Month: November 2019
Deloitte: Mobile Consumer Survey shows tepid demand for 5G
Research from Deloitte suggests consumers are currently struggling to become enthusiastic about 5G networks. Wireless network operators all over the world are currently trying to create excitement for 5G, often in a bid to get customers to pay more each month for the service. But for the most part, they haven’t come up with any compelling NEW 5G applications or use cases.
The 5G focus continues to be on enhanced mobile broadband which most consumers are not very much interested in. The reason is that 4G-LTE is perfectly adequate for most video streaming and other high bandwidth applications today. 5G is yet to have a “killer application” for general consumers. Until that happens, it’s going to be a hard sell, according to Deloitte.
Author’s Note:
We have repeatedly stated that the real value of 5G will be in industrial automation, robotics and medical wearables all of which will take advantage of ultra high reliability/availability and ultra low latency. That is hopefully coming in 3GPP Release 16 which MUST be folded in to 3GPP’s IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT submission to ITU-R WP 5D sometime in mid to late 2020.
From the Deloitte report:
As 5G rolls out, we’re starting to see Australians value different dimensions of connectivity, such as reliability and latency. And this will require operators, handset manufacturers and other parts of the ecosystem to get the consumer proposition right – and continue to evolve it.
Some possible emerging technologies like VR/AR could be an important 5G application, but only when ultra low latency is included in IMT 2020 and has been widely implemented. Mobile game streaming, like Google Stadia and Project xCloud, might be another use-case for 5G networks at that time.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From Deloitte’s Mobile Consumer Survey – a multi-country study of mobile users:
• The impending roll out of 5G in Australia is being met with a lukewarm reception from consumers. Current use cases appear tilted towards the enterprise and up to 84% of consumers are not convinced it is worth the proposed $15 monthly premium operators are vying for.
• 5G interest among consumers is decreasing, with the percentage of respondents who would switch to 5G as soon as it is available or upon hearing good things, down by 5% compared to 2018.
• Consumers are increasingly wary of the data they share and conscious of their right to withhold information, with 52% of respondents having used privacy enhancing applications and 89% at some point having denied an app access to location, photos, contacts, or other mobile phone features.
• Convenience and growing availability are driving increased use of biometric authentication.
• Since 2017, adoption of facial recognition software on the phones of respondents has seen a 100% compound annual growth rate (supported by the release of the iPhone X and other handsets), while fingerprint-authorized payments is also on the rise, especially among millennials.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Peter Corbett, Deloitte Partner and National Telecommunications lead stated:
“We are probably entering a period of disillusionment with the technology until it becomes clearer for consumers on how 5G will improve their day-to-day lives.”
Corbett believes 5G early adopters should be prepared to not receive the experience they’d expect from a new generation network.
“Consumers should prepare to be disappointed with 5G in the short-term, as the network will experience growing pains until it is fully established which will come with small-cell deployments and the auction of mmWave in early 2021.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Hype around the globe:
Part of the tepid reception to the 5G roll out may be due to infrastructure delays. In South Korea, where the technology was first rolled out, a million subscribers signed up within 69 days; 11 days faster than 4G’s uptake.
However, this was driven by aggressive commercial promotions from local mobile operators showing K-pop idols as the world’s first subscribers rather than due to 5G-service functionality, which had a number of issues with coverage and speed on launch.13 Korean consumer hype was also driven by strong demand for 5G devices, with the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G’s launch based in South Korea.
Similar hype was experienced in the UK, with mobile operator EE launching 5G in June this year, to be quickly followed by Vodafone, Three and O2 by the end of the year.15 Initial reviews indicate the potential for uptake is there but coverage has a long way to go, with maximum speeds yet to be reached in the first six cities for 5G deployment.15 The consensus has been that the roll out of 5G has been smoother than 4G, and that moving to a 5G plan is not worse. However, it will likely only be the early adopters using the network until greater coverage and device diversity are available.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The complete 2019 Deloitte Mobile Consumer Survey (Australia Edition) can be downloaded here after you complete a brief form. The 2019 study comprises more than 44,150 responses across 28 countries. Australian findings are based on a nationally representative sample of over 2000 consumers aged 18 to 75, polled online during June 2019.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
U.S. Mobile Consumer Survey:
Information about the U.S. edition is here. It will be available in December 2019. For this year’s report, Deloitte surveyed 2,000 US-based consumers to learn more about behaviors and trends that are influencing a wide range of wireless and mobility products and services. This eighth edition of the Global
Mobile Consumer Survey also highlights the differences among US consumers across generational divides—capturing findings from six distinct age groups, ranging from ages 18 to 75. Here are a few key data points from the executive summary of the survey:
- While smartphones continued to thrive over the past year, other mobile platforms (including tablets) showed signs that the market is still trying to figure out if—and where—they fit. At the same time, all consumer age groups showed increased awareness about data privacy and security.
- U.S. consumers expressed growing interest in voice assisted technologies, certain Internet of Things (IoT) applications
and devices, and the introduction of fifth-generation (5G) wireless
technologies. - Overall, 60 percent of respondents indicated that 5G is either “fairly” (34 percent) or “very” (26 percent) important to them now, compared with 55 percent who felt that way a year ago (see figure 12). The perceived importance of 5G is highest among the 25–34 age group (77 percent believe it’s either “fairly” or “very” important), followed by the 35–44 (73 percent) and 18–24 (69 percent) age groups.
