Uncategorized
HKT & Huawei Open Digital Transformation Practice Center in Hong Kong; Indoor 5G Whitepaper
Hong Kong network operator HKT and China IT powerhouse Huawei jointly inaugurated the Digital Transformation Practice Center (DTPC) yesterday in Hong Kong. The DTPC will share the experience and practices of HKT gained during its digital transformation journey, and help guide the digitalization process of other carriers in their development of digital transformation, HKT said.
The DTPC will provide on-site sharing of HKT’s experience and practices gained in its successful digital transformation journey.
At the DTPC, a project team will assess different transformational scenarios through the five stages of digital transformation: Envisioning, Ideating, Prototyping, Realizing and Scaling. The goal is to realize digital transformation in a more agile and low-cost manner. By connecting to Huawei Cloud Open Labs, visitors can also experience on-the-spot the transformed services.
“We are glad to cooperate with Huawei to carry out the digital transformation project. During the process, we have encountered many challenges in terms of user experience, business processes, business support systems and network infrastructure,” HKT head of strategic wireless technology and core networks Dr Henry Wong said. “Thanks to the joint team, the company has launched new services through the transformed cloud platform and gained a lot of valuable experience in the process. We hope to share our digital transformation experience with the industry around the world through the DTPC,” Wong added.
The digital transformation practice facility aims to offer consultancy from half a day or a full day to chief executives, through to several weeks with specialist staff, said Derry Li, Huawei’s vice president of consulting and systems integration. “The center will support the construction of solutions. We will uncover user pain points,” Li said. The process will include prototyping of front-end and back-end solutions, he added.
By the end of this year, the facility will also advise on other technologies such as internet of things (IoT), the executive said. Li also said that Huawei and Hong Kong Telecom plan to extend the scope of the new facility to include 5G services in the first half of 2019.
HKT had previously worked with Huawei to carry out the end-to-end digital business transformation project, covering service and operation transformation as well as infrastructure cloudification for the realization of customer-centric “ROADS” (Real-time, On-demand, All-online, DIY, Social) experience.
During his keynote presentation at the opening of the event, Huawei’s board Chairman Liang Hua said that a full digitalization process can take at least 18 months to get through the toughest period of the implementation.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, HKT, Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), and Huawei have jointly issued Indoor 5G Networks White Paper which explains the complexity of indoor 5G network deployment. It discusses 5G indoor service network requirements, the evolution of existing network, and challenges in target network deployment, and recommends appropriate construction strategies.
The white paper points out that more than 80% of service usage on 4G mobile networks occurs indoors. The industry predicts that a greater number of mobile services will take place indoors as 5G spurs service diversity and extends business boundaries. As a result, says the white paper, indoor mobile networks in the 5G era will become essential to operators’ competitiveness.
The white paper discusses key requirements and performance indicators for indoor 5G target networks based on the features of the three major types of 5G services (enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low-latency communication and massive machine-type communication). The specific requirements of augmented reality (AR), VR, high-definition (HD) video, telemedicine, and smart manufacturing are elaborated.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/press-events/news/2018/9/hkt-huaei-practice-center
https://www.huawei.com/en/press-events/news/2018/2/Huawei-HKT-Digital-Transformation-Practice-Center
https://www.huawei.com/en/press-events/news/2018/9/indoor-5g-networks-whitepaper
Allied Telesis Introduces Single & Multi-Channel Blanket Hybrid WiFi Solution

Century Link tops Mid-Year 2018 U.S. Carrier Ethernet LEADERBOARD
CenturyLink maintains the top spot in Vertical Systems Group’s (VSG) mid-year 2018 U.S. Carrier Ethernet Services Leaderboard. AT&T, #1 in 2017, claimed the #2 spot, followed by Verizon, Spectrum Enterprise, Comcast, Windstream and Cox. All of the companies maintained their year-end positions. The leaderboard ranks incumbent telcos in order based on U.S. retail Ethernet port share. VSG calls this an industry benchmark for measuring Ethernet market presence.
