MVNO
Astound Broadband to launch MVNO service powered by T-Mobile
Astound Broadband (Astound), the sixth-largest U.S. cable provider, will soon debut its new Astound Mobile service, powered by T-Mobile. Known for its award-winning customer service, Astound will make its mobile offering available to customers in approximately 4 million homes currently passed by the company across 12 states.
The service will be exclusively available to Astound home internet customers who are eligible residents in Massachusetts and Corpus Christi, Midland-Odessa, Temple, and Waco Texas in June. The company plans to continue to launch Astound Mobile in its remaining markets by the end of the year.
“Astound’s entrance into the wireless market comes at a time when the need for fast, reliable, high-value broadband and mobile services is at an all-time high and more critical than ever,” said Jim Holanda, Astound CEO. “Through our relationship with T-Mobile, we’ll bring exceptional choice, value and savings, and competitive, award-winning services that customers need to stay connected to their world.”
“Astound has a collective commitment to serving customers with innovative technologies and award-winning customer service in the regional broadband marketplace. By choosing the T-Mobile nationwide network, Astound will further their commitment by creating custom applications that benefit their customers beyond their home or business on T-Mobile’s nationwide 5G network,” said Dan Thygesen, Senior Vice President of T-Mobile Wholesale and head of T-Mobile’s growing wholesale business.
Astound’s mobile product will leverage the nation’s largest, fastest and most awarded 5G network through T-Mobile and will offer a variety of plans that when bundled with Astound’s ultra-fast, award-winning internet service, customers will have access to savings and competitive offerings. Astound will offer two “pay by the gig” plans and two unlimited talk and text plans. Customers can choose a plan whereby they only pay for the data they need or they can expand to an unlimited plan with data allotted to each user. Customers will be able to stream, browse, talk and text with confidence knowing Astound Mobile runs on T-Mobile’s powerful network with 5G service in all 50 states.

Astound didn’t reveal the price of its mobile plans today but said it will offer a variety of plans bundled with its internet service, including two “pay by the gig” plans and two unlimited talk and text plans. Customers can choose a plan whereby they only pay for the data they need or they can expand to an unlimited plan with data allotted to each user, according to the press release.
Astound Broadband is comprised of organizations formerly known as RCN, Grande Communications, Wave Broadband and enTouch. The company’s markets include Chicago, Indiana, eastern Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, New York City, Maryland, Washington, D.C., Texas and regions throughout California, Oregon and Washington.
Last month, Astound, which is the sixth largest U.S. cable provider, announced that it had partnered with Reach, the software-as-a-service company, to offer mobile service.
On a net basis, cable accounted for about 75% of total industry phone net additions in Q1 2023, according to analyst Craig Moffett. Combined, cable now serves nearly 12 million wireless subscribers.
Earlier this year, the National Content & Technology Cooperative (NCTC) made arrangements with AT&T to provide its members with a white-label MVNO service. Reach also is involved in that deal.
About Astound Broadband:
Astound Broadband (astound.com) is the sixth largest cable operator in the U.S., providing award-winning high-speed internet, broadband communications solutions, TV, phone services, and fiber optic solutions for residential and business customers across the United States. Astound Broadband is comprised of organizations formerly known as RCN, Grande Communications, Wave Broadband, and enTouch. The company services Chicago, Indiana, Eastern Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, New York City, Maryland, Washington, D.C., Texas, and regions throughout California, Oregon, and Washington.
References:
CableLabs Evolved MVNO Architectures for Converged Wireless Deployments
CableLabs and its members (cablecos/MSOs) initiated a technical working group to create an evolved architectural blueprint for mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs). The working group’s aim is to explore new converged architectures that will benefit CableLabs members’ wireless deployments while highlighting the benefits, impacts to existing deployments and features needed to be supported by both mobile network operator (MNO) and MVNO networks.
As cable operators in the US and abroad enter the mobile game or look to enhance their existing mobile services through MVNO partnerships, the working group’s intention is to “create an evolved architectural blueprint for mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs),” Omkar Dharmadhikari, wireless architect at CableLabs, explained this week in a blog post.