- 29 percent of survey respondents now believe that their current 4G/LTE network speed at home is either “a little” or “much” faster than their home Wi-Fi (vs. 27 percent in 2017). 29 percent perceive no difference in speed, and 22 percent say their 4G/LTE is either “a little” or “much” slower than their home Wi-Fi.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www2.deloitte.com/au/mobile-consumer-survey
https://www.telecomstechnews.com/news/2019/nov/14/deloitte-consumers-apathetic-5g-networks/
Market Research Firms say Telcos Need to Invest in AI now!
Due to ever increasing demand for data, saturated mobile markets, and stiff opposition from cloud companies, global telecom network providers are facing difficult times. These market pressures have led to vicious price wars for mobile services and, as a result, declining average revenue per user (ARPU). This is especially true in India where Vodafone Idea and Bharti Airtel have recently announced huge losses, write-downs as their share prices collapsed.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Artificial Intelligence (AI) use in Telecommunications:
For many global telecoms, shoring up market share under today’s pressures while also future-proofing operations means having to invest in AI. The telecom industry is expected to invest $36.7 billion annually in AI software, hardware, and services by 2025, according to Tractica.
Through its ability to parse large data sets in a contextual manner, provide requested information or analysis, and trigger actions, AI can help telecoms cut costs and streamline by digitizing their operations. In practice, this means leveraging the increasingly vast gold mine of data generated by customers that passes through wireless networks — the amount of data that moves through AT&T’s wireless network has increased 470,000% since 2007, for example.
AI applications in the telecommunications industry use advanced algorithms to look for patterns within the data, enabling telcos to both detect and predict network anomalies, and allowing them to proactively fix problems before customers are negatively impacted.

Some forward-thinking telcos have focused their AI investments on four main areas:
- Network optimization
- Preventive maintenance
- Virtual Assistants
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
In these areas, AI has already begun to deliver tangible business results, according to blogger Liad Churchill
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Meanwhile, a Tractia report on AI for Telecommunications Applications identifies the following functions which will benefit from AI:
- Network Operations Monitoring & Management
- Customer Service & Marketing VDAs (Voluntary Disclosure Agreements)
- Intelligent CRM Systems
- Customer Experience Management
- Cybersecurity & Fraud Mitigation
- Other Use Cases
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Here are a few takeaways from the AI in Telecommunications report by Business Insider Intelligence:
- Telecoms have long struggled with their customer experience image: In 2018, telecommunications had the lowest average Net Promoter Score (NPS), a measure of how favorably a company is viewed by customers, of any industry.
- Companies that use advanced analytics, which can be accessed via AI, to improve this image and the overall customer experience are seeing revenue gains and cost reductions within a few years of adoption.
- Most (57%) executives believe that AI will transform their companies within three years, per Deloitte’s State of AI in Enterprise.
- Overall, telecoms should focus on a hybrid organizational model to move beyond pilots to launch full-scale AI solutions that can have the biggest impact on their companies.
References:
https://www.businessinsider.com/the-ai-in-telecommunications-report-2019-7
https://techsee.me/blog/artificial-intelligence-in-telecommunications-industry/
ZTE, China Telecom and China Unicom complete 5G co-build, co-share verification
ZTE Corporation, in partnership with China Telecom and China Unicom, has today completed the network verification based on the co-build, co-share mode in the commercial 5G environment, launching the world’s first NSA co-build co-share sites of 1.8 G/2.1 G/3.5 G in Hangzhou, China. That fully verifies the large-scale commercial capabilities of the 5G co-build co-share mode, and lays a solid foundation for greatly reducing initial investment in 5G and efficiently promoting 5G constructions.
The verification, based on the real 5G commercial network environment, covers the basic functions of network selection and anchor carrier triggering, network management functions of rights management and northbound interface in the data transmission environment, as well as multi-dimensional deep network sharing capability verification, such as multi-vendor, multi-operator mobility.
The co-build, co-share mode is capable of providing the broadband multi-operator 5G services on the same 5G base station, and reasonably allocating spectrum resources based on user requirements and service requirements. It fully demonstrates the system’s stability and outstanding performance, as well as its complete capacity for large-scale commercial use.
In addition, compared with the original construction strategy that each operator builds its own 5G networks, 5G co-build co-share sites across operators will effectively save investment in 5G networks. By promoting the sharing of infrastructure between operators, the co-build co-share mode can help operators build 5G networks with lower costs and more effective methods.
On September 9, 2019, China Telecom and China Unicom signed the 5G network co-build co-share framework cooperation agreement. As a strategic partner of China Telecom and China Unicom, ZTE fully supports their network construction and service operation. ZTE has innovatively proposed a flexible ultra-broadband spectrum application solution to support the co-build co-share mode, which helps reduce infrastructure construction costs, thereby further realizing the economic and social value of 5G.
In the future, ZTE will continue to partner with China Telecom and China Unicom to explore the applications of new 5G technologies in commercial networks, improve network quality, build more high-quality 4/5G networks, in a bid to provide users with better services.
ZTE is a provider of advanced telecommunications systems, mobile devices, and enterprise technology solutions to consumers, carriers, companies and public sector customers. As a part of ZTE’s strategy, the company is committed to providing customers with integrated end-to-end innovations to deliver excellence and values as the telecommunications and information technology sectors converge. Listed in the stock exchanges of Hong Kong and Shenzhen (H share stock code: 0763.HK / A share stock code: 000063.SZ), ZTE sells its products and services in more than 160 countries.
To date, ZTE has obtained 35 commercial 5G contracts in major markets, such as Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa (MEA). ZTE commits 10 percent of its annual revenues to research and development and takes leadership roles in international standard-setting organizations.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
ZTE and and Guangdong Branch of China Mobile have won Best Industry Solution Award from ICT by virtue of ZTE’s Common Edge solution at PT Expo China 2019:
Based on ZTE’s Common Edge platform, Guangdong branch of China Mobile and ZTE jointly piloted MEC edge computing services, conducting pre-commercial verification of the SA networking, construction mode, edge service application scenarios, and the cooperation mode with third parties.