CenturyLink’s acquisition of Level 3 Communications, along with continued growth in Ethernet ports for both companies, allowed it to power its way to the top of the year-end ranking.

“After a flurry of M&A activity duing the past two years, the Ethernet marketplace stabilized during the first half of 2018,” said Rick Malone, VSG principal. “U.S. port growth was more than 6 percent for the period, with accelerating deployments of multi-gigabit speed services. Most providers experienced acute price compression across all data rates, partially offsetting the revenue typically generated from higher-speed services. All providers are grappling with longer sales cycles due to SD-WAN, however the impact on the U.S. Ethernet base has been negligible to date.”
Other providers selling Ethernet services in the U.S. are segmented into two tiers as measured by port share. The first, or challenge tier, includes Altice USA, Cogent, Frontier Communications, GTT, Sprint – which is attempting to merge with T-Mobile – and Zayo.
The second or Market Player tier includes all providers with port share below 1%. Companies in the Market Player tier include the following providers (in alphabetical order): Alaska Communications, American Telesis, BT Global Services, Cincinnati Bell, Consolidated Communications, Crown Castle Fiber, DQE Communications, Expedient, FiberLight, FirstLight, Fusion, Global Cloud Xchange, Great Plains Communications, Hawaiian Telecom, Logix Fiber Networks, LS Networks, Lumos Networks, Masergy, MegaPath, Midco, NTT America, Orange Business, RCN Business, Tata, TDS Telecom, Telstra, TPx Communications, Unite Private Networks, US Signal, Vodafone, WOW!Business and other companies selling retail Ethernet services in the U.S. market.
Verizon’s Network Roadmap includes NG-PON2 and Open Daylight
Lee Hicks, Vice President of network planning at Verizon said the carrier is focused on a single core MPLS network supporting wireless, residential and business services that will use NG-PON2 as an access method for all three. Mr. Hicks made those remarks at ADTRAN Connect 2018 in Huntsville, Alabama. Hicks said that an important goal is to reduce the cost per bit by 45% while also providing low latency to support services such as augmented and virtual reality and telemedicine, he said. Speaking about the company’s fiber investment, Hicks said: “This has become the base for what we do in the industry. We are big believers in taking fiber all the way.”
In comparison with other 10 Gbps PON options, Hicks said, “It’s not the easiest to go from GPON to NG-PON2, but it’s the best long-term step.” NG-PON2 initially will have four wavelengths, each operating at 10 Gbps. “In the future, we have a roadmap to be able to bond these wavelengths,” Hicks said. “We have a built-in ability to go beyond a 10-Gig to 20-Gig, 30-Gig, even 40-Gig down the road. Today with 1-Gig service becoming common place, it’s only a matter of time before 10-Gig and beyond become important. You need to be thinking about that. We are and we’re trying to pick a platform that could help us do that. Having multiple wavelengths available is important.”
Hicks said that tunable optics for NG-PON2 will allow operators to assign different subscriber types to different wavelengths. Using dynamic load balancing, a service provider could move a data hog to a separate wavelength via a provisioning command to the optical network tuners. He touted the enhanced reliability that multiple wavelengths and tunable optics will support. Verizon has demonstrated pulling a fiber off of a PON and having the optical line terminal automatically switch to a backup wavelength within a few seconds. “Having multiple wavelengths available helps when you have to take a PON card out of service,” he said.
NG-PON2 also will enable network operators to load balance traffic, Hicks noted. If one customer on a PON is a wavelength hog, other customers could be moved to a different wavelength. NG-PON2 equipment currently uses a separate broadband network gateway and gateway router but Verizon is working with Adtran to incorporate BNG functions into the optical line terminal.
“Broadband is no longer a want to service; it’s a have to service. We’re at 40%, 50% per customer growth in consumption every year. But what’s coming on top of that now is the demand for low latency. Whether it’s augmented reality, virtual reality, or telemedicine, all these things require very low latency. We’re looking for solutions that continue to help with that.
