OpenRAN
Why It’s IMPORTANT: Telefonica, Rakuten MOU on Open RAN, 5G Core Network and OSS
Rakuten Mobile, Inc., and Telefónica, S.A. announced today the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to cooperate on a shared vision to advance OpenRAN, 5G Core and OSS (operations support systems).
“We’re excited to collaborate with Telefónica on this shared vision of advancing OpenRAN,” said Tareq Amin, Representative Director, Executive Vice President and CTO of Rakuten Mobile. “I envision our partnership to also co-explore further development around the Rakuten Communications Platform that will enable operators around the world to take advantage of cost-effective cloud-native mobile network architecture that is secure and reliable.” (Emphasis added)
Amin emphasised the partnership is not just about opening the interfaces: “It’s about the future possibilities when these networks become fully autonomous. What makes a difference is automation, as it enables much needed operational savings. We’re going to spend a lot of energy around joint development of automation, especially what we call OSS transformation to move away from legacy systems.”
Enrique Blanco, Chief Technology & Information Officer (CTIO) at Telefónica, said: “Telefónica strongly believes that networks are evolving towards end-to-end virtualization through an open architecture, and OpenRAN is a key piece of the whole picture. Beyond the flexibility and simplicity that OpenRAN will provide, it will change the supplier ecosystem and revolutionise the current 5G industry in the medium and long term. At the same time, open and virtualized networks will lead to a new telco operating model. Telefonica and Rakuten Mobile have signed this MoU to work towards evaluating and demonstrating the capability and feasibility of OpenRAN architectures and make them a reality.”
“This is a massive opportunity for all of us. This is an inclusive approach and how we can guarantee we are building the network for the future,” Blanco added. In addition to defining the interfaces, the companies are exploring procurement of hardware and software, Blanco said.
Under the terms of the MoU, Rakuten Mobile and Telefónica plan to collaborate on the following:
- To research and conduct lab tests and trials to support OpenRAN architectures, including the role of the AI (Artificial Intelligence) in the RAN Networks.
- To jointly develop proposals for optimal 5G RAN architecture and OpenRAN models as part of industry efforts to achieve quicker time to market, new price-points, and the benefits of software-centric RAN.
- To collaborate in building an open and cost-effective 5G ecosystem, based on open interfaces, that will help accelerate the maturity of 5G with global roaming.
- To develop a joint procurement scheme of OpenRAN Hardware and Software that will help increase volumes and reach economies of scale, including CUs, DUs, RRUs, and other necessary network equipment and/or software components.
In addition, the companies will also jointly work on 4G/5G Core and OSS technology utilized by Rakuten Mobile in Japan and its Rakuten Communications Platform.
“Vendor selection typically takes a long time in the telecoms industry compared with the web-scale companies. Maybe together with Telefonica the discussions with vendors might change a bit and require us to create new business models.”
Telefonica plans to introduce open RAN in three phases, with pilots starting this year, initial rollouts in 2021 and mass deployments in 2022. “I’m extremely convinced we’ll hit these targets, but we are trying to be conservative,” Blanco said. From 2022 to 2025, up to half of Telefonica’s 5G deployments will use open RAN, he added.
Why this MOU is IMPORTANT:
- As there are no ITU recommendations or 3GPP specs detailing how to implement a 5G Core/5G SA network, the Rakuten-NEC 5G core could become a defacto standard. As we’ve stated many times, the 3GPP specs on 5G Core are network architecture specs that leave the various implementation choices to the implementer. And 3GPP is not even sending their 5G non-radio specs to ITU-T for consideration as future recommendations.
- Meanwhile, Rakuten and NEC have created a 5G “cloud native” core spec (proprietary of course) built on containers, which NEC (and likely other vendors) will implement in Rakuten’s 5G network. Rakuten and NEC plan to offer there 5G Core as a product to other 5G network operators.
- The Rakuten Communications Platform for Open RAN could similarly be sold to other carriers that want to deploy an Open RAN 4G/5G network. The catch here is that any legacy wireless carrier wanting to do so would have to support two incompatible sets of cellular infrastructure to serve its customers: 1] The traditional “closed box base stations” (from Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung, ZTE, etc) in cell towers AND 2] The new Open RAN, multi-vendor base stations using totally different hardware/software platforms which requires a significant amount of systems integration and tech support/trouble resolution. Rakuten’s platform could, at the very least, simplify systems integration and avoid “finger pointing” when troubleshooting a failure or degraded service.
- Both the Rakuten-NEC 5G Core and Rakuten Communications Platform for Open RAN could be terrific products to sell to greenfield carriers (with no existing wireless infrastructure). Apparently, that’s too late for Dish Network and Reliance Jio, which claim they’re building their own “open 5G” network. Meanwhile, India based Tech Mahindra claims it can build a complete 5G network now, which they would surely sell to would be 5G network providers, utilities, and government agencies around the world.
- The OSS co-operation amongst these two carriers is significant, because (once again) there are no standards for 5G SA OSS’s such that the deliverable output of cooperation here could become a defacto standard.