ZTE’s Common Edge solution features converged access of wireless network and fixed network, which supports multiple systems such as 4G, 5G, and WiFi, thereby building a unified fixed and mobile convergence platform.
Moreover, this solution supports cloud-based deployment and unified O&M. Embedded MEC, edge MEC and central cloud are deployed on the same base in a distribution mode. The dual-core (OpenStack+K8S) driving function provides efficient, flexible and flowing computing power, offering a unified edge cloud view and improving management efficiency. Based on AI engines, cloud-edge collaboration and edge-to-edge collaboration, the solution implements dynamic follow-up service flows and intelligent optimization of power. By means of unified management and local unattended O&M, this solution significantly reduces O&M costs. In addition, this solution features embedded hardware in the site equipment room, such as IT BBU V9200 and TITAN C600, to implement zero-site and close-to-user deployment. With front wiring design, it is easy to maintain E5410/E5430 short chassis servers in the edge equipment room and compatible with mainstream acceleration hardware (GPU / FPGA / SmartNIC), supporting AI, image processing and video processing.
ZTE’s Common Edge solution revolutionizes the traditional closed telecom network architecture, and exposes the edge network infrastructure, hardware acceleration capability, edge network shunting capability and wireless network perception capability to the third-party applications, thereby helping various industries construct a win-win 5G ecosystem.
ZTE’s Common Edge solution has been widely used in the fields of industrial manufacturing, smart grid, Internet of Vehicles, entertainment & media, public safety, education, health, finance and agriculture. It focuses on industrial applications of wireless network capability exposure, big video, Internet of Vehicles, intelligent manufacturing and electric power. To date, by means of this solution, ZTE has carried out extensive cooperations and piloted with more than 100 strategic partners and over 200 industrial users to accelerate the penetration of 5G into various industries.
ZTE is a provider of advanced telecommunications systems, mobile devices, and enterprise technology solutions to consumers, carriers, companies and public sector customers. As a part of ZTE’s strategy, the company is committed to providing customers with integrated end-to-end innovations to deliver excellence and values as the telecommunications and information technology sectors converge. Listed in the stock exchanges of Hong Kong and Shenzhen (H share stock code: 0763.HK / A share stock code: 000063.SZ), ZTE sells its products and services in more than 160 countries.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/20191112e1.html
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/20191101e1
Strand Consulting: Why the Quality of Mobile Networks Differs
Many believe that a mobile application can measure the quality of the mobile and fixt network. Strand Consult’s new report “The Moment of Truth – Why the Quality of Mobile Networks Differs” describes the many factors that affect the network’s capacity and coverage and the user’s experience.
It assesses and compares the mobile apps which claim to measure network quality at a time when mobile networks are evolving from 2G, 3G and 4G to a combination of 4G and 5G. The next generation mobile networks are more complex and use technologies such as carrier aggregation, spectrum management, and multiple input/multiple output (MIMO). These innovations change how a network is built and operated and therefore also how the networks performance can be measured.
As each cellular network is constructed differently, making comparisons across operators is difficult. The simple measurements collected and presented on a glossy app and the user’s experience will also differ considerably for various reasons.
While the effort to bring facts and evidence to policy and regulatory discussions is welcome, network measurement data from mobile apps is increasingly presented without adequate scientific and methodological background. Users of the various apps are perplexed about wildly differing measurements reported by the individual app even if the tests are run at the same time, in the same location and on the same device.
The same data may be used to praise a mobile operator one day but then to rank it in the bottom the next. Moreover, the performance of mobile operators varies widely across different apps. Vodafone, Orange, EE, Telia, Telenor, AT&T, Verizon, and Telefonica, and others have appeared either at the top or bottom of any one app report. This says more about the design of the app than the quality of any one network.
The report “The Moment of Truth – Why the Quality of Mobile Networks Differs” reviews the mobile apps and provides a common framework to judge their usefulness and applicability by better understanding they inner workings, potential and pitfalls.
Strand Consult’s report “The Moment of Truth – Why the Quality of Mobile Networks Differs” is offered either with or without a workshop. The report focuses on the many factors that influence the experience of network coverage, quality, and the capacity.
The report’s chapters include:
- A review of the leading mobile network measurement apps. We describe and categorize how and which data the apps collect. We assess the marketing strategies of the apps in what they purport to measure versus the scientific state of the art of what can be measured.
- An analysis of how the app interacts with the mobile phone and how the phone’s specifications can influence resulting network measurement. International examples are provided to demonstrate how wildly measurements can vary.
- A review of the question of network quality in light of the relevant market factors. Network performance is mapped against factors such as gross domestic product (GDP), churn, ARPU, and so on.
- An examination of the conditions for infrastructure development in the relevant country and different policies used by government actors for network deployment. It details how rollout policies vary considerably and compares these results to reported network quality, coverage, and capacity.
- The report also examines measurement tools either mandated or preferred by telecom regulatory policies. The report examines the scientific basis for these tools and whether they can measure what they claim.
- Viewpoints and analysis which is helpful to improve the discussion about the quality of mobile coverage and its measurement and can help to increase the scientific understanding of policymakers, press, and the public.
Strand Consult’s new report “The Moment of Truth – Why the Quality of Mobile Networks Differs” provides valuable scientific, policy, and market background to bring context to the growing popularity of network quality measurement by mobile apps. The report will help policymakers focus on the facts and other important scientific information when deciding how to measure network quality and what role apps should have in policy.
