Counterpoint Research
Apple leads 128+% YoY increase in foreign mobile phones shipped within China; Global market share leaders
In November 2025, the volume of foreign-branded mobile phones shipped within China experienced a substantial year-over-year increase of 128.4%. This surge was primarily due to increased sales of Apple iPhones, especially iPhone 17. According to data released by the government-affiliated China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), 6.93 million units of international brands were shipped last month. This sharp rise occurred within the context of a broader market increase — total national mobile phone shipments for November reached 30.16 million units, representing a more modest overall year-on-year growth of 1.9%.
The exceptional increase in foreign branded phones is largely attributed to the robust reception of the new iPhone 17 series in the Chinese market. Reports indicate the iPhone 17 line accounted for a substantial portion of Apple’s sales during the period, successfully recapturing market share that had been lost to strong local competition, such as Huawei, throughout the year.
This marks a significant turnaround for Apple in China. In the first month after the iPhone 17 launch, sales reportedly jumped 22% compared to the iPhone 16 launch the previous year. The performance stands in stark contrast to previous periods in 2024 where Apple’s sales had faced challenges and decline due to intensified competition and market saturation. In October 2025, iPhones reportedly accounted for one in every four smartphones sold in China, their highest market share since 2022.
Meanwhile, domestic phone brands like Huawei and Xiaomi saw slower momentum as they delayed some new product launches. That gave Apple a wider sales window and helped foreign brands capture about 23% of the market, compared with roughly 10% in past months.
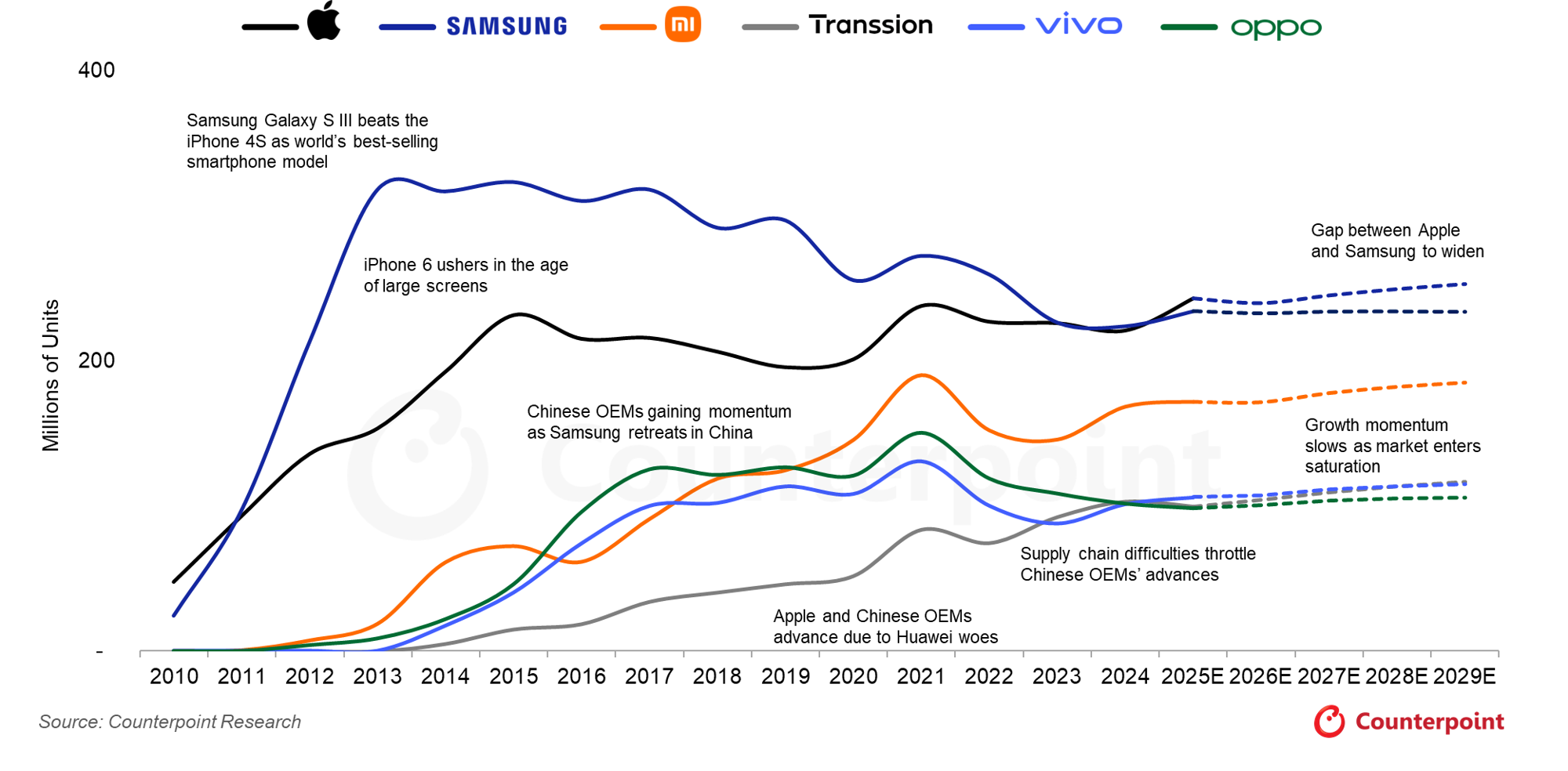
China brands account for eight of the top 10 global smartphone market share positions after Samsung and Apple.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
https://counterpointresearch.com/en/insights/Global-Smartphone-Forecast-for-2025
IDC: Worldwide Smartphone Shipment +7.8% YoY; Samsung regains #1 position
Huawei forecast to increase mobile phone shipments despite Android ban