- Co-operative work on automation of network functions and operations will also be vitally important. Otherwise, that too will be proprietary to the wireless network provider which would require different software for the SAME functions for different carriers. The work will probably start with these 2800 series 3GPP specs: TS 28.554 Management and orchestration; 5G end to end Key Performance Indicators (KPI); TS 28.555 Management and orchestration; Network policy management for 5G mobile networks; Stage 1 TS 28.556 Management and orchestration; Network policy management for 5G mobile networks; Stage 2 and stage 3. There are similar ITU-T SG 13 high level Recommendations on these subjects.
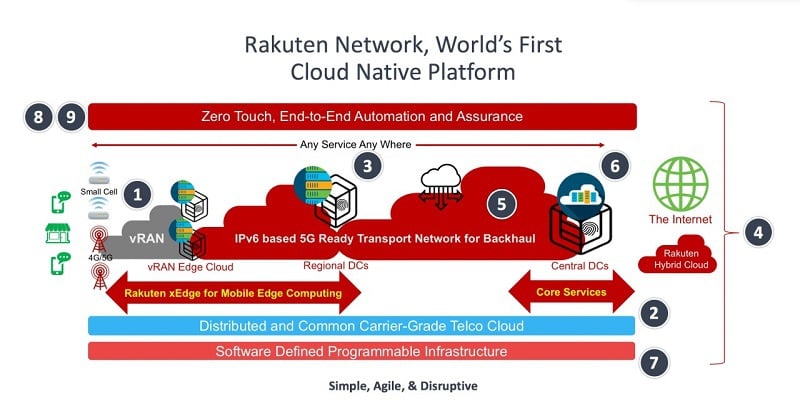
Image Credit: STL Partners
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Rakuten Mobile
Rakuten Mobile, Inc. is a Rakuten Group company responsible for mobile communications, including mobile network operator (MNO) and mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) businesses, as well as ICT and energy. Through continuous innovation and the deployment of advanced technology, Rakuten Mobile aims to redefine expectations in the mobile communications industry in order to provide appealing and convenient services that respond to diverse customer needs.
About Telefónica
Telefónica is one of the largest telecommunications service providers in the world. The company offers fixed and mobile connectivity as well as a wide range of digital services for residential and business customers. With 342 million customers, Telefónica operates in Europe and Latin America. Telefónica is a 100% listed company and its shares are traded on the Spanish Stock Market and on those in New York and Lima.
Telefonica was a co-founder of the Open RAN Policy Coalition, and previously partnered with five companies including Altiostar and Intel to foster the approach.
For more information about Telefónica: www.telefonica.com
References:
https://stlpartners.com/research/5g-bridging-hype-reality-and-future-promises/
Analysis of Open Network Foundation new 5G SD-RAN™ Project
Executive Summary:
In a move that will help promote multi-vendor interoperability, the Open Networking Foundation (ONF) today announced the formation of the SD-RAN project (Software Defined Radio Access Network) to pursue the creation of open source software platforms and multi-vendor solutions for mobile 4G and 5G RAN deployments. Initially, the project will focus on building an open source Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (nRT-RIC) compatible with the O-RAN architecture.
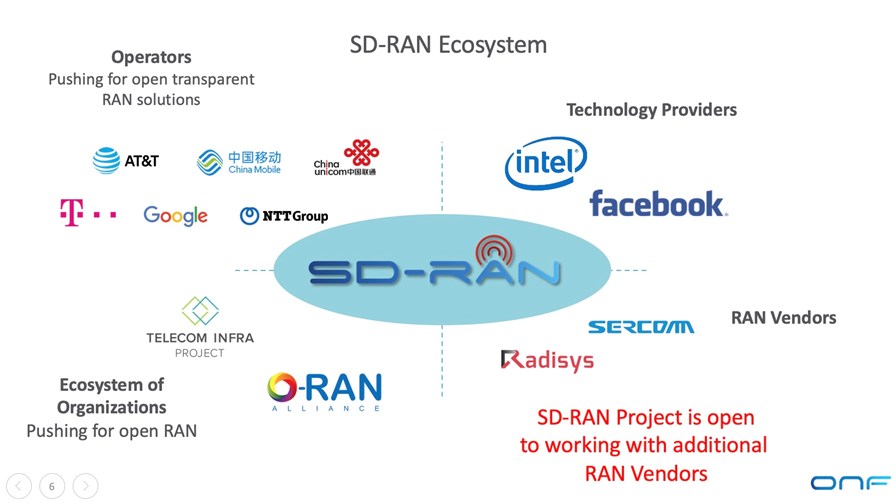
The new SD-RAN project is backed by a consortium of leading operators and aligned technology companies and organizations that together are committed to creating a truly open RAN ecosystem. Founding members include AT&T, China Mobile, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Facebook, Google, Intel, NTT, Radisys and Sercomm. All the project members will be actively contributing, and this includes the operators contributing use cases and trialing the results, according to the ONF. However, the larger cellular base station vendors that are ONF members, Nokia, Samsung, ZTE, Fujitsu, NEC were silent on their participation in this SD-RAN project.