The report demonstrates that relying on mobile apps to measure network quality provides an incomplete and inaccurate picture of the network. It is based in part upon 7 years of experience of working with mobile coverage policy, regulatory issues and mobile measurement app initiatives across several countries.
If you want to know more, please request more information about our unique new report.
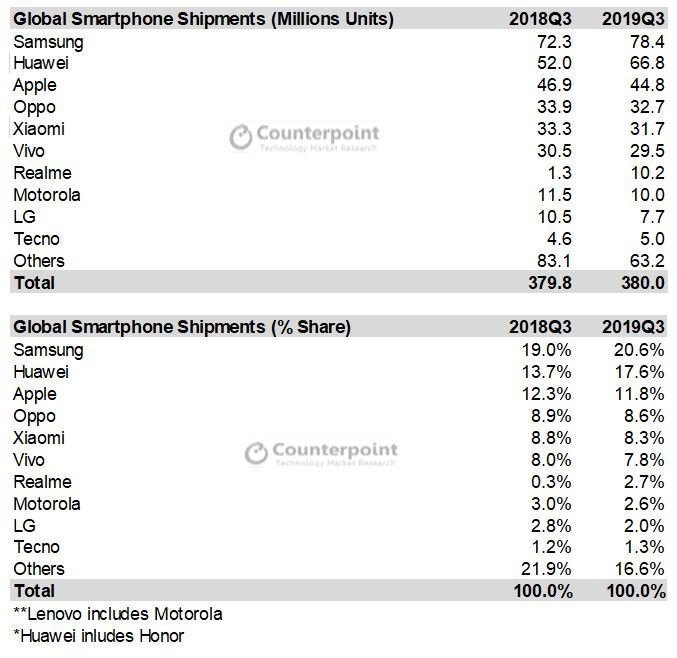
Counterpoint Research: Smartphone Market Decline Ends, What Might Help it Grow?
The global smartphone market showed signs of recovery ending a long period of continuous quarterly YoY declines. Shipments during 3Q 2019 were flat at 380 million units. The two markets that helped halt the slide are India, which has been growing steadily, and China, now showing a slower decline.

Both countries saw healthy channel builds, in India, OEMs prepared early for Diwali and online sales. In China, Huawei, Oppo and Vivo enjoyed healthy demand ahead of the National Day Golden Week holiday in October. The upcoming holiday season should drive smartphone demand into growth for the second half of the year.
Highlights:
- Samsung continued its growth thanks to strong sales of the Galaxy Note 10 and Galaxy A series. The improved product-mix helped it post better profits.
- Huawei grew a healthy 28.5% YoY globally. It captured a record 40% market share in China. It rebounded in Europe after the decline mid-year caused by the US trade ban. As it continues its aggressive push, there’s an increased need for careful inventory management in China and Europe in Q4 2019.
- Apple iPhone shipments were down 4% YoY. However, initial uptake for the iPhone 11 series was robust. In the US, pre-orders and the first week of sales, saw more demand for the iPhone 11 Pro Max and iPhone 11 Pro, but the standard iPhone 11 rose quickly into the best-seller’s list.
- Apple’s price corrections in China and elsewhere with iPhone 11 and iPhone XR stimulated demand during the last week of September.
- Realme was the fastest-growing brand for the second successive quarter, capturing 7th place globally. Strong performances in India and Indonesia drove its growth.
Counterpoint believes the key OEMs with the largest installed bases, especially in developed regions, will rely on 5G as a key point of differentiation and will encourage their users to upgrade. Already, 5G rollouts have been faster than 4G was in its first few months, with 15 commercially available 5G devices and many more lined-up for launch in the last few months of 2019. Nevertheless, 5G smartphones only accounted for 2% of shipments in Q3 2019 and will contribute relatively little to the overall market for the full year 2019. But, 2020 will likely be a breakout year for 5G smartphone adoption,rekindling smartphone demand.
Note: This author completely disagrees with that last conclusion. We don’t think 5G smartphone adoption will achieve any real market traction till late 2021-early 2022.
Analyst Contacts:
SOURCE Counterpoint Research
…………………………………………………………………………………….
Looking at the current scenario, Xiaomi, famous for its commitment to affordability, launched the cheapest 5G model in China at the end of September. The new flagship of Xiaomi’s number series, MI 9 Pro 5G, has a starting price of roughly US$520.
Exhibit 1: 5G enabled new models in 2019
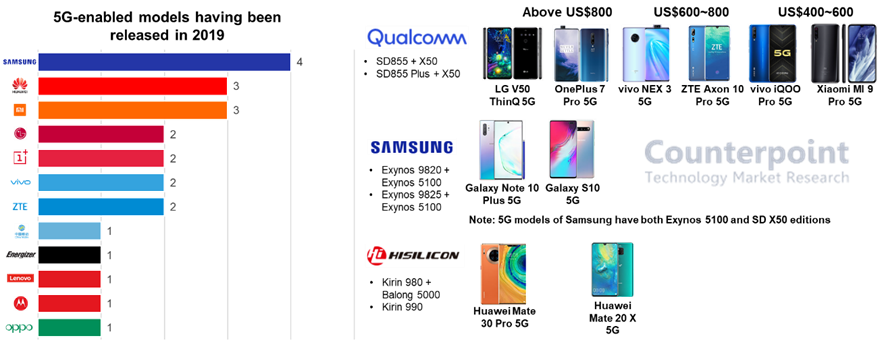
According to the analysis of the 5G cost structure, we expect an addition of US$50 to implement the sub-6Ghz only by using a standalone 5G modem.
