ITU
Key Objectives of WG Technology Aspects at ITU-R WP 5D meeting June 24-July 3, 2025
ITU-R WP 5D is responsible for the overall radio system aspects of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) systems, comprising the current IMT-2000, IMT-Advanced and IMT-2020 as well as IMT for 2030 and beyond. Note that 5D’s work is only for terrestrial radio access network interfaces. It does not include 5G or 6G Core network or satellite network access.
ITU-R WP5D Technology Aspects Working Group (WG) consists of several Sub Working Groups (SWGs):
SWG IMT SPECIFICATIONS, SWG EVALUATION, SWG RADIO ASPECTS, SWG IMT UNWANTED EMISSIONS, SWG IMT COORDINATION
Key objectives of WG Technology Aspects at their June 24-July 3, 2025 meeting include:
- Continue revising Recommendation ITU-R M.2150-2 (5G) and Recommendation ITU‑R M.2012-6 (IMT Advanced aka 4G), including consideration of further revision based on contribution;
- Continue working on revision of Document IMT-2030/2 “Process” – submission, evaluation process and consensus building process for IMT-2030;
- Start to work on candidate technology submission template for IMT-2030 (6G);
- Continue working on Report ITU-R M.[IMT-2030.TECH PERF REQ] – minimum requirements related to technical performance for IMT-2030 radio interface(s);
- Continue working on Report ITU-R M.[IMT-2030.EVAL] – Guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT-2030;
- Continue working on Report ITU-R M.[IMT-TROPO DUCT MITIGATION] – Mitigation of interference for IMT network under tropospheric ducting effect;
- Continue working on the documents of unwanted emission characteristics of base/mobile stations using the terrestrial radio interfaces of IMT-2020.
Backgrounder on IMT 2030 (6G):
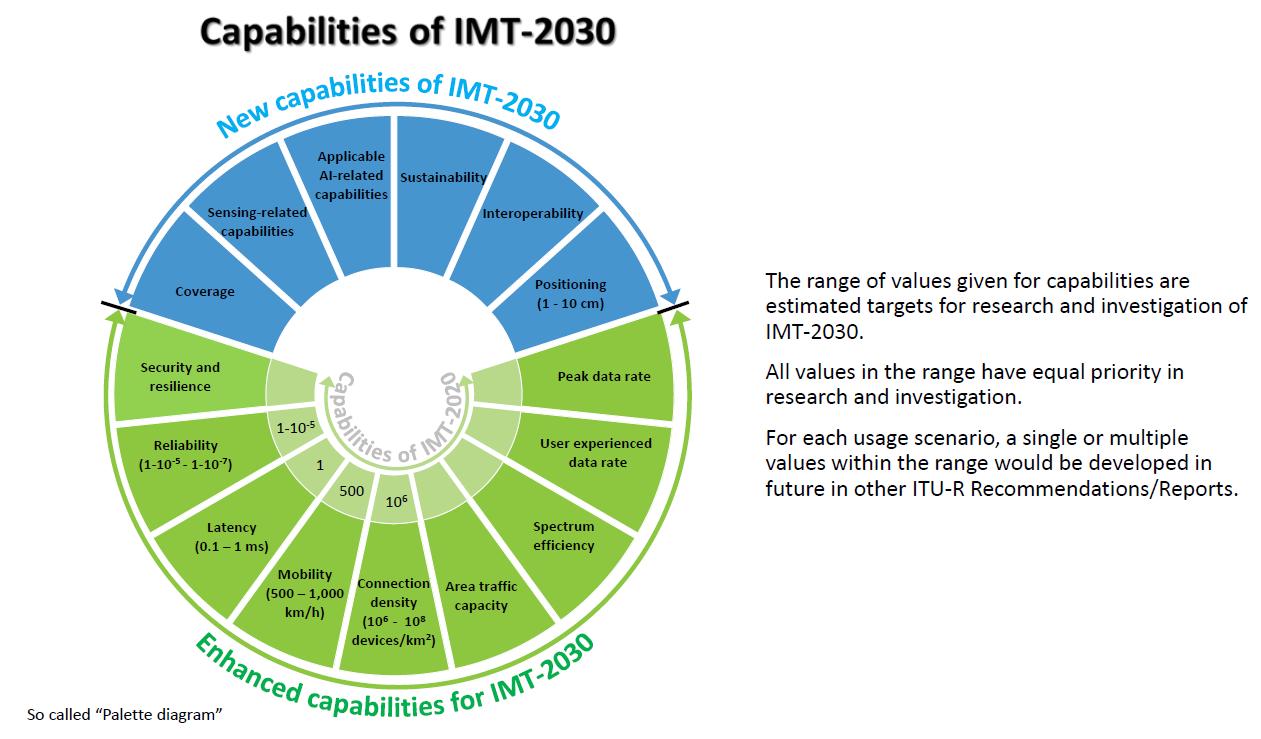
Recommendation ITU R M.2160 ‒ “Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and Beyond” identifies IMT-2030 capabilities which aim to make IMT-2030 (6G) more capable, flexible, reliable and secure than previous IMT systems when providing diverse and novel services in the intended six usage scenarios, including immersive communication, hyper reliable and low latency communication (HRLLC), massive communication, ubiquitous connectivity, artificial intelligence and communication, and integrated sensing and communication (ISAC).
