Month: December 2018
India 5G Delayed due to spectrum sale and lack of fiber connectivity
The Indian government expects initial “5G” rollouts by late 2020. But sector experts say the country is running late and could be at least three years behind South Korea, Japan, Australia, the US, China, France and Germany in rolling out 5G networks. Pre IMT 2020 standard 5G services are likely to be rolled out in those markets by late 2019 or early 2020.
Some of the key reasons why India is slipping behind in 5G – after having missed the 3G and 4G early adoption train – include dismal state of fiber network infrastructure (needed for backhaul), absence of relevant use-cases and a very modest presence of household electronics plugged into the Internet.
Financial stress in the industry and a missing handset/mobile device ecosystem have already delayed a 5G spectrum sale to late 2019.
Further, high debt levels and the prospect of high reserve prices could further kill the appetite of telcos even when 5G airwaves are auctioned, especially for older carriers such as Vodafone Idea and Bharti Airtel, whose India operations remain in the red, say experts.
Problems related to setting up and maintaining fiber networks and poor 4G Internet availability in the villages and small towns, they say, could further scale down the business case for early 5G rollouts in India. 5G smartphones won’t come to India before 2020, although they will be available in early adopter markets next year (again, pre-standard and likely based on 3GPP release 15 5G NR).
Sunil Mittal-led Bharti Airtel said recently that the current wave of popular 5G use-cases such as “driverless cars to remote surgery are not practical in the Indian context,” which is why it expects deployments are four years away. He also said the company is in no hurry to bid for 5G spectrum.
Experts say a major deterrent to India’s 5G ambitions is lack of adequate fiber connectivity – less than 20% of the country’s telecom towers are linked by fiber. This can limit the capacity to connect the core of a mobile network to nodes and then on to towers for transmitting data. A reliable fiber-based network is critical to support 5G data speeds of 10 Gbps and next-gen applications such as video-on-demand and internet of things (IoT) to smart cities.
“If 5G is to succeed in India, at least 70-80% of mobile towers will have to be fiberised, failing which, severe data speed limitations will continue as present backhaul networks in India use microwave spectrum,” says TR Dua, director general of Tower & Infrastructure Providers Association, an industry grouping representing Indus Towers, Bharti Infratel, American Tower Corporation, GTL, Reliance Infratel and Tower Vision.
TV Ramachandran, president of the Broadband India Forum, agrees, saying, “Most 5G use-cases would fall if we don’t provide strong fibre connectivity.” The forum counts Huawei, Qualcomm, Facebook, Google, Microsoft, Hughes and Intel among its members.
In comparison to India, China already has 75-80% of its mobile towers fiberised.
Moody’s Investors Service expects China to commercially deploy 5G services in late-2019 or by 2020, with pilot trials already under way. The Chinese government allocated 5G spectrum this month to the country’s top 3 telcos – China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom – to conduct field trials in the run-up to the commercial rollout of 5G services.
By contrast, India’s telecom department said that the 5G spectrum sale would take place in the secondhalf of 2019. It though recently invited telcos, equipment vendors and other stakeholders to partner with the government for 5G trials. Sources say trials are still some time away.
Nitin Soni, director (corporates) at global rating company Fitch, does not expect 5G to arrive in India before 2022 at the earliest because the telecom industry balance sheet – saddled with Rs 7 lakh crore in debt – is in no shape to support a 5G spectrum sale in the next one year.
“Even if 5G spectrum is auctioned by late-2019, I don’t foresee enthusiastic bidding, especially if reserve prices are high as older carriers are still struggling. Besides, India is nowhere near having ubiquitous fibre connectivity or a devices ecosystem comparable with China or Korea, which could delay 5G rollouts by another three years,” says the Singapore-based Fitch director.
Rajan Mathews, director general of the Cellular Operators Association of India, which represents Vodafone Idea, Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio Infocomm, says the primary reason South Korea, Germany, Japan or the UK have been able to brace for 5G early is due to the strong “financial condition of their telecom operators.”
The reserve price of 5G spectrum recommended by India’s telecom regulator, he said, “is much higher compared to Germany, South Korea or UK.”
In August, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai) set Rs 492 crore per unit as the minimum rate for 5G spectrum (in the 3.4-3.5 GHz bands), compared with Rs 131 crore per unit and Rs 66 crore per unit in South Korea and the UK, respectively.
A key global learning, Rajan says, is “pricing the spectrum at reasonable rates” to allow telcos to bid aggressively and roll out 5G services.
Fitch’s Soni says China has stolen a march over India as “it’s streets ahead in developing data-intensive 5G content coupled with music, movie and sport apps in regional languages,” which is slated to drive consumption once 5G services get rolled out there.
Experts also say that unlike India, China already has a buzzing internet of things ecosystem, wherein cars, machines and ordinary home appliances are plugged to the internet, providing the perfect springboard for 5G to rapidly gain traction.
The Modi government, though, doesn’t want India to miss the 5G bus – like the country did on 3G and 4G – as the economic impact alone of this superfast wireless broadband technology is estimated at over $1 trillion by 2035.
The government has set up a highpowered 5G Forum to advise on the path forward, which has suggested that most rules on regulatory matters be promulgated by next March to pave the way for early rollouts.
US chipmaker Qualcomm has downplayed concerns around 5G ecosystem challenges, saying that although the global infrastructure ecosystem is diverse, the vendors overseas and in India are the same.
“Different countries are at different stages of mass deployment of fibre and so on,” says Durga Malladi, senior vice president, Engineering & GM (4G/5G), at Qualcomm Technologies.