However, costs can be reduced through the integration of a modem with the SoC (System on a Chip). Huawei’s Kirin 990 and Samsung’s Exynos 980 had taken a step ahead in this direction, and Qualcomm is expected to launch its first 5G SoC in the Snapdragon 700 family by the end of 2019. Besides, both Qualcomm, MediaTek plans to mass-produce respective 5G flagship platform SDM865, MTK6885, in Q1 2020.
Exhibit 2: 5G platform timeline in 2019 & 2020
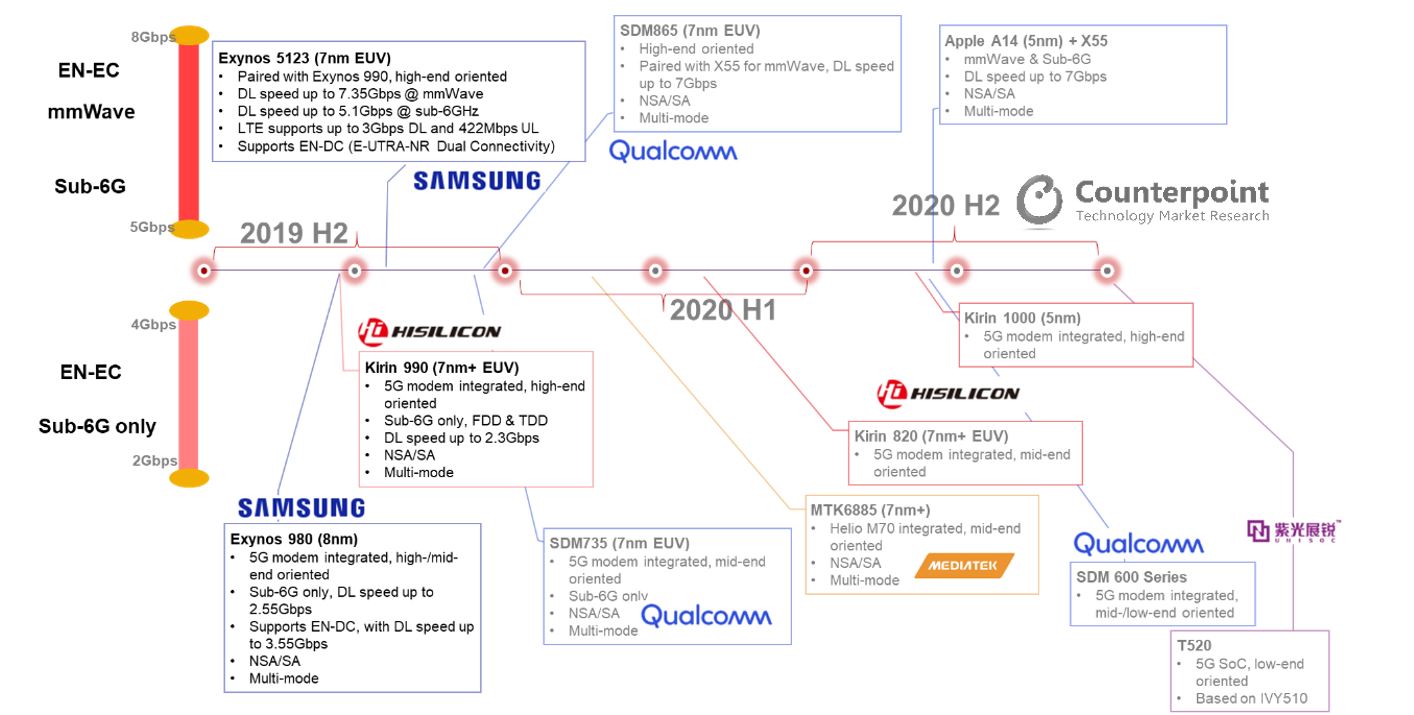 Given the fragmented frequency allocation, we expect smartphone brands targeting North America and parts of European markets will customize designs with an external 5G model for mmWave, even though, most 5G models will resort to a 5G SoC for a cheaper sub-6Ghz only solution.
Given the fragmented frequency allocation, we expect smartphone brands targeting North America and parts of European markets will customize designs with an external 5G model for mmWave, even though, most 5G models will resort to a 5G SoC for a cheaper sub-6Ghz only solution.
To sum up, we believe that 5G smartphones will be available in the mid-end price bands over the course of 2020. As a result, cheaper solutions for a next-generation offering will unlock consumer demand for upgrades of their smartphones.
SK Telecom top winner at Global Telecoms Awards in London, UK
South Korean network operator SK Telecom’s early success in 5G helped it win three awards at the Global Telecoms Awards (GLOTEL Awards), held on November 7 in London, UK. SK Telecom received awards in the categories of ‘5G Implementation Excellence,’ ‘Best Operator,’ and ‘BSS/OSS Transformation Excellence.’
SK Telecom was also highly commended in the consumer IoT and fixed network categories, bringing its awards total on the night to five. Other notable performers were Huawei, with two wins and a highly commended, and ZTE with one win and two highly commended.
With the aim to provide customers with the best 5G service quality, SK Telecom has deployed the fastest and widest 5G network in Korea, arming it with quantum cryptography technologies and an AI-based network management system named TANGO (T Advanced Next Generation OSS). Moreover, by combining its 5G with cutting-edge ICT, the company has introduced a wide range of powerful solutions including 5G-AI Machine Vision, 5G Live Golf Broadcast, AI Video Security and 5G-based Cooperative Intelligent Transportation System.