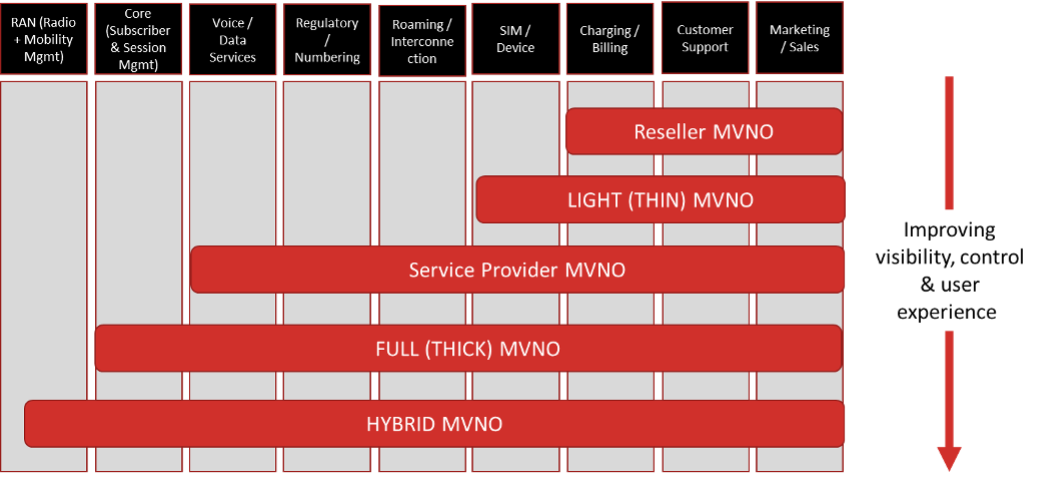
Many traditional broadband services providers—also known as multiple system operators (MSOs)—might not own mobile infrastructure but have (or are in the process of negotiating) MVNO arrangements with MNOs. These kinds of arrangements allow them to bundle fixed and mobile broadband services into a single service package. Traditionally, most MSOs adopt a reseller-type “Wi-Fi first” MVNO, where the MVNO doesn’t own any mobile network infrastructure and resells the services leveraging MNO infrastructure.
Source: CableLabs
The MVNO models vary based on the amount of mobile network infrastructure that the MVNO owns and the degree of control over the management of different aspects of MVNO subscriptions and their service offerings. One common aspect of all traditional MVNO models is leveraging the radio access network (RAN) of a partner MNO.
With the advent of 5G and the availability of shared spectrum, many MSOs are actively evaluating offload opportunities for enhancing MVNO economics and are contemplating deploying their own mobile radio infrastructure in specific geographic areas (in addition to their substantial Wi-Fi footprint).
Such MSOs now have to contend with three disparate sets of wireless infrastructures:
- the MSO’s community Wi-Fi network,
- the MNO’s 4G/5G network, and
- the MSO’s own 4G/5G network.
This creates a new type of MVNO model called hybrid-MVNO (H-MVNO) that enables MVNOs to offload their subscribers’ traffic from the MNO network—not just to their Wi-Fi networks but also to the MVNO-owned mobile network when inside the coverage footprint of their wireless network(s).
Maximizing data offload via the H-MVNOs’ own wireless assets—thus ensuring a consistent user experience and enforcing uniform and personalized policies as users move in and out of coverage of these three networks—will require the deployment of new converged network architecture and related capabilities.
While CableLabs working group’s focus on the hybrid MVNO challenge is new, several cable operators, including a group in North America, are already pursuing that initiative.
Comcast and Charter Communications have MVNO deals with Verizon, operate their own metro and in-home Wi-Fi networks, and have secured CBRS licenses in areas where mobile traffic is anticipated to be heaviest. Charter plans to launch a field trial involving “thousands” of CBRS small cells in one market in early 2022, and use that as a blueprint of sorts for deployments in additional markets.
Canada’s Cogeco plans to enter the wireless business in Canada via a proposed H-MVNO framework. Tied into that plan, Cogeco secured 38 spectrum licenses in the 3500MHz band at auction, and says it now has spectrum licenses to cover about 91% of its broadband footprint.
H-MVNOs intend to offload as much traffic as possible to help offset the costs of going to their mobile network operator partners. But they’ll also need a new converged network architecture and related capabilities to ensure a consistent user experience and the enforcement of uniform and personalized policies as customers move in and out of these different networks, Dharmadhikari explained.
The new CableLabs working group is exploring H-MVNO architectures that use dual-SIM and single-SIM approaches.
Unlike architectures with dual SIMs, single-SIM devices allow the H-MVNO network to enable seamless low-latency mobility for data applications across the MNO and H-MVNO networks. An ideal architecture for offering mobile services with single-SIM device usage is to combine the roaming architecture and a mobility interface, both of which are standardized in 3GPP.
