net adds in 2022
- The top wireline phone companies lost about 80,000 total broadband subscribers in 2023 – compared to about 180,000 net losses in 2022
- Wireline Telcos had about 1.97 million net adds via fiber in 2023, offset by about 2.05 million non-fiber net losses
- Fixed wireless/5G home Internet services from T-Mobile and Verizon added about 3,665,000 subscribers in 2023 – compared to about 3,185,000 net adds in 2022
- Fixed wireless services accounted for 104% of the total net broadband additions in 2023, compared to 90% of the net adds in 2022, and 20% of the net adds in 2021
“Top broadband providers added about 3.5 million subscribers in 2023, similar to the number of broadband adds in 2022,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for Leichtman Research Group, Inc. “Over the past four years, top providers added about 15.9 million broadband subscribers, compared to about 10.2 million net broadband adds in the prior four (pre-pandemic) years.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/us-broadband-subscriber-pace-slows-across-the-board
https://www.statista.com/statistics/217938/number-of-us-broadband-internet-subscribers/
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
Fiber and Fixed Wireless Access are the fastest growing fixed broadband technologies in the OECD
Verizon’s 2023 broadband net additions led by FWA at 375K
Charter Communications: surprise drop in broadband subs, homes passed increased, HFC network upgrade delayed to 2026
Altice USA transition to fiber access; MoffettNathanson analysis of low population growth on cablecos broadband growth
FCC increases broadband speed benchmark (x-satellites) to 100/20 Mbit/s
The U.S. FCC voted this week to implement a 4x increase to its “broadband” benchmark, from 25/3 Mbit/s to 100/20 Mbit/s (download/upload speeds). The Commission’s Report was issued pursuant to section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996. The FCC concluded “that advanced telecommunications capability is not being deployed in a reasonable and timely fashion based on the total number of Americans.”
Using the agency’s Broadband Data Collection deployment data for the first time rather than FCC Form 477 data, the Report shows that, as of December 2022:
• Fixed terrestrial broadband service (excluding satellite) has not been physically deployed to approximately 24 million Americans, including almost 28% of Americans in rural areas, and more than 23% of people living on Tribal lands;
• Mobile 5G-NR (ITU-R M.2150/3GPP Release 16) coverage has not been physically deployed at minimum speeds of 35/3 Mbps to roughly 9% of all Americans, to almost 36% of Americans in rural areas, and to more than 20% of people living on Tribal lands;
• 45 million Americans lack access to both 100/20 Mbps fixed service and 35/3 Mbps mobile 5G-NR service; and
• Based on the new 1 Gbps per 1,000 students and staff short-term benchmark for schools and classrooms, 74% of school districts meet this goal.
The Report also sets a 1 Gbps/500 Mbps long-term goal for broadband speeds to give stakeholders a collective goal towards which to strive – a better, faster, more robust system of communication for American consumers.
FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in a statement discussing the agency’s new 100/20 Mbit/s benchmark.
“This fix is overdue. It aligns us with pandemic legislation like the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the work of our colleagues at other agencies. It also helps us better identify the extent to which low-income neighborhoods and rural communities are underserved. And because doing big things is in our DNA, we also adopt a long-term goal of 1 Gigabit down and 500 Megabits up.”
“One more thing. The law requires that we assess how reasonable and timely the deployment of broadband is in this country.”
Don’t expect much change. As noted by Engadget, U.S. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offering speeds under the new benchmark won’t be able to call their services “broadband” on the new telecom information labels the FCC will soon begin requiring. However, ISPs and network providers are not required to hit the FCC’s new 100/20 Mbit/s speeds.
Moreover, it will not impact the NTIA’s massive $42.45 billion Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program, which already requires 100/20 Mbit/s speeds on networks receiving government subsidies.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The FCC’s definition of broadband excludes satellites at a time of frenzied investments in Internet services from space. Championed by Elon Musk’s Starlink, companies ranging from Amazon to OneWeb to Telesat are planning similar low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations for space-based Internet.
Starlink’s parent company – SpaceX – this week conducted another test of its massive Starlink rocket. That rocket is in part intended to launch Starlink’s second generation satellites.