Reference:
Addendum:
Reliance Jio president Mathew Oommen told ETTelecom: “For service providers, just voice or even traditional data revenue alone is not going to be the cure. They have to invest and innovate so that they would not get displaced by other aggressive providers or more importantly by OTT companies.”
India telecom market leader Reliance Jio, second ranked Bharti Airtel and financially stressed Vodafone Idea (Vi) have filed applications for participation in the upcoming 4G spectrum auctions, due to start on March 1. The auction for over 2300 MHz of airwaves—valued at Rs 3.92 lakh crore at base price—though is likely to see limited bidding intensity for spectrum worth less than Rs 48,000 crore, with Jio and Airtel expected to be the main players. Industry executives have confirmed to ET that the three telcos have filed in their applications although Airtel, Jio and Vi did not respond to ET’s queries.
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/jio-airtel-vodafone-idea-apply-to-bid-in-spectrum-auctions/80769608
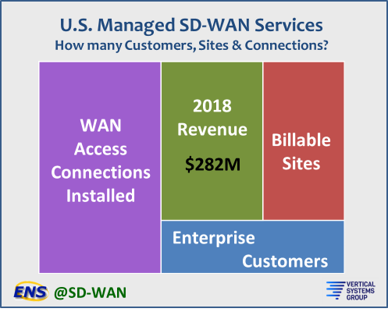
SD-WAN Market to Grow in 2019 with Managed Services Leading the Charge
The managed SD-WAN services market is expected to generate more than $282 million in revenue in the U.S. by the close of 2018, according to researcher Vertical Systems Group. The figure is based on billable U.S. customer sites and WAN access connections installed and under management. Rick Malone, principal of Vertical Systems Group, said he expects a major boost in revenue next year with network operators fully ramped up to sell, deliver and support managed SD-WAN services.
A managed SD-WAN service is defined as a carrier-grade network offering for enterprise and business customers, which is managed by a network operator, and delivered over a software-defined network (SDN) service architecture that has separate control (overlay) and data (underlay) planes, according to MEF.
Service providers currently selling managed SD-WAN services in the U.S. include: Aryaka, AT&T, CenturyLink, Cogent, Comcast, Fusion Connect, GTT, Hughes, Masergy, MetTel, Sprint, Verizon, Windstream and Zayo by Vertical’s count. Other network operators both domestic and foreign are expected to enter the U.S. market, which will grow the segment’s size, Vertical said.
While the managed SD-WAN services market in the U.S. is small, it began to pick up steam in the last half of 2018, said Malone. “Carrier-grade managed SD-WAN services in the U.S. began to generate notable revenue in the second half of 2018,” he said.
One main reason the market’s revenue is small is because money is new to it. However, SD-WAN has proved to be more complex than customers previously believed. “Prior to this, most providers supported customers with pilot SD-WAN services that were not substantively monetized,” Malone said. “A key driver for managed services is the growing appreciation that migration to SD-WAN is considerably more complex than the promise of ‘easily deployed’ plug-and-play DIY solutions.”
“In 2019, we’ll continue to see SD-WAN as a key enabler for enterprise customers’ digital transformations. The integration between MPLS and internet, combined with the move to cloud, requires a different network and security design – particularly on a global scale. With SD-WAN, enterprises can address these requirements and introduce automation to make networks even more efficient. Future-proof solutions with simple interfaces, like Flexible SD-WAN from Orange, enable enterprises to use their networks dynamically to anticipate and respond to changes in their business environments while migrating applications to the cloud.” Rob Willcock, senior vice president, Americas, Orange Business Services.
In 2018, Cisco integrated its Viptela SD-WAN, which is bought in 2017 for $610 billion, more deeply across its enterprise routing platform. Also this year, VMware integrated VeloCloud’s SD-WAN technologies—which it bought last year for an undisclosed sum, into its product lines. Both acquisitions have turned out to be solid moves. Oracle is looking to duplicate Cisco and VMware’s successes next year after buying buying Talari Networks , also for an undisclosed sum, this year.
While some of the current SD-WAN vendors will fall by the wayside next year, others will be bought by companies that serve the enterprise and business sectors. Oracle, Cisco and VMWare?Dell bought such SD WAN start ups in 2018.
Another trend that will likely continue into 2019 is more firewall vendors entering the SD-WAN market. In 2018, Fortinet and WatchGuard Technologies moved from supplying security to SD-WAN vendors to offering their own flavors of it.
There will likely be more partnerships between SD WAN vendors and cloud providers, similar to the deal that Versa Networks did with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to offer SD-WAN to AWS partners. Citrix and Riverbed also announced availability of their SD-WAN offerings on Microsoft Azure cloud and AWS in 2018.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Vertical Systems has launched a new research service covering the carrier-based managed SD-WAN services market, focusing on service migration, network connectivity and market sizing. The research content it offers at this time spans managed SD-WAN purchase drivers, customers, WAN access connections, site configuration profiles, pricing and revenue.
At this point, SD-WAN research is a “moving target,” said Erin Dunne, Vertical’s research services director, in a video. “First of all the issue is definition. There’s no true definition out there. We pride ourselves on being able to lay out definitions that are from a market perspective — what service providers are selling and what enterprise, or business customers, are buying or what they want to buy.”
According to Vertical, managed SD-WAN services are a carrier-grade network offering for enterprise and business customers, managed by a network operator, and delivered over a software defined network service architecture that has separate control and data planes. Not included in this analysis are do-it-yourself SD-WAN solutions purchased directly from an SD-WAN technology supplier or a systems integrator.
