capex
AT&T Earnings Down; Cost Cutting & Lower CAPEX for Remainder of 2020, 5G Uncertainty?
As expected, AT&T reported first quarter (Q1) 2020 revenues down 4.6 percent to $42.8 billion. The mega telco/media company continued to lose pay-TV subscribers while its WarnerMedia division suffered from the Covid-19 outbreak’s impact on the film and TV industry.
AT&T estimates the coronavirus pandemic reduced EPS 5 cents in the first quarter, which otherwise would have been in line with analyst expectations. Adjusted EPS fell to $0.84 from $0.86 a year ago, but would have increased to $0.89 without the extraordinary virus effect. The adjusted operating profit margin reached 21.2 percent in Q1, down slightly from 21.4 percent a year ago.
- Telecom business revenues were down 2.6 percent to $34.2 billion, while adjusted EBITDA rose 2.1 percent to $12.8 billion.
- AT&T Wireless grew service revenues 2.5 percent.
- Revenues continued lower at the Entertainment group as AT&T lost another 1.035 million pay-TV subscribers in the quarter.
- Mobile subscriber growth slowed to 27,000 postpaid net adds (+163,000 with phones), and the broadband base fell by another 73,000 customers in the three months.

Highlights from today’s AT&T earnings call transcript:
In Mobility, service revenue grew by 2.5% in the quarter. EBITDA of $7.8 billion grew by more than $500 million or 7%, and EBITDA margins expanded by 280 basis points. COVID did impact our top line revenue numbers in the quarter by about $200 million due to lower equipment and roaming revenues. Our subscriber counts for wireless, video and broadband this quarter exclude customers who we agreed not to terminate service for non-payment. For reporting purposes, we are treating those subscribers has disconnects. Even with that, our industry-leading network and FirstNet drove postpaid phone net adds of 163,000. Postpaid phone churn was down 6 basis points to 0.86% and our 5G deployment continues. We now cover more than 120 million people in 190 markets, and we expect we’ll be nationwide this summer.
In our Entertainment Group, cash generation remains a focus. We added 209,000 AT&T Fiber subscribers and now serve more than 4 million. We continue to drive ARPU growth in both video and IP broadband. In fact, premium video ARPU was up about 10% as we continue to focus on long-term value customers. We launched AT&T TV nationally late in the quarter and subscriber growth was in line with our expectations even with COVID impacts. Premium video net losses again improved sequentially.
Business Wireline performance was solid, with EBITDA and EBITDA margins remaining stable. Revenues were consistent with recent trends as declines in legacy products were partially offset by growth in strategic and managed services. Business Wireline continued to be an effective channel for our Mobility sales. Including wireless, total business revenues grew 1.7%.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The negative coronavirus financial impact was palpable at WarnerMedia, which lost around $1 billion in revenue year-on-year and over $500 million in adjusted EBITDA. The unit suffered from the suspension of key events such as the NCAA basketball tournament and new cinema releases, a slowdown in advertising due to the reduced economic activity and a halt to most production activities.
Operating cash flow totaled $8.9 billion in the quarter, and capital expenditure (CAPEX) reached $5.8 billion, leaving free cash flow of USD 3.9 billion. Net debt was at about 2.6x EBITDA at the end of the quarter.
AT&T said its liquidity position and balance sheet remained strong and it had already adjusted capital spending plans and suspended its share buybacks. It will continue investing in critical growth areas like 5G, fiber broadband and HBO Max, while maintaining its dividend commitment and paying down debt,
AT&T President & COO John Stankey said during AT&T’s earnings call:
Our 5G deployment continues, although we continue to navigate workforce and permitting delays. We expect nationwide coverage this summer. We also continue to be opportunistic with our fiber build beyond the 14 million household locations we reach today.
Stankey said the operator would encourage customers to install their own equipment and would shift customers to its fiber network. He also said the operator would use artificial intelligence (AI) and other capabilities to reduce initial “truck rolls” (technician visits to customer locations) and to eliminate the need for a second visit.
“These efficiencies will enhance our ability to continue to invest in our key growth initiatives,” including HBO Max and 5G, Stankey said of AT&T’s cost-cutting program.
Regarding CAPEX, before the coronavirus pandemic, AT&T said it would spend around $20 billion on CAPEX throughout 2020, which is significantly lower than the $23 billion it spent in 2019 and the $22 billion that most Wall Street analysts had expected AT&T to spend in 2020. AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson gave mixed messages on CAPEX plans for the remainder of the year on today’s earnings call:
“It’s not just writing checks for CAPEX. There’s people out doing things,” he said, explaining that some technicians may not be able to visit cell sites due to the spread of COVID-19, while some local officials may not be able to issue cell site construction permits.
“While we have no intention of slowing down on 5G and fiber deployment, the reality is that a lot of it is not in our control,” Stephenson said. “So there’s probably going to be – relative to the targets we gave you in CAPEX – some downward proclivity on that number, just because of the logistical issues we’re running into.”
AT&T declined to provide any financial guidance for the remainder of 2020 due to the pandemic. The operator/media giant spent roughly $5 billion on CAPEX during its most recent quarter, slightly above some Wall Street estimates.
AT&T’s management said the company had begun a cost-cutting program that the operator hopes will trim $6 billion from its budget by 2023. The huge cost cutting effort may include layoffs. Stankey didn’t specifically mention that word, but instead said the operator would enact a “headcount rationalization,” a term that could include layoffs as well as reductions by not hiring replacements for workers who retire or leave. That program, he said, would reduce the operator’s labor expenses by 4%, or roughly $1.5 billion, by the end of 2020. He added that the reduction would target employees in AT&T’s call centers, management structures and distribution strategy. AT&T employed roughly 252,000 people at the end of September.
CEO Stephenson made the following illuminating comments during the call:
In Mobility, the most immediate impacts are the reduction of roaming revenues as well as a reduction in late fees. The waiving of late fees is a commitment to our customers during these difficult economic times and roaming should gradually increase as people start to travel more. The first quarter impact of these items was approximately $50 million, with virtually all of it in the second half of March. We’re augmenting our digital sales team to mitigate the impact of store closures on equipment and service revenues, but we’re still forecasting lower wireless gross adds and upgrades. In fact, equipment revenues were down nearly 25% year-over-year in March. As a result of COVID, we anticipate an increase in bad debt expense across the various businesses, and accordingly, have recorded a $250 million incremental reserve in anticipation of that.