“I feel confident in saying that this was the strongest set of entries to the awards we’ve had yet,” said Telecoms.com Editor Scott Bicheno (pictured above with Chang-min Park of SK Telecom), who hosted the awards alongside comedian Miles Jupp and was also one of the judges. “Our judges had a really tough job choosing between so many great products, services and projects this year and for that I thank them. The fact that so many entries were highly commended shows how close the scoring was. My congratulations to the winners and thanks everyone who contributed to our best awards yet.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
Here’s the complete list of winners:
5G Implementation Excellence
Winner – SK Telecom: World’s First 5G Commercialization
Advancing Artificial Intelligence
Winner – Telefónica: Aura
Highly Commended – Nokia: AI as a Service for CMCC Hainan
Automation Initiative of the Year
Winner – Huawei: AUTIN
Best 5G Innovation
Winner – Vodafone Germany: Automotive Factory of the Future
Highly Commended – China Mobile, China Southern Power and Huawei: Smart Grid 5G Slice Operation and Monetization
Best Digital Transformation Project
Winner – Infosys and Vodafone UK: Digital Platform
Highly Commended – Singtel: Unboxed
Best Operator
Winner – SK Telecom
Highly Commended – Reliance Jio Infocomm
BSS/OSS Transformation Excellence
Winner – SK Telecom: OSS Evolution for E2E integration and 5G Business
Connecting the Unconnected
Winner – Ufinet: Rural connectivity case studies
Consumer IoT Initiative of the Year
Winner – O2 and Accenture: Making UK homes smarter energy users
Highly Commended – SK Telecom: V2X Service Enabler (VSE)
Digital Transformation Innovation
Winner – BT: The Digital Business Marketplace
Highly Commended – Netcracker: Digital Transformation Solution
Fixed Network Evolution
Winner – Turkcell: Customer Oriented Failure Prioritization and Complaint Management
Highly Commended – SK Telecom: Giga Premium 10G Residential Broadband Internet Service
Ground-breaking Virtualization Initiative
Winner – AT&T: Edge Solutions
Industrial IoT Initiative of the Year
Winner – Dialog Axiata: Affordable and Purpose-built IoT Solutions for Industries in Emerging Markets
Highly Commended – ZTE: ZTE NMVP Solution
Innovating in the Cloud
Winner – MYCOM OSI: The Assurance Cloud
Managed Services Innovation of the Year
Winner – Ericsson and Telenor: Common Delivery Center for innovative Managed Services model
Highly Commended – Saudi Telecom Company: STC Fixed Network Customer Operations Service transformation
Mobile Device Innovation
Winner – Reliance Jio Infocomm: JioPhone
Mobile Money Mastery
Winner – AsiaHawala and Comviva: AsiaHawala powered by mobiquity Money
Most Innovative Cloud Service
Winner – Tata Communications Transformation Services: Cloud Networking and Security as a Service
Highly Commended – Red Hat: Red Hat open hybrid cloud technologies
Project Delivery Perfection
Winner – ZTE: ZTE for China Mobile ‘He-Fetion’ Project
Highly Commended – X by Orange: X by Orange with Red Hat
Security Solution of the Year
Winner – Mobileum Signalling Firewall
Highly Commended – CUJO AI: AI-powered cybersecurity technology
Telecoms Transformation
Winner – Huawei: NFV-SDN based telco cloud technology initiative
Highly Commended – ZTE: 5G Slicing Wholesale Solution for New B2B2C Business Model
………………………………………………………………………………………..
About SK Telecom
SK Telecom is the largest mobile operator in Korea with nearly 50 percent of the market share. As the pioneer of all generations of mobile networks, the company has commercialized the fifth generation (5G) network on December 1, 2018 and announced the first 5G smartphone subscribers on April 3, 2019. With its world’s best 5G, SK Telecom is set to realize the Age of Hyper-Innovation by transforming the way customers work, live and play.
Building on its strength in mobile services, the company is also creating unprecedented value in diverse ICT-related markets including media, security and commerce.
For more information, please contact: [email protected] or [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Global Wireless Solutions (GWS): Only about 25% of mobile phone users of Wi-Fi/VoIP calling
Global Wireless Solutions (GWS) surveyed approximately 5,000 mobile phone consumers and found that its survey results “are even more surprising, because [we found] Wi-Fi calling is not being used in places where cellular service isn’t available or there can be poor signal issues –including the home.”
Only 25% of those surveyed said they were using Wi-Fi calling “often,” compared to 32% who responded that they either had never heard of Wi-Fi calling or didn’t know how to turn it on. Another 18% said they had turned on the feature but didn’t know how often they were actually using it.
The likely reason, from this author’s experience, is the voice quality varies greatly and is awful most of the time, especially from Starbucks or other public hotspots. I use Google Voice over WiFi/IP on my Samsung smart phone, but prefer to use SPRINT CDMA for all my voice calls.

https://www.howtogeek.com/234608/how-to-enable-wi-fi-calling-on-an-android-phone/
……………………………………………………………………………………..
When consumers did use Wi-Fi calling, though, they generally had a good experience with it. Among the survey respondents, 88% who had used Wi-Fi calling said that it worked as well or better than cellular, while 12% who had used Wi-Fi calling ended up turning the feature off because the call performance was worse than their cellular connection.
Asked where they use their mobile phone the most, half of respondents said at home, compared to in the local area (17%), at work (15%) and while commuting (12%).
GWS also asked consumers about factors that will play into their next decision on cellular service contract or purchases. The top three factors were monthly contract cost (19% of those surveyed said it was a factor), the value they felt they were getting for the money (18%) and network reliability (18%). Network coverage (16%), network speed (13%), mobile device cost (8%), availability of a specific mobile device (4%) and contract length (3%) also will impact their decision, consumers reported.