STATFlash: Managed SD-WAN Services Market Tops $282 Million in the U.S.
2021 Commercial 5G pilots in India; Cisco #1 in India Network Equipment
Commercial 5G pilot networks in India are expected by 2021. Upstart wireless network operator Reliance Jio has the advantage to transform its telecom network to offer newer technology, said a Cisco Systems top executive responsible for the APAC region.
“By 2021, India should finally see 5G commercial pilots,” Cisco Head of Asia Pacific & Japan – Service Provider Business Sanjay Kaul told ETT, adding that most of the country’s service providers were already on the journey towards 5G.
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has already asked equipment vendors— Cisco, Samsung, Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia— to partner with India service providers Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea and state-run Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) to start 5G-based field trials as early as January 2019 and demonstrate India-specific use cases to smoothe commercial rollouts.
Cisco has enabled the Mumbai-based Reliance Jio to foray into the fourth generation (4G) technology-based voice over long-term evolution (VoLTE) services in September 2016, and the two companies are currently working together to develop content delivery through the cloud in a lower latency environment— a key 5G feature.
“Jio has an advantage with its greenfield network while others like Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea and even BSNL are transforming their network at a rapid pace,” Kaul said.
Earlier, billionaire Mukesh Ambani-controlled Reliance Jio has said that it could launch 5G services within the few months after acquiring the required spectrum. Kaul believes that Reliance Jio and other telco incumbents would launch 5G-based digital services as the India government makes spectrum available at a cost bearable to the industry.
Cisco said that in a 5G environment, telecom networks network would truly become a service platform, and digital services uniquely crafted for small-and-mid-sized companies and consumers would help telcos to monetise their investments in network transformation and data center architecture.
“5G technology and architecture will truly provide service provider another opportunity to evolve from being a communication service provider to a true digital value player,” the Cisco executive added.
Jio also feels that telecom service operators should innovate to become a digital player in a competitive landscape.
4G and 5G networks would co-exist, according to Kaul, who attributed 4G for mass adoption of data and social networks, and added that 5G technology, unlike 3G and 4G, has technical features like low latency and high density.
Kaul believes that 4G is progressing with full throttle, and in a year’s time, it would be closer to 90% penetration in the country.
The incumbents— Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea are investing to make 4G networks widespread while the youngest telecom player Jio that has built next-generation all-IP data network, has already penetrated more than 90% of the country. The public-sector BSNL is yet to get 4G spectrum from the government to compete with rivals.
“We have covered 90% of the Indian population with 4G, and we’ll soon reach to 99% of the country,” Jio president Mathew Oommen said.
“4G is showing good results, and I think all operators are really going for country-wide coverage and are accelerating their efforts,” Kaul said, adding that the time for 5G has arrived in the country.
The department has said that it would be ready to hold mega airwaves sale including frequencies in the 3300-3600 Mhz range, used to offer high-speed 5G services, in the second half of 2019.
The Narendra Modi-led NDA government is banking on the newer technology with the telecom department setting up a high-level 5G Forum to oversee 5G roadmap and rollout of services in tandem with matured markets worldwide.
The company feels that the newer technology would be unique in terms of creating and enabling mission-critical applications in various vertical domains such as transport, healthcare, finance, and security.
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/commercial-5g-pilots-in-2021-cisco/67254020
………………………………………………………………………………
Cisco Systems has emerged as a leader in India’s network equipment market with a clear lead over rivals such as Nokia and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) in the Ethernet, router and wireless local area network (WLAN) segments in the third quarter of 2018, according to an International Data Corporation (IDC) market research report.
“Cisco continues to dominate the Ethernet Switch market with a 65.7% share in Q3 2018, followed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Huawei,” IDC said, adding that Cisco accounted three-fourth of the router market in the same quarter.
With 65.7% market share, Cisco took a huge lead over Hewlett Packard Enterprise (6.7%), Huawei (3.3%) and Nokia (2.8%) in the Ethernet Switch market in the quarter.
According to IDC’s latest Asia/Pacific Quarterly Ethernet Switch Tracker, the Q3 2018 Ethernet Switch market in India stood at USD 160.3 million (by vendor revenue) with an excellent YoY growth of 34.4%.
ADC and Layer 3 categories predominantly drove the overall growth with high double-digit individual YoY rise, while Layer 2 also saw a YoY growth, though only marginal. The India government’s push towards digitalization through upgrade of public infrastructure and multiple smart city initiatives; telecom infrastructure modernization drives and banking sector’s continual investment in network infrastructure to improve customer experience, is expected to drive growth in the coming quarters. The router market in India reached $214.9 million with an exceptional year-on-year growth of 140.4%.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The San Jose, CA based company also dominated the router segment with 75% share, while Nokia (11.2%), Huawei (7%) and Juniper (5.5%) trailed behind in Q3 2018.
Cisco has retained the top spot in the WLAN market with a 24.8% market share in Q3 2018, followed by TP-Link (17.3%) and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (15.3%).
“The Ethernet switch, router, and WLAN market are expected to grow in single digits in terms of compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for 2017-2022,” IDC said in a statement.
“Software-defined networking solutions are expected to gain prominence as the enterprise infrastructure evolves from human-dependent systems to self-servicing, fully automated and seamlessly integrated systems,” Ranganath Sadasiva, Director— Enterprise at IDC India said.
The market research firm, however, believes that government and enterprise digitalization initiatives would be expected to drive growth across product categories.