There may be some confusion caused by ONF’s SD-RAN project as it is the third Open RAN consortium. The O-RAN Alliance and TIP Open RAN project are working on open source hardware and open interfaces for disaggregated RAN equipment, like a 4G/5G combo base station.
In a brief video chat yesterday, Timon Sloane, VP of Ecosystem and Marketing for ONF told me that this new ONF SD-RAN project would be in close contact with the other two Open RAN consortiums and distinguished itself from them by producing OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE for disaggregated RAN equipment—something he said the O-RAN Alliance and TIP Open RAN project were NOT doing.
That should go a long way in dispelling that confusion, but it nonetheless presents a challenge on how three consortiums can effectively work together to produce meaningful open source software code (ONF) and hardware (O-RAN Alliance and TIP) specifications with joint compliance testing to ensure multi-vendor interoperability.
Sloane told Matt Kapko of SDXCentral: “The operators really are pushing for separation of hardware and software and for enabling new innovations to come in in software without it being tightly coupled to the hardware that they purchase. And xApps are where the functionality of the RAN is to be housed, and so in order to do this in a meaningful way you have to be able to do meaningful functions in these xApps,” Sloane said.
However, no mention was made in the ONF press release of a liaison with either 3GPP or ITU-R WP5D which are producing the standards and specs for 5G and have already done so for 4G-LTE. Neither of the aforementioned O-RAN consortiums have liaisons with those entities either.
There are other complications with Open RAN (independent of SD-RAN), such as U.S. government’s attempt to cripple Huawei and other China telecom equipment vendors, need for a parallel wireless infrastructure, legacy vs greenfield carriers. These are addressed in Comment and Analysis section below.
µONOS-RIC:
Central to the project is the development of an open source near-real time RIC called µONOS-RIC (pronounced “micro-ONOS-RIC”).
µONOS is a microservices-based SDN controller created by the refactoring and enhancement of ONOS, the leading SDN controller for operators in production tier-1 networks worldwide. µONOS-RIC is built on µONOS, and hence features a cloud-native design supporting active-active clustering for scalability, performance and high availability along with the real-time capabilities needed for intelligent RAN control.
µONOS-RIC is designed to control an array of multi-vendor open RAN equipment consistent with the O-RAN ALLIANCE architecture. In particular, the O-RAN ALLIANCE E2 interface is used to interface between µONOS-RIC and vendor supplied RAN RU/DU/CU RAN components.
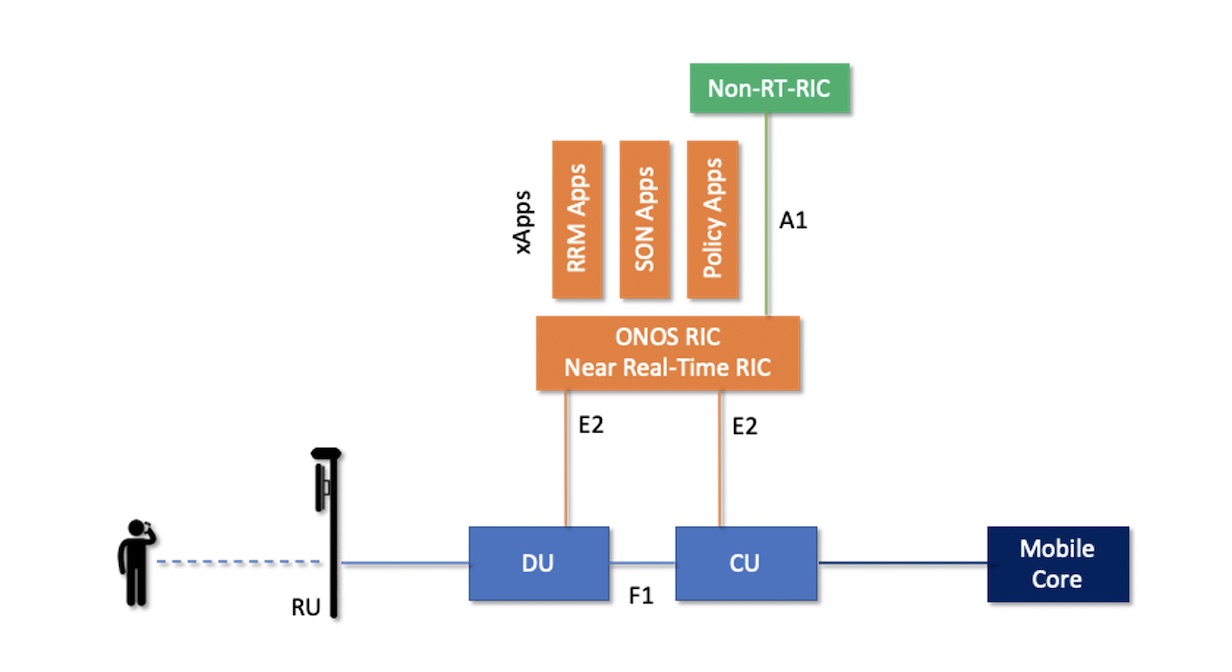
xApps running on top of the µONOS-RIC are responsible for functionality that traditionally has been implemented in vendor-proprietary implementations. A primary goal of the SD-RAN project (and, not coincidentally, for the operators who founded the O-RAN consortium) is to enable an external intelligent controller to control the RAN so that operators have both visibility and control over their RAN networks, thus giving operators ownership and control over how spectrum is utilized and optimized along with the tools to deliver an optimal experience for users and applications.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Relationship to O-RAN Alliance, O-RAN Software Community and TIP:
The participating members of the SD-RAN project plan to implement, prototype and trial an advanced architecture that enables intelligent RIC xApps to control a broad spectrum of SON and RRM functionality that historically has been implemented as vendor-proprietary features on bespoke base station equipment and platforms. SD-RAN’s focus and goals are complementary to various efforts across the industry, including work taking place within the O-RAN ALLIANCE, the O-RAN Software Community and the TIP OpenRAN Project Group.