Counterpoint Research: eSIM adoption now entering high-growth phase; +11% YoY in 2022
More than 6 billion xSIM (eSIM + iSIM) capable devices will be cumulatively shipped over the next five years, covering all form factors including hardware-based eSIM (eUICC), iSIM (iUICC), nuSIM and Soft SIM, according to Counterpoint’s latest eSIM Devices Market Outlook report.
Editor’s Note: An embedded SIM card – or eSIM – is pre-installed in a device and cannot be physically swapped. Instead, it is programmed remotely and can hold several SIMs at the same time. An integrated SIM (iSIM), meanwhile, is integrated in a device’s main processor, doing away with any form of dedicated hardware.
eSIM adoption has passed the inflection point and is now entering a high-growth phase, driven by the rising adoption of eSIM in smartphones, connected vehicles and cellular IoT applications. The next phase of growth will be driven by greater awareness of eSIM among mobile network operators (MNOs) and device manufacturers, facilitated by the flexibility, cost efficiency, security, cost savings and above all, the key role eSIM is playing in the digital transformation of MNOs.
In 2022, eSIM-capable device shipments grew 11% YoY to reach 424 million units despite a 3% YoY fall in overall cellular-connected device shipments due to weaker demand for smartphones. Globally, more than 275 MNOs support eSIM and provide connections to 30+ different eSIM-capable consumer device models on average. Furthermore, the number of cellular IoT modules and devices is continuously growing.
By 2030, 70% of all cellular devices are expected to support eSIM technology. Adoption will reach 100% in the smartwatch and drone segments; 92% for connected cars; 82% for smartphones; and 79% for tablets. Around 40% of eSIM devices will be smartphones, while 55% of eSIM devices shipped between 2021 and 2030 will be consumer devices.
Commenting on the outlook for xSIM-capable device shipments, Research Vice President Neil Shah said, “The physical MFF2/WLCSP form-factor soldered eSIM chip has been the go-to standard for eSIM implementation alongside the other niche alternative implementations such as soft SIM and nuSIM. Over the next five years, hardware-based eSIM (eUICC) will remain the dominant eSIM form factor and will account for more than half of all shipments.”