“Mobile workforce, anytime anywhere access to enterprise networks, security across multiple channels and shift towards cloud-based application workload are key drivers for investment in network infrastructure,” Dileep Nadimpalli, Research Manager— Storage at IDC India said.
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prAP44587818
Thailand to start 5G trial in January 2019; KT deploys 5G-based barista robot in Korea
- Thailand 5G Trials
a] AIS has become the first mobile phone network operator in Thailand to commence 5G technology testing in Thailand, including making it available for trial at “5G the First LIVE in Thailand by AIS” in collaboration with global partners Nokia, Huawei and ZTE Corporation.
“AIS is all about developing and providing the best digital infrastructure for Thailand,” explains Weerawat Kiattipongthaworn, Chief Corporate Officer.
“As operator of the biggest spectrum, 120 MHz, our educational initiatives, research & development, and new technologies create value and benefits for everyone.”
“5G is going to create new recreational and business opportunities and considerably enhance socio-economic potential.”

The first “5G the First Live in Thailand by AIS” event showcased five 5G-enabled innovative features:
• 5G Super Speed showcasing the performance of the 5G network including total throughput and latency.
• 5G Ultra Low Latency demonstrating the latency of 5G using three robots to find a balancing point that controls the position of a ball position in the middle of a board. The time difference to achieve balance between 4G and 5G technology will be clear.
• 5G for Industry 4.0 demonstrating the role robots will play in Industry 4.0. The collaborative work of machines from various production lines requires wireless connection with low latency and high reliability. This speeds up production lines and makes them more flexible and efficient. Meanwhile, ABB’s Yumi Dual-Arm Collaborative Robot will demonstrate how connectivity through a 5G network can enhance production efficiency.
• 5G Virtual Reality immersive video via 5G network enabling VR headsets so people can see what a 360° virtual reality experience is really like. Clear VR viewing requires the very high bandwidth that only 5G can provide, especially for live streaming.
• 5G FIFA Virtual Reality will test 5G speed against virtual soccer penalty kicks.
https://www.bangkokpost.com/business/news/1580894/ais-leads-the-way-with-5g-in-thailand
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
b] Thailand’s Digital Economy and Society (DE) Ministry plans to begin the trial for the 5G testbed in the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) in January 2019, according to the Bangkok Post which cites DE Minister Pichet Durongkaveroj. This move will prepare the country for 5G adoption by 2020. Initially focusing on transport, healthcare and tourism, the 5G trial will feature the recently announced alliance of private firms and state agencies, including Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, Qualcomm, Intel, Nokia, major telecom operators, the Thai Federation of ICT Technology Association, and the National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC).The NBTC was asked to provide spectrum ranges for the 5G testbed in the EEC, particularly 3,500MHz and 26-28GHz. The alliance’s representatives are members of the working committee on the 5G testbed set up on Oct 31.
The DE Ministry said it’s looking for potential 5G developers to cooperate in the 5G alliance’s trial.
The 5G testbed’s lab in Sri Racha district is just 1.5 kilometres from Thailand’s first digital innovation park in Chon Buri province. The 5G sites and lab will be at the science faculty, Kasetsart University Sriracha Campus. The DE Ministry’s project runs in parallel with the NBTC’s 5G test centre in Bangkok under a partnership with Chulalongkorn University.
2. KT deploys 5G-based barista robot at Gangnam cafe – new use case for 5G?
South Korean network operator KT (Korea Telecom) has applied 5G network technology to a barista robot at an unmanned cafe near Gangnam Station in southern Seoul, The Korea Times reports, citing a company statement. At the ‘Beat’ café operated by local coffee franchise dal.komm, a robot barista takes orders and serves customers drinks and coffee. KT installed a 5G mobile hotspot in the coffee shop so that the robot can receive 5G signals from base stations.
“The 5G network in the cafe is used to send the status of the robot and high-quality CCTV to the control tower 24 hours a day”, said a KT representative. “With the CCTV equipped inside the robot, the robot also recognizes visitors to the coffee shop and sends video footage of the inside of the shop to the manager”, the KT representative added.
“The 5G barista cafe is the world’s first 5G robot cafe to offer real 5G service”, said Park Hyun-jin, head of KT’s 5G business division. KT will also provide the robot with voice recognition and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. With these features, customers will be able to make voice orders and receive more customized service through the AI technology, KT added.
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/kt-deploys-5g-based-barista-robot-at-gangnam-cafe–1274554

The 5G testbed lab in Sri Racha district is just 1.5 kilometres from Thailand’s first digital innovation park in Chon Buri province. The 5G sites and lab will be at the science faculty, Kasetsart University Sriracha Campus.
Telia, TalTech, Ericsson launch pilot 5G network in Tallinn, Estonia
Nordic network operator Telia, in cooperation with Ericsson and Tallinn University of Technology (TalTech), has launched a pilot 5G network in Tallinn. Estonia’s first 5G pilot network is located throught the TalTech university campus. Companies and startups have been invited to use the 5G network to develop future services and new business models.
The network will provide mobile data for the whole TalTech campus, which enables the development of innovative new services and solutions, Telia said.
Kirke Saar, CTO at Telia Estonia, says this marks the launch of the fifth-generation mobile technology in Estonia.
“We hope to see new and exciting future services and business models built upon 5G. Thus, different stakeholders are welcome to test the possibilities of the new technology at the TalTech University. It is the perfect place for this, combining technical knowledge, smart people and cooperation experiences with very different partners. Additionally, 5G technology supports our newly opened NB-IoT network which now has its first commercial user,“ Kirke Saar said.