SD-RAN will follow O-RAN specifications as they are developed and will also make use of components of existing open source to facilitate interoperability. As the project pioneers new functionality, all extensions and learnings that come from building the system will be contributed back to O-RAN ALLIANCE, with the intent that these extensions can inform and advance the O-RAN specifications.
The SD-RAN work inside the ONF community will take place in parallel with work being contributed to the O-RAN Software Community. The intent is for interoperable implementations to come out of both efforts, so that a mix of open source and vendor proprietary components can be demonstrated and ultimately deployed.
Timing and Availability:
The SD-RAN project already has a working skeleton prototype of the µONOS-RIC controller above a RAN emulation platform through the E2 interface. This implementation is demonstrating handover and load balancing at scale, supporting over 100 base stations and 100,000 user devices with less than 50ms handover latency (less than 10ms latency for 99% of all handovers).
The SD-RAN community is advancing towards a field trial by early 2021, working with RAN vendors to integrate carrier-grade RU/DU/CU components while in parallel implementing xApps to demonstrate SON and RRM functionality. Interested parties are encouraged to contact ONF for additional information.
Quotes Supporting the SD-RAN Project:
“AT&T strongly supports the development of specifications and components that can help drive openness and innovation in the RAN ecosystem. The O-RAN ALLIANCE’s specifications are enabling the ecosystem, with a range of companies and organizations creating both open source and proprietary implementations that are bringing the open specifications to life. The ONF SD-RAN project, along with the O-RAN OSC, will expand the ecosystem with an nRT-RIC that can support xApps and help demonstrate their interoperability. This project will help accelerate the transition to an open RAN future.”
Andre Fuetsch, President and Chief Technology Officer, AT&T Labs
“China Mobile co-founded O-RAN in order to promote both the opening of the RAN ecosystem for multi-vendor solutions and the realization of RAN with native intelligence for performance and cost improvement. An open nRT-RIC with support for open xApps that go beyond policy-based control and SON to also enhance Radio Resource Management (RRM) will make it possible for operators to optimize resource utilization and application performance. We are excited to see the development of an open nRT-RIC and xApps in the SD-RAN project led by ONF, and expect this work to help advance the state-of-art for open and intelligent RAN.”
Dr. Chih-Lin I, Chief Scientist, Wireless Technologies, China Mobile
“China Unicom has been a long-term partner with ONF. We continue to see the benefits of the ONF’s work and the impact it has on our industry. The SD-RAN project is now applying the ONF’s proven strategy for disaggregating and creating open source implementations to the 5G RAN space in order to foster innovation and ecosystem transformation. We are excited by this work, and are committed to trialing a solution as it becomes available.”
Dr. Xiongyan Tang, Network Technology Research Institute, China Unicom
“Deutsche Telekom is a huge believer in applying disaggregation and open source principles for our next-generation networks. DT has ONF’s mobile core platform (OMEC) in production and we are taking ONF’s broadband access (SEBA/VOLTHA) platform to production towards the end of 2020. This journey has shown us the tremendous value that is created when we can build solutions based on interoperable multi-vendor components intermixed with open source components. ONF’s SD-RAN project is leveraging these same principles to help accelerate innovation in the RAN domain, and we are excited to be an active collaborator in this journey.”
Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi, SVP Strategy & Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom
“Connectivity is an integral part of Facebook’s focus to bring people closer together. We work closely with partners to develop programs and technologies that make connectivity more affordable and accessible. Through our collaboration with ONF on their SD-RAN project, we look forward to engaging with the community to improve connectivity experiences for many people around the world.”
Aaron Bernstein, Facebook’s Director of Connectivity Ecosystem Programs
“Google is an advocate for SDN, disaggregation and open source, and we are excited to see these principles now being applied to the RAN domain. ONF’s SD-RAN project’s ambition to create an open source RIC can help invigorate innovation across the mobile domain.”