IMT-2030 can be considered from multiple perspectives, including users, manufacturers, application developers, network operators, verticals, and service and content providers. Therefore, it is recognized that technologies for IMT-2030 can be applied in a variety of deployment scenarios and can support a range of environments, service capabilities, and technology options.
IMT-2030 is also expected to be built on overarching aspects which act as design principles commonly applicable to all usage scenarios. These distinguishing design principles of the IMT‑2030 are including, but are not limited to sustainability, security and resilience, connecting the unconnected for providing universal and affordable access to all users independent of the location, and ubiquitous intelligence for improving overall system performance.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
Ericsson and e& (UAE) sign MoU for 6G collaboration vs ITU-R IMT-2030 framework
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
NGMN: 6G Key Messages from a network operator point of view
IMT-2030 Technical Performance Requirements (TPR) from ITU-R WP5D
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
ITU Journal: NexGen Computer Communications & Networks

These solutions can include network optimization, effective data management, cognitive computing, block-chain solutions, and unconventional hardware and software design and implementation.
-
Network optimization:This can involve using techniques such as traffic engineering, load balancing, and caching to improve the performance of networks.
-
Effective data management:This can involve using techniques such as data compression, data encryption, and data analytics to improve the efficiency and security of data storage and transmission.
-
Cognitive computing:This can involve using techniques such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve the ability of networks to learn from data and make decisions autonomously.
-
Block-chain solutions:This can involve using techniques such as distributed ledgers and smart contracts to improve the security and transparency of networks.
-
Unconventional hardware and software design and implementation:This can involve using techniques such as open source software, software-defined networking, and network function virtualization to improve the flexibility and scalability of networks.
| Issue 1 – Editorial Volume 5 (2024), Issue 1 Enhancing user experience in home networks with machine learning-based classification Adaptive HELLO protocol for vehicular networks On the extraction of RF fingerprints from LSTM hidden-state values for robust open-set detection Unsupervised representation learning for BGP anomaly detection using graph auto-encoders A framework for automating environmental vulnerability analysis of network services Automated Wi-Fi intrusion detection tool on 802.11 networks Optimizing IoT security via TPM integration: An energy efficiency case study for node authentication |
ITU World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 opens in Dubai, UAE
The World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 (WRC-23) opened today in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE), bringing governments together for negotiations on the allocation of radio-frequency spectrum. Overall, 4,000 participants are expected for WRC-23, including delegates from ITU Member States and ITU Radiocommunication Sector Members representing international organizations, equipment manufacturers, network operators and industry forums attending as observers.
The conference, organized every three to four years by the ITU, will review and update the Radio Regulations, the international treaty governing the use of spectrum and geostationary and non-geostationary satellite orbits.
Much of the technology in everyday life uses radio-frequency spectrum allocated by ITU’s world radiocommunication conferences. Ensuring that the Radio Regulations reflect the changing demand for spectrum use is critical for the efficient operation of existing and future radiocommunication services and equipment.
“We are at an inflection point in tech history, and radiocommunications are at the top of the global agenda,” said Doreen Bogdan-Martin, ITU Secretary-General. “Equitably managed spectrum and the associated satellite orbits are among the best tools in our toolbox to make good on our commitment to build a digital future that works for everyone and for our planet.”
“While today’s world is full of challenges, this conference comes to set the course and direct the compass toward sustainable human development by updating the Radio Regulations and establishing international consensus on the frequencies necessary for the coming era,” said H.E. Eng. Majed Sultan Al Mesmar, Director General of the UAE Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority (TDRA). “With the broad horizons it brings in the fields of smart cities, digital economy, knowledge society, space and others, we are confident that this conference will achieve the results that meet the expectations and aspirations of our peoples.”