What can we do is simplify our network by driving the costs per bit down,” Hicks said. “We’re very focused on that. We have an internal goal to every year to reduce the cost per bit by 40%. That’s what I charge my team with figuring out how to do, that’s what I charge Adtran and all of our suppliers to do. Our goal is to continue to develop a roadmap on how to reduce the cost per bit so that we can give good value to our customers. That’s our vision. And so now how do we think about meeting that, especially on a fiber network? We believe that NG-PON2 is the right platform to do that.”

Verizon’s Lee Hicks talks about some of the telco’s networking goals at Adtran Connect. (Photo by FierceTelecom)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Other elements of the Verizon network roadmap:
- The company will consolidate real estate across its wireless, residential and business networks into what Hicks called “shared hub sites” for the “aggregation and service edge.” These could be central offices, points of presence or C-RAN huts, he said.
- Verizon currently has more than 40 platforms and 200,000 network elements, including some that are up to 30 years old, that will be decommissioned.
- The company’s platform “allows us to do circuit emulation” to support customers currently using DS-1 or Sonet services, which will be converted to Ethernet at the central office
- Services such as FiOS, virtual private networks and others will share an uplink
- The company will manage the network using a base network controller (BNC) that will use standard interfaces to an orchestration and abstraction network in place of traditional vendor-specific element management systems
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
On Network Automation, Telemetry and Control, Hicks said Verizon is using OpenDaylight for its Base Network Controller (BNC), which is the focal point for gathering streaming telemetry from network elements.
“The model there is we’re going to create standard interfaces to our orchestration and extract the network,” Hicks said. “Southbound from the BNC, we will use industry standards, things like NETCONF and YANG models for provisioning, and then we’ll use OpenFlow to do network control. We’re going to be using this to do telemetry.”
In the past, Hicks said every Verizon service had its own set of network probes to gather data, which was then put into separate data lakes with their own set of analysis tools.
“We’re not going to be buying probes anymore,” Hicks said. “We’re going to be using the intelligence that’s in the network elements themselves and using streaming telemetry to gather all that. We’re going to be bringing it to a single data lake and then doing analytic engines on top of that with closed-loop automation.
“Our vision is on this new network where I have a single data lake, without probes, that I can then do closed-loop automation,” Hicks concluded.
Super fast broadband boosts UK business; Calls to break up BT & sell Openreach
The roll out of super fast broadband in the UK has increased revenues for businesses and created jobs, says a report by the UK Department for Culture, Media and Sporttitled: “The Evaluation of the Economic Impact and Public Value of the Super fast Broadband Programme, covering 2012 to 2016.”
“We’ve also recently introduced a raft of lower wholesale prices to help drive higher take-up of faster fiber services which will help to further fuel the boost to the UK economy,” Openreach chief Clive Selley said.
https://www.bbc.com/news/business-45238452
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/need-for-speed-drives-superfast-broadband-boost-for-wales
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From the FT (see reference below):
KT to build fiber optic network in Philippines as part of $1.8B broadband project
KT Corp, South Korea’s largest telecommunications network operator, will participate in a nationwide project to greatly improve Internet connectivity in the Philippines, gaining a major foothold in the Southeast Asian country and neighboring region.
KT signed a 53 billion won (US$ 47 million) contract last week with the Philippines’s Converge ICT Solutions Inc. to build an optical fiber network along some 1,570 kilometers (975 miles) of main roads in the northern region of Luzon. The company hopes the contract will lead to more business partnerships with the top Philippines Internet provider in the future.
The latest deal is part of Converge’s $1.8 billion endeavor to expand its broadband coverage throughout the Philippines over the next five years. KT is increasing efforts to expand its business presence and partnerships overseas, notably in Asia, Europe and Africa, with the company’s latest Internet solutions, including GiGA Wire, GiGA WiFi and GiGA LTE.
“The partnership with Converge ICT Solutions is a great opportunity to introduce our technological expertise in telecommunications network planning, construction and operation not only in the Philippines but also in neighboring countries,” said Yun Kyoung-Lim, head of KT’s future convergence and global businesses. “KT will continue its efforts in representing the Republic of Korea to the world as the global ICT leader.”