In our Entertainment Group, we anticipate increases in premium TV subscriber cord-cutting as well as lower revenues from commercial locations such as hotels, bars, and restaurants. Labor unit costs will increase temporarily from the 20% boost in pay we’re providing our frontline employees.
At WarnerMedia, content production has been placed on hiatus. Theatrical releases have been postponed and we’re seeing lower advertising revenues and lower costs from sports rights. This crisis has shown the value of premium streaming entertainment and we anticipate strong demand for HBO Max when it launches next month.
Fiber and broadband are more important than ever and we saw a pickup in demand for both in the quarter. We’re also seeing higher demand for VPN bandwidth and security. We do expect a negative impact on small business, which makes up about 15% of our total business wireline revenues. A detailed schedule of the COVID impacts is included in our investor briefing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Lightreading’s Mike Dano made the following comments on AT&T’s 5G deployments and CAPEX in a blog post:
One Wall Street analyst wondered if AT&T is moving its 5G goal posts slightly for 2020. Jennifer Fritzsche at Wells Fargo pointed out that AT&T executives now promise nationwide low band 5G by “summer” 2020. In contrast, during previous calls they had said the operator would reach that target by the “middle” of 2020.
AT&T’s low band 5G offering works on its 850MHz spectrum and doesn’t provide speeds that are much faster than its 4G LTE network. The operator also operates faster 5G services in millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum in parts of roughly 30 cities, but AT&T executives have remained conspicuously silent on that effort.
Verizon, in contrast, has promised to expand its own mmWave 5G network to an additional 30 cities this year.
AT&T’s 2020 CAPEX warning, on its network in general and on 5G specifically, has been echoed by some other players in the industry.
“COVID-19 and actions taken by governments to slow down the spread are making our service delivery and supply harder due to lockdowns and travel restrictions in many countries,” Ericsson CEO Börje Ekholm said earlier on Wednesday. Ericsson sells 4G and 5G equipment to a wide range of global operators, including AT&T. “In addition, while we have seen no material effects on our demand situation, it is prudent to believe that the slowdown in the general economy may lead some operators to delay investment programs.”
Ekholm said some operators are accelerating their investments in 5G and 4G capacity, pointing to providers in China specifically. Those comments dovetail with concerns of a 5G slowdown in Europe, largely due to decisions by some officials there to delay 5G spectrum auctions.
“We’re having to understand better what will happen as we exit the COVID pandemic in terms of [5G] investment,” noted EXFO CEO Philippe Morin in response to a question about how the pandemic might affect US operators’ 5G spending, according to a transcript of his remarks. He made his comments during his company’s recent quarterly conference call with investors. EXFO sells network testing equipment, including for 5G, to mobile network operators globally.
“In certain other countries in Europe, we’ve seen actually some of the [5G] spectrum auctions to be delayed as the countries have to deal with the virus,” Morin continued. “So, we’re going to – this is part of the discussions we’re having and dialogs we are having with our customers to better understand how – once we emerge out of the crisis, how the investments and where are the priorities are going to be.”
Stephenson acknowledged that it’s “pretty difficult” to predict what’s going to happen next as Americans and the rest of the world fight COVID-19. He said the world’s smartest economists disagree about what’s going to happen in the next quarter, much less the rest of the year.
AT&T’s CFO John Stephens said that mobile service remains an essential expense to most people. “The last thing that people don’t want to pay is probably their cellphone bill,” he said.
Indeed, in its most recent quarter – which suffered from the initial effects of widespread stay-at-home orders – AT&T reported postpaid phone net customer additions of 163,000, ahead of most Wall Street expectations. AT&T executives said the operator’s mobility business would help bolster its troubled media operation.
“The bottom line here is that Mobility performed its role admirably in Q1,” wrote the analysts at Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson of AT&T’s financial performance, in a note to investors Wednesday.
However, AT&T executives warned that if an economic recession deepens wireless users may look to reduce their spending by paying less for their service or holding onto an existing phone longer rather than upgrading to a new phone.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/services/atandt-starts-$6b-cost-cutting-program/d/d-id/759075?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
UPDATE:
April 24 (Reuters) – AT&T Inc said Friday that Chief Operating Officer John Stankey will take over as chief executive officer, effective July 1. The announcement was made during AT&T’s annual meeting.
AT&T Earnings Down; Cost Cutting & Lower CAPEX for Remainder of 2020, 5G Uncertainty?
As expected, AT&T reported first quarter (Q1) 2020 revenues down 4.6 percent to $42.8 billion. The mega telco/media company continued to lose pay-TV subscribers while its WarnerMedia division suffered from the Covid-19 outbreak’s impact on the film and TV industry.
AT&T estimates the coronavirus pandemic reduced EPS 5 cents in the first quarter, which otherwise would have been in line with analyst expectations. Adjusted EPS fell to $0.84 from $0.86 a year ago, but would have increased to $0.89 without the extraordinary virus effect. The adjusted operating profit margin reached 21.2 percent in Q1, down slightly from 21.4 percent a year ago.
- Telecom business revenues were down 2.6 percent to $34.2 billion, while adjusted EBITDA rose 2.1 percent to $12.8 billion.
- AT&T Wireless grew service revenues 2.5 percent.
- Revenues continued lower at the Entertainment group as AT&T lost another 1.035 million pay-TV subscribers in the quarter.
- Mobile subscriber growth slowed to 27,000 postpaid net adds (+163,000 with phones), and the broadband base fell by another 73,000 customers in the three months.

Highlights from today’s AT&T earnings call transcript:
In Mobility, service revenue grew by 2.5% in the quarter. EBITDA of $7.8 billion grew by more than $500 million or 7%, and EBITDA margins expanded by 280 basis points. COVID did impact our top line revenue numbers in the quarter by about $200 million due to lower equipment and roaming revenues. Our subscriber counts for wireless, video and broadband this quarter exclude customers who we agreed not to terminate service for non-payment. For reporting purposes, we are treating those subscribers has disconnects. Even with that, our industry-leading network and FirstNet drove postpaid phone net adds of 163,000. Postpaid phone churn was down 6 basis points to 0.86% and our 5G deployment continues. We now cover more than 120 million people in 190 markets, and we expect we’ll be nationwide this summer.