However, due to the targeted nature of H-MVNO mobile deployments, the signaling load can increase on MNO mobility management core network elements, as the H-MVNO subscribers move in and out of H-MVNO network coverage.
To overcome this problem, CableLabs evaluated new MVNO architectures that make use of dedicated network elements within the MNO domain to serve H-MVNO subscriber traffic, thereby isolating it from the MNO subscriber traffic and eliminating the increase in signaling load on core network elements that serve MNO subscribers.
In addition, CableLabs evaluated voice handling in scenarios where H-MVNOs don’t want to deploy their own voice platforms. One option is to offer voice via a third-party voice service provider; another is to enable additional interfaces between the MNO and the H-MVNO network to leverage the MNO’s voice platform.
If you have any further questions, please feel free to reach out to the MVNO Interconnect Technical WG Lead, Omkar Dharmadhikari ([email protected]).
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/cable-tech/cablelabs-sizes-up-hybrid-mvno-architectures-/d/d-id/773484?
AT&T to be the primary network services provider for DISH MVNO customers
The ten-year agreement, which CNBC said was worth at least $5 billion, will serve as a back-up while the company rolls out its own mobile network. Dish has relied to date mainly on the T-Mobile network, as part of the deal signed last year to acquire Boost Mobile and other assets from T-Mobile following its merger with Sprint.
AT&T will also provide transport and roaming services, to support Dish’s 5G network roll-out. Dish said it is committed to becoming the fourth facilities-based carrier in the U.S. and is aiming to bring its cloud-native, OpenRAN-based 5G network to 70% of the population by 2023.
“With an MVNO deal past 2027, Dish can focus on denser markets and leave rural to AT&T,” said MoffettNathanson principal analyst Craig Moffett. “Dish desperately needs an MVNO to fall back on past 2027, because the economics of building to rural are awful, and a network that doesn’t have rural isn’t tenable.”
Tammy Parker, Senior Analyst at GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company, offered her opinion:
This deal is highly beneficial to AT&T as the company not only gains at least $5bn in revenue streams over the term of this ten-year agreement from new MVNO subscribers, it will also have access to DISH’s spectrum holdings to support DISH customers on the AT&T network. The NSA is not exclusive for either party, so both can go out and find new dance partners; however, given the depth and breadth of this agreement, that would appear both unlikely and unnecessary.
Both companies are poised to ride the US wireless industry’s ongoing growth wave. This is increasingly driven by the rollout of 5G, which enables faster network speeds, lower latency and new use cases, including Internet of Things services, that will result in many users having multiple wireless subscriptions. According to GlobalData’s latest forecasts, the number of unique mobile users in the US will increase by 5% over the next five years. Furthermore, total mobile subscriptions in the US will expand by more than 30% during that time and there will be nearly 692.6 million US mobile subscriptions by year-end 2026.
A fascinating part of this new arrangement is that it provides a glimpse into AT&T’s concerns regarding the possibility that DISH could sell out to another entity, perhaps even Amazon or Google. Rumors have abounded, even before DISH agreed to build its 5G network on Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) cloud platform, about possible negotiations between Amazon and DISH regarding the former’s potential use of DISH’s forthcoming 5G network to offer new services. Though there is nothing new to report there, this NSA stipulates that AT&T will be allowed to terminate the NSA in the event of a qualifying change of control of DISH. This could include a rival wireless provider, US cable company or ‘certain large technology companies’ taking over 50% more of the voting power or economic value of DISH. AT&T would still have to support DISH’s MVNO customers for up to two years after such a termination. “T-Mobile, and its Sprint network, is currently the primary MVNO partner for Boost and Republic. Ting operates on every nationwide network except AT&T. However, although DISH’s involvement saved T-Mobile’s acquisition of Sprint, the relationship between DISH and T-Mobile appears to have been fraught from the start. T-Mobile’s plans to shutter its 3G network by January 2022, leaving many of DISH’s customers without network service, has created an especially contentious standoff between the two companies, which likely helped pave the way for DISH’s new agreement with AT&T.”
Dish has 8.89 million retail wireless subscribers as of its last quarterly earnings report, while AT&T has more than 186 million mobile subscribers.