Ankur Jain, Distinguished Engineer, Google
“Intel is an active participant of the ONF’s SD-RAN project to advance the development of open RAN implementations on high volume servers. ONF has been leading the industry with advanced open source implementations in the areas of disaggregated Mobile Core, e.g. the Open Mobile Evolved Core (OMEC), and we look forward to continuing to innovate by applying proven principles of disaggregation, open source and AI/ML to the next stepping stone in this journey – the RAN. SD-RAN will be optimized to leverage powerful performance, AI/ML, and security enhancements, which are essential for 5G and available in Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, network adapters and switching technologies, including Data-Plane Development Kit (DPDK) and Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel SGX).”
Pranav Mehta, Vice President of Systems and Software Research, Intel Labs
“NTT sees great value in transforming the RAN domain in order to foster innovation and multi-vendor interoperability. We are excited to be part of the SD-RAN ecosystem, and look forward to working with the community to develop open source components that can be intermixed with vendor proprietary elements using standard O-RAN interfaces.”
Dai Kashiwa, Evangelist, Director of NTT Communications
“Radisys is excited to be a founding member of the SD-RAN project, and we are committed to integrating our RAN software implementation (CU & DU) with O-RAN interfaces to the µONOS-RIC controller and xApps being developed by the SD-RAN project community. This effort has the potential to accelerate the adoption of O-RAN based RIC implementation and xApps, and we are committed to working with this community to advance the open RAN agenda.”
Arun Bhikshesvaran, CEO, Radisys
“As a leading manufacturer of small cell RAN equipment and an avid supporter of the open RAN movement, Sercomm is excited to collaborate with the SD-RAN community to open E2 interfaces and migrate some of our near-real-time functionalities from the RAN equipment into xApps running the μONOS-RIC controller. This is a nascent yet dynamic area full of potential, and we are committed to working with the SD-RAN ecosystem to build solutions ready for trials and deployment.”
Ben Lin, CTO and Co-Founder, Sercomm
“TIP’s OpenRAN solutions are an important element of our work to accelerate innovation across all elements of the network including Access, Transport, Core and Services. We are excited about the collaboration between our RIA subgroup and ONF’s SD-RAN project to accelerate RAN disaggregation and adoption of open interfaces. Through this collaboration we will enable the OpenRAN ecosystem to leverage the strengths of data science and AI/ML technologies to set new industry benchmarks on performance, efficiency and total cost of ownership.”
Attilio Zani, Executive Director for Telecom Infra Project (TIP)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Comment and Analysis of Open RAN Market:
Disclaimer: Like all IEEE Techblog posts, opinions, comment and analysis are ALWAYS by the authors and do NOT EVER represent an opinion or position by IEEE or the IEEE Communications Society. This should be obvious to all in the 11 1/2 years of this author’s contribution to the IEEE Techblog and its predecessor- ComSoc Community blogs.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Besides NOT having a liaison with either 3GPP or ITU-R, the following Open RAN issues may limit its market potential. These are NOT specific to the ONF SD-RAN project, but generic to Open RAN deployments.
- U.S. officials promoting Open RAN as a way to decrease the dominance of Huawei, the world’s biggest vendor of mobile equipment by market share and also to thwart the rise of other vendors like ZTE and China Information and Communication Technology Group (CICT) which recently won a small part of s China Mobile contract. Obviously, China’s government will fight back and NOT allow any version of Open RAN to be deployed in China (likely to be the world’s biggest 5G market by far)! That despite China Mobile and China Unicom’s expressed interest in Open RAN (see Quotes above). Remember, that the three big China carriers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) are all state owned.
- Dual infrastructure: If a legacy wireless carrier deploys Open RAN, existing wireless infrastructure equipment (base stations, small cells, cell tower equipment, backhaul, etc) must remain in place to support its customers. Open RAN gear (with new fronthaul and backhaul) won’t have wide coverage area for many years. Therefore, current customers can’t simply be switched over from legacy wireless infrastructure to Open RAN gear. That means that a separate separate and distinct WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK must be built and physically installed for Open RAN gear. Yet no one seems to talk or write about that! Why not?
- Open RAN is really only for greenfield carriers with NO EMBEDDED WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE. Rakuten and Dish Network are two such carriers ideally suited to Open RAN. That despite a lot of noise from AT&T and Deutsche Telekom about Open RAN trials. All the supporting quotes from legacy carriers are indicative of their interest in open source software AND hardware: to break the stranglehold the huge wireless equipment vendors have on cellular infrastructure and its relatively high costs of their proprietary network equipment and element management systems.
- Open RAN should definitely lower initial deployment costs (CAPEX), but may result in INCREASED maintenance cost (OPEX) due to the difficulty of ensuring multi-vendor interoperability, systems integration and MOST IMPORTANTLY tech support with fault detection and rapid restoration of service.
Conclusions:
Considering all of the above, one may conclude that traditional cellular infrastructure, based on vendor specific equipment and proprietary interfaces, will remain in place for many years to come. As a result, Open RAN becomes a decent market for greenfield carriers and a small market (trial or pilot networks) for legacy carriers, which become brownfield carriers after Open RAN is commercially available to provide their cellular services.