NYC will build Power over Ethernet-based IoT system to track traffic & reboot as needed
New York City [1] officials will put Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) switches at 10,000 intersections in order to remotely repair dysfunctional stoplights. City traffic engineers are working with vendor Transition Networks (Minneapolis, MN) to build PoE systems in which a single cable can power a number of device such as VoIP phones, IP cameras and wireless access points, the city said.
Note 1. NYC is this author’s home town (he grew up in Manhattan). This seems to be a very real and useful IoT project!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
PoE systems pass electric power and data on single cable to various devices, including wireless access points, IP cameras, and VoIP phones. The Managed Hardened Gigabit PoE+ Switch from Transition is designed for outdoor environments and can supply up to 30 watts per port on all eight ports simultaneously.
The switches power cameras and sensors at intersections. The cameras track traffic and pedestrian flows while the sensors count cars and support the city’s Connected Vehicle project. The data is transmitted to the city’s traffic monitoring center.
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Transition Networks, a unit of Communications Systems, provides services and devices for security and surveillance, data center networking, business Ethernet, Fiber-to-the-Desk and wireless backhaul. Customers include enterprises, integrators, service providers, federal agencies, and the military.
According to a company press statement, “This application brings intelligent transportation infrastructure citywide and reinforces the relevance and timeliness of Transition Networks’ strategy of developing smart city Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. Transition Networks is working with a major North American telecommunication services company on the deployment of the solution.”
Anita Kumar, a director of product management and software engineering at Transition Networks, said in a news release.”Installing smart devices across cities allows transit agencies to enact changes that improve safety and traffic flow. Our solution provides the power and connection to make it all possible. Smart device installation will grow in importance as transit agencies look to improve service, create efficiencies and increase quality of life for growing cities.”

Photo courtesy of Transition Networks
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The Connection Vehicle project will support Vision Zero, a plan to eliminate traffic deaths and injuries and reduce damage to vehicles and infrastructure. The NYC deployment uses vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), and infrastructure-to-pedestrian (IVP) communications. V2V communications include blind spot and lane change warnings. V2I communications track cars that speed and run red lights. IVP alerts include warnings to cars when people are in a crosswalk and guidance to blind pedestrians via cell phones.
The new system includes a reboot feature. When there is a problem with a traffic signal, a technician goes out to check the device and reset it manually. Transportation officials will use this new system to reset the devices remotely, without having to close lanes and stop traffic.
Transition’s Device Management System (DMS) software also creates an interactive map of all connected devices, making it easier for city engineers to identify problems in the system. (DMS) software creates an interactive map to see all connected devices, enabling the agency to pinpoint issues and quickly take action. DMS has been an important function for several smart city projects including an installation at New York City’s Brooklyn Bridge.
Transition Networks, “Currently, if a device stops working at an intersection, the agency must take multiple actions prior to deploying a repair technician. This includes scheduling a technician to evaluate the issue and deploying a bucket truck to reach the device. Once the technician is at the site, the lane closures cause significant stress and traffic delays for motorists. Many times the fix only requires a reboot of the device. Transition Networks’ Auto Power Reset (APR) feature provides the ability to remotely reboot or manage Transition Networks’ equipment fixing the issue within minutes and eliminating all of the lane closure requirements. This feature alone will save the agency significant costs and lessen traffic disruptions by reducing the need to send a technician to inspect equipment.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
New York City is counting on these new tools and data collection to improve safety, traffic management and transportation citywide.
New York needs all the help it can get with traffic. Uber and Lyft have increased traffic congestion and trucks deliver 1.5 million packages from Amazon to city residents every day. In Manhattan, the average speed is 7 mph, about 23% slower than 10 years ago.
References:
India’s Airtel, Vodafone Idea preparing for commercial NB-IoT after pilots
Danish Khan | ET Telecom (editd and corrected by Alan J Weissberger)
Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea Limited are now preparing to launch commercial narrow-band IoT (NB-IoT) service in India in the coming months having brought various partners on board to develop a complete device and sensor ecosystem. Both Indian telcos are in currently in various stages of pilot runs in different circles.
Airtel is now deploying around 20,000 sites in Karnataka and Chennai to conduct NB-IoT trials. “We’ll be going with a pilot in a denser way rather than just a few trial sites..in a couple of months, we will be commercially rolling out,” Ajay Chitkara, Director and CEO, Airtel Business, told ET.
Vodafone Idea Limited, on the other hand, has already conducted commercial pilots in eight cities in India, and is now hoping to win its first commercial NB-IoT deployment deal in the coming weeks.
“We’re looking at winning our first commercial deployments over the next six weeks. So commercially we’re also seeing customers now, wanting to buy that. Once we contract them will go and deploy,” Nick Gliddon, chief enterprise business officer separately told ET.
Gliddon said that all eight pilots were conducted in cities like Kochi, Jaipur, Bengaluru, and Chennai and involved smart meters. “We’ve run a long-term trial with those guys to understand how the network and services work.
Airtel’s Chitkara said that the telco’s IoT services are already growing in the country and NB-IoT technology will help it address the demand. “We have around five and a half million subscribers on our IoT side and the way growth is happening, we need to eventually get into NB-IoT.”
Chitkara added that NB-IoT will offer scale as compared to traditional IoT technologies. “130 million devices need to be connected on meter and that is the reason people say that you can’t run on the existing ecosystem.”
Vodafone is also aiming to expand its NB-IoT in India in the next 12 months to tap specific opportunities in the smart city space along with other applications.