In our Entertainment Group, cash generation remains a focus. We added 209,000 AT&T Fiber subscribers and now serve more than 4 million. We continue to drive ARPU growth in both video and IP broadband. In fact, premium video ARPU was up about 10% as we continue to focus on long-term value customers. We launched AT&T TV nationally late in the quarter and subscriber growth was in line with our expectations even with COVID impacts. Premium video net losses again improved sequentially.
Business Wireline performance was solid, with EBITDA and EBITDA margins remaining stable. Revenues were consistent with recent trends as declines in legacy products were partially offset by growth in strategic and managed services. Business Wireline continued to be an effective channel for our Mobility sales. Including wireless, total business revenues grew 1.7%.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The negative coronavirus financial impact was palpable at WarnerMedia, which lost around $1 billion in revenue year-on-year and over $500 million in adjusted EBITDA. The unit suffered from the suspension of key events such as the NCAA basketball tournament and new cinema releases, a slowdown in advertising due to the reduced economic activity and a halt to most production activities.
Operating cash flow totaled $8.9 billion in the quarter, and capital expenditure (CAPEX) reached $5.8 billion, leaving free cash flow of USD 3.9 billion. Net debt was at about 2.6x EBITDA at the end of the quarter.
AT&T said its liquidity position and balance sheet remained strong and it had already adjusted capital spending plans and suspended its share buybacks. It will continue investing in critical growth areas like 5G, fiber broadband and HBO Max, while maintaining its dividend commitment and paying down debt,
AT&T President & COO John Stankey said during AT&T’s earnings call:
Our 5G deployment continues, although we continue to navigate workforce and permitting delays. We expect nationwide coverage this summer. We also continue to be opportunistic with our fiber build beyond the 14 million household locations we reach today.
Stankey said the operator would encourage customers to install their own equipment and would shift customers to its fiber network. He also said the operator would use artificial intelligence (AI) and other capabilities to reduce initial “truck rolls” (technician visits to customer locations) and to eliminate the need for a second visit.
“These efficiencies will enhance our ability to continue to invest in our key growth initiatives,” including HBO Max and 5G, Stankey said of AT&T’s cost-cutting program.
Regarding CAPEX, before the coronavirus pandemic, AT&T said it would spend around $20 billion on CAPEX throughout 2020, which is significantly lower than the $23 billion it spent in 2019 and the $22 billion that most Wall Street analysts had expected AT&T to spend in 2020. AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson gave mixed messages on CAPEX plans for the remainder of the year on today’s earnings call:
“It’s not just writing checks for CAPEX. There’s people out doing things,” he said, explaining that some technicians may not be able to visit cell sites due to the spread of COVID-19, while some local officials may not be able to issue cell site construction permits.
“While we have no intention of slowing down on 5G and fiber deployment, the reality is that a lot of it is not in our control,” Stephenson said. “So there’s probably going to be – relative to the targets we gave you in CAPEX – some downward proclivity on that number, just because of the logistical issues we’re running into.”
AT&T declined to provide any financial guidance for the remainder of 2020 due to the pandemic. The operator/media giant spent roughly $5 billion on CAPEX during its most recent quarter, slightly above some Wall Street estimates.
AT&T’s management said the company had begun a cost-cutting program that the operator hopes will trim $6 billion from its budget by 2023. The huge cost cutting effort may include layoffs. Stankey didn’t specifically mention that word, but instead said the operator would enact a “headcount rationalization,” a term that could include layoffs as well as reductions by not hiring replacements for workers who retire or leave. That program, he said, would reduce the operator’s labor expenses by 4%, or roughly $1.5 billion, by the end of 2020. He added that the reduction would target employees in AT&T’s call centers, management structures and distribution strategy. AT&T employed roughly 252,000 people at the end of September.
CEO Stephenson made the following illuminating comments during the call:
In Mobility, the most immediate impacts are the reduction of roaming revenues as well as a reduction in late fees. The waiving of late fees is a commitment to our customers during these difficult economic times and roaming should gradually increase as people start to travel more. The first quarter impact of these items was approximately $50 million, with virtually all of it in the second half of March. We’re augmenting our digital sales team to mitigate the impact of store closures on equipment and service revenues, but we’re still forecasting lower wireless gross adds and upgrades. In fact, equipment revenues were down nearly 25% year-over-year in March. As a result of COVID, we anticipate an increase in bad debt expense across the various businesses, and accordingly, have recorded a $250 million incremental reserve in anticipation of that.
In our Entertainment Group, we anticipate increases in premium TV subscriber cord-cutting as well as lower revenues from commercial locations such as hotels, bars, and restaurants. Labor unit costs will increase temporarily from the 20% boost in pay we’re providing our frontline employees.
At WarnerMedia, content production has been placed on hiatus. Theatrical releases have been postponed and we’re seeing lower advertising revenues and lower costs from sports rights. This crisis has shown the value of premium streaming entertainment and we anticipate strong demand for HBO Max when it launches next month.
Fiber and broadband are more important than ever and we saw a pickup in demand for both in the quarter. We’re also seeing higher demand for VPN bandwidth and security. We do expect a negative impact on small business, which makes up about 15% of our total business wireline revenues. A detailed schedule of the COVID impacts is included in our investor briefing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Lightreading’s Mike Dano made the following comments on AT&T’s 5G deployments and CAPEX in a blog post:
One Wall Street analyst wondered if AT&T is moving its 5G goal posts slightly for 2020. Jennifer Fritzsche at Wells Fargo pointed out that AT&T executives now promise nationwide low band 5G by “summer” 2020. In contrast, during previous calls they had said the operator would reach that target by the “middle” of 2020.
AT&T’s low band 5G offering works on its 850MHz spectrum and doesn’t provide speeds that are much faster than its 4G LTE network. The operator also operates faster 5G services in millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum in parts of roughly 30 cities, but AT&T executives have remained conspicuously silent on that effort.
Verizon, in contrast, has promised to expand its own mmWave 5G network to an additional 30 cities this year.