Given a smaller than commonly believed market for Open RAN, this author believes the SD-RAN project is a very good idea. That’s because it will make open source software available for Open RAN equipment, something that neither the O-RAN Alliance of TIP Open RAN project are doing. Of course, having more vendors producing Open RAN white boxes and software does add to the systems integration and tech support that only large (tier 1) telcos (like AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, NTT and cloud companies (like Google, Facebook, Microsoft) have the staff to support.
In a follow up phone conversation today, Timon Sloane told me that network operators want a fully functional and powerful RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) to gain visibility and control over their RANs, but that has yet to be realized. To date, such controllers have been proprietary, rather than open source software.
The ONF µONOS-RIC is a key software module to realize that vision, Timon said. It is very much like a (near) real time operating system for an Open RAN. If successful, it will go a long way to promote multi-vendor interoperability for Open RAN deployments. Success and good luck ONF!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/onf-announces-new-5g-sd-ran-project-301117481.html
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/onf-picks-up-where-o-ran-alliance-falls-short/2020/08/
Mavenir and Altiostar Collaborate to Deliver OpenRAN Radios for U.S. Market; Parallel Wireless CEO Opinion
Mavenir and Altiostar are among a number of networking software start-ups focusing on delivering Open RAN solutions to wireless network operators . Both companies specialize in cloud telecoms software – so one would expect them to be competing with each other. However, they have decided to collaborate to deliver a wide portfolio of radios based on OpenRAN principles for the US market.
Both companies will be supporting the development of radios through third party OEM’s that will be based on O-RAN open interfaces and will address the frequencies of Tier-1 and Regional/Rural operators in the US.
Analysis:
The two companies will NOT design or build the radios themselves, which is not within the scope of networking software startups. In essence, they will be using O-RAN compliant radios built by (mostly Asian) OEMs/ODMs- many of which are members of the O-RAN Alliance. One has to wonder, however, why such an agreement is necessary? Why aren’t O-RAN compliant interface specifications complete and well enough accepted to ensure multi-vendor interoperability?
The joint press release answers those questions:
“Very few companies are participating in the current (OpenRAN) supply chain and mostly offering proprietary radio solutions lacking open interfaces that are not interoperable with other network elements. In addition, the requirement to procure products from trusted vendors in the US market is also causing operators to reconsider supplier options. OpenRAN radios provide new possibilities for operators to implement a secure, cost effective and best of breed solution as networks move to 5G and beyond.”
Parallel Wireless CEO Steve Papa commented to Light Reading that Open RAN (aka O-RAN) “will only be as good as the radios that are available,” he said. “If Ericsson and Nokia are struggling to be competitive with Huawei’s radios, we should not expect O-RAN to magically solve this problem by using the same semiconductors available to Ericsson and Nokia at present.”
Papa blames a lack of U.S. semiconductor innovation for Huawei’s lead in radios. He has repeatedly urged U.S. authorities to pump an extra $1 billion into radio semiconductor research. He has even suggested using the $1 billion the US recently fined Ericsson for corruption, a remark that is unlikely to win him many friends in Stockholm.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
As part of this effort, it is also planned to have these radios available to support the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act that was signed into law on March 12, 2020.
Public Law No: 116-124 (03/12/2020)
Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act of 2019
This bill establishes (1) a mechanism to prevent communications equipment or services that pose a national security risk from entering U.S. networks, and (2) a program to remove any such equipment or services currently used in U.S. networks.
Specifically, the bill prohibits the use of certain federal funds to obtain communications equipment or services from a company that poses a national security risk to U.S. communications networks. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) must publish and maintain a list of such equipment or services.
Each communications provider must submit an annual report to the FCC regarding whether it has purchased, rented, leased, or otherwise obtained any prohibited equipment and, if so, provide a detailed justification for such action.
The bill also establishes the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement Program to supply small communications providers (i.e., providers with 2 million or fewer customers) with funds to offset the cost of removing prohibited equipment or services from their networks and replacing it with more secure communications equipment or services.
In addition, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration must establish a program to share information regarding supply chain security risks with trusted communications providers and suppliers.
For a short video describing O-RAN’s progress, see www.o-ran.org/videos
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Altiostar has been at the forefront of the OpenRAN movement that is now being embraced by mobile operators around the world,” said Ashraf Dahod, CEO of Altiostar Networks. “Our collaboration with Mavenir on OpenRAN radios will ensure operators in the US have a truly open end-to-end infrastructure that will be cost effective and allows them to grow their business.”
“We are collaborating with Altiostar to realize the full promise of OpenRAN. Our Radios will have O-RAN compliant interfaces and will interwork with other vendors’ solutions,” said Pardeep Kohli, President and CEO of Mavenir. “I encourage other companies in the OpenRAN Policy Coalition to open their radios and ensure a broad supply of radios with open interfaces that are interoperable with third party equipment.”
Mavenir and Altiostar have committed to work together to develop a full set of FCC banded radios to be available starting June 2020, with a complete set of radios in the market by Q1 2021. The parties are also committed to making these OpenRAN radios available to be sourced by all OpenRAN vendors and system integrators, widening the OpenRAN supply chain in the US market to meet the frequency band needs of Tier-1 and Regional/Rural operators.