NB-IoT is a new 3GPP spec which will likely be included in IMT 2020. It is designed to broaden the future of IoT connectivity, providing significantly improved and deeper network coverage for communication between machines while lowering power consumption by devices.
Both telcos are taking a partner-led approach building a complete ecosystem including sensors, devices and to bring the overall cost down for devices.
Chitkara said that building applications is a challenge, thereby Airtel is bringing partners on board. “…another issue is with all the sensors and other things there is a cost involved so it’s a chicken and egg story…the cost of those 2G sensors still is cheaper so we are making sure at least this whole ecosystem is build up so that we can bring from some more sites,” he added.
Vodafone Idea has already brought over 25 partners on-board and is working towards doubling this number soon to build new use cases around the new technology. These partners are mainly startups and small and medium enterprises that will bring in hardware and software capabilities to enable new NB-IoT use cases.
Rival Reliance Jio Infocomm had last year launched an NB-IoT network with a commercial network available in Mumbai. It is preparing to foray into enterprise services and may expand its IoT services accordingly.
Jio recently claimed that it is the only telco in India to have the capability and network footprint for a nationwide launch of NB-IoT services. Airtel, however, countered the claim by saying that the company’s pan-India 4G network is also ready to support the technology, along with LTE-M.
Within the enterprise business, IoT is expected to be the growth area going forward, given that the consumer retail business continues to face competitive headwinds. India’s IoT market size is expected to increase to $9 billion by 2020 from $1.3 billion in 2016, according to consultancy firm Deloitte.
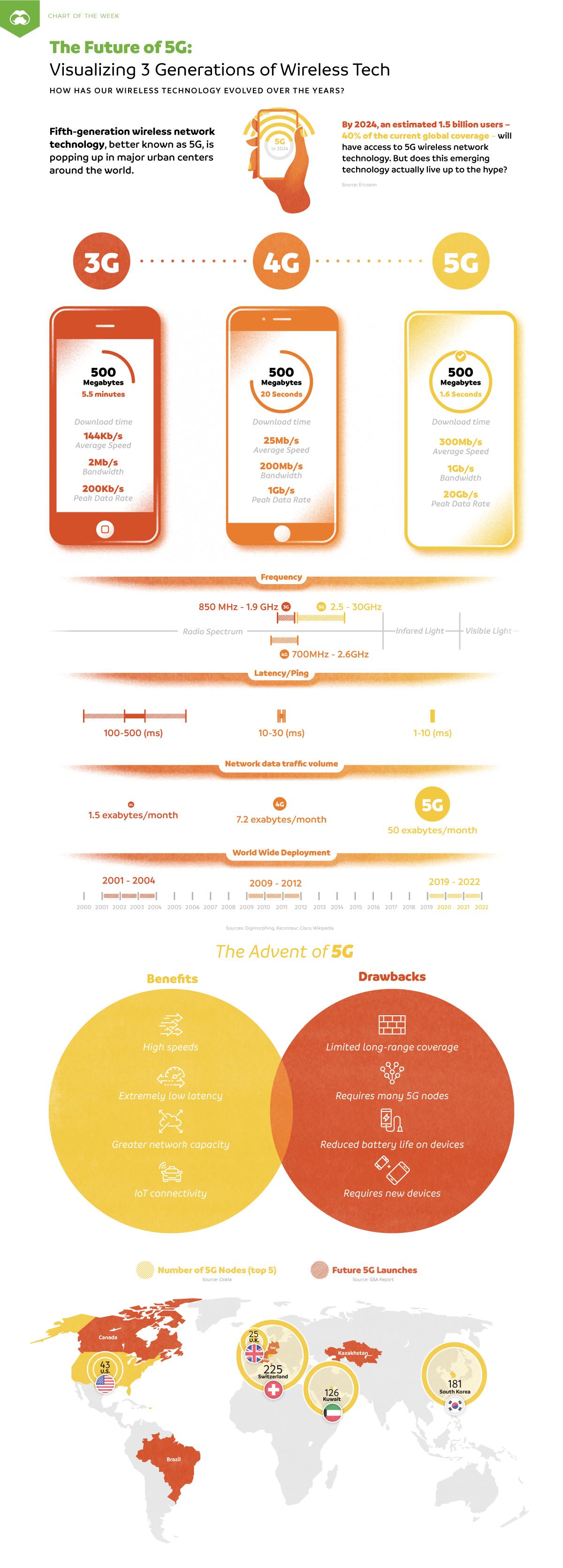
Visual Comparison of 3G, 4G, and 5G
Courtesy of Ashley Viens at Visual Capitalist
Summary:
Wireless technology has evolved rapidly since the turn of the century. From voice-only 2G capabilities and internet-enabled 3G, today’s ecosystem of wireless activity is founded on the reliable connection of 4G.
Fifth-generation wireless network technology, better known as 5G, is now being rolled out in major cities worldwide. By 2024, an estimated 1.5 billion mobile users?which account for 40% of current global activity?will be using 5G wireless networks.
Today’s chart highlights three generations of wireless technology in the 21st century, and the differences between 3G, 4G, and 5G networks.
5G: The Next Great Thing?
With over 5 billion mobile users worldwide, our world is growing more connected than ever.
Data from GSMA Intelligence shows how rapidly global traffic could grow across different networks:
- 2018: 43% of mobile users on 4G
- 2025: 59% of mobile users on 4G, 15% of mobile users on 5G
What Does This Mean For 4G?
4G isn’t going anywhere anytime soon. As 5G gradually rolls out, 4G and 5G networks will need to work together to support the wave of IoT devices entering the market. This network piggybacking also has the potential to expand global access to the internet in the future.