KT is a global leader in next-generation wireless technology. The company is preparing for the commercial launch of the country’s first nationwide 5G network early next year and successfully showcased trial 5G services with the world’s first 5G-ready network. The company is also a pioneer in future technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), autonomous driving, and virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR).
In recent years, KT has installed more than 5,500 kilometers (3400 miles) of optical fiber networks in Myanmar, Bangladesh and other countries. For the Philippines-based project, the company plans to cooperate with many Korean small- and mid-sized companies, which have proven their high quality through previous overseas projects. KT expects to have more business opportunities in the Philippines, including smart energy, corporate and public innovations, and disaster and safety management.
The Korean telecom leader also signed an agreement last month with Germany-based albis-elcon to provide its GiGA solutions and next-generation technologies to communications service providers in Europe and other parts of the world. KT is also now working on various projects to improve ICT infrastructure in Africa, including broadband networks in Rwanda, Gabon and Botswana and a public security network in Angola.
Luzon is the largest of more than 7,000 islands in the Philippines and is home to the Southeast Asian country’s capital, Manila. More than half of the country’s population, estimated at over 106 million, live on Luzon. Because the country consists of so many islands, the Philippines has experienced difficulties in improving its Internet speed and telecommunications service environment.
When the optical fiber cables project in Luzon is completed in June 2020, a great number of people in the Philippines are expected to benefit from high-speed home Internet connections. Philippines President Rodrigo Duterte has established the Department of Information and Communications Technology, and the administration is promoting e-government services and ICT development.
About KT:
KT Corporation, Korea’s largest telecommunications service provider reestablished in 1981 under the Telecommunications Business Act, is leading the era of innovations in the world’s most connected country. The company leads the 4th industrial revolution with high speed wire/wireless network and innovative ICT technology. After installing 4.5 million fixed lines for 20 million users in just 12 years, KT was the first telecom provider to introduce 5G broad-scale trial service in 2018. It is another step in KT’s continuous efforts to deliver essential products and services as it seeks to be the No.1 ICT Company and People’s Company.
For more information, please visit our English website at https://corp.kt.com/eng/
Samsung’s Digital City Provides a Glimpse of What’s Possible with 5G
Samsung’s digital city in South Korea showcases many of the perceived benefits of 5G. Samsung has deployed a 5G hot spot (or hot zone) within its campus to demonstrate how quickly a person in a moving vehicle could download and upload large video files to the network. The company’s pre-5G standard technology already supports some in-vehicle services, as well as smart city initiatives such as traffic, smart lighting and CCTV, and as it gains widespread coverage, even more innovations will occur.
Sporting venues will likely use 5G hot zones to deliver a new in-stadium fan experience that offers personalized video feeds of a customer’s favorite player to their mobile device. One example of this was the time slice feature that was available for the winter Olympics. Moreover, remote healthcare use cases will get a boost with better bandwidth to enhance the video and enable new use cases such as assisted surgery with augmented and virtual reality.
https://news.samsung.com/global/video-5g-city-samsungs-preview-of-the-5g-era
Cignal AI’s Optical Customer Markets Report: Optical spending up in China & NA; Down for cloud service providers & other regions
Cignal AI’s (Andrew Schmitt) latest Optical Customer Markets Report states that spending growth by cable Multiple System Operators (MSOs) led all other North American industry verticals during first quarter 2018. The report also reveals that contrary to continued increase in China’s optical spending, incumbent network operator spending in North America and Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) on optical transport equipment continues to decline. Spending in North America grew 30 percent and outpaced all other customer verticals, including cloud operators.
Indeed, optical equipment spending by cloud operators has stalled due to rapidly declining prices and the use of IP-over-WDM as a substitute. Despite the downward trend, however, Ciena and Infinera continue to increase market share in the cloud optical network market.

“In North America, cable MSOs were the strongest performing customer market during the first quarter of 2018,” says Andrew Schmitt, lead analyst at Cignal AI. “Cloud operators are not increasing purchases of optical equipment, though common belief right now is just the opposite. The revenue growth from cloud operators experienced by Ciena and Infinera came at the expense of other vendors’ sales.”