“The first wave of mainstream iSIM adoption will be seen across IoT applications driven by leading IoT chipset and module players such as Quectel, Telit, Sequans and Sony Semi (Altair) in partnership with leading xUICC players like Kigen, G+D and Thales. Other key stakeholders driving the adoption of iSIMs would include Qualcomm, IDEMIA, Truphone, Redtea Mobile, Oasis SmartSIM, Apple, Samsung and Nokia. Beyond 2028, iSIM is projected to take over as the dominant SIM form factor, with the shipments of iSIM-capable devices poised to climb to a cumulative 4 billion units by 2030.”
eSIM Has Reached an Inflection Point, Set to Enter a Period of Hyper-Growth
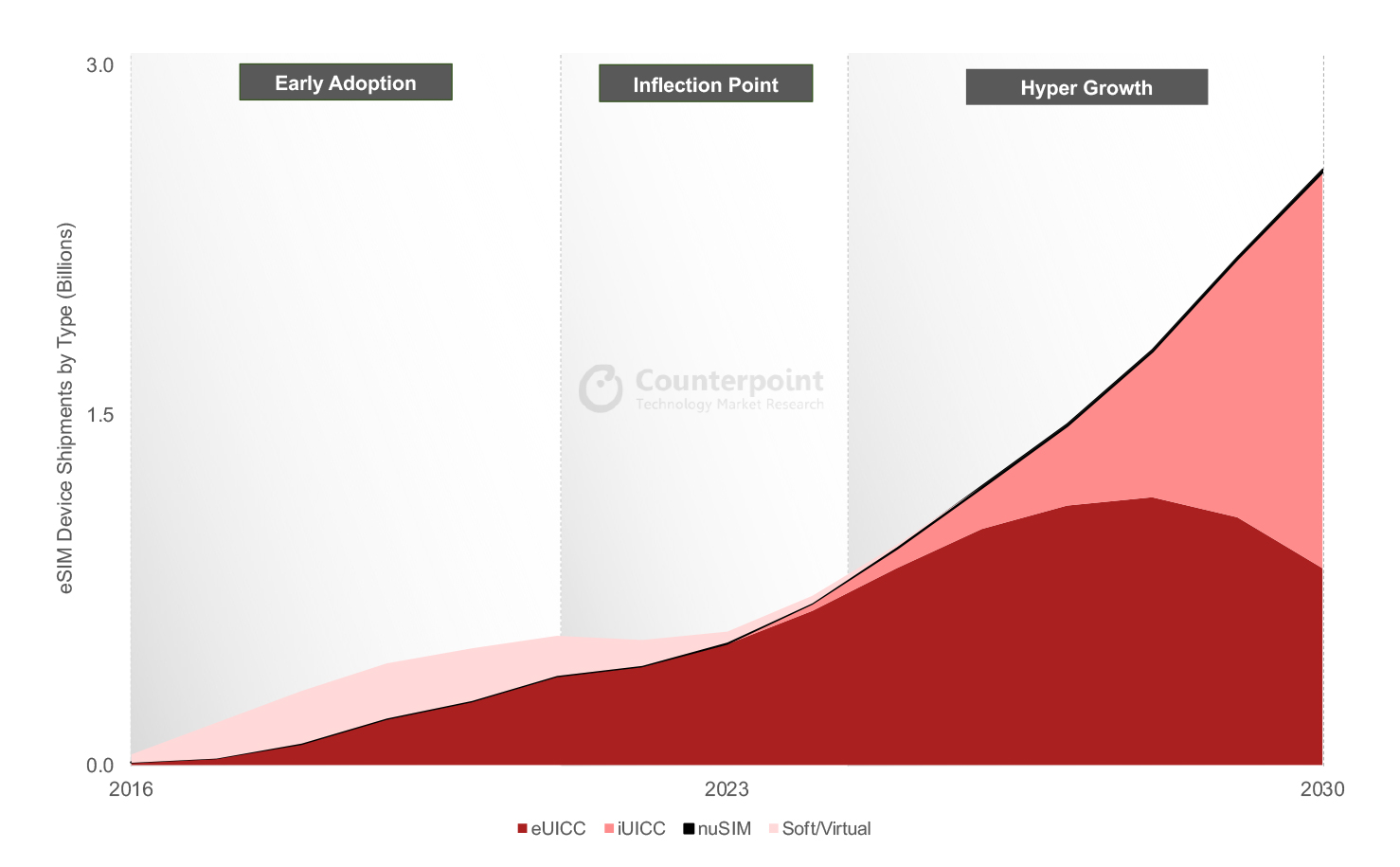
Source: Global eSIM Landscape – Market Outlook and Forecast
Commenting on eSIM adoption across different device categories, Senior Analyst Ankit Malhotra said, “Smartphones have been key in driving primary eSIM awareness among consumers and MNOs, and will continue to be the dominant eSIM-capable device category. Cellular connectivity in smartwatches is growing steadily which is also helping increase the penetration of eSIM-supported smartwatches. The adoption of entitlement servers by MNOs worldwide is a testament to the growing number of smartwatches and other companion devices powered by eSIM. Other cellular-capable consumer devices such as laptops and tablets will also see rapid eSIM adoption in the coming years.”
