Dell’Oro: Private 5G ecosystem is evolving; vRAN gaining momentum; skepticism increasing
Private 5G ecosystem is evolving:
Private 5G is running behind schedule. Dell’Oro’s VP Stefan Pongratz adjusted the firm’s private wireless forecast downward to reflect the current state of the market. Still, the slow uptake is not dampening the enthusiasm for private wireless. If anything, the interest is growing and the ecosystem is evolving as suppliers with different backgrounds (RAN, core, Wi-Fi, hyperscaler, in-building, SI) are trying to solve the enterprise puzzle.
According to Dell’Oro’s data, the total private wireless small cell market outside of China exceeds $100 million. But Pongratz indicated that’s not very much. “Commercial private wireless revenues are still so small. We estimate private wireless small cells is still less than 1% of the overall public-plus-private RAN market in 2022.”
He did concede that the private wireless small cell market outside of China is growing at double digits. “It’s heading in the right direction,” said Pongratz. “A lot of suppliers see good things for 2023.”
According to Stefan, the top three private wireless vendors in the world are Nokia, Huawei and Ericsson. Celona has said that its goal is to overtake Nokia in private wireless. Celona CEO Rajeev Shah said that based on Nokia’s public earnings reports, the company seems to be garnering about 30-35 private wireless customers a quarter and has about 515 of these customers in total. Shah said these numbers aren’t huge, and the industry has a long way to go.
Below is a summary of the private RAN, core, and SI/services providers that Stefan is currently monitoring.
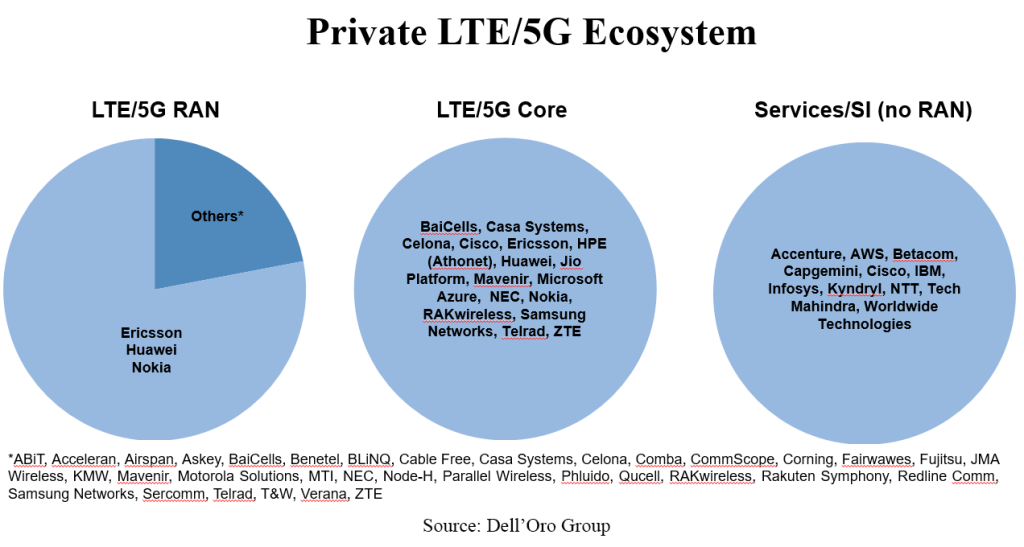
Pongratz said the private wireless market can also be segmented by macro versus small cell. He said private wireless has been around for quite some time — since 2G. But traditionally, it was used as a wide area network (WAN), using the 3GPP definition for non-public networks. Often these networks deployed macros for very large organizations such as utility companies.
“The shiny new object is really the local campus deployments; that’s really small cells,” said Pongratz. “There will be a component of the new shiny that is also WAN, like a car manufacturer that could use both macros and small cells.”