Other key findings in the report include China being the largest source of optical hardware market growth, almost single-handedly representing the one-third global spending by Asia. Global spending by cable MSOs grew 5% year-over-year in the first quarter, with North America increasing 30%.
Other findings of the report were outlined in the press release and included:
- Ciena and Infinera sales growth in the cloud and colo market came during a period of overall spending decline among these customers (see above chart).
- Optical equipment spending by cloud operators has stalled, which contradicts the common perception that cloud operators like Amazon, Google and Microsoft are increasing spending on optical transport equipment. Growth in the cloud market has been inhibited by rapidly declining prices and the use of IP over WDM as a substitute.
- One third of global spending on optical hardware is in Asia, with almost all coming from Chinese incumbent operators.
- Cable MSO global spending grew 5 percent year-over-year in the first quarter.
Cignal AI’s Optical Customer Markets Report is issued quarterly and quantifies optical equipment sales to five key customer markets as well as equipment vendor market share for sales to cloud operators.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
From a separate Cignal AI market research report, here’s the latest YoY Revenue % increase/decrease for various segments of the optical networking market by country or region and Grand Total:

Chart courtesy of Cignal AI
FTTH/FTTP Update: Migration from HFC to Distributed Access Architecture for MSOs
by Jon Baldry, Director Metro Marketing at Infinera
Fibre to the Home (FTTH) or Building (FTTP) is now a very popular choice for new housing developments and business parks across the globe. Extending broadband availability and raising public expectations provides a major boost for the industry, but there is a greater challenge in regions with a well-established copper or cable infrastructure. Telcos are already stretching DSL technology to discourage customer churn. Cable too has significant territory to defend: it begins with a more powerful offering, but MSOs cannot be complacent.
QoS is the new battle cry, and Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) offers a major challenge to the spread of Fibre to the Home. The migration to DAA is inevitable, but not to be undertaken lightly. The global advance of FTTH has been dramatic, and it is expected to provide nearly 50% of all broadband subscriptions by 2022. But it is worth noting that this has been driven by exceptional uptake in certain countries, notably the Far East, where the legacy copper and cable infrastructure was less established.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
China accounts for over a third of the global broadband total, and over 70% of those connections are on FTTH. Singapore has 95% FTTH, South Korea over 80% and Hong Kong over 70% according to the Fibre Broadband Association. Compare that with Europe, with its legacy copper and cable infrastructure, where FTTH penetration is barely 10%.
Editor’s Note: Point Topic said that in 12 months to the end of Q1 2018, China added nearly 63 million FTTH connections. This figure constituted 80% of global FTTH net adds in the period.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Fibre still has a long way to go, and installation will take time in the old world with its stricter planning regulations and narrow old-town streets. What does the world want from broadband?
Expectations are changing rapidly. Optical fibre now delivers about six times the capacity that DSL can manage. There is still huge demand for downloads and streaming video and services like 4K HDTV are pushing demand way beyond the capabilities of current DSL technology. More significantly, in addition to the video demands, users also use a broad range of services such as social media, gaming and potentially, in the not too distant future, virtual or augmented reality where upload speeds and latency become much more important. Here legacy cable delivery does have a distinct disadvantage – although it has accelerated its download speeds to stay around 80% of fibre capacity, cable’s upload speeds are more like one third of what FTTH can offer. Cable was in a strong position in the days of asymmetric Internet usage, but today’s soaring demand for massive bandwidth, fast uploads, low latency and high reliability presents a serious challenge, and the industry is looking to a new Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) to meet this challenge. This is a radical move that will impact the entire system for cable multiple service operators’ (MSOs) optical networks, from “fiber-deep” access networks to support Remote PHY Devices (RPDs) to the need for enormous bandwidth scalability throughout their entire networks.