“The number of IoT/M2M devices equipped with eSIM is poised to grow faster than consumer device categories due to the natural cost, space and remote device management benefits that eSIM offers. The new eSIM IoT specifications SGP.31 by GSMA will accelerate eSIM adoption in the IoT segments potentially eradicating complexities of the existing eSIM Remote Service Provisioning (RSP) platform SM-DP/SM-SR for M2M/IoT segments.”
eSIM Devices Forecast and Analysis
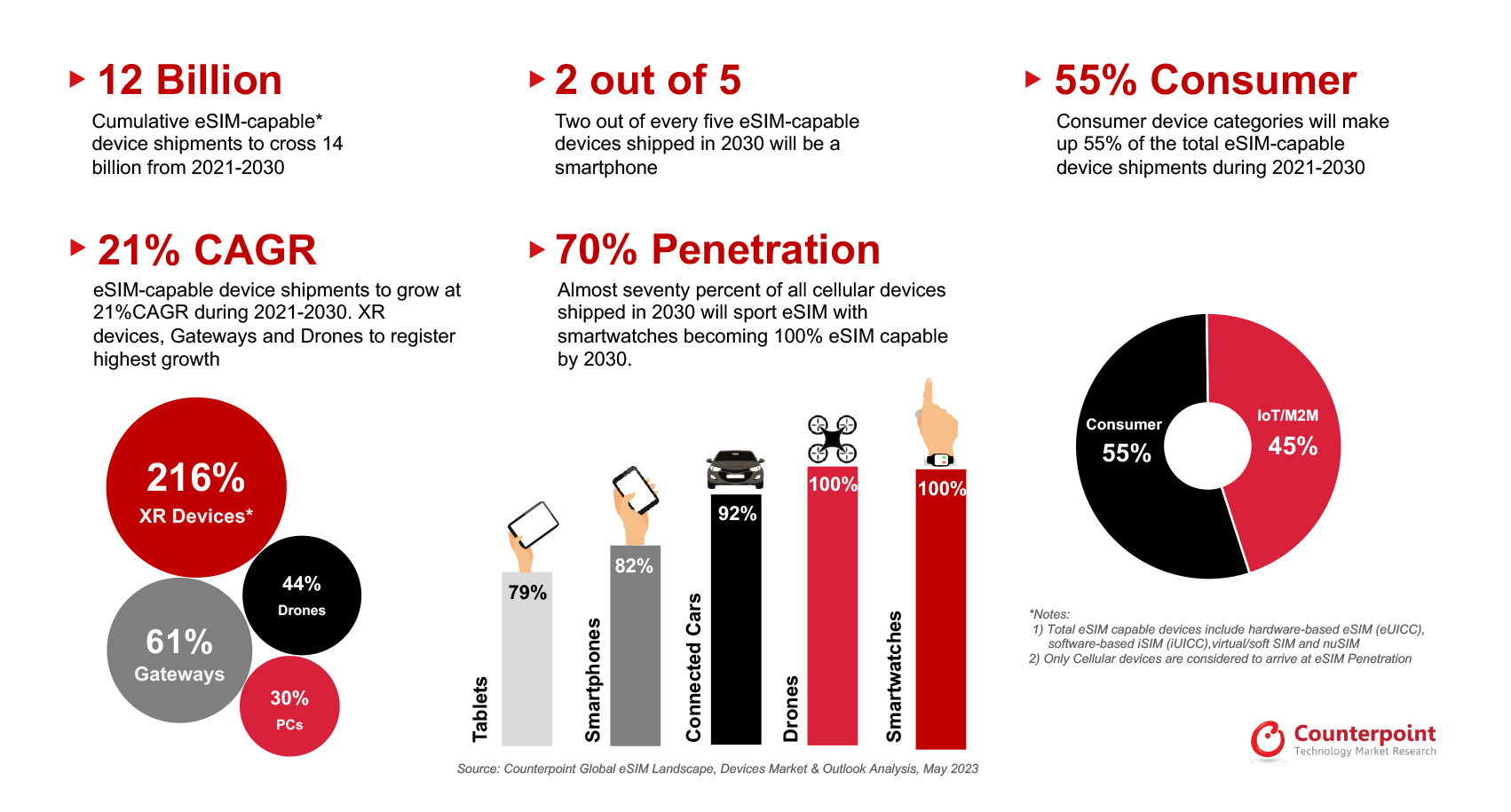
Emerging device categories such as XR, drones and cellular gateways/FWA CPEs will be the fastest-growing categories. 5G-connected drones are another category that will benefit from eSIM technology and drive adoption across several use cases like last-mile delivery, disaster management, search and rescue, education, construction and agriculture. Regulation of beyond-visual-range drones in regions such as Europe will increase the adoption of eSIMs as well.
Automotive and smart mobility are huge growth areas as well. Connected cars are one of the largest and most obvious use cases for eSIMs. Consistent connectivity experience for mobility applications is becoming paramount, particularly for safety use cases such as eCall and the future rise of autonomous driving.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to Omdia (owned by Informa), there is a compelling business case (subscription required) for eSIMs in the IoT market as they could help resolve connectivity issues plaguing enterprises. Some of the areas that could benefit include energy, healthcare and the financial sector, Omdia says.
Counterpoint forecasts iSIM will become the predominant type of SIM post-2028, with cumulative device shipments to reach 4 billion by 2030. Initial demand will come mainly from IoT applications, it says.
According to Omdia, the iSIM can alleviate issues such as chip shortages, energy and size constraints and increased security concerns. It also notes that cellular service providers such as AT&T, Vodafone and Deutsche Telekom have shown more enthusiasm for iSIMs than eSIMs.
References:
eSIM-Capable Devices Set for Hyper-Growth After Crossing Inflection Point
https://www.t-mobile.com/resources/what-is-an-esim-card
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/23/technology/personaltech/esim-sim-cards-travel.html
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
There was steady growth in 5G network coverage in 2022, with the number of subscribers reaching almost 1 billion worldwide. Although most of the 5G deployments in 2022 were in the developed economies of the world, Counterpoint Research expects that the bulk of 5G network roll outs in 2023 will be in emerging markets. This will drive the continuing transition from 5G NSA to 5G SA. To date, 42 network operators have deployed 5G SA commercially.
