IoT
IEEE/SCU SoE Virtual Event: May 26, 2022- Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G), IoT, and Cloud Resident Data Centers
This virtual event on ZOOM will be from 10am-12pm PDT on May 26, 2022.
Session Abstract:
IEEE ComSoc and SCU School of Engineering (SoE) are thrilled to have three world class experts discuss the cybersecurity threats, mitigation methods and lessons learned from a data center attack. One speaker will also propose a new IT Security Architecture where control flips from the network core to the edge.
Each participant will provide a 15 to 20 minute talk which will be followed by a lively panel session with both pre-planned and ad hoc/ extemporaneous questions. Audience members are encouraged to submit their questions in the chat and also to send them in advance to [email protected].
Below are descriptions of each talk along with the speaker’s bio:
Cybersecurity for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G NSA and SA) and the IoT
Jimmy Jones, ZARIOT
Abstract:
Everyone agrees there is an urgent need for improved security in today’s cellular networks (3G/4G, 5G) and the Internet of Things (IoT). Jimmy will discuss the legacy problems of 3G/4G, migration to 5G and issues in roaming between cellular carriers as well as the impact of networks transitioning to support IoT.
Note: It’s important to know that 5G security, as specified by 3GPP (there are no ITU recommendations on 5G security), requires a 5G Stand Alone (SA) core network, very few of which have been deployed. 5G Non Stand Alone (NSA) networks are the norm, but they depend on a 4G-LTE infrastructure, including 4G security.
Cellular network security naturally leads into IoT security, since cellular networks (e.g. NB IoT, LTE-M, 5G) are often used for IoT connectivity.
It is estimated that by 2025 we will interact with an IoT device every 18 seconds, meaning our online experiences and physical lives will become indistinguishable. With this in mind it is as critical to improve IoT security as fastening a child’s seatbelt.
The real cost of a security breach or loss of service for a critical IoT device could be disastrous for a business of any size, yet it’s a cost seldom accurately calculated or forecasted by most enterprises at any stage of IoT deployment. Gartner predicts Operational Technologies might be weaponized to cause physical harm or even kill within three years.
Jimmy will stress the importance of secure connectivity, but also explain the need to protect the full DNA of IoT (Device, Network and Applications) to truly secure the entire system.
Connectivity providers are a core component of IoT and have a responsibility to become part of the solution. A secure connectivity solution is essential, with strong cellular network standards/specifications and licensed spectrum the obvious starting point.
With cellular LPWANs (Low Power Wide Area Networks) outpacing unlicensed spectrum options (e.g. LoRa WAN, Sigfox) for the first time, Jimmy will stress the importance of secure connectivity and active collaboration across the entire IoT ecosystem. The premise is that the enterprise must know and protect its IoT DNA (Device, Network & Application) to truly be secure.
Questions from the audience:
I am open to try and answer anything you are interested in. Your questions will surely push me, so if you can let me know in advance (via email to Alan) that would be great! It’s nice to be challenged a bit and have to think about something new.
One item of interest might be new specific IoT legislation that could protect devices and data in Europe, Asia, and the US ?
End Quote:
“For IoT to realize its potential it must secure and reliable making connectivity and secure by design policies the foundation of and successful project. Success in digital transformation (especially where mission and business critical devices are concerned) requires not only optimal connectivity and maximal uptime, but also a secure channel and protection against all manner of cybersecurity threats. I’m excited to be part of the team bringing these two crucial pillars of IoT to enterprise. I hope we can demonstrate that security is an opportunity for business – not a burden.”
Biography:
Jimmy Jones is a telecoms cybersecurity expert and Head of Security at ZARIOT. His experience in telecoms spans over twenty years, during which time he has built a thorough understanding of the industry working in diverse roles but all building from early engineering positions within major operators, such as WorldCom (now Verizon), and vendors including Nortel, Genband & Positive Technologies.