For a couple of decades cable operators have used Hybrid Fibre Coax (HFC) to connect the core to the access networks. The fibre carries the data as analogue radio frequency (RF) signals, similar to those in the coaxial access cables, rather than digital packets as in a typical fibre network like FTTH (Fig 1). This analogue infrastructure is expensive to operate and maintain. Digital signals are more tolerant of signal to noise degradation and are therefore less affected by attenuation, whereas analogue signals need a chain of power hungry amplifiers along the route to maintain signal strength and quality. This analogue technology was designed to suit earlier network requirements, which it supported well, but it cannot scale to meet today’s increasing demands.
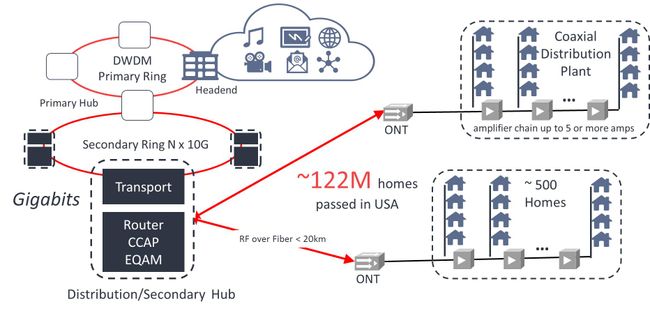 Figure 1: The Current HFC Access Network
Figure 1: The Current HFC Access Network
Note also that each Optical Network Terminal (ONT) typically serves several hundred homes, requiring costly analogue equipment that requires considerable maintenance. With so many subscribers per node, the system struggles to support bursts in demand, slowing down delivery at those most critical times.
The new “fibre deep” approach pushes today’s default packet-based digital fibre technology out closer to the end point (see Figure 2). Replacing analogue channels and the older transmission protocol also frees up spectrum in the remaining shorter coaxial plant for more efficient use of capacity, enabling Full Duplex delivery so that upload speeds will be able to match download speeds. This narrows that gap between FTTH and Cable for interactive gaming, virtual reality and social media purposes – as well as increasing its potential for future Internet of Things (IoT) applications where masses of data may be uploaded from countless small devices.
Note also in Figure 2. below that increasing in the number of nodes closer to the end users means that each one serves around one tenth of the number of subscribers, and this facilitates exceptional interactive services. The cable network has for many years supported on-demand content, and the updated network architecture makes room for more locally stored content. Being closer improves responsiveness and Quality of Service (QoS), especially during peak hours. These developments will present a serious challenge to the arrival of FTTH providers, who already have to compete against an existing infrastructure and established customer base.
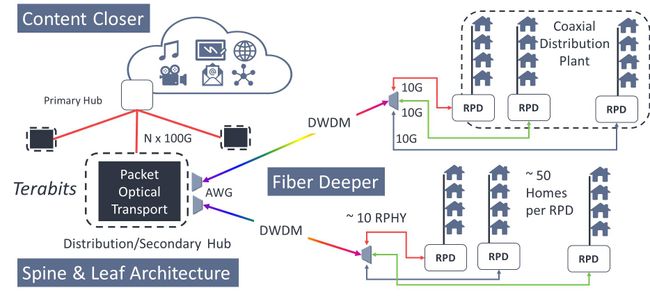
Figure 2: HFC to Distributed Access Architecture (DAA)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Huge potential versus tricky demands of DAA:
Selecting suitable equipment will no longer be a simple matter of asking a preferred supplier to meet the required performance levels, it will be necessary to look closely at the specifications to see if devices are sufficiently compact and power efficient to optimise scarce secondary hub real estate and to provide additional capabilities that can address the significant operational challenges of managing such a high density aggregation. With a tenfold or so increase in the number of RPDs terminating the DWDM network, installation and operating expenses will soar unless care is taken to choose the most compact, reliable and easy to maintain equipment.