AT&T’s 2020 CAPEX warning, on its network in general and on 5G specifically, has been echoed by some other players in the industry.
“COVID-19 and actions taken by governments to slow down the spread are making our service delivery and supply harder due to lockdowns and travel restrictions in many countries,” Ericsson CEO Börje Ekholm said earlier on Wednesday. Ericsson sells 4G and 5G equipment to a wide range of global operators, including AT&T. “In addition, while we have seen no material effects on our demand situation, it is prudent to believe that the slowdown in the general economy may lead some operators to delay investment programs.”
Ekholm said some operators are accelerating their investments in 5G and 4G capacity, pointing to providers in China specifically. Those comments dovetail with concerns of a 5G slowdown in Europe, largely due to decisions by some officials there to delay 5G spectrum auctions.
“We’re having to understand better what will happen as we exit the COVID pandemic in terms of [5G] investment,” noted EXFO CEO Philippe Morin in response to a question about how the pandemic might affect US operators’ 5G spending, according to a transcript of his remarks. He made his comments during his company’s recent quarterly conference call with investors. EXFO sells network testing equipment, including for 5G, to mobile network operators globally.
“In certain other countries in Europe, we’ve seen actually some of the [5G] spectrum auctions to be delayed as the countries have to deal with the virus,” Morin continued. “So, we’re going to – this is part of the discussions we’re having and dialogs we are having with our customers to better understand how – once we emerge out of the crisis, how the investments and where are the priorities are going to be.”
Stephenson acknowledged that it’s “pretty difficult” to predict what’s going to happen next as Americans and the rest of the world fight COVID-19. He said the world’s smartest economists disagree about what’s going to happen in the next quarter, much less the rest of the year.
AT&T’s CFO John Stephens said that mobile service remains an essential expense to most people. “The last thing that people don’t want to pay is probably their cellphone bill,” he said.
Indeed, in its most recent quarter – which suffered from the initial effects of widespread stay-at-home orders – AT&T reported postpaid phone net customer additions of 163,000, ahead of most Wall Street expectations. AT&T executives said the operator’s mobility business would help bolster its troubled media operation.
“The bottom line here is that Mobility performed its role admirably in Q1,” wrote the analysts at Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson of AT&T’s financial performance, in a note to investors Wednesday.
However, AT&T executives warned that if an economic recession deepens wireless users may look to reduce their spending by paying less for their service or holding onto an existing phone longer rather than upgrading to a new phone.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/services/atandt-starts-$6b-cost-cutting-program/d/d-id/759075?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
UPDATE:
April 24 (Reuters) – AT&T Inc said Friday that Chief Operating Officer John Stankey will take over as chief executive officer, effective July 1. The announcement was made during AT&T’s annual meeting.
Investment Analysts: Soft Telecom Capital Spending (CAPEX), but 5G in China to Grow 25% in 2020
Investor’s Business Daily reports that Goldman Sachs‘ Rod Hall and Bank of America‘s Tal Liani issued separate notes Tuesday and Wednesday which came to the same conclusion: Despite the ultra hyped 5G buildup, they see overall telecom capital spending remaining soft in 2020.
Hall said, “Telco capital spending trends look set to be muted with China being the only driver of growth,” in his note, issued Tuesday. He sees 5G growth in China of 25% this year, but predicts only a 2% hike in global telecom capital spending.
Hall added: “The carrier environment is challenged globally by flat or declining revenue streams with 5G thus far offering limited or no additional revenue opportunities.”
BofA’s Liani concurred in his Wednesday note. He sees global telecom capital spending up only 1% to 2% in 2020, despite 5G network build-outs. The 5G build-out may fail to impress U.S. wireless customers over the next 12 months, he adds. “Contrary to the belief that the U.S. is an early leader with 5G, we see potential for users to be disappointed with either lack of coverage or lack of improvement, or both,” Liani said. Here is an excerpt of his January 8, 2020 note to clients:
5G becomes mainstream, but the U.S. will likely lag:
5G traction remains front and center for 2020, and we expect the first phase of a major smartphone refresh cycle in 2H20, with all major vendors launching 5G devices. In 2019, we saw initial network build-outs, and we expect the device/semiconductor ecosystem to catch up in 2020, supporting and enabling ubiquitous 5G devices. However, some regions may lag behind, particularly the US where a lack of quality 5G spectrum injects delays vs. certain parts of Europe, China, Korea and Japan where mid-band spectrum is more readily available. Our top pick related to this theme is Qualcomm as the semi provider benefits from 5G devices and the China launch.
Verizon Communications and AT&T likely will lower spending on existing fourth-generation networks, says Goldman Sachs’ Hall. They’ll also pare back spending on wireline networks. “Although U.S. 5G deployments should advance in 2020 our U.S. telecom team expects wireless capex to be roughly flat in 2020 as 5G increases are mostly offset by slowing non-5G spending,” Hall said.
Makers of electronic chips, network gear and fiber-optic technologies should gain from the 5G build-out, analysts say. Other5G stocks to watch will be tied to the deployment of “small cell” antennas, radio access network equipment as well as cloud computing infrastructure. Goldman Sachs favors fiber-optic play Corning. It’s cautious on gear makers Nokia and Ericsson.
Liani said Apple’s expected launch of 5G iPhones in late 2020 could be a game-changer. However, he says consumers may be disappointed in the 5G network coverage and 5G speeds provided by Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile US and Sprint. That’s because not enough mid-band radio spectrum is available yet for 5G services, Liani said.
He calls Qualcomm one of the best 5G stocks to buy because it’s dependent on smartphone sales, not core network upgrades. Qualcomm‘s customers include Apple and Chinese smartphone makers.
In 2020, we see potential for mass device availability to usher in the first meaningful device upgrade cycle for 5G,” Liani added. “In 2021 and 2022, we expect the network equipment investments to potentially pick up once again as 5G usage accelerates and new applications emerge. Most importantly, however, spectrum availability drives both network upgrades and likely customer satisfaction with the new 5G networks.