In 2005 Jimmy started to focus on telecom security, eventually transitioning completely in 2017 to work for a specialist cyber security vendor. He regularly presents at global telecom and IoT events, is often quoted by the tech media, and now brings all his industry experience to deliver agile and secure digital transformation with ZARIOT.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Title: Flip the Security Control of the Internet
Colin Constable, The @ Company
The PROBLEM:
With the explosion of Internet connected devices and services carrying user data, do current IT architectures remain secure as they scale? The simple and scary answer is absolutely no, we need to rethink the whole stack. Data breaches are not acceptable and those who experience them pay a steep price.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data sent over the Internet to ensure that eavesdroppers and hackers are unable to see the actual data being transmitted. However, the Router needs meta data (the IP and Port) to make it work. What meta data does the Data level Router have access to?
We need to discuss how to approach the problem and selectively discard, but learn from previous IT architectures so that we can build a more solid, secure IT infrastructure for the future.
Proposition:
I will provide a glimpse of a future security focused IT architecture.
- We need to move most security control functionality to the edge of the network.
- Cloud data center storage should be positioned as an encrypted cache with encryption keys at the edge.
- No one set of keys or system admin can open all the encrypted data.
When data is shared edge to edge we need to be able to specify and authenticate the person, entity or thing that is sharing the data. No one in the middle should be able to see data in the clear.
Issues with Encryption Keys:
- IT and Data security increasingly rely on encryption; encryption relies on keys; who has them?
- Is there really any point to VPN’s Firewalls and Network segmentation if data is encrypted?
- We use keys for so many things TLS, SSH, IM, Email, but we never tend to think about the keys.
- Do you own your keys? If not someone else can see your data!
- What do we need to flip the way IT is architected?
Recommendations for Keys:
- Keys should be cut at the edge and never go anywhere else.
- You should be able to securely share keys along with the data being transmitted/received.
- There needs to be a new way to think about identity on the Internet.
The above description should stimulate many questions from attendees during the panel discussion.
Biography:
Colin Constable’s passion is networking and security. He was one of the founding members of the Jericho Forum in the 2000s. In 2007 at Credit Suisse, he published “Network Vision 2020,” which was seen by some as somewhat crazy at the time, but most of it is very relevant now. While at Juniper, Colin worked on network virtualization and modeling that blurred the boundaries between network and compute. Colin is now the CTO of The @ Company, which has invented a new Internet protocol and built a platform that they believe will change not just networking and security, but society itself for the better.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The Anatomy of a Cloud Data Center Attack
Thomas Foerster, Nokia
Abstract:
Critical infrastructure (like a telecommunications network) is becoming more complex and reliant on networks of inter-connected devices. With the advent of 5G mobile networks, security threat vectors will expand. In particular, the exposure of new connected industries (Industry 4.0) and critical services (connected vehicular, smart cities etc.) widens the cybersecurity attack surface.
The telecommunication network is one of the targets of cyber-attacks against critical infrastructure, but it is not the only one. Transport, public sector services, energy sector and critical manufacturing industries are also vulnerable.
Cloud data centers provide the required computing resources, thus forming the backbone of a telecommunications network and becoming more important than ever. We will discuss the anatomy of a recent cybersecurity attack at a cloud data center, review what happened and the lessons learned.
Questions:
- What are possible mitigation’s against social engineering cyber- attacks?
-Multifactor authentication (MFA)
-Education, awareness and training campaigns
- How to build trust using Operational Technology (OT) in a cloud data center?
Examples:
- Access monitoring
- Audits to international standards and benchmarks
- Security monitoring
- Playbooks with mitigation and response actions
- Business continuity planning and testing
Recommendations to prevent or mitigate DC attacks:
- Privileged Access Management across DC entities
- Individual credentials for all user / device entities
- MFA: One-Time Password (OTP) via text message or phone call considered being not secure 2-Factor Authentication anymore
- Network and configuration audits considering NIST/ CIS/ GSMA NESAS
- Regular vulnerability scans and keep network entities up to date
- Tested playbooks to mitigate security emergencies
- Business continuity planning and establish tested procedures
Biography:
Thomas Foerster is a senior product manager for Cybersecurity at Nokia. He has more than 25 years experiences in the telecommunications industry, has held various management positions within engineering and loves driving innovations. Thomas has dedicated his professional work for many years in product security and cybersecurity solutions.