However, the FCC has excluded such satellite efforts from most of its broadband programs. For example, it rejected Starlink’s application for government funding through its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) program.
“It is evident that fixed wireless access (FWA) offerings already compete aggressively with traditional wired broadband services, and LEO satellite-based services are poised to do the same. Accordingly, all three should be treated as robust rivals within a single ‘home Internet’ product market,” wrote the Free State Foundation, another think tank.
According to FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr, a Republican, the agency specifically excludes Starlink from its overall efforts because he thinks President Biden dislikes SpaceX chief executive Elon Musk. “The Biden Administration is choosing to prioritize its political and ideological goals at the expense of connecting Americans,” Carr alleges.
With its roughly 5,000 satellites, Starlink currently offers median speeds of around 64 Mbit/s, according to Ookla, and counts around 2.6 million customers globally.
References:
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401205A1.pdf
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401205A2.pdf
BroadbandNow Research: Best & Worst States for Broadband Access
FCC proposes 100 Mbps download as U.S. minimum broadband speed
Fiber Connect 2023: Telcos vs Cablecos; fiber symmetric speeds vs. DOCSIS 4.0?
GAO: U.S. Broadband Benchmark Speeds Too Slow; FCC Should Analyze Small Business Speed Needs
FCC Says Broadband Deployment Lacking; Redefinition (25M/3M) Has Huge Implications for AT&T, Verizon & Comcast
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
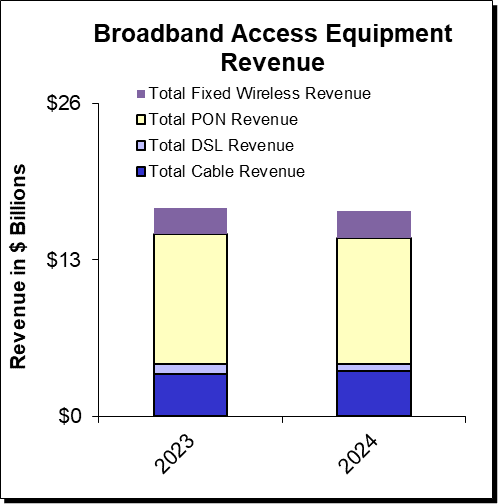
Dell’Oro Group expects broadband access equipment sales to decline by 1% in 2024 versus 2023, with the first half of 2024 seeing continued weakness followed by a surge in spending in the second half of the year. The first half of 2024 will continue to see some of the inventory corrections that marked a tough 2023 that saw a spending decline of 8% to 10%, according to Dell’Oro VP Jeff Heynen.
“Although the inventory corrections seen in 2023 will continue through the first half of 2024, the second half of the year is expected to be the turning point towards renewed growth,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “Service providers still have the same goals of increasing their fiber footprint, increasing the bandwidth they can offer their customers, and improving the reliability of their broadband services through the distribution of intelligence closer to subscribers,” added Heynen.
Additional highlights from the Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year January 2024 Forecast Report:
- PON equipment revenue is expected to grow from $10.8 B in 2023 to $11.8 B in 2028, driven largely by XGS-PON deployments in North America, EMEA, and CALA and early 50 Gbps deployments in China.
- Revenue for Cable Distributed Access Equipment (Virtual CCAP, Remote PHY Devices, Remote MAC/PHY Devices, and Remote OLTs) is expected to reach $1.3 B by 2028, as operators continue their DOCSIS 4.0 and early fiber deployments.
- Revenue for Fixed Wireless CPE is expected to reach $2.5 B by 2028, led by shipments of 5G sub-6GHz and a growing number of 5G Millimeter Wave units.
- Revenue for Wi-Fi 7 residential routers and broadband CPE with WLAN will reach $9.3B by 2028, as the technology is rapidly adopted by consumers and service providers alike.