Mavenir and Altiostar have been pioneers of OpenRAN, including founding board members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition, as well as part of the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) and O-RAN Alliance.
Members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition include Airspan, Altiostar, AT&T, AWS, Cisco, CommScope, Dell, DISH Network, Facebook, Fujitsu, Google, IBM, Intel, Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Microsoft, NEC Corporation, NewEdge Signal Solutions, Nokia, NTT, Oracle, Parallel Wireless, Qualcomm, Rakuten Mobile, Samsung Electronics America, Telefónica, US Cellular, US Ignite, Verizon, VMWare, Vodafone, World Wide Technology, and XCOM-Labs.
Other software start-ups that are pursuing Open RAN include Parallel Wireless, Robin io., WiSig Networks, and several others. This author has talked with principals of Robin.io and WiSig who have been invited to write guest articles about their work for the IEEE Techblog.
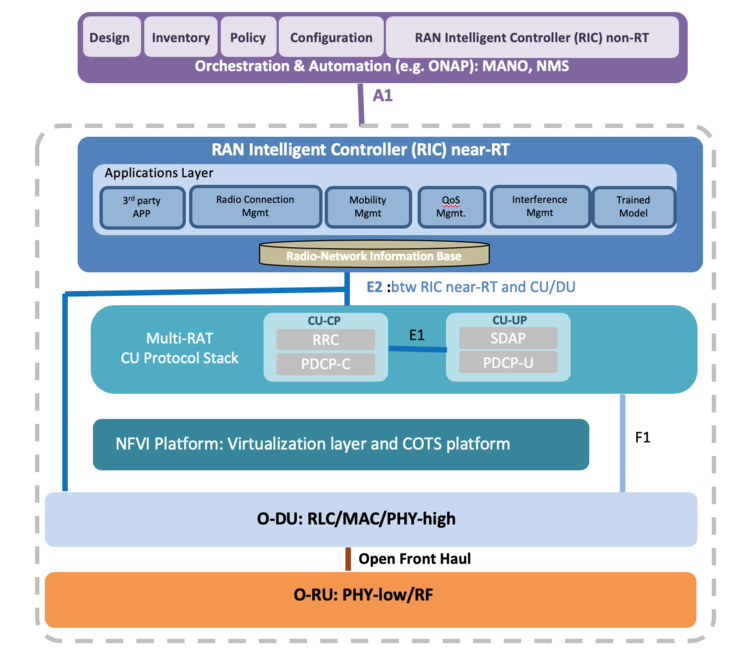
Below is the O-RAN reference architecture model:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Mavenir:
Mavenir is the industry’s only end-to-end, cloud-native Network Software and Solutions/Systems Integration Provider for 4G and 5G, focused on accelerating software network transformation for Communications Service Providers (CSPs). Mavenir offers a comprehensive end-to-end product portfolio across every layer of the network infrastructure stack. From 5G application/service layers to packet core and RAN, Mavenir leads the way in evolved, cloud-native networking solutions enabling innovative and secure experiences for end users. Leveraging innovations in IMS (VoLTE, VoWiFi, Advanced Messaging (RCS)), Private Networks as well as vEPC, 5G Core and OpenRAN vRAN, Mavenir accelerates network transformation for more than 250+ CSP customers in over 140 countries, which serve over 50% of the world’s subscribers.
Mavenir embraces disruptive, innovative technology architectures and business models that drive service agility, flexibility, and velocity. With solutions that propel NFV evolution to achieve web-scale economics, Mavenir offers solutions to help CSPs with cost reduction, revenue generation, and revenue protection. www.mavenir.com
About Altiostar:
Altiostar provides a 4G and 5G open virtualized RAN software solution that supports open interfaces and disaggregates the hardware from the software to build a multi-vendor web-scale network. This solution supports indoor and outdoor massive MIMO, as well as macro and small cells, enabling interference management, carrier aggregation and dual connectivity to improve the efficiency of the network. It also enhances the Quality of Experience for the end user, while providing broadband speeds. Operators can add intelligence, quickly adapt the software for different services and automate operations to rapidly scale the network and reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). The Altiostar open vRAN solution has been deployed globally, including the world’s first cloud native-mobile network with Rakuten in Japan. www.altiostar.com
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Ultra Oxymoron: GSMA teams up with O-RAN Alliance without liaison with 3GPP or ITU
Open RAN Policy Coalition: U.S. attempt to exclude Chinese 5G network equipment vendors?
Believe it or not, there is now a third Open RAN consortium, joining the ORAN Alliance and TIP OpenRAN. Even more astonishing is that none of the three consortiums have any liaison or co-operation with ITU-R or ITU-T which are standardizing 5G as IMT 2020 radio and non-radio aspects, respectively. Nor do these consortiums liaise with 3GPP which is the REAL mover and shaker developing 5G specs that are implementable.
Thirty-one global technology companies have launched the Open RAN Policy Coalition to promote policies that will advance the adoption of open and interoperable solutions in the Radio Access Network (RAN) as a means to create innovation, spur competition and expand the supply chain for advanced wireless technologies including 5G.