But regardless, whether the private wireless market is segmented by macro or small cell, Dell’Oro still finds the top three suppliers are Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Virtualized RAN is gaining momentum:
As we now know, vRAN started out slow but picked up some speed in 2022 in conjunction with the progress in the US. The challenge from a forecasting perspective is that the visibility beyond the greenfields and the early brownfield adopters is limited, primarily because purpose-built RAN still delivers the best performance and TCO. As a result, there is some skepticism across the industry about the broader vRAN growth prospects.
During MWC, Steffan learned four things: 1) Near-term vRAN visibility is improving – operators in South Korea, Japan, US, and Europe are planning to deploy vRAN in the next year or two. 2) vRAN performance is firming up. According to Qualcomm, Vodafone (and Qualcomm) believes the energy efficiency and performance gap between the traditional and new Open vRAN players is shrinking (Vodafone publicly also praised Mavenir’s OpenBeam Massive MIMO AAU). Samsung also confirmed (again) that Verizon is not giving up any performance with Samsung’s vRAN relative to its purpose-built RAN. 3) vRAN ecosystem is expanding. In addition to existing vRAN suppliers such as Samsung, Ericsson, Mavenir, Rakuten Symphony, and Nokia announcing improvements to their existing vRAN/Cloud RAN portfolios, more RAN players are jumping on the vRAN train (both NEC and Fujitsu are expecting vRAN revs to ramp in 2023). And perhaps more interestingly, a large non-RAN telecom vendor informed us they plan to enter the vRAN market over the next year. 4) The RAN players are also moving beyond their home turf. During the show, Nokia announced it is entering the RAN accelerator card segment with its Nokia Cloud RAN SmartNIC (this is part of Nokia’s broader anyRAN strategy).
Skepticism is on the rise
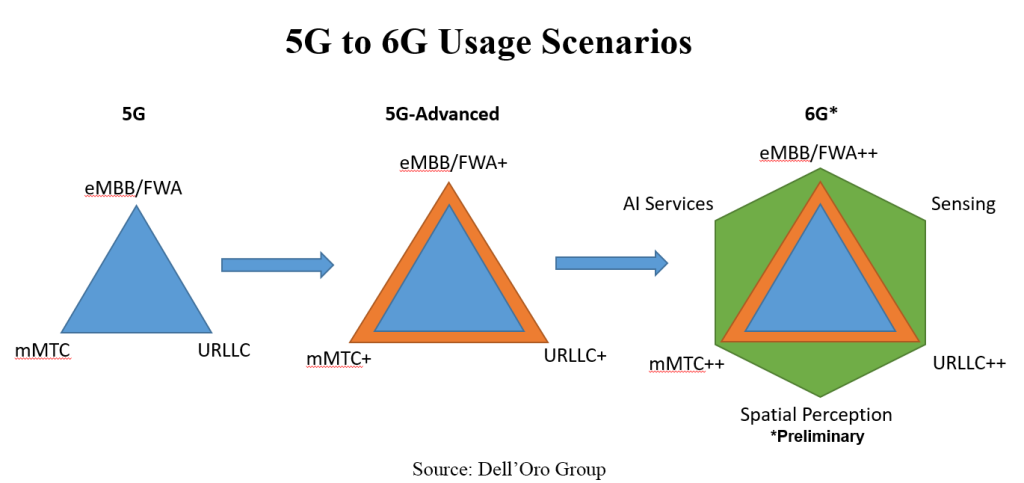
Not surprisingly, disconnects between vision and reality are common when new technologies are introduced. Even if this is expected, we are sensing more frustration across the board this time around, in part because RAN growth is slowing and 5G still has mostly only delivered on one out of the three usage scenarios outlined in the original 5G use case triangle. With 5G-Advanced/5.5G and 6G starting to absorb more oxygen, people are asking if mMTC+/mMTC++ and URLLC+/URLLC++ are really needed given the status of basic mMTC and URLLC. Taking into consideration the vastly different technology life cycles for humans and machines, there are more questions now about this logic of assuming they are the same and will move in tandem. If it is indeed preferred to under-promise and over-deliver, there might be some room to calibrate the expectations with 5G-Advanced/5.5G and 6G.
References:


