Starlink doubles subscriber base; expands to to 42 new countries, territories & markets
Starlink, the satellite internet service by SpaceX, has nearly doubled its internet subscriber base in 2025 to over 9 million global customers. This rapid expansion from approximately 4.6 million subscribers at the end of 2024 has been driven by new service launches in 42 countries and territories, new subscription options, and the company’s focus on bridging the digital divide in remote and underserved areas.
- Total Subscribers: As of December 2025, Starlink connects over 9 million active customers across 155 countries.
- Growth Rate: The company added its most recent million users in just under seven weeks, a record pace of over 20,000 new users daily. Overall internet traffic from users more than doubled in 2025.
- Geographic Expansion: Starlink’s growth is heavily fueled by international markets where traditional broadband is limited. The U.S. subscriber base alone reached over 2 million by mid-2025.
- Infrastructure: SpaceX has focused heavily on scaling its network capacity, operating more than 9,000 active satellites in orbit and investing heavily in ground infrastructure.
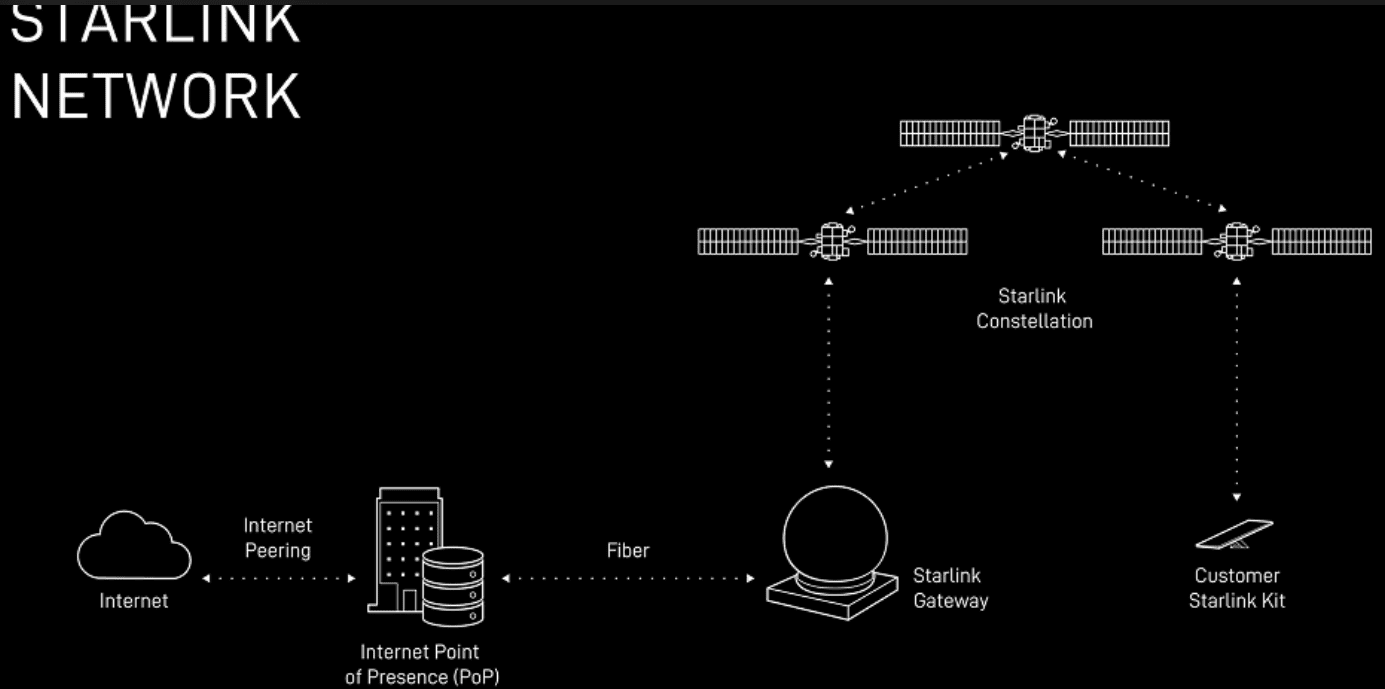
Starlink’s Ground Network:
Starlink has also deployed the largest satellite ground network with more than 100 gateway sites in the United States alone – comprising a total of over 1,500 antennas – are strategically placed to deliver the lowest possible latency, especially for those who live in rural and remote areas.