Source: Dell’Oro Group
About the Report:
The Dell’Oro Group Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year Forecast Report provides a complete overview of the Broadband Access market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and port/unit shipments for PON, Cable, Fixed Wireless, and DSL equipment. Covered equipment includes Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP), Distributed Access Architectures (DAA), DSL Access Multiplexers (DSLAMs), PON Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Customer Premises Equipment ([CPE] for Cable, DSL, PON, Fixed Wireless), along with Residential WLAN Equipment, including Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 Gateways and Routers. For more information about the report, please contact [email protected].
References:
Calix and Corning Weigh In: When Will Broadband Wireline Spending Increase?
Dell’Oro: Broadband network equipment spending to drop again in 2024 to ~$16.5 B
Dell’Oro: Broadband Equipment Spending to exceed $120B from 2022 to 2027
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
Alaska Communications uses XGS-PON, FWA, DSL in ~5K homes including Fairbanks and North Pole
AT&T to deploy FTTP network based on XGS-PON in Amarillo, TX
Telefonica España to activate XGS-PON network in 2022; DELTA Fiber to follow in Netherlands
Charter Communications: surprise drop in broadband subs, homes passed increased, HFC network upgrade delayed to 2026
Charter Communications posted a surprise drop in broadband subscribers in the Q4-2023, the company announced on Friday. Charter’s internet customers decreased by 61,000 (-62,000 residential and +1,000 business) in the 4th quarter, with nearly all of the decline from residential customers. That was much worse than expectations for 17,290 additions, according to Visible Alpha and a year-ago gain of +105,000. The broadband subscriber drop was especially disappointing given Charter’s homes passed growth accelerated to 2.5% year-over-year, Craig Moffett said in a research note.
“Internet growth in our existing footprint has been challenging, driven by admittedly more persistent competition from fixed wireless and similar levels of wireline overbuild activity,” CEO Chris Winfrey said on a post-earnings call, adding that new investments will help drive growth despite the “temporary challenges.” Chief Financial Officer Jessica Fischer had warned in December that the company could lose internet customers in the quarter. At the time, speaking at an analyst conference, she said the company was facing short-term challenges and that results would be in line with the rest of the industry.
Charter was not the only cableco/MSO to report decreased broadband internet subscribers in the 4th quarter. Last week, rival Comcast reported a loss of 34,000 broadband customers, fewer than expectations, but exceeding the 18,000 broadband customers it lost in the previous quarter.
Stiff competition across broadband and wireless mobile and the decline of traditional television have been causes of concern, with Charter trying to expand its reach into rural areas in an effort to boost subscriber and earnings growth. Charter is facing heightened competition from Verizon and T-Mobile’s wireless home internet offerings, and the cable company could soon lose even more subscribers when a key government program runs out of funding in April, JPMorgan analysts say in a research note. In particular, the end of the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), which provided up to $30 per month to eligible customers to put toward their internet bills, could hurt Charter more than its peers. If ACP is not refunded, “we’ll work very hard to keep customers connected,” Winfrey said. Charter has more than 5 million ACP recipients, the highest in the industry. The majority of them were Charter broadband subscribers before the program began.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Charter added 142,000 broadband subs via its rural subsidy program in Q4, for a total of 420,000, and an overall penetration rate of 33.8% – up from 27.2% in the year-ago quarter. The company posted $74 million in rural revenues, up from $39 million a year earlier. Charter pulled in subsidy revenues of $29 million in Q4. Total capex for the project in Q4 was $426 million, down from $567 million in the year-ago quarter. Charter plans to activate 450,000 new subsidized rural passings in 2024. With all programs rolled up, Charter has committed to build 1.75 million subsidized rural passings.
Charter expects to complete its Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) builds by the end of 2026 – two years ahead of schedule. Charter also intends to participate in the much larger $42.45 billion Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program.

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Completion of Charter’s hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) network upgrade has been delayed to 2026 due in part to a lengthier certification process for distributed access architecture (DAA) technology. Charter’s original plan was to complete its HFC upgrades by the end of 2025. Charter’s HFC evolution plan consists of three steps:
- An upgrade to 15% of its network to 1.2GHz with an upstream-enhancing “high-split” using traditional integrated cable modem termination systems (CMTSs). That enables multi-gigabit downstream speeds and upstream speeds up to 1 Gbit/s.