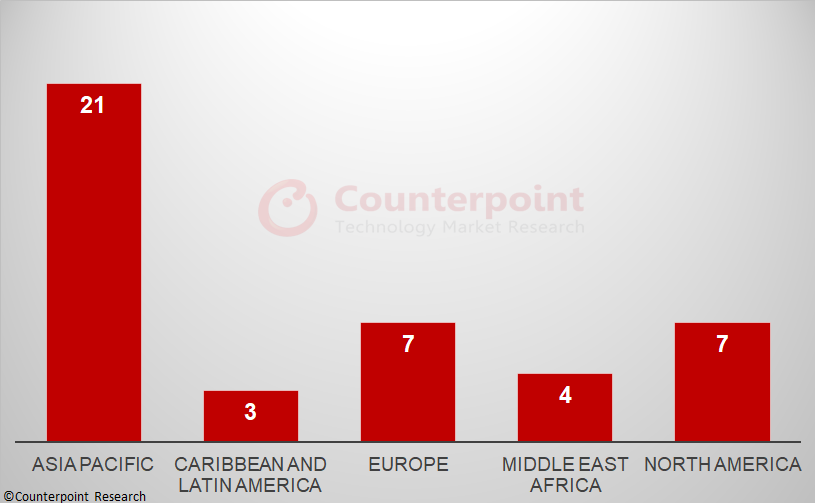
Counterpoint Research ‘s recently published 5G SA Tracker is a culmination of an extensive study of the 5G SA market. It provides details of all operators with 5G SA cores in commercial operation at the end of 2022, with market share by region, vendor and by frequency band. As shown in Exhibit 1, the Asia-Pacific region led the world at the end of 2022, followed by North America and Europe, with the other regions – Middle East and Africa and Latin America – lagging behind.
Key Points:
Key points discussed in the report include:
- Operators – 42 operators have deployed 5G SA commercially [1.] with many more testing and in trials. Most of the deployments are in the developed economies of the world with those in emerging economies lagging. In some markets, operators have adopted a “wait-and-see” approach and are looking for evidence of successful use cases before switching from 5G NSA to SA. The ongoing economic headwinds might also delay commercial deployment of SA particularly during the first half of 2023.
Note 1. By the end of 2022, Dell’Oro Group had identified 39 MNOs that had deployed 5G SA eMMB networks.
- Vendors – Ericsson and Nokia lead the 5G SA Core market globally and are benefiting from the geopolitical sanctions on Chinese vendors Huawei and ZTE in some markets. Asian vendors Samsung and NEC are mainly focused on their respective domestic markets, but and are expanding their reach to Tier-2 operators and emerging markets, while US vendor Mavenir is active across all regions, with multiple deployments due to become live in 2023, including several with Tier-1 operators.
- Spectrum – most operators are deploying 5G in mid-band frequencies, for example, n78, as it provides faster speeds and good coverage. A small number of operators have also launched commercial services in the sub-1GHz and millimetre wave bands. FWA seems to be the most popular use case at present but there is a lot of interest in edge services and network slicing as well.
Report Overview:
Counterpoint Research’s 5G SA Core Tracker, January 2023 tracker provides an overview of the 5G Standalone (SA) market, highlighting the key trends and drivers shaping the market, plus details of commercial launches by vendor, by region and by frequency band. In addition, the tracker provides details about the 5G SA vendor ecosystem split into two categories: public operator and private network markets.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Market Update
- 5G SA Market Deployments
- Commercial Deployment by Operators
- Network Engagements by Region
- Network Engagements by Deployments Status
- Leading 5G Core Vendors
- Mobile Core Vendor Ecosystem
- 5G Core Vendors Market Landscape
- Outlook
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
During its recent Q4 2022 earnings call, Nokia CEO Pekka Lundmark was asked about 5G SA core networks. Lundmark said, “Obviously 5G standalone is now the name of the game because you need 5G standalone in terms of getting the full benefits of 5G. There is going to be a lot of investment in 5G core, and operators will be implementing some critical important services like slicing, which require investment in the 5G core.”
That’s an understatement because 5G SA is needed to realize 3GPP defined 5G features and functions, like security and network slicing. 5G NSA, which is mostly deployed today, is actually 4G with 3GPP 5G-NR for the RAN.
References:
Update on 5G Stand-Alone (SA) Core Networks
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
Global Data: Wireless telcos don’t know how to market 5G SA
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
Why are 5G SA Core networks taking so long to be commercially deployed?
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market driven by 5G SA networks in China
Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Market—A Look into 2023
Mobile Core Network (MCN) growth to slow due to slow roll-out of 5G SA networks