Starlink produces these gateway antennas at our factory in Redmond, Washington where they rapidly scaled production to match satellite production and launch rate.
Network Resilience:
With more than 7,800 satellites in orbit, Starlink customers always have multiple satellites in view, as well as multiple gateway sites and internet points-of-presence locations (PoPs). As a result, Starlink customers benefit from continuous service even when terrestrial broadband is suffering from fiber cuts, subsea cable damage, and power outages that can deny service to millions of individuals for days.
Additionally, each Starlink satellite is equipped with cutting-edge optical links that ensure they can relay hundreds of gigabits of traffic directly with each other, no matter what happens on the ground. This laser network enables Starlink satellites to consistently and reliably deliver data around the world and route traffic around any ground conditions that affect terrestrial service at speeds that are physically impossible on Earth.
Starlink’s Latency:
To measure Starlink’s latency, the company collects anonymized measurements from millions of Starlink routers every 15 seconds. In the U.S., Starlink routers perform hundreds of thousands of speed test measurements and hundreds of billions of latency measurements every day. This high-frequency automated measurement assures consistent data quality, with minimal sampling bias, interference from Wi-Fi conditions, or bottlenecks from third-party hardware.
As of June 2025, Starlink is delivering median peak-hour latency of 25.7 milliseconds (ms) across all customers in the United States. In the US, fewer than one percent of measurements exceed 55 ms, significantly better than even some terrestrial operators.
- Addressing the Digital Divide: Starlink has positioned itself as a critical solution for rural and remote communities, offering high-speed, low-latency internet where fiber or cable is unfeasible.
- New Services: The company is expanding beyond individual households to include services for airlines, maritime operators, and businesses. There are also plans for a direct-to-cell service in partnership with mobile carriers like T-Mobile.
- Next-Generation Satellites: To manage the growing user base and increasing congestion, SpaceX plans to launch its larger, next-generation V3 satellites in 2026, which are designed to offer gigabit-class connectivity and dramatically increase network capacity.
- IPO Considerations: Starlink’s significant growth and role as SpaceX’s primary revenue driver have positioned the parent company for a potential initial public offering (IPO) in 2026.
Competition:
Starlink’s main LEO competitors are Amazon Leo (Project Kuiper) and OneWeb (Eutelsat), aiming for similar high-speed, low-latency service, while established providers Hughesnet and Viasat (mostly GEO) offer more traditional, affordable satellite options but with higher lag, though they’re adapting. Starlink leads in consumer availability and speed currently, but Amazon and OneWeb are rapidly scaling to challenge its dominance with LEO constellations, offering faster speeds and lower latency than older satellite tech.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://starlink.com/updates/network-update
Elon Musk: Starlink could become a global mobile carrier; 2 year timeframe for new smartphones
Amazon Leo (formerly Project Kuiper) unveils satellite broadband for enterprises; Competitive analysis with Starlink
NBN selects Amazon Project Kuiper over Starlink for LEO satellite internet service in Australia
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
One NZ launches commercial Satellite TXT service using Starlink LEO satellites
Reliance Jio vs Starlink: administrative process or auction for satellite broadband services in India?
FCC: More competition for Starlink; freeing up spectrum for satellite broadband service
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
Starlink Direct to Cell service (via Entel) is coming to Chile and Peru be end of 2024



Amazon Leo Dec 30, 2025 Update:
Amazon’s satellite broadband ambitions progressed this year as the company officially fired its first satellites into orbit, firmed up deployment partnerships, won millions in preliminary grants from the BEAD program and began shipping terminals. Formerly called Project Kuiper, the satellite arm of Amazon also got a new name in November: “Leo.”