- An upgrade to 1.2GHz with DAA and a virtual CMTS in 50% of the HFC footprint, enabling downstream speeds up to 5 Gbit/s and upstream speeds up to 1 Gbit/s.
- A full DOCSIS 4.0 upgrade by deploying 1.8GHz with DAA and a vCMTS to 35% of the HFC footprint. That’ll put Charter in position to deliver up to 10 Gbit/s downstream and at least 1 Gbit/s upstream.
Speaking on today’s Q4 2023 earnings call, Charter CEO Chris Winfrey said the operator has launched symmetrical speed tiers in two markets (Reno and Rochester, Minnesota, an official confirmed), with deployments in six additional markets underway that, once completed, will fulfill the phase one plan. Charter expects to start DAA deployments in its phase two markets later this year, Winfrey said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Charter added 546,000 mobile lines in Q4, down from a gain of +615,000 in the year-ago quarter and +594,000 in the prior quarter. Analysts were expecting Charter to add 594,000 mobile lines in the 4th quarter and +2.5 million lines for full 2023, up from 1.7 million in full 2022. The MSO ended 2023 with 7.76 million mobile lines. Charter is also expanding its deployment of CBRS spectrum to help the company offload MVNO costs in high-usage areas. Winfrey said “thousands” of CBRS units have been deployed in one “large” market (believed to be Charlotte, North Carolina). Charter expects to roll CBRS to an additional market later this year, he said.
References:
Charter Communications adds broadband subs and raises CAPEX forecast
Precision Optical Technologies (OT) in multi-year “strategic partnership” to upgrade Charter Communications optical network
Charter Communications selects Nokia AirScale to support 5G connectivity for Spectrum Mobile™ customers
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
Comcast Xfinity Communities Wi-Fi vs Charter’s Advanced Wi-Fi for Spectrum Business customers
Dell’Oro: Broadband network equipment spending to drop again in 2024 to ~$16.5 B
Executive Summary:
Operator spending on broadband network equipment will remain sluggish well into 2024, forecasts Dell’Oro’s Jeff Heynen. “Inventory Correction, Inventory Realignment,” or whatever term you prefer to call the root cause of 2023’s broadband spending slowdown will likely persist well into 2024, he wrote. Without the benefit of fourth quarter numbers, total spending on broadband equipment in 2023 is expected to show a decline of around 10%. Early projections for 2024 indicate an additional 5% year-over-year decrease, as the lagging impact of interest rate increases to curb inflation will be felt more acutely. This additional 5% decrease would put total spending to around $16.5 B—roughly equal to 2021 spending levels.
The expected declines in 2023 and 2024 follow three straight years of white-hot growth in broadband network and service investments from 2020 to 2022. During this period, year-over-year growth rates reached 9%, 15%, and 17%, respectively. Similar periods of growth from 2003-2006 and 2010-2014 were both followed by two subsequent years of reduced spending, as operators—particularly in China—shifted their capital expenditure focus from broadband to mobile RAN.
However, there are signs of a return to growth in 2025 as money from BEAD and other broadband subsidy programs trickle down to broadband equipment suppliers. Well before that, pockets of growth in fixed wireless CPE, cable DAA equipment and CPE, and continued spending on PON equipment by tier 2 and tier 3 operators should make the broadband market one in which the headlines might communicate malaise, but a peek under the hood shows clear signs of resilience powering an inevitable return to growth.
Cable Operators Travel Different Paths to Fend off Fixed Wireless and Fiber:
Just like last year, in the minds of cable consumers, cable operators find themselves stuck battling against the perception that they are the provider with inferior copper technology that can’t be flexible when it comes to offering plans that meet a consumer’s budget, like fixed wireless currently can. As a result of this situation, larger cable operators are seeing increased broadband subscriber churn and quarters of net subscriber losses.
Comcast is pushing hard to counter those perceptions and is already offering its X-Class Internet tiers, which offer symmetrical speeds of 2 Gbps in Atlanta, Colorado Springs, and Philadelphia. Additional cities are expected to roll out these service tiers in 2024. Comcast’s use of full-duplex DOCSIS 4.0 (FDX), including brand new CPE using Broadcom’s D4.0 silicon in a two-box configuration. Later this year, we expect to see a combined gateway that also incorporates Wi-Fi 7, as Comcast looks to battle back against FTTH providers by providing the most advanced residential gateway to customers.