Optical equipment suppliers are aware of these concerns and are rising to the challenge of mass deployment of DAA networks. Great advancements are being made in terms for density, power consumption and addressing the operational challenges of managing potentially 1000s of fibers within a secondary hub rack. What’s more, the industry has been working to bring the International Telecommunications Union’s (ITU) vision of autotuneable WDM-PON optics up to the performance levels required to support the reach and capacity requirements of DAA networks. This eases the pressures of commissioning and maintaining extensive DWDM optical networks by replacing the technicians’ burden of determining and adjusting wavelengths at every installation. Autotuneable technology will automatically select the correct wavelength without any configuration by the remote field engineer enabling them to treat DWDM installations with the same simplicity as grey optics.
These are the sort of challenges that will be faced as MSOs migrate to DAA, and they will need to take a very close look at their choice of equipment and solutions in order to meet the very specific challenges of fibre-deep access networks. However, a successful DAA rollout is not just about what happens in the access network. DAA will also create a surge in bandwidth demand throughout the entire infrastructure – from access through transport to core. Unless steps are taken to reinforce, optimise and automate the entire network capability, the most powerful, responsive and efficient access network could become its own worst enemy.
Conclusions:
Already nearly a half of all US consumers are using streaming video services and 70% “binge watch” TV series, while virtual and enhanced reality services and 4K high definition TV are still poised to go mainstream. So future-proofing a cable MSO’s network means preparing for a highly uncertain future.
Network operators will need help from specialist optical equipment providers to optimise optical transport platforms to their specific needs, creating network architectures that will be highly scaleable, that simplify operations, accelerate the launch of new services, and minimize total cost of ownership. Something that will only be achieved by installing intelligent networks that integrate best-in-class technology and automate a significant proportion of manual operations.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2Q-2018 Status & Direction of AT&T Communications, by CEO John Donovan
2Q-2018 for AT&T had 76,000 IP broadband net adds with 23,000 total broadband net adds. That’s the seventh consecutive quarter of broadband growth for AT&T Communications. About 95% of our consumer broadband base is now on our IP broadband as our transition from DSL is drawing to a close. Our fiber build continues at a fast clip, now passing more than 9 million customer locations, and we expect that this time next year to reach 14 million locations.
This gives us a long runway for broadband growth. We’re doing very well in our fiber markets, including a 246,000 net increase in subs on our fiber network in the second quarter.
Now I’d like to update you on several key initiatives we have underway, so we’ll turn to Slide 17. Evolving our video portfolio is top priority for us. We believe we’re well positioned as our customers move toward a more personalized set of streaming products.
Our new platform was launched in May as the DIRECTV NOW user interface, and it’s now live on all supported device operating systems and has been well received with strong engagement by customers. It offers a new cloud-based DVR and more robust video-on-demand experience with new pay-per-view options. Over time, it will bring additional advertising and data insight opportunities. This new video platform gives us flexibility to adapt to the market with new offerings and products. Late in the quarter, we added our third video offering called WatchTV, a small package of 30 live channels and 15,000 on-demand titles.
We include WatchTV in our unlimited, more wireless plans where you can purchase it for $15 a month, making it perfect for customers who want video but not at the cost of a large package. This complements DIRECTV NOW where we continue to see success in attracting cord cutters and cord severs. And later this year, we will begin testing a premium product extension, which is a streaming product that will give the full DIRECTV experience over any broadband, ours or competitors’. It will have additional benefits of an improved search and discovery feature and an enhanced user interface. We’re excited that this will complement our top-end product for those who don’t want or can’t have a satellite dish.
Our open-video platform also dovetails nicely with our ongoing focus on driving the industry’s leading cost structure. The new platform is low touch with lower acquisition costs as streaming services becomes a bigger part of our business.