“This conference will revise and update the Radio Regulations to support the introduction of new radio-based technologies, systems, technologies and services and their growing spectrum requirements while continuing to protect the vital radio services we rely on today,” said Mario Maniewicz, Director of ITU’s Radiocommunication Bureau. “Newer innovative technologies will allow us to better monitor our changing planet, and better connect communities and people everywhere: on land, at sea, in the air, and in space. I count on the spirit of cooperation of the ITU Membership and your technical expertise to make WRC-23 a resounding success and leave a legacy of prosperity for billions of people across the globe.”
The WRC-23 agenda items include:
- Identifying additional frequency bands for the continued development of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT), including the use of high-altitude platform stations as IMT base stations for the universal deployment of wireless networks. This work will include the integration of satellites into 5G and 6G services. As noted by Via Satellite, there’s a WRC-23 agenda item to consider adding spectrum bands for phone-to-satellite communications.
- Improvements to the international regulatory framework for geostationary orbit (GSO) and non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellites while promoting equitable access for all countries.
- Use of satellite technologies for broadband services to improve connectivity, particularly in remote areas.
- New spectrum to enhance radiocommunications in the aeronautical mobile service, including by satellite, and to facilitate the use of the space research and Earth exploration-satellite services for climate monitoring, weather prediction and other scientific missions.
- The modernization of the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS).
- The regulatory framework for the use of earth stations in motion on board aircraft and ships for communication with GSO and NGSO satellites.
- The future of the ultra-high frequency (UHF) broadcasting band which has implications for television broadcast, programme-making and special events, as well as public protection and disaster relief.
- ITU-R Resolution 65 paves the way for “studies on the compatibility of current regulations with potential 6th generation IMT radio interface technologies for 2030 and beyond.”
A complete list of matters to be considered at WRC 23 is available here.
The Radio Regulations ensure that the use of the radio-frequency spectrum is rational, equitable, efficient, and economical – all while aiming to prevent harmful interference between different radiocommunication services.
The international treaty on radiocommunications dates back to 1906, when the International Radiotelegraph Convention was signed. In the 117 years since, the Radio Regulations have undergone 38 revisions and expanded to a four-volume agreement of more than 2,000 pages.
WRC-23 was preceded by the ITU Radiocommunication Assembly (RA-23) which met in Dubai from 13-17 November to establish the structure, working methods and program of the ITU Radiocommunication Sector.
Discussion highlights during RA-23:
- Agreement on “IMT-2030″ as the technical reference for the 6th generation of International Mobile Telecommunications;
- Revision of ITU-R Resolution 65, paving the way for studies on the compatibility of current regulations with potential 6th generation IMT radio interface technologies for 2030 and beyond;
- Adoption of the new Recommendation ITU-R M. 2160 on the “IMT-2030 Framework,” setting the basis for the development of IMT-2030. The next phase will be the definition of relevant requirements and evaluation criteria for potential radio interface technologies (RIT);
- Adoption of a new resolution on the use of IMT technologies for fixed wireless broadband;
- In accordance with Resolution 219 (Bucharest, 2022), adoption of a new resolution on space sustainability to facilitate the long-term sustainable use of radio-frequency spectrum and associated satellite orbit resources used by space services. This will be supportive of further cooperation with other United Nations organisations and beneficial to the satellite industry;
- Conclusion of a new ITU-R Recommendation on the protection of the radio navigation-satellite service and amateur satellite services;
- Revision of Resolution ITU-R 8-3 to promote the participation of engineers and scientists from developing countries in propagation campaigns in tropical and subtropical regions of the world for which there is limited data monitoring.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About ITU:
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs), driving innovation in ICTs together with 193 Member States and a membership of over 900 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations. Established over 150 years ago, ITU is the intergovernmental body responsible for coordinating the shared global use of the radio spectrum, promoting international cooperation in assigning frequencies and, if necessary, associated satellite orbits, improving communication infrastructure in the developing world, and establishing the worldwide standards that foster seamless interconnection of a vast range of communications systems. From broadband networks to cutting-edge wireless technologies, aeronautical and maritime navigation, radio astronomy, oceanographic and satellite-based earth and oceanographic monitoring as well as converging fixed and mobile phone, Internet and broadcasting technologies, ITU is committed to connecting the world.
For more information, visit: www.itu.int
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR-2023-11-20-WRC23-opening-ceremony.aspx
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/act/R-ACT-CPM-2023-PDF-E.pdf
https://techchannel.news/itu-sets-the-stage-for-the-development-of-6g/