Meanwhile, in 2024, Charter’s Remote PHY and vCMTS rollouts will kick into high gear. (At the time of this publication, we are awaiting fourth quarter earnings from both Harmonic and Vecima, the announced RPD partners for Charter’s buildout to determine how much equipment the operator purchased in advance of this significant deployment.) For Charter, which is employing Extended Spectrum DOCSIS 4.0, 2024 will also bring much wider availability of 1.8 GHz amplifiers and taps, as well as a choice of CPE with dedicated silicon for ESD, as well as silicon that combines both FDX and ESD variants.
Charter will likely also announce additional vendors for its upgrade efforts, as the operator has been public about its desire for a multi-vendor environment.
Cox will also begin rolling out 1.8 GHz amplifiers this year but, like Charter, will likely run those at 1.2 GHz until taps and CPE become more widely available.
Meanwhile, for those operators that weren’t part of the initial DOCSIS 4.0 Joint Development Agreement (JDA) with Broadcom (and for some of those who were), DOCSIS 3.1 Plus is quickly becoming an important stopgap measure to help increase throughput within the existing DOCSIS 3.1 framework by leveraging additional OFDM channels. Operators can either use existing integrated CCAP chassis (with either legacy line cards supporting 3 OFDM blocks or newer cards supporting 4 OFDM blocks) or vCMTS platforms. This can be combined with either DOCSIS 4.0 modems or modems designed specifically for D3.1 Plus deployments, which won’t require the additional gain amplifier (and cost) needed for full DOCSIS 4.0.
While it remains to be seen which type of CPE operators deploying DOCSIS 3.1 Plus will move forward with, the fact that there is significant interest in the technology means that there will now be additional operators who will likely move on from DOCSIS 4.0 and instead buy themselves time with DOCSIS 3.1 Plus before moving forward with fiber overbuilds. The biggest question here is just how many operators will do so.
As Light Reading previously reported, Broadcom and MaxLinear are working on new D3.1 chipsets that can beef up downstream capacity and speed through the support of additional OFDM (orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) channels. Some operators are likewise exploring the deployment of new D4.0 modems on their D3.1 networks to achieve similar capacity gains.
That approach could extend the life of DOCSIS 3.1 networks, delay D4.0 upgrades or become an interim step before a future leap to fiber-to-the-premises. But it’s still not clear how many operators will pursue this path.
Heynen expects to see additional FTTH deployments—both greenfield and overbuild—by cable operators around the world. Whether using Remote OLT platforms or more traditional OLT platforms, cable operators will take advantage of work being done at CabeLabs to standardize the integration of ITU-T PON recommendations into existing DOCSIS management frameworks. This will make it far easier for MSOs (aka Cablecos) to deploy XGS-PON, as well as 25GS-PON and, potentially 50G- and 100G-PON.
XGS-PON to Dominate Fiber Spend This Year:
The PON equipment market will be the most dynamic this year, with tier 1 operators besides of BT OpenReach and Deutsche Telekom, all continuing to better align their inventories with anticipated subscriber growth, as well as reduced homes passed goals. For larger tier 1s, the short-term reduction in homes passed goals will ultimately give way to a renewed construction phase beginning in 2025 that should propel the overall PON market through the end of the decade.
But while the tier 1s slow, there will be no slowing the continued efforts by tier 2 and tier 3 operators in both North America and Europe to both upgrade and expand their fiber networks. In fact, the same dynamic that played out in North America in 2023 will likely repeat in 2024, as tier 2, tier 3, utilities, municipalities, and co-ops all continue their buildouts.
The technology beneficiary will be XGS-PON, which already surpassed 2.5 Gbps GPON revenue back in 2022, but will more than double it in 2024. And in markets where operators are beginning to see cable operators deliver symmetric 2 Gbps services, there is a strong chance they will also sprinkle in some 25GS-PON to comfortably deliver symmetric 5-10 Gbps services.