The Rector of TalTech –Jaak Aaviksoo sees 5G a brave step into the unknown.
“It´ll open limitless opportunities for communication in a virtual world. TalTech, Telia and Ericsson take this step together because we believe in the creativity of both scientists and students in using this platform and generating new ideas. 5G means a thousand steps into the future for the whole Estonia.”
Andrus Durejko, Head of Ericsson Estonia, said:
“The launch of a 5G network in Estonia using commercial and standardized radio and core products serves as an important step toward launching early commercial 5G services in the country. Building a 5G network in one of Estonia’s most creative environments, TalTech campus, demonstrates Ericsson’s and Telia Company’s joint commitment to drive innovation and the continued digitalization of Estonia.”
4K live-stream milestone
Today at the network inauguation, the newly opened 5G network performed its first official task: 5G base stations installed on the university campus transmitted 4K live stream from the Tallinn Old Town Christmas market, recently voted the best in Europe.
“As far as we know, up until now, 4K has never been transmitted live in Estonia or its neighboring countries, and our 5G network did an excellent job on transmitting the stream,“ Kirke Saar said.
Telia’s CTO also said that Telia is planning and working on opening 5G for residential customers next year.
TalTech has built a self-driving car named Iseauto, which will become one of the first cooperation projects within the 5G pilot’s scope. The next milestone will come in 2019, when the project partners will showcase Iseauto driving around and communicating with the surrounding infrastructure with the help of 5G.
https://www.teliacompany.com/en/news/news-articles/2018/estonias-first-5g-network-goes-live/
Editor’s Note:
Earlier this month, Telia Company, Ericsson and KTH Royal Institute of Technology launched a 5G network on the KTH campus in Stockholm that will serve as an innovation and research platform for the academia and partner companies.

- Ericsson, Telia Company and KTH Royal Institute of Technology launched a 5G network on the KTH campus in Stockholm
- First 5G network on air in Sweden based on standardized and commercial radio and core products
- Testbed for innovation and research open for industry partners and academia
Point Topic: Global fixed broadband take-up & forecasts to 2025 + Rethink TV: China to lead in gigabit broadband services
1. Point topic – FTTH/FTTP/FTTB:
Market research firm Point Topic predicts that 59% of broadband subscribers worldwide will be served by fiber to the home/premises/building (FTTH/FTTP/FTTB) by the end of 2025. That represents an 11% jump from current levels. Please see Rethink TV’s findings below, which corroborate the rise of fiber access based broadband network access.
Point Topic forecasts that there will be 1.2 billion fixed broadband subscribers worldwide by the end of 2025. Broadband subscriber totals exceeded 1 billion in the third quarter of this year, the market research firm points out. Approximately 89% of these subscribers reside in one of the top 30 markets as defined by subscriber numbers recorded in this year’s second quarter.
Within these markets, FTTH and related options will grab market share primarily from xDSL, which should decline 19% to 9% during the forecast period. While overall subscriber numbers for fiber to the curb (FTTC) and VDSL, as well as DOCSIS-based hybrid fiber/coax (HFC), should climb during the forecast window, market share will remain fairly stable. FTTC will account for approximately 12% of connections, while HFC will check in at 19%, the researchers estimate.

While legacy copper networks have been losing customers to more advanced technologies for years. It looks like direct fibre networks will attract the majority of new customers, with DSL figures forecast to drop to hundreds or tens of thousands in most technologically advanced markets.
However, one cannot completely discount FTTC/VDSL and cable platforms, preferred by some operators, and especially their more advanced versions such as G.fast and Docsis 3.1 which are capable of gigabit speeds. We have seen their deployment gather pace in certain regions of the world (see their latest map).

The advent of 5G should have a dampening effect on fixed broadband in the forecast period, according to Point Topic. They are awaiting data from the field as 5G service is rolled out before predicting how much of an impact that market will have on fixed broadband.
The forecasts include data for the top 30 fixed broadband markets and the rest of the world. Point Topic has based them on historical data on fixed broadband take up. The forecasts include trends in subscriber churn for various broadband technologies, the size of the addressable market at country level, and current and planned network upgrades.
http://point-topic.com/free-analysis/fixed-broadband-take-up-forecasts/
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Point Topic’s most recent outputs put the total number of global fixed line broadband subscribers at 983 million at the end of June. Current adoption rates mean that the billionth broadband line appeared in September 2018, probably in China they say.
Technologies rarely manage to spread through the world so quickly, in only twenty years more than half the households in the world have a fixed broadband line.
http://point-topic.com/billion-lines-fixed-broadband-half-world/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. Rethink TV – China to lead in gigabit broadband:
A recent report from Rethink TV, the video research arm of Rethink Technology Research, says that “in advanced countries such as France, Switzerland and South Korea, more than 50% of households will take 1Gbps broadband by 2023.” Rethink TV says that 57% of the world’s 1Gbps connections installed by 2023 will be in China. Over 42% of all Chinese homes will have access to 1Gbps services, thanks to “a series of massive build-outs led by China Mobile.” Rethink CEO and co-founder Peter White, says that China will have 191 million homes connected to 1Gbps by 2023, leading the world market. Japan will have 19.4 million and South Korea will have 9.5 million 1Gbps homes. Today, China is already substantially in the lead with 18.8 1 Gbps lines, with France on 4 million, Japan on 3.8 million and the US on 3 million.
In sharp contrast, only 11% of North America households will have 1Gbps connections by 2023 (see map) – even though the US, at 33.5 million households, will be the second largest market behind China.
“Gigabit broadband will accelerate faster than previous forecasts have imagined, growing tenfold over the next five years,” said Rethink. “After a two-year period of being high priced luxuries, 1Gbps broadband will become commonplace and inexpensive.”
Fiber optics based network access will take over in most parts of the world from copper-based technologies such as G.fast, except in the US, where cable TV networks will rely on DOCSIS 3.1. “Laggards in percentage terms will include the United Kingdom and Germany and much of Latin America,” said Rethink.
https://rethinkresearch.biz/report/gigabit-broadband-forecast-to-2023/
Point Topic: Global fixed broadband take-up & forecasts to 2025 + Rethink TV: China to lead in gigabit broadband services
1. Point topic – FTTH/FTTP/FTTB:
Market research firm Point Topic predicts that 59% of broadband subscribers worldwide will be served by fiber to the home/premises/building (FTTH/FTTP/FTTB) by the end of 2025. That represents an 11% jump from current levels. Please see Rethink TV’s findings below, which corroborate the rise of fiber access based broadband network access.
Point Topic forecasts that there will be 1.2 billion fixed broadband subscribers worldwide by the end of 2025. Broadband subscriber totals exceeded 1 billion in the third quarter of this year, the market research firm points out. Approximately 89% of these subscribers reside in one of the top 30 markets as defined by subscriber numbers recorded in this year’s second quarter.
Within these markets, FTTH and related options will grab market share primarily from xDSL, which should decline 19% to 9% during the forecast period. While overall subscriber numbers for fiber to the curb (FTTC) and VDSL, as well as DOCSIS-based hybrid fiber/coax (HFC), should climb during the forecast window, market share will remain fairly stable. FTTC will account for approximately 12% of connections, while HFC will check in at 19%, the researchers estimate.

While legacy copper networks have been losing customers to more advanced technologies for years. It looks like direct fibre networks will attract the majority of new customers, with DSL figures forecast to drop to hundreds or tens of thousands in most technologically advanced markets.
However, one cannot completely discount FTTC/VDSL and cable platforms, preferred by some operators, and especially their more advanced versions such as G.fast and Docsis 3.1 which are capable of gigabit speeds. We have seen their deployment gather pace in certain regions of the world (see their latest map).

The advent of 5G should have a dampening effect on fixed broadband in the forecast period, according to Point Topic. They are awaiting data from the field as 5G service is rolled out before predicting how much of an impact that market will have on fixed broadband.
The forecasts include data for the top 30 fixed broadband markets and the rest of the world. Point Topic has based them on historical data on fixed broadband take up. The forecasts include trends in subscriber churn for various broadband technologies, the size of the addressable market at country level, and current and planned network upgrades.
http://point-topic.com/free-analysis/fixed-broadband-take-up-forecasts/
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Point Topic’s most recent outputs put the total number of global fixed line broadband subscribers at 983 million at the end of June. Current adoption rates mean that the billionth broadband line appeared in September 2018, probably in China they say.
Technologies rarely manage to spread through the world so quickly, in only twenty years more than half the households in the world have a fixed broadband line.
http://point-topic.com/billion-lines-fixed-broadband-half-world/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. Rethink TV – China to lead in gigabit broadband:
A recent report from Rethink TV, the video research arm of Rethink Technology Research, says that “in advanced countries such as France, Switzerland and South Korea, more than 50% of households will take 1Gbps broadband by 2023.” Rethink TV says that 57% of the world’s 1Gbps connections installed by 2023 will be in China. Over 42% of all Chinese homes will have access to 1Gbps services, thanks to “a series of massive build-outs led by China Mobile.” Rethink CEO and co-founder Peter White, says that China will have 191 million homes connected to 1Gbps by 2023, leading the world market. Japan will have 19.4 million and South Korea will have 9.5 million 1Gbps homes. Today, China is already substantially in the lead with 18.8 1 Gbps lines, with France on 4 million, Japan on 3.8 million and the US on 3 million.
In sharp contrast, only 11% of North America households will have 1Gbps connections by 2023 (see map) – even though the US, at 33.5 million households, will be the second largest market behind China.
“Gigabit broadband will accelerate faster than previous forecasts have imagined, growing tenfold over the next five years,” said Rethink. “After a two-year period of being high priced luxuries, 1Gbps broadband will become commonplace and inexpensive.”
Fiber optics based network access will take over in most parts of the world from copper-based technologies such as G.fast, except in the US, where cable TV networks will rely on DOCSIS 3.1. “Laggards in percentage terms will include the United Kingdom and Germany and much of Latin America,” said Rethink.
https://rethinkresearch.biz/report/gigabit-broadband-forecast-to-2023/
Mexico’s Federal Telecommunications Institute (IFT) makes 600MHz band available for 5G services-AT&T or Telcel?
International Law Office (subscription required):
In October 2018, after relocating more than 200 TV channels, Mexico’s Federal Telecommunications Institute (IFT) approved the relocation of the last two TV channels that transmitted in the 600MHz band in order to free it up for 5G broadband services. In doing so, Mexico became the first country to finish implementing this transition and liberate the 600MHz band.
This transition will enable Mexico to make the 600MHz band available to the market through a bidding process and exploit international mobile telecoms (IMT) applications for 5G mobile broadband services. It is anticipated that the 600MHz band auction will be launched in 2020 so that the deployment of the network can commence in 2021.

Mexico had already successfully switched off the 700MHz band for analogue TV in November 2015. In such band, the government implemented the Red Compartida (or Shared Network) project through a public-private partnership in order to:
- provide broadband in areas that lacked coverage;
- improve service quality;
- reduce the price of mobile services;
- promote competitiveness; and
- improve digital service innovation.