“Like most early Amazon projects, the program needed a code name, and the team began operating as ‘Project Kuiper’—inspired by the Kuiper Belt, a ring of asteroids in our outer solar system …Now, we’re ready to share our permanent brand for the program: Amazon Leo, a simple nod to the low Earth orbit satellite constellation that powers our network,” wrote Rajeev Badyal, vice president of Amazon Leo, in a blog post about the name change.
Amazon Leo has more than 150 satellites in orbit, compared to Starlink’s 8,000+. Starlink also claims over 8 million global subscribers.
Amazon is supposed to meet an FCC deadline of having half of its full constellation – so, roughly 1,600 of 3,236 satellites – in orbit by July 2026. But the company is unlikely to come near that goal and is expected to file for a deadline extension with the FCC.
As Bloomberg reported in April, Amazon’s satellite launches have been set back in part by a lack of adequate launch infrastructure.: “Amazon has booked billions of dollars’ worth of rockets built by ArianeGroup, Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin, ULA and SpaceX. But most of those vehicles are still in development or not being built as quickly as Kuiper brass and the companies expected,” according to Bloomberg.
Regardless, Amazon’s slow rollout has not stopped a variety of firms from forming partnerships with the nascent satellite provider. JetBlue was the first airline to announce a partnership with Amazon to deploy its satellite service for in-flight Wi-Fi, beginning in 2027. Amazon has also inked partnerships with Hunt Energy Network, based in Dallas, and agricultural connectivity solutions provider Connected Farms.
In August, Amazon announced a deal with Australia’s NBN to enable the government-owned wholesale broadband operator to sell Amazon Leo satellite connections to more than 300,000 customers across regional, rural and remote parts of Australia. NBN said that Amazon expects to launch Project Kuiper in Australia by mid-2026.
Amazon has further firmed up Leo distribution agreements with DIRECTV Latin America and Sky Brasil, which will offer its connectivity services to households in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Uruguay. The company also announced an agreement with Vanu Inc., to deliver connectivity to rural Africa.
Moreover, despite not existing yet as a commercial service Amazon’s Leo picked up over $210 million in preliminary awards through the US federal government’s BEAD program, to deliver service to over 321,500 locations, according to a BEAD tracker from Connected Nation. (The other LEO provider in the mix, SpaceX’s Starlink, comparatively, won $670.4 million to reach over 426,000 locations.)
Closing out 2025, Amazon tip-toed closer to the launch of its Leo service. In late November, the company announced the debut and initial trials of Leo Ultra, a new enterprise-grade terminal offering download speeds of up to 1 Gbit/s and upload speeds up to 400 Mbit/s. The company said in a blog that it has begun shipping Leo Ultra, as well as Leo Pro units (designed for 400 Mbit/s download), to “select companies as part of this new enterprise preview” and that it will “expand the program to more customers as we add coverage and capacity to the network.”
https://www.lightreading.com/satellite/looking-ahead-here-comes-amazon-leo-
The Short Life Expectancy of Starlink’s LEO Satellites
According to FCC filings Starlink shut down almost 500 Starlink satellites during the first half of 2025. The company had them reenter the atmosphere where they burned up. What is striking is that these satellites were all less than 5 years old. The general consensus is that LEOs have a life expectancy ranging from 5 to 8 years. Shorter than expected life spans for the satellites will hit Starlink’s income statement hard by increasing network depreciation and replacement needs. However, Starlink has managed to lower its LEO’s manufacturing costs down to $500K versus initial figures around $1 million. So these production economies of scale might offset some of the higher than expected depreciation. However, there are also rocket launch costs as well. It costs Starlink about $3 million to put a satellite into orbit. The Falcon 9 costs $67 million per flight and delivers 23 LEOs into low Earth orbit.
As a private company Starlink financials are a bit of mystery. The company press releases indicate a hefty $8 billion in 2024 revenue. But costs have remained invisible. My concern is that the financial picture may not be as rosy as the revenue figure suggests. Depreciation for LEO networks is quite high because low orbit means they will eventually experience a fiery death. Their orbits are not stable. With Starlink satellites lasting less than the five year minimum typically projected for these systems, depreciation and capital expenditures end up quite high. We also don’t know how much revenue is recurring versus one time installation charges.