Thomas holds a Master of Telecommunications Engineering from Beuth University of Applied Sciences, Berlin/ Germany.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Video recording of this event: Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks, IoT, and Cloud-Resident Data Centers – YouTube
Previous IEEE ComSoc/SCU SoE March 22, 2022 event: OpenRAN and Private 5G – New Opportunities and Challenges
Video recording: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i7QUyhjxpzE
India’s Airtel, Vodafone Idea preparing for commercial NB-IoT after pilots
Danish Khan | ET Telecom (editd and corrected by Alan J Weissberger)
Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea Limited are now preparing to launch commercial narrow-band IoT (NB-IoT) service in India in the coming months having brought various partners on board to develop a complete device and sensor ecosystem. Both Indian telcos are in currently in various stages of pilot runs in different circles.
Airtel is now deploying around 20,000 sites in Karnataka and Chennai to conduct NB-IoT trials. “We’ll be going with a pilot in a denser way rather than just a few trial sites..in a couple of months, we will be commercially rolling out,” Ajay Chitkara, Director and CEO, Airtel Business, told ET.
Vodafone Idea Limited, on the other hand, has already conducted commercial pilots in eight cities in India, and is now hoping to win its first commercial NB-IoT deployment deal in the coming weeks.
“We’re looking at winning our first commercial deployments over the next six weeks. So commercially we’re also seeing customers now, wanting to buy that. Once we contract them will go and deploy,” Nick Gliddon, chief enterprise business officer separately told ET.
Gliddon said that all eight pilots were conducted in cities like Kochi, Jaipur, Bengaluru, and Chennai and involved smart meters. “We’ve run a long-term trial with those guys to understand how the network and services work.
Airtel’s Chitkara said that the telco’s IoT services are already growing in the country and NB-IoT technology will help it address the demand. “We have around five and a half million subscribers on our IoT side and the way growth is happening, we need to eventually get into NB-IoT.”
Chitkara added that NB-IoT will offer scale as compared to traditional IoT technologies. “130 million devices need to be connected on meter and that is the reason people say that you can’t run on the existing ecosystem.”
Vodafone is also aiming to expand its NB-IoT in India in the next 12 months to tap specific opportunities in the smart city space along with other applications.
NB-IoT is a new 3GPP spec which will likely be included in IMT 2020. It is designed to broaden the future of IoT connectivity, providing significantly improved and deeper network coverage for communication between machines while lowering power consumption by devices.
Both telcos are taking a partner-led approach building a complete ecosystem including sensors, devices and to bring the overall cost down for devices.
Chitkara said that building applications is a challenge, thereby Airtel is bringing partners on board. “…another issue is with all the sensors and other things there is a cost involved so it’s a chicken and egg story…the cost of those 2G sensors still is cheaper so we are making sure at least this whole ecosystem is build up so that we can bring from some more sites,” he added.
Vodafone Idea has already brought over 25 partners on-board and is working towards doubling this number soon to build new use cases around the new technology. These partners are mainly startups and small and medium enterprises that will bring in hardware and software capabilities to enable new NB-IoT use cases.
Rival Reliance Jio Infocomm had last year launched an NB-IoT network with a commercial network available in Mumbai. It is preparing to foray into enterprise services and may expand its IoT services accordingly.
Jio recently claimed that it is the only telco in India to have the capability and network footprint for a nationwide launch of NB-IoT services. Airtel, however, countered the claim by saying that the company’s pan-India 4G network is also ready to support the technology, along with LTE-M.
Within the enterprise business, IoT is expected to be the growth area going forward, given that the consumer retail business continues to face competitive headwinds. India’s IoT market size is expected to increase to $9 billion by 2020 from $1.3 billion in 2016, according to consultancy firm Deloitte.
Highlights of IDTechEx: IoT Connectivity Sessions and Exhibits: November 15-16, 2017
Introduction:
The Internet of Things (IoT) will connect existing systems and then augment those by connecting more things, thanks to wireless sensor networks and other technologies. Things on the ‘edge’ form mesh networks and can make their own automated decisions. This article reviews key messages from conference technical sessions on IoT connectivity and describes a new Wireless Mesh Sensor network which is an extension of IEEE 802.15.4.