The auction was won by Altán Redes, a new joint venture responsible for the design, implementation, operation and maintenance of the Red Compartida.
In addition, in 2018 the IFT conducted a bidding procedure in which it allocated 120MHz of the 2.5GHz band in favour of AT&T and Telefonica.
In light of the above, Mexico has allocated 584MHz to IMT, which represents 44.9% of the International Telecommunications Unit recommended spectrum allocation for 2015.
With the future auction of the 600MHz band, the IFT will take the lead in providing more spectrum for telephony and 5G mobile internet services. This is in line with the spectral policy, which has allocated more than double the amount of spectrum to the market over the past five years, resulting in greater benefits for Mexican users.
In addition, the IFT is considering using the 3.3GHz to 3.6GHz band for 5G technology, as some companies are already using this band for such purposes.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
With this, Mexico becomes the first country in the world to completely dislodge the frequencies from 614 to 698 Mhz to start testing the 5G network.
AT&T will likely be the first operator to deploy its 5G network in Mexicoo (at some point next year). Telcel would follow closely with the launch of its own technology a year later, in 2020 . The reality is that there is still a lot of work to be done , but apparently Mexico is on the right track.
In Xataka Mexico | 5G, everything you need to know about the new generation of mobile networks
References:
Mexico’s Federal Telecommunications Institute (IFT) makes 600MHz band available for 5G services-AT&T or Telcel?
International Law Office (subscription required):
In October 2018, after relocating more than 200 TV channels, Mexico’s Federal Telecommunications Institute (IFT) approved the relocation of the last two TV channels that transmitted in the 600MHz band in order to free it up for 5G broadband services. In doing so, Mexico became the first country to finish implementing this transition and liberate the 600MHz band.
This transition will enable Mexico to make the 600MHz band available to the market through a bidding process and exploit international mobile telecoms (IMT) applications for 5G mobile broadband services. It is anticipated that the 600MHz band auction will be launched in 2020 so that the deployment of the network can commence in 2021.

Mexico had already successfully switched off the 700MHz band for analogue TV in November 2015. In such band, the government implemented the Red Compartida (or Shared Network) project through a public-private partnership in order to:
- provide broadband in areas that lacked coverage;
- improve service quality;
- reduce the price of mobile services;
- promote competitiveness; and
- improve digital service innovation.
The auction was won by Altán Redes, a new joint venture responsible for the design, implementation, operation and maintenance of the Red Compartida.
In addition, in 2018 the IFT conducted a bidding procedure in which it allocated 120MHz of the 2.5GHz band in favour of AT&T and Telefonica.
In light of the above, Mexico has allocated 584MHz to IMT, which represents 44.9% of the International Telecommunications Unit recommended spectrum allocation for 2015.
With the future auction of the 600MHz band, the IFT will take the lead in providing more spectrum for telephony and 5G mobile internet services. This is in line with the spectral policy, which has allocated more than double the amount of spectrum to the market over the past five years, resulting in greater benefits for Mexican users.
In addition, the IFT is considering using the 3.3GHz to 3.6GHz band for 5G technology, as some companies are already using this band for such purposes.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
With this, Mexico becomes the first country in the world to completely dislodge the frequencies from 614 to 698 Mhz to start testing the 5G network.
AT&T will likely be the first operator to deploy its 5G network in Mexicoo (at some point next year). Telcel would follow closely with the launch of its own technology a year later, in 2020 . The reality is that there is still a lot of work to be done , but apparently Mexico is on the right track.
In Xataka Mexico | 5G, everything you need to know about the new generation of mobile networks
References:
AT&T to deploy live mobile “5G” in the U.S. on Dec. 21st, but limited to single WiFi hotspot endpoint
Whew! I don’t have to hold my breath any longer! But is it really 5G? And whom other than stadiums/parks will buy it with only a single end device offered- a WiFi hotspot?
AT&T announced today that they will be offering their so called “5G” mobile network service in 12 cities on December 21st. The telco/media conglomerate says: “AT&T will be the first and only company in the U.S. to offer a mobile 5G device over a commercial, standards-based mobile 5G network.”
Please see Author’s Closing Comments below, which refute that “standards based” claim. We’ve repeatedly pounded the table that 3GPP Release 15 NR NSA is not 5G and nothing that comes out of 3GPP is a standard (as per their own website!).
As expected, AT&T’s initial 5G launch will use mmWave spectrum [1], which is claimed to offer users a faster mobile experience than standard LTE. The 5G service starts small and will be limited. AT&T’s mobile 5G network is live in parts of 12 cities: Atlanta, Charlotte, N.C., Dallas, Houston, Indianapolis, Jacksonville, Fla., Louisville, Ky., Oklahoma City, New Orleans, Raleigh, N.C., San Antonio and Waco, Texas.
Note 1. Millimeter waves occupy the frequency spectrum from 30 GHz to 300 GHz. They’re found in the spectrum between microwaves (1 GHz to 30 GHz) and infrared (IR) waves, which is sometimes known as extremely high frequency (EHF). The wavelength (λ) is in the 1-mm to 10-mm range.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“This is the first taste of the mobile 5G era,” said Andre Fuetsch, president, AT&T Labs and chief technology officer. “Being first, you can expect us to evolve very quickly. It’s early on the 5G journey and we’re ready to learn fast and continually iterate in the months ahead.”