Open RAN Policy Coalition founding members include Airspan, Altiostar, AT&T, AWS, Cisco, CommScope, Dell, DISH Network, Facebook, Fujitsu, Google, IBM, Intel, Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Microsoft, NEC Corporation, NewEdge Signal Solutions, NTT, Oracle, Parallel Wireless, Qualcomm, Rakuten Mobile, Samsung Electronics America, Telefónica, US Ignite, Verizon, VMWare, Vodafone, World Wide Technology, and XCOM-Labs.
“Open RAN networks are a significant departure from the traditional industry model and legislators need to know the advantages and how government actions can help accelerating the development and deployment of open and interoperable solutions,” said Thierry Maupilé, Altiostar’s executive vice president, in a statement.
“As evidenced by the current global pandemic, vendor choice and flexibility in next-generation network deployments are necessary from a security and performance standpoint,” said Diane Rinaldo [1.], Executive Director, Open RAN Policy Coalition. “By promoting policies that standardize and develop open interfaces, we can ensure interoperability and security across different players and potentially lower the barrier to entry for new innovators.” Yet that is exactly what the O-RAN Alliance and TIP OpenRAN project were set up to do.
Note 1. Ms. Rinaldo was until recently the deputy assistant secretary for communications and information at the US Department of Commerce (DoC).
In past generations of mobile networks, the networks were deployed using fully integrated cell sites, where the radios, hardware and software were provided by a single manufacturer as a closed proprietary solution. Today, the industry is working towards standards and technical specifications that define open interfaces between the radios, hardware and software so that networks can be deployed using more than one vendor.
Multi-vendor deployments enable a more competitive marketplace and give network operators greater ability to manage their networks and flexibility to draw on the innovations of multiple suppliers to upgrade their infrastructure with the latest technology.
Using multiple interoperable suppliers also allows operators to potentially move more quickly to replace or address vulnerable network equipment when reacting to threats, and shift network capacity on demand.
The coalition believes that the U.S. Federal Government has an important role to play in facilitating and fostering an open, diverse and secure supply chain for advanced wireless technologies, including 5G, such as by funding research and development, and testing open and interoperable networks and solutions, and incentivizing supply chain diversity.
Isn’t that a clear indication the coalition has and will continue to exclude Chinese vendors like Huawei and ZTE?
The launch of the new group, interestingly, comes several weeks after a bipartisan group of US senators proposed investing more than $1 billion in open RAN technologies. Under their plans, the funds would come from spectrum auction proceeds and be managed by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rakuten leads the way forward for Open RANs:
Rakuten Mobile has deployed a version of Open RAN in Japan. The greenfield virtualized, open RAN build was made available for commercial LTE services in April with plans to move to 5G on the virtualized infrastructure. A number of Rakuten Mobile’s vendors, including NEC, are members of the Open RAN Policy Coalition. Further, Rakuten Mobile has expressed interest in providing its network model to other operators interested in following a similar virtualized OPEN RAN 5G network.
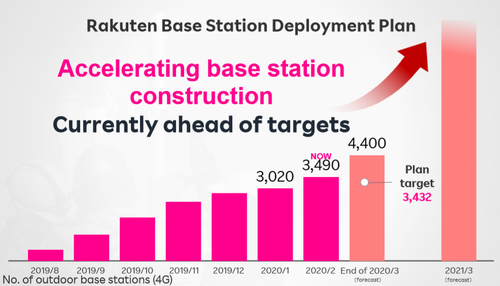
However, analysts have remained skeptical that Rakuten can challenge Japan’s old guard with a cloud-only mobile network. In a research note published in March, shortly before Rakuten’s launch, Atul Goyal, an analyst with Jefferies, flagged “numerous connectivity issues” when Rakuten introduced its beta service in late 2019. “A poor-quality, low-price network is likely to fail in Japan,” he wrote. Its failure would be a huge setback for open RAN.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Parallel Wireless is on board:
Parallel Wireless CEO Steve Papa told RCR Wireless that the open RAN business model matches the generational shifts in cellular. “The economics of a coverage technology and architecture don’t scale well as a capacity architecture. The entire business models of the incumbent vendors don’t work and don’t map to what the people deploying the equipment require given the economic realities.”
Papa continued to say that open RAN “is exposing this to more innovators to participate, which is good. But more importantly, the U.S. government is waking up to its role in supporting the semiconductor market.” He noted the Made in China 2025 focus on developing semiconductor expertise and other moves he characterized as “a state actor tipping to playing field…Our commercial market in communications infrastructure equipment is being distorted by a state actor. We can let that happen or we can counter it in a similar way.”
“We see this coalition as an important addition to the standards work that O-RAN Alliance is doing and also global deployments driven by TIP,” said Steve Papa, the CEO of Parallel Wireless, in comments emailed to Light Reading.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20200505/policy/open-ran-policy-coalition-launches
TIP OpenRAN and O-RAN Alliance liaison and collaboration for Open Radio Access Networks