Sessions Attended:
1. Overcoming Adoption Barriers To Achieve Mass IIoT Deployment, Iotium
Early adopters are realizing the complexities involved in scalable mass deployment of Industrial IoT. These includes deployment complexities, security issues starting from hardware root of trust to OS, network, cloud security and application vulnerabilities, and extensibility. This session will focus on these 3 areas in-depth to help you successfully deploy your own IIoT strategy.
2. Overcoming The Connectivity Challenge Limiting IoT Innovation, Helium
The hardware and application layers of IoT systems are supported by robust, mature markets, with devices tailored for any use case and pre-built infrastructure platforms from Microsoft, Google and AWS. But the connectivity layer, without which the entire system is useless, still has numerous challenges. It takes too much knowledge and time to get data from sensors to apps that most staffs don’t have. The speaker discussed a streamlined, secure approach to connectivity that will make building a wireless IoT network as easy as designing a mobile app, thereby removing the greatest barrier to mass IoT adoption.
3. Whitelabel The Future: How White Label Platforms Will Streamline The IoT Revolution, Pod Group
As expectations tend towards personalized, data-driven services, responding immediately to market changes is becoming a key differentiator, creating the need for mutual insight on both sides of the market. Whitelabelled platforms are an effective intermediary, allowing unprecedented levels of customer interaction and paving the way for truly end-to-end IoT systems.
Barriers to achieving a sustainable IoT business model:
-Businesses must have flexible resources and structures:
a] lacking tools to implement (new technology/billing)
b] organizational changes (retraining staff/expertise at top level)
-55% of large enterprises are not pursuing IoT (Analysys Mason)
-Digital proficiency lacking in 50% of companies (Price Waterhouse Cooper)
-IoT platforms can introduce users to systems as a whole & streamline management
There are several different types of IoT platforms:
-IoT Application Enablement Platform – in-field application (eg. device) management
-Connectivity Management Platform (CMP) – management of network connections
-Back-end Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – hosting space and processing power
-Hardware-specific Platform – only works with one type of hardware
Many platforms tied to specific provider/device:
– ‘Agnostic’ platforms ideal to integrate different types & retain adaptability (eg. connectivity management integrating device mgmt. & billing capabilities).
-CMPs offer a range of services: managing global connections, introducing providers to clients, integration with hardware vendors, etc.
-CMPs focus on centralized network management- not on building new services.
-Application Enablement Platforms focus on device management/insight–billing hierarchy enables new business services with additional layers, e.g. analytics.
What will the IoT landscape look like in the near future?
-Various connectivity technologies competing, platform technology and open-source driving software/service innovation.
-Hybrid platform offers ease of management, solid foundation for building recurring revenue from value-added services – ensures business is scalable and able to roll-out services quickly.
-Capable platform shifts focus from day-to-day management to building new bus. models and recurring rev. streams..
-Whitelabel platforms help to implement new business models throughout business, consolidate management of legacy and future systems, and build recurring revenue from end-to-end value-added services.
Choose right platform for your business – ease-of-use, billing hierarchies, multi-tech integration key to generating recurring revenue.
With a strong platform in place to future-proof devices and manage customer accounts and business, enterprise can be part of full IoT ecosystem, gaining value from every stage.
4. From Disappointing To Delightful: How To build With IoT, Orange IoT Studio
Many engineers, designers and business folks want to work with IoT devices, but don’t know where to begin. Come learn which mistakes to avoid and which best practices to copy as you integrate with IoT or build your own IoT products. This presentation examines the consistent, systematic ways that IoT tends to fail and delight. The talk explained what makes IoT unique, and examined why it’s not at all easy to classify IoT platforms and devices.
5. Many Faces Of LPWAN (emphasizing LoRaWAN), Multi-Tech Systems
Until recently, most M2M and Internet of Things (IoT) applications have relied on high-speed cellular and wired networks for their wide area connectivity. Today, there are a number of IoT applications that will continue to require higher-bandwidth, however others may be better suited for low-power wide-area network options that not only compliment traditional cellular networks, but also unlock new market potential by reducing costs and increasing the flexibility of solution deployments.
Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN)s are designed to allow long range communications at low bit rates. LPWANs are ideally suited to connected objects such as sensors and “things” operating on battery power and communicating at low bit rates, which distinguishes them from the wireless WANs used for IT functions (such as Internet access).
Many LPWAN alternative specifications/standards have emerged – some use licensed spectrum such as ITU-R LTE Cat-M1 and 3GPP NB-IoT, while other alternatives such as LoRaWAN™ are based on as specification from the LoRA Alliance and uses unlicensed industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) radio band/spectrum.
IoT has many challenges – from choosing the right device, to adding connectivity and then managing those devices and the data they generate. Here are just a few IoT connectivity challenges:
- Long battery life (5+ yrs) requires low power WAN interface
- Low cost communications (much lower than cellular data plans)
- Range and in-building penetration
- Operation in outdoor and harsh environments
- Low cost infrastructure
- Robust communications
- Permits mobility
- Scalable to thousands of nodes/devices
- Low touch management and provisioning – Easy to attach assets
- Highly fragmented connectivity due to a proliferation of choices
Mike Finegan of Multi-Tech presented several LPWAN use case studies, including tank monitoring in Mt. Oso, CA; point of sales terminals, kiosks, vending machines; oil and gas; distributed energy resources; agriculture; and a real time control school traffic sign (T-Mobile using NB-IoT equipment from MultiTech (the first public NB-IoT demo in North America).
Mr. Finegan concluded by emphasizing the importance of security functions needed in an IoT Connectivity Platform. A “trusted IoT platform” should reduce attack vectors, provide secure and reliable end to end communications, and device to headquarters management services.
6. What Makes a City Smart? Totem Power
The framework necessary to build holistic infrastructure that leverages capabilities essential to realizing the full potential of smart cities – concepts including curbside computing power, advanced energy resiliency and ubiquitous connectivity.
An interesting observation was that fiber trenches being dug to facilitate 5G backhaul for small cells and macro cells could accommodate electrical wiring for power distribution and charging of electric vehicles within the city limits.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
At it’s booth, Analog Devices/ Linear Technology displayed an exhibit of SmartMesh® – a Wireless Mesh Sensor Network that was based on a now proprietary extension of IEEE 802.15.4 [1]. SmartMesh® wireless sensor networking products are chips and pre-certified PCB modules complete with mesh networking software; enabling sensors to communicate in tough Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) environments.
Note 1. IEEE 802.15.4 is a standard which defines the operation of low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs) via PHY and MAC layers. It focuses on low-cost, low-speed ubiquitous communication between devices.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) wireless sensor networks (WSNs) must support a large number of nodes while meeting stringent communications requirements in rugged industrial environments. Such networks must operate reliably more than ten years without intervention and be scalable to enable business growth and increasing data traffic over the lifetime of the network.
More information on SmartMesh® is here.
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.idtechex.com/internet-of-things-usa/show/en/
https://www.idtechex.com/internet-of-things-usa/show/en/agenda
http://www.linear.com/dust_networks/
Ericsson Survey: Network Operators Focus on New Markets for 5G Revenue
Survey Highlights:
Most network operators say they’re ready for “5G” even if they don’t know what it will actually deliver (the RAN and other key functions haven’t even been discussed by ITU-R WP5D for IMT 2020, let alone agreed upon), Ericsson found in a survey of wireless network operators around the world (see References and hyper-links below). Many expect the enterprise market and Internet of Things (IoT) applications to drive revenue growth from 5G technology.
More than three-quarters of the respondents said they were in the midst of 5G trials. That corresponds with research from the Global Mobile Suppliers Association research which found 81 5G trials underway in 42 countries.
23% of survey respondents plan to migrate 4G subscribers to 5G with enhanced services and revenues (but when?). Yet nearly two thirds (64%) of operators said they can’t pay for 5G by simply raising rates on consumers, because consumers are “tapped out.” Eighteen percent of respondents said they expect to monetize 5G by “expanding to new markets—enterprise/ industry segments.”