In the first half of 2019 AT&T plans to deploy mobile 5G in parts of these 7 additional cities: Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Nashville, Orlando, San Diego, San Francisco and San Jose, Calif. The company says that as the 5G ecosystem evolves customers will see enhancements in coverage, speeds and devices.
“As the ecosystem evolves, this technology will ultimately change the way we live and conduct business,” said Mo Katibeh, chief marketing officer, AT&T Business. “We expect that our initial adopters will be innovative, growing businesses. They’re the starting point for what we think will be a technology revolution like we’ve never seen before.”
“Today’s news is a seminal moment in the advancement of mobile 5G technology,” said David Christopher, president of AT&T mobility and entertainment, in a statement. “This proves we are well on our way to the promise of mobile 5G for consumers.”
Early adopters will only have one choice of end user equipment: the NETGEAR® Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot (aka “a puck”) on the mobile 5G+ network. AT&Ts 5G service will start out in dense urban areas. Through an initial offer, AT&T says they will deliver select businesses and consumers their first mobile 5G device plus 5G data usage at no cost for at least 90 days. Next spring, customers will be able to get the Nighthawk for $499 upfront and 15GB of data for $70 a month on a compatible plan and no annual commitment [2].
AT&T said its hot spot and the data it uses will be free for subscribers in the first 90 days of the rollout. After that period, the device will sell for $499 with a 15-gigabyte data plan priced at $70 per month—a rate slightly cheaper per-datum than the 10-GB for $50 it offers with 4G LTE hotspots.
An AT&T spokesperson said businesses and customers in the initial rollout areas can express interest in joining the early phase of the network on the company’s website. The spokesperson also said the network should eventually reach theoretical peak speeds of 979 megabits per second, but actual average rates will be lower.
In December, AT&T announced two 5G-capable smartphones for 2019. A Samsung-branded 5G smartphone operating on AT&Ts mmWave is will be released in the spring of 2019. Toward the end of 2019, AT&T will release another Samsung 5G smartphone with multi-frequency band support. None of those devices will meet the still uncompleted IMT 2020 standard for mobile 5G (see Closing Comments below).
Note 2. The NETGEAR Nighthawk device will require a 5G compatible AT&T data plan. Device availability and 5G+ coverage areas are limited.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Expect to hear more about 5G soon at events like the big consumer electronics trade show CES in January in Las Vegas and MWC Barcelona (formerly the Mobile World Congress) in February in Spain. Wireless service providers including AT&T and Verizon are already talking up 5G. And device makers are previewing gadgets that will work with the technology.
Samsung recently demonstrated prototypes of 5G smartphones that are expected to operate on both Verizon and AT&T networks. Many other manufacturers are racing to follow suit, though Apple is not expected in the initial 5G wave. Analysts predict that iPhones with the new technology won’t arrive until 2020.
Qualcomm, the wireless chip maker, said it had demonstrated peak 5G download speeds of 4.5 gigabits/second, but predicts initial median speeds of about 1.4 gigabits/secon. That translates to roughly 20 times faster than the current 4G LTE experience, but is much lower than IMT 2020 objectives for peak and average bit rates.
The 5G speeds will be particularly noticeable in higher-quality streaming video.Downloading a typical movie at the median speeds cited by Qualcomm would take 17 seconds with 5G, compared with six minutes for 4G.
………………………………………………………………………………………….
From a previous IEEE Techblog post–AT&T’s 5G Roadmap (only mobile 5G was shown on Al Burke’s SCWS 2018 presentation – nothing on fixed 5G):
- 2019: 5G NR access with LTE Core network and LTE Access (=signaling?). The spectrum for AT&Ts initial mobile 5G rollout was not disclosed, but many believe it will be mmWave.
- 2020-2022+: 5G NR access with 5G Core network (3GPP Release 16 SA or IMT 2020?); also LTE Core with LTE Access
- 2019-2022+: mmWave NR : Evolution to Ultra High Speed and lower latency
- End of 2019-2022+: (unspecified time frame?), AT&T will provide sub 6 GHz 5G coverage in the U.S. speed and latency; dedicated & shared spectrum (LTE-NR-Coexistence)
When AT&T introduces its “5G” FWA residential service it will be based on LTE, according to Mr. Burke. In answer to a question from this author during the Q&A session, he said it would start as LTE but then transition to 5G NR based FWA. The spectrum to be used was not revealed by Mr. Burke, but it will likely be mmWave (like Verizon’s 5G Home).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Author’s Closing Comments:
A claim we’ve heard before (by Ericsson and Vodafone), but don’t believe: LTE network and terminal equipment will upgrade to 5G NR via “only a software upgrade.”As noted many times by this author and others,
AT&T has repeatedly stated they would roll out “standards based 5G” in 12 cities by the end of 2018 (they have only 3 weeks to fulfill that promise) and 19 cities in 2019. Some of the cities identified by AT&T for the 2018 launch include Houston TX, Dallas TX, Atlanta TX, Waco TX, Charlotte NC, Raleigh NC, Oklahoma City OK, Jacksonville FL, Louisville, KY, New Orleans LA, Indianapolis IN, and San Antonio TX.
How long can AT&T claim their “5G” network is standards based when they only support 3GPP release 15 “5G NR” NSA access with a LTE core network and LTE signaling? The ONLY 5G RAN/RIT standard is IMT 2020 which won’t be completed till the end of 2020. AT&T knows this well because one of their representatives is the Chairman of ITU-R WP 5D where IMT 2020 is being standardized.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
SCWS Americas: Verizon and AT&T 5G Roadmaps Differ on FWA vs mobile “5G”
https://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/what-is-5g/