Meanwhile in China, which is expected to show a marked decline in new OLT port shipments in 2023, will likely see another decline until 50G-PON rollouts begin in earnest later this decade. On the flip side, ONT unit shipments in China are expected to increase as FTTR (Fiber to the Room) deployments expand, delivering 2-3 ONTs per home as opposed to the traditional architecture of using a single ONT to terminate fiber.
Wi-Fi 7 Progress Will Accelerate:
With the Wi-Fi Alliance recently announcing the opening of certification testing for Wi-Fi 7 products, don’t be surprised to see dozens of Wi-Fi 7 residential routers and broadband CPE models being deployed by operators by the end of this year. Early gateway models, though pricey, have already been introduced to the market and will become much more widely available this Spring, and then well before the Holiday season. As of our July 2023 forecast, we expect over 2.5 million residential Wi-Fi routers and broadband gateways to ship in 2024, though we are undoubtedly increasing this forecast based on the certification testing opening up.
Operators can’t wait to deploy Wi-Fi 7 products to help differentiate themselves in increasingly crowded broadband markets and to eliminate much of the confusion in the market with the coexistence of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E.
References:
2024 Outlook: Broadband Market Faces Challenge Amidst Lower Spending from 2023
https://www.lightreading.com/broadband/broadband-equipment-spending-to-dip-again-in-2024-dell-oro
Dell’Oro: Broadband Equipment Spending to exceed $120B from 2022 to 2027
MTN Consulting: Top Telco Network Infrastructure (equipment) vendors + revenue growth changes favor cloud service providers
Dell’Oro: U.S. suppliers ~20% of global telecom equipment market; struggling in RAN business
Dell’Oro: Worldwide Telecom Equipment Market Growth +3% in 2022; MTN: +2% Network Infrastructure Growth in 2022
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
According to a senior executive, ZTE Corp has seen “tremendous” opportunities due to the increased demand for high-speed internet and smart home solutions globally following the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s despite a slower-than-expected development of 5G outside of China.
“Deployment of 5G technology in overseas markets has been slower than what we previously thought and investments in the field have also lagged behind,” said Chen Zhiping, vice-president of ZTE Corp.
“However, we have seen rapid growth of two sectors in our business – fixed broadband and home network solutions – internationally, especially in the Latin American market.”

The COVID-19 pandemic has pushed up demand for these two types of businesses, as people who were confined to their homes became more reliant on high-speed internet connections and home automation, she said.
“We are actively promoting these two areas of business in Latin America. Besides, the Asia-Pacific region is also where we put great focus on, such as Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand, as the region has a huge demand for network convergence, network modernization and digitalization,” Chen said.
The Asia-Pacific region is a market from which the company generates most of its overseas revenue, she added.
ZTE posted 60.7 billion yuan ($8.36 billion) in operating revenue in the first half of the year, up 1.5 percent from the year-ago period, according to its interim results announced on Aug 18. Of the total, 17.6 billion yuan, or 29 percent, came from international markets.
Net profit grew 19.9 percent on a yearly basis to 5.47 billion yuan.
“Exploring the domestic market is far from enough for a technology company, whether it is research and development or marketing. We have been committed to the international markets and promoting the globalization of research and development, supply chain and collaboration all along,” she said.
Chen acknowledged that factors such as geopolitical tensions, economic slowdown and a deteriorating business environment in some countries have posed serious challenges to ZTE‘s operations in overseas markets. She stressed that the company had established a sound system of management as well as risk identification and control to deal with potential risks.
On November 225, 2022, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) voted unanimously to ban U.S. sales of new Chinese telecommunications equipment and devices produced by Huawei and ZTE—as well as to restrict the use of other Chinese-made video surveillance equipment—over national security concerns. The Chinese companies have denied the allegations.
According to a report by German market intelligence platform Statista, the global ICT market is expected to reach $6 trillion in 2023, up from $5.5 trillion last year. China would rank third in global market share with over 11%, following the United States and European Union (EU).
References:
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202309/02/WS64f26e23a310d2dce4bb384f.html