“In 2016, 90% pointed to consumers as the central segment in their planning and only 34% focused on specialized industries,” the Ericsson researchers wrote in this year’s report. An increased emphasis on the enterprise market is a key shift since a previous Ericsson 5G operator survey was conducted in 2016.
“This year, operators are seeing that the consumer market is saturated, so planning for 5G is more evenly split across specialized industry segments (58%), business users (56%) and consumers (52%),” the Ericsson researchers added.
Specific industry segments on which operators expect to focus 5G monetization efforts include media/entertainment (cited by 69% of respondents), automotive (59%), public transport (31%), healthcare (29%) and energy/ utilities (29%).
Providing industry-specific services to these industry segments will be important in 5G monetization, according to 68% of respondents. The single most important use case in the media/entertainment segment is high-quality streaming, respondents said. Other top use cases by segment included:
- Automotive: autonomous vehicle control
- Public transport: Smart GPS
- Healthcare: Remote robotic surgery
- Energy & utilities: Control of edge-of-grid generation
More than three quarters (77%) of respondents said third-party collaboration is an essential element in 5G monetization and 68% said they need to find new revenue-sharing models.
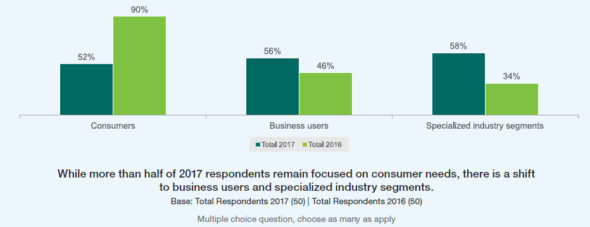
Chart courtesy of Ericsson’s 5G Readiness Survey
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
Survey Questions and Methodology:
Some of the questions asked in the survey:
-Exactly how have preparations for 5G evolved over the past year?
-Where do telcos stand now in their 5G activities and developments?
-What actions are service providers taking now in anticipation of 5G?
-What priorities drive their initiative?
-How ready are they to take leadership positions in the 5G future?
The survey’s objective was to obtain a snapshot of the state of the industry in relation to next-generation mobile technology. Last year, we struggled to find 50 executives globally who were far enough along in 5G to answer the survey questions.
This year, Ericsson says they “easily identified 50 executives, both business and technical leaders, from 37 operators around the world. As leaders of their organizations’ 5G efforts, they are at the center of the 5G evolution. That increase clearly signifies the growing recognition among industry leaders of 5G’s importance.”s
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/assets/local/narratives/networks/documents/5g-readiness-survey-2017.pdf
5G Monetization Survey: Operators Look to IoT for Revenue Growth
NSR: Satellite IoT market forecast at $2.9B by 2026
The global satellite M2M and IoT market is expected to grow to $2.9 billion in revenue by 2026, according to satellite based market research company NSR.
This growth will be driven by over 6.8 million in-service terminals, NSR said in their new report. Potential applications include (see chart below): land transport and especially cargo tracking, which is expected to be the most profitable and sought after segment of the emerging industry.
“Revenues are growing year-over-year across each of the 22 applications NSR identified, and will accelerate as new M2M capacity supply, in the form of new constellations, come online in the medium term,” NSR senior analyst and lead report author Alan Crisp said.
“Most increases in new demand for M2M service today stem from basic product offerings, as for many use cases bandwidth requirements remain in the kilobyte range,” Crisp added.
While most M2M and IoT services require only low bandwidth, NSR also predicts that over the next decade some verticals will demand additional bandwidth to support applications such as big data analytics, engine telematics and live data streaming.
The report states that a number of small satellite constellations will target low bandwidth and latency insensitive applications in agriculture and tracking market segments.
Despite the huge revenues predicted, the report notes that despite growing demand for IoT satellite services, the business case for IoT exclusive satellite constellations has yet to be proven – especially considering the exponential growth of LPWANs, LTE-M and NB-IoT terrestrial networks for IoT.