Let’s close with an interesting graph from Dell’Oro Group which shows very little growth in telecom equipment/services through 2023:
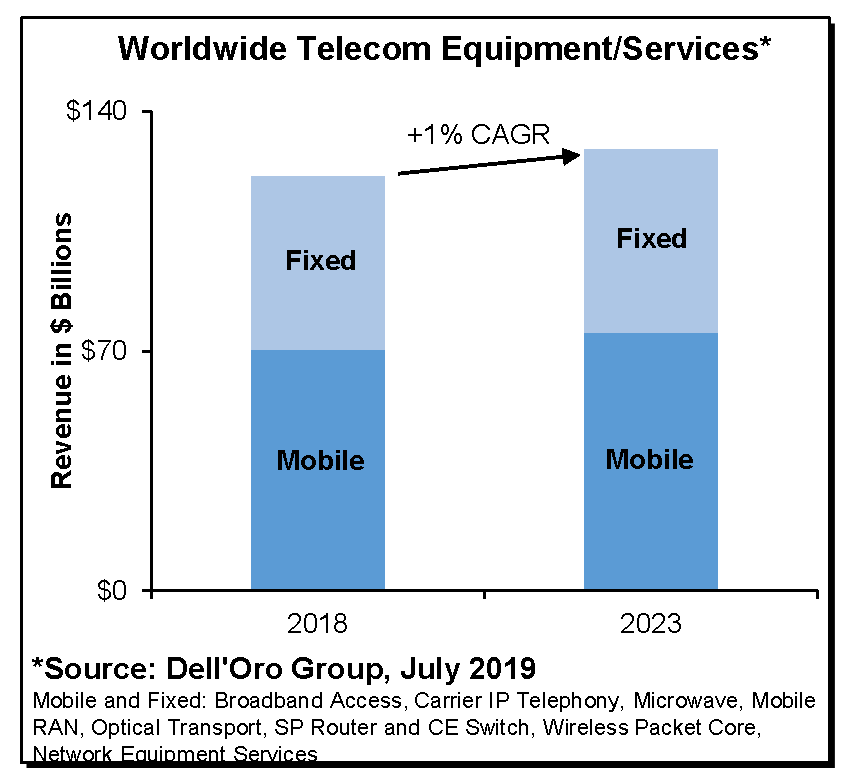
Reference:
https://www.investors.com/news/technology/5g-stocks-telecom-capital-spending/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Addendum: BoAML – Hardware vendors bow to the white box:
Hardware standardization and white box networking continue and drive changes in IT equipment purchasing behavior. Hardware vendors are increasingly being forced to react to three major realities:
1) public cloud capex represents the majority of growth and some companies (e.g. Cisco) find it hard to penetrate,
2) software is taking the forefront, with vendors of traditional networking gear, like ADC, switching, or routing, facing significant pricing pressure and a new breed of competitors, and
3) the value is also pushed to semiconductors, with Cisco’s SiliconOne semiconductor strategy and the proposed acquisition of Acacia designed to address the associated risk and opportunity
Lastly, the trends of software-defined networking, white boxes, and cloud migration come together to support our fifth major trend for 2020: the shift to software-defined branch/campus offices. In our view, this trend began with SD-WAN, continued with Cisco’s Catalyst 9k introduction, and comes fully together with the acceleration of WiFi 6.
Dell’Oro: Worldwide Capex Forecast to Rise 2017 – 2020 Despite Flat Carrier Revenues with only 2% from IoT
According to a recently published report from Dell’Oro Group, worldwide newtork operator capex is forecast to rise from 2017 through 2020 despite flat carrier revenues. The most notable increases come from AT&T, Sprint, Megafon, Orange, Etisalat, and Deutsche Telekom.
“We have adjusted our overall three-year CapEx expectations upward to reflect a more optimistic investment view than we had originally envisioned in both the US and Chinese markets,” Stefan Pongratz, a senior analyst at Delloro, said in a blog post online. The increase in global CapEx is being driven by increased spending in the US, as the country tries to position itself at the front of the queue for 5G deployment.
“After three consecutive years of declining capex, short-term and near-term market expectations have shifted up,” Pongratz said.
“Here in the US, we maintain the view that conditions are stabilizing and both capex and capital intensity will continue to trend upward. There are multiple factors that support our renewed optimism for capex in the US:
- We are seeing our first signs of US Federal tax reductions translating into increases in capex with a clear boost in AT&T’s 2018 capex projections.
- We see Sprint investing again
- FirstNet investments are set to commence in 2018
- Larger data plans are propelling capacity investments
And lastly, overall carrier revenue trends are stabilizing,” continued Pongratz.
However, total capex spending in China [Figure 1. below] is still expected to decline year-on-year in 2018 and stay flat in 2019 before returning to growth in 2020.

Currency adjusted operator revenues are projected to remain flat between 2017 and 2020, with operators expected to struggle to find new revenue streams to offset slower smartphone revenue growth.
While the IoT has long-term revenue generation possibilities, there is expected to be limited benefit over the next few years. Dell’Oro estimates that carrier IoT revenues will account for just 2% of total mobile revenues by 2020. Preliminary IoT connection pricing trends for 2017 are cause for concern, with downside risks to the IoT carrier revenue forecast, should price trends prevail. Please see Figure 2. below for Dell ‘Oro forecast of IoT Carrier revenue growth through 2020.

About the Report
The Dell’Oro Group Carrier Economics Report provides in-depth coverage of more than 50 carriers’ revenue, capital expenditure, and capital intensity trends. The report provides actual and forecast details by carrier, by region, by country (United States, Canada, China, India, Japan, and South Korea), and by technology (wireless/wireline). The report also discusses further capex accelerating factors such as preparation for 5G and inhibiting factors such as the flat revenue trend. The report assumes operators will struggle to identify new revenue streams.
To purchase this report, please contact Matt Dear at +1.650.622.9400 x223 or email [email protected].
About Dell’Oro Group
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, networks, and data center IT markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
AT&T at DB Investor Conference: Strategic Services, Fiber & Wireless to Drive Revenue Growth
At the Deutsche Bank Media, Telecom and Business Services Conference, John Stephens, senior executive vice president and chief financial officer, AT&T discussed the company’s plans for 2018 and beyond. Mr. Stephens said AT&T remains confident that it is on the right track to get its wireline business services back to positive growth as more customers transition to next-generation strategic services like SD-WAN and Carrier Ethernet. However, the drag from legacy services will continue to be an issue for the near term. He then outlined the company’s priorities for 2018, which include closing its pending acquisition of Time Warner and investing $23 billion in capital to build the best gigabit network in the United States.
On the entertainment side of the business, AT&T plans to launch the next generation of its DIRECTV Now video streaming service in the first half of 2018. The new platform will include features like cloud DVR and a third video stream. Additional features expected to launch later in 2018 include pay-per-view functionality and more video on demand. Note that DIRECT TV Now can operate over a wireline or wireless network with sufficient bandwidth to support video streaming. Stephens said during the interview:
“……Giving us this opportunity to come up with a new platform later in this first half of this year, the second-generation plant for giving customers Cloud DVR, additional ability to pay per view and most sporting events and movies, and all kinds of other capabilities is what we’re seeing here, that’s what we want to do with regard to that entertain business and transitioning and we’re confident that we’re on the right track and it’s going quite well.”
The company’s 2018 plans also include improved profitability in its wireless operations in Mexico and, after the Time Warner acquisition closes, deployment of a new advertising and analytics platform that will use the company’s customer data to bring new, data-driven advertising capabilities within premium video. And, as always, AT&T remains laser-focused on maintaining an industry-leading cost structure.
AT&T’s investment plans include deployment of the FirstNet network, America’s first nationwide public safety broadband network specifically designed for our nation’s police, firefighters, EMS and other first responders.
“We were 56 out of 56, 50 states, 5 territories and the districts, probably all choose to put their public safety network, their FirstNet, their first responder network with AT&T, so that’s thrilling for us, that gives us the full funding of the program, it gives us the full authority to be the public service provider for the country, we’re really proud of that, and only because of the business aspects that’s serving our fellow citizens and being able to participate in the honorable job of saving lives and protecting people. So we’re really jazzed up about that.
Secondly, our plans were made last year for how to build out, and we’ve now been given the authority and the official build plans, approved build plans from the FirstNet authority. We spend last year investing in the core network, I think if people filed us in the fourth quarter; they said we actually got a $300 million reimbursement from the FirstNet authority for the expenditures we incurred last year. So the relentless preemption, the prioritized service refers to prices for police and fire and handling some emergency medical personal; all of that’s been done and now we’re out deploying the network, not only the 700 but also our AWS and WCS, our inventoried network that we now get to put into service on a very economic basis because we can do one tower client, we have the crane out there once, we have the people out there once and they’ve put all three pieces of spectrum at it once.”
The company will also enhance wireless network quality and capacity and plans to be the first to launch mobile “5G” service in 12 cities by the end of the year. AT&T announced in February that Atlanta, GA; Dallas and Waco, TX. will be among its first “5G” markets.
“We think about 5G is 5G evolution and I say that because it’s really important to put it all in perspective. So we think FirstNet, put WCS, AWS with 700 band 14 [ph], and use carrier aggregation and you use forward [indiscernible]; we’ve done that kind of test without the 700, we did that in San Francisco, we got 750 mag speeds in the City of San Francisco on this new network, this new 5G evolution; it’s using the LTE technology, it’s using the existing network but all this new technology. So if you think about that evolution now, when you lower that network hub, those 750 theoretical speeds might go down to 150 or 100 or somewhere down but tremendous speed even on a loaded network; so that’s the first step, we’re doing that now extensively and we’re going to do more of that as we build the first step that work out and put the 700 band in. So that’s the first step for us in this evolution.
Second, people might not think about this way but for us absolutely critical is the fiber bill. We’re taking a lot of fiber out to the Prime [ph], we’re taking a lot of fiber out to business locations, currently we have about 15 million locations with fiber between business and consumer, and by July next year, we’ll have about 22 million, about 8 million business, about 14 million to the Prime if you will, for consumers. So fiber is the key, and it’s a key not only delivering to the home or to the business but for the backhaul support. So if you’re an integrated carrier like we are and you’re building this fiber to go to the home, you’re going to pass the tower, you’re going to get fiber to that tower, you’re going to pass the business location, shopping mall, strip center, you’re going to build out to those.
So 5G is the second stage, we’ve got to think all the inter-gig this is the ability to deliver broadband overall electrical power lines, we’re testing that, we’ll see how that goes, that’s another step. If you think about using millimeter wave to do backhaul for small cells in really congested areas, we have high traffic volumes, you want to take a lot of traffic off, we have tested that, we have used millimeter wave to do that, we can do that. If you think about millimeter wave to do fixed wireless; so from the ally to my home, we have tested that we have the capability to do that, the challenges on that is where do you take it from the ally, where do you offload it, give it on to the network at what those costs are, but we can do that.
Lastly, you will see us put 5G into the core network. All of those things that were going to have to be measured by one of the chipsets ready for the handsets, we expect the chipsets might be next year, handset will come after that but we’re looking at the historically slow upgrade timeframe for phones. We had a couple of quarters last year that the upgrade rates were about 4%, that would equate the 25 quarters before your phone base turned over in an extreme example; so suggesting that things are going to be in the core network, it’s going to take a while, we’ll have pucks [ph] out by the end of the year, that will help but you have to have balance with regard to this.
When you think about those business cases, you think about those augmented reality and virtual reality and robotics and autonomous cars and things on the edge, those are going to be really important, that’s where the business cases will take us but we’ve got a long way to go before we get there. As we build FirstNet, we have been good fortunate being able to so to speak build the network house and leave the room for our 5G capability so that when it’s ready, we can just plug it in to do it with software defined network design, we had a great advantage for that but we’re going to have to make sure we have all of the equipment, not only switching equipment, the radio, the antenna but also the handset equipment before we start — if you will over-indexing on the revenues opportunities, they will be there, we will lead in the gigabit network.
We’ll have the best one because what FirstNet provides us and what the technology developments have allowed us and we will use 5G in that network but I want to be careful about how we think about when it’s going to be — you’re going to have a device in your hand and walking around on a normal kind of usage basis using 5G.”
Stephens said that AT&T reaches about 15 million customer locations with fiber. This includes more than 7 million consumer customer locations and more than 8 million business customer locations within 1,000 feet of AT&T’s fiber footprint. He expects this to increase to about 22 million locations by mid-2019.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
For 2018, AT&T expects organic adjusted earnings per share growth in the low single digits, driven by improvements in wireless service revenue trends, improving profitability from its international operations, cost structure improvements from its software defined network/network function virtualization efforts and lower depreciation versus 2017.