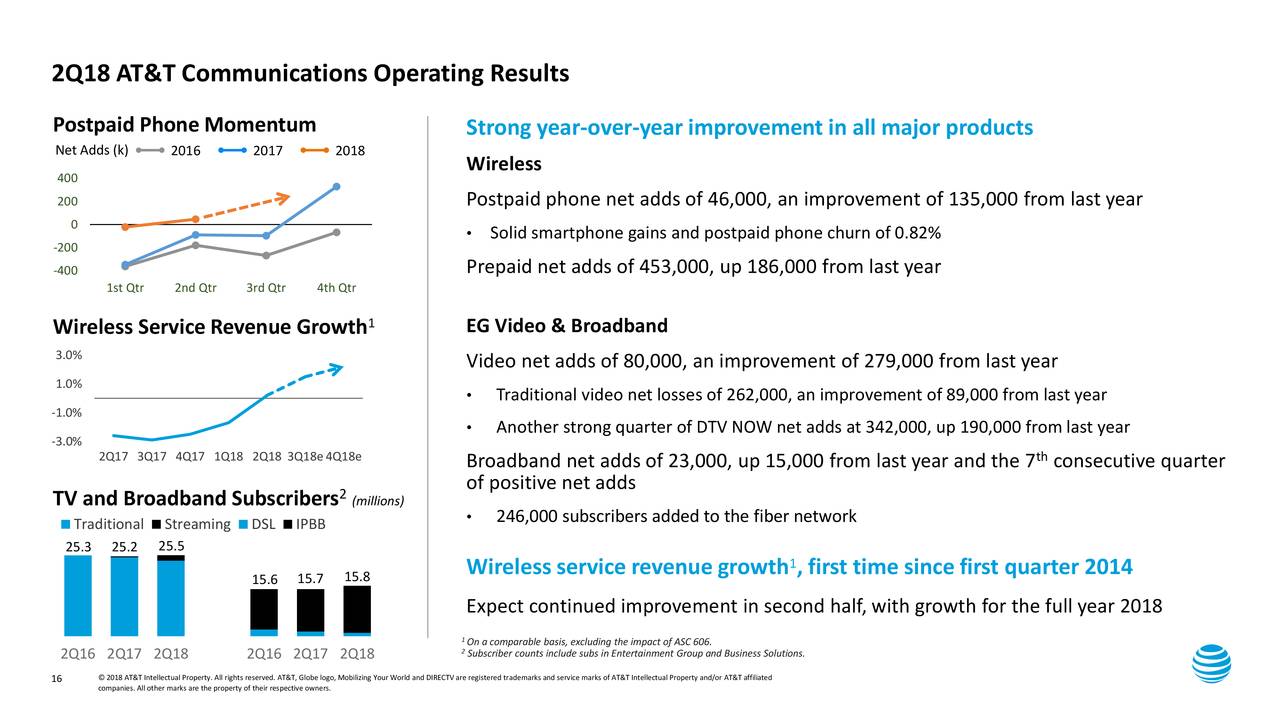
Digital sales are a cost-efficient way of customer engagement, and we’re seeing double-digit growth in our digital sales and service. We’re also seeing operating expense savings from our move to a virtualized software-defined network.
More than 55% of our network functions were virtualized at the end of 2017, and we’re well on our way to meet or exceed our goal of 75% virtualized by 2020. These and other cost management initiatives have helped drive 13 straight quarters of cost reductions in our technology and infrastructure group.
Finally, I’d like to give an update on our FirstNet build and other network investments. Our FirstNet network build is accelerating. We expect to have between 12,000 and 15,000 band 14 sites on air by the end of this year 2018, and we’re ahead of our contractual commitment. And don’t forget, when we’re putting in equipment for FirstNet, we’re also deploying our AWS and WCS spectrum, utilizing the one touch, one tower approach. This approach allows all customers access to our improved network. FirstNet also gives us an opportunity to sell to first responders. So far, more than 1,500 public safety agencies across 52 states and territories have joined FirstNet, nearly doubling the network’s adoption since April.
In addition to our efforts with FirstNet, 5G and 5G Evolution work continues its development in several different areas that will pave the way to the next generation of higher speeds for our customers.
We now have 5G Evolution in more than 140 markets, covering nearly 100 million people with theoretical peak speeds of at least 400 megabits per second with plans to cover 400-plus markets by the end of this year. Our millimeter wave mobile 5G trials are also going well, and we’re on track to launch service in parts of 12 markets by the end of this year.

References:
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4189949-t-inc-2018-q2-results-earnings-call-slides