For example, last week China Mobile-Hong Kong demonstrated a smart parking service carried over its commercial NB-IoT network. Meanwhile, rival wireless network operators 3 Hong Kong (part of Hutchinson-HK) and SmarTone have also made recent announcements of NB-IoT deployments. 3 HK and Huawei have built the NB-IoT infrastructure with NB-IoT modules designed in accordance with the 3GPP standard to facilitate tests and development of NB-IoT applications.

This report answers key questions on the satellite M2M/IoT market:
- Which applications, frequencies and regions exhibit the greatest growth potential?
- How important are latency, security and high bandwidth requirements for upcoming M2M/IoT applications?
- What role will small satellites have with IoT connected devices, and how will this impact the existing satellite M2M/IoT operators?
- How can satellite benefit from the growth of Low Power Wide Area networks?

References:
https://www.telecomasia.net/content/satellite-iot-market-tipped-hit-29b-2026?src=related
China Telecom: IoT partnerships with 3 network operators; Huawei NB-IoT award from GSMA
China Telecom’s 3 New IoT Partnerships:
China Telecom has entered three new partnership agreements aimed at accelerating the development of services based on an Internet of Things (IoT) open platform.
The operator has announced an expanded partnership with HKT to cover the development of a common IoT open platform to serve the operators’ customers in the combined geographical footprints of mainland China and Hong Kong.
With the arrangement, each network operator’s customers will be able to deploy IoT and M2M services on the other’s network.
The joint offering will allow seamless switching of IoT subscription between networks by integrating the two commonly-deployed embedded universal integrated circuit card platforms. The multi-domestic service is supported by the Ericsson Device Connection Platform (DCP).
China Telecom also announced a similar strategic partnership with Norway-based Telenor Group. That partnership will allow customers from China Telecom and Telenor Connexion to deploy IoT and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) services in each other’s network. It enables China Telecom’s multi-national enterprise customers with outbound IoT business to deploy their assets and offerings under Telenor Connexion’s networks in the European and other Asian Markets.
Similarly, Telenor Connexion’s global customers can enjoy the benefits of the rapidly growing Chinese market by leveraging on China Telecom’s IoT network resources and business capabilities. The seamless switching of IoT subscription between networks is achieved by the integration of the two commonly deployed eUICC platforms which are the key component of IoT collaboration across borders.
To recap, China Telecom’s multi-national enterprise customers will gain access to Telenor Connexion’s IoT networks in Europe and Asian markets, and will serve as Telenor Connexion’s preferred partner for connectivity in China.
…………………………………………………………………………..
A separate agreement with Orange Business Services will enable both companies to serve their respective enterprise customers through a combined footprint across three continents – Asia, Europe and Africa.
The network operators have also agreed to collaborate on the development of new service models supporting global IoT opportunities and to explore the potential of enhancing existing IoT capabilities and applying emerging technologies such as mobile IoT.
GSMA functions to connect participants throughout the global mobile communications ecosystem, including almost 800 operators and over 300 enterprises. The association lays significant emphasis on addressing common concerns to best serve the interests of mobile operators worldwide. GSMA’s “Best IoT Innovation for Mobile Networks” award identifies and rewards Internet of Things (IoT) products, solutions, services, and new business models to highlight innovative breakthroughs based on new technological developments and standards of mobile networks.
Huawei’s NB-IoT solution comprises an NB-IoT terminal chipset, terminal operation system LiteOS, NB-IoT RAN and EPC, OceanConnect (a cloud platform for IoT management), and OpenLab that helps related enterprises develop IoT services and applications. The goal of the Huawei NB-IoT solution is to jointly build a better connected IoT solution and ecosystem with operators and partners from a diverse range of vertical industries. Huawei was the first to launch associated products after 3GPP released standards formulated for NB-IoT – one of multiple competing “standards” for Low Power WANs (LPWANs) targeted at the (non LAN) IoT market.
In 2016, Huawei began conducting NB-IoT trial applications in conjunction with mainstream network operators and partners. In early 2017, Huawei launched Boudica120, the world’s first commercial NB-IoT chip.
http://www.huawei.com/en/news/2017/6/GSMA-Best-IoT-Innovation-Mobile-Networks-Award
Highlights of IoT Developers Conference, April 26-27, 2017 in Santa Clara, CA