Like earlier quarters, the challenges in the fourth quarter for AT&T came from declines in legacy services like Frame Relay and ATM. The company noted that fourth-quarter declines in legacy products were partially offset by continued growth in strategic business services. Total business wireline revenues were $7.4 billion, down 3.5% year-over-year but up sequentially.
Stephens said that more AT&T customers are adopting next-gen services, creating a new foundation for wireline business revenue growth.
“What’s happened is our customers have embraced the strategic services,” Stephens said. “Strategic services are over a $12 billion annual business and are over 42% or so of our revenue and are still growing quickly.”
Indeed, AT&T’s fourth-quarter strategic business services revenues grew by nearly 6%, or $176 million, versus the year-earlier quarter. These services represent 42% of total business wireline revenues and more than 70% of wireline data revenues and have an annualized revenue stream of more than $12 billion. This growth helped offset a decline of more than $400 million in legacy service revenues in the quarter.
Stopping short of forecasting overall wireline business service revenue growth, Stephens said that AT&T will eventually see a point where strategic services will surpass legacy declines.
“As we get past this inflection point where strategic services are growing at a faster than the degradation of legacy, we can get to a point where we are growing revenues,” Stephens said. “We’re not predicting that but we see the opportunity to do that.”
To achieve these business services revenue goals, AT&T’s business sales team is taking a two-pronged approach: retaining legacy services or converting them to strategic services.
While wireline business services continue to be a key focus for AT&T, the service provider is not surprisingly looking at ways to leverage its wireless network to help customers solve issues in their business. The wireless network can be used to support a business customer’s employee base while enabling IoT applications like monitoring of a manufacturing plant or a trucking fleet. Stephens expanded on the role of IoT to close out the interview:
“…you (‘ve) got to realize that if you build this FirstNet network out, things like IoT, things like coverage for business customers, things like the ability to connect factories that are automated, the robotics that have to have wireless connectivity to a controlled center for business customers, all improves dramatically and with that comes this opportunity to sell these wireless services. When you’re in — with the CIO and you can solve his security business, you can solve his big pipe of strategic services but you can also solve some wireless issues that his HR guy has for his connectivity for his employees, you can solve some issues that his engineering department has because they want to get real-time information about how their products are working out, whether it’s a car or a jet engine or a tractor, how it’s working in the field in real-time or you can give them new product and services demand for their internal sources like their pipelines or their shipping fleet.
This IoT capability can solve a lot of issues, you can make that CIO as the success factor for all his related peers, that’s a great thing to great solutions approach to business and that’s what we’re trying to do. Our team is trying to provide solutions for the business customers and we think having those two things together are really important.”
References:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180306006770/en/John-Stephens-ATT-CFO-Discusses-Plans-2018
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2018/01/14/att-mobile-5g-will-use-mm-wave-small-cells/
Sprint to increase CAPEX to focus on mobile 5G deployment in 1H-2019
Sprint will increase its network capital expenditure by at least $1 billion for the coming year as promised on Friday morning’s earnings call. The #4 U.S. wireless carrier plans to deliver mobile 5G in the first half of 2019.
–>That’s 1 year before the IMT 2020 standards will be completed!
Sprint Corp talked about its mobile 5G plans: “We’re working with Qualcomm [and others] in order to deliver the first truly mobile 5G network in the US in the first half of 2019,” CEO Marcello Claure said on the call.
Mr Claure said that Sprint will be able to deploy mobile 5G nationwide on 2.5GHz band in 100MHz channels. “We have the spectrum to lead on 5G, and basically lead in a different way,” he noted. Claure said later in the question and answer session that Sprint had a commitment from a “leading Korean” device vendor that it will have a 5G device ready within its 2019 timeframe.
This implies an increase in capital expenditure spending for Sprint’s network for fiscal 2018, new CFO Michel Combes said. Sprint’s total capex spending for fiscal 2017 will be in the $3.5-$4 range. Capex will hit $5-$6 billion in fiscal 2018, which starts in April 2018.
Sprint will spend to increase the number macro cell sites by 20%, and support its 2.5GHz, 1900MHz, and 850MHz bands on nearly all of its existing macro sites. Currently, around half of its macro sites have tri-band support.
The CEO added that Sprint plans to deploy more than 40,000 outdoor small cells, and “more than 1 million Magic Boxes,” the wireless small cells that it uses to improve in-home coverage.
In the field, Sprint expects to update sites with multiple-antenna array hardware, or “Massive MIMO” in 2018. “Massive MIMO will serve as Sprint’s bridge to 5G,” Claure said. (See Sprint Says No to mmWave, Yes to Mobile 5G.)
This is because the MIMO hardware can be updated to 5G NR standard over-the-air, the CEO said.
Our strategy is predicated on creating on amazing customer-experience, offering customers the best products and services, while delivering superior financial results. First, we recognize that to be a truly great company we have to have a great product, which for us is our network. While our network is much improved, we believe our next-gen network will truly differentiate Sprint over the next couple of years, due to our strong spectrum assets that enables Sprint to be the leader in the true mobile 5G.
This is the biggest network capital program in many years. And I will share more details of our network strategy in a few moments. I cannot wait to, once and for all, be able to sell the product that is best in the industry with competitive coverage, the fastest speed and the highest capacity.
Second, we will continue to deliver the most compelling value proposition to our customers across all of our segments. We will continue to play from a position of strength by leveraging our spectrum holdings and continue to lead with the best-only net offering in the market. Data usage strength are projected to grow exponentially, especially with 5G.
By having the most spectrum, combined with new technology that massively increases our capacity, we’re certain that we’ll be best position for to support unlimited data in the future.
Third, we will continue to drive a smart distribution strategy, with over 1,000 new stores open year-to-date across our Sprint and Boost brand, and several hundred several hundred throughout next year. We have designed a dynamic distribution model that allows to continuously optimize the right balance of physical and distribution – and digital distribution.
Sprint will also leverage its partnerships with Altice and Cox Communications Inc. to expand its backhaul capabilities for LTE-Advanced and 5G. Sprint CTO John Saw chimed in briefly on the call to say that some of the capex spend could be on “dark fiber” for backhaul needs.
Against this backdrop, Claure said there would be continuing job cuts at Sprint, including at the executive level, aiming for “a leaner and more agile company across our non-customer-facing workforce.” Sprint has cut thousands of jobs during the past couple of years.
True to his reputation as a “turnaround specialist,” new CFO Michel Combes said he is looking at more ways to “decrease cost structures” at Sprint. He promised to reveal more details in the March quarter. (See Sprint Appoints Ex-AlcaLu Boss Combes as CFO.)
For the quarter, Sprint reported revenue of $8.24 billion, down from $8.55 billion a year ago. Net income for the quarter was $7.16 billion (or $1.76 per share) thanks almost entirely to tax reform gains of about $7.1 billion, compared with a net loss of $479 million a year ago.
References:
IHS Markit: Telecom Revenue +1.1%; CAPEX -1.8% in 2017
Despite unabated exponential growth in network usage, global telecom revenue is on track to grow just 1.1 percent in 2017 over the prior year, according to a new report [1] by business information provider IHS Markit.
Global economic growth prospects, meanwhile, are looking up. IHS Markit macroeconomic indicators point to moderate global economic growth of 3.2 percent for 2017, up from 2.5 percent in 2016, and world real gross domestic product (GDP) is projected to increase 3.2 percent in 2018 and 3.1 percent in 2019.
“Although the telecom sector has been resilient, revenue growth in developed and developing economies has slowed dramatically due to saturation and fierce competition,” said Stéphane Téral, executive director of research and analysis and advisor at IHS Markit. “At this point, every region is showing revenue growth in the low single digits when not declining, and there is no direct positive correlation between slow economic expansion and anemic telecom revenue growth or decline as seen year after year in Europe, for instance.”
China alone is tamping down global telecom capex in 2017:
IHS Markit forecasts a 1.8 percent year-over-year decline in global telecom capital expenditures (capex) in 2017, mainly a result of a 13 percent year-over-year falloff in Chinese telecom capex. Asia Pacific outspends every other region in the world on telecom equipment.
“Call it precision investment, strategically focused investment or tactical investment, but all three of China’s service providers — China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom — scaled back their 2017 spending plans, and the end result is another double-digit drop in China’s telecom capex bucket, with mobile infrastructure hit the hardest,” Téral said. “Bringing down capital intensity to reasonable levels of 15 to 20 percent is the chief goal of these operators.”
The virtualization trend:
A transformation is underway in service provider networks, epitomized by software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV), which involve the automation of processes such as customer interaction, as well as the addition of more telemetry and analytics with feedback loops into network operations, operations and business support systems, and service assurance.
“Many service providers have deployed new architectural options — including content delivery networks, distributed broadband network gateways, distributed mini data centers in smart central offices, and video optimization,” said Michael Howard, executive director of research and analysis for carrier networks at IHS Markit. “Nearly all operators are madly learning how to use SDN and NFV, and the growing deployments today bring us to declare 2017 as The Year of SDN and NFV.”
Data is the new oil, and AI is the engine:
Big data is becoming more manageable, and operators are leveraging subscriber and network intelligence to support the automation and optimization of their networks using SDN, NFV and initial forays into using analytics, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
“Forward-thinking operators are experimenting with how to use anonymized subscriber data and analytics to create targeted services and broker this information to third parties such as retailers and internet content providers like Google,” Téral said. “No matter their size, market or current level of digitization, service providers need to rethink their roles in the new age of information and reset the strategies needed to capitalize on this opportunity.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Note 1. The Telecom Trends & Drivers Market Report is published twice annually by IHS-Markit to provide analysis of global and regional market trends and conditions affecting service providers, subscribers, and the global economy. These roughly 40- page reports assess the state of the telecom industry, telling the story of what’s going on now and what we expect in the near and long term, illustrated with charts, graphs, tables, and written analysis. These critical analysis reports are a foundation piece for all market forecasts.
The reports include top takeaways on the economic health of the global telecom/datacom space; regional and global trends, drivers, and analysis for the service provider network sector in the context of the overall economy; financial analysis of the world’s top 10 service providers (revenue growth, capital intensities, free cash flow, debt level); regional enterprise and carrier spending trends; top-level service provider and subscriber forecasts; macroeconomic drivers; and key economic statistics (e.g., unemployment, OECD indicators, GDP growth). The reports are informed by all of IHS Technology research, from market share and forecasts to surveys with telecom service providers and small, medium, and large businesses.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The chart below from Bharti Airtel (India’s largest telecom company) shows that telecom industry revenue has declined in 2017 Q2, Q3, and Q4 with only Q1 showing positive growth.
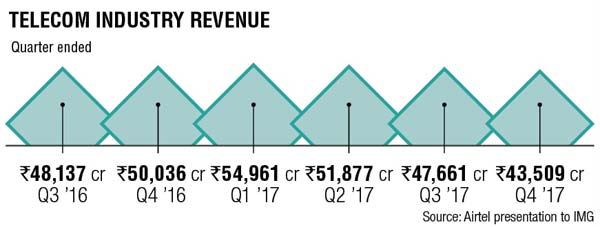
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Optical Network Equipment Vendors:
In a service provider survey report on Optical Networking and equipment vendors, IHS-Markit found Ciena, Huawei and Nokia as the three most popular optical networking equipment vendors. The report also highlighted Data Center Interconnection (DCI) is a huge growth opportunity.
IHS-Markit predicts DCI will be a significant driver for the optical equipment market, surging from 19 percent of overall equipment sales at mid-2017 to nearly 30 percent by 2021.
Ciena was deemed the top DCI vendor by 39 percent of those surveyed by IHS-Markit. Cisco, Coriant, and Infinera each garnered 36 percent of the votes.Last year Ciena reportedly won a DCI deal from rival ADVA Optical, which had a negative impact on ADVA’s operational results.
Ciena also topped the list of top (optical) transport software-defined networking (SDN) vendors, with 46 percent of those surveyed citing the company as a leader in the segment. Adams noted that while this market was still in its early days, Ciena’s continued integration of its Blue Planet software platform with its optical equipment products was driving differentiation in the market.
Cisco attracted the second most votes in terms of transport SDN leadership, followed by Nokia and Infinera.