CNBC said that the pact is a potential precursor to a DirecTV-Dish merger since it brings AT&T and Dish closer together. Jonathan Chaplin, an analyst at New Street Research, said in a note to clients that one of the biggest obstacles to a merger has been the notion that “AT&T hates Dish.” Some of those bad feelings stem from the botched 2007 merger, when AT&T felt Ergen had reached a handshake deal and negotiated in bad faith, according to people familiar with the deal who asked not to be named because the discussions were private.
But the telecommunications world has dramatically shifted from 2007. AT&T is no longer run by Randall Stephenson, who stepped down as CEO last year. The wireless giant is reorganizing itself around 5G and fiber networks. AT&T could use the $5 billion Dish will give it over the next 10 years to pay down debt from its two enormous acquisitions of WarnerMedia and DirecTV.
While AT&T’s MVNO pact allows Dish to be a stronger competitor to AT&T, “getting access to Dish’s spectrum could help improve AT&T’s competitive position,” noted Chaplin, and facilitating a merger between DirecTV and Dish will help both companies.
Bringing together two competing satellite-TV providers — especially as both companies lose pay-TV customers each quarter as the world shifts to digital streaming television — would unlock billions in synergies, as satellites can be retired, duplicative jobs eliminated and competitive costs eradicated.
Still, regulators would need to feel comfortable that a Dish-DirecTV would be beneficial for consumers. While that remains uncertain, “it is a hurdle, not a barrier,” wrote Chaplin.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Upstart Wytec International 5G small cell technology for cable operators
Wytec International, Inc., a small San Antonio based technology company with with 11 employees, is ramping up to bring 5G mobile wireless services to cable operators. The company wants to upend the MVNO industry in the U.S. so that cable operators are able to compete on par with mobile carriers. That means removing excess costs with which cable operators currently contend. Wytec owns patented small cell technology now recognized as a key component to delivering 5G fixed and mobile wireless services.
“Our 5G mobile services, offered through a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) Agreement, will include a three-option plan designed for cable operators to “compete on par” with U.S. mobile carriers,” comments William Gray, CEO of Wytec.
Since the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) awarded Wytec its small cell patent known as the Light-Pole Node (LPN-16) on September 15th 2017, Wytec has been testing its unique features, capable of supporting a robust, “neutral host” dense wireless network, utilizing utility poles as its distribution access throughout America’s cities. This feature collaborates exceptionally well with cable operators due to its existing utility pole access. In conjunction with its LPN-16 technology, Wytec’s MVNO solution includes carrier “roaming agreements” allowing cable subscribers access to a worldwide mobile network.
Wytec is nearing completion of a multi-test trial in the Central Business District (CBD) of Columbus, Ohio in preparation of securing its first MVNO Agreement to prospective cable operators in early March of 2020.
As Robert Merola, Wytec’s Chief Technology Officer and President of Wytec, states, “Our initial network deployment originates from one of the top ten Tier One providers in the U.S. and will expand accordingly in support of multiple MVNO cable operators throughout the U.S. We are excited to provide 5G services to the cable industry.”
Wytec has invested more than five years advancing its intellectual property related to fixed and mobile wireless distribution. In September of 2017 Wytec was awarded a “utility” patent on its LPN-16 Small Cell technology from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) clearing a path for the development of its first 5G network deployment in Columbus, Oho.

Columbus, OH is the site of Wytec’s first 5G trial
……………………………………………………………………………………….
In June of 2019, the FCC awarded an “experimental use” license to Wytec for the testing of the newly issued Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum operating in the 3.5 GHz frequency band. The company plans to add fifteen (15) additional markets under an agreement with the sixth largest cable operator in the U.S. (unnamed).
Wytec has been funding its LPN-16 R&D through private Regulation D 506c PPM Offerings (Wytec’s Pre-IPO Offering) to accredited investors and subsequently filed an SEC S-1 registration (Now Effective) in preparation for listing its shares on a public market.
About Wytec
Wytec International, Inc. is a facilities-based wireless operator located in San Antonio, Texas with wireless networks located in San Antonio, Texas; Columbus, Ohio; and Denver, Colorado. Wytec owns six wireless patents with its latest patent focused on 5G small cell technology called the LPN-16. Wytec was named one of San Antonio’s Best Tech Startups in 2018 and 2020 by The Tech Tribune. Learn more at www.wytecintl.com.
Media Contact:
Brianna Lohse, Media Relations
(210) 233-8980
[email protected]
References:


