Dell’Oro: 5G SA indecisions slowing 5G Core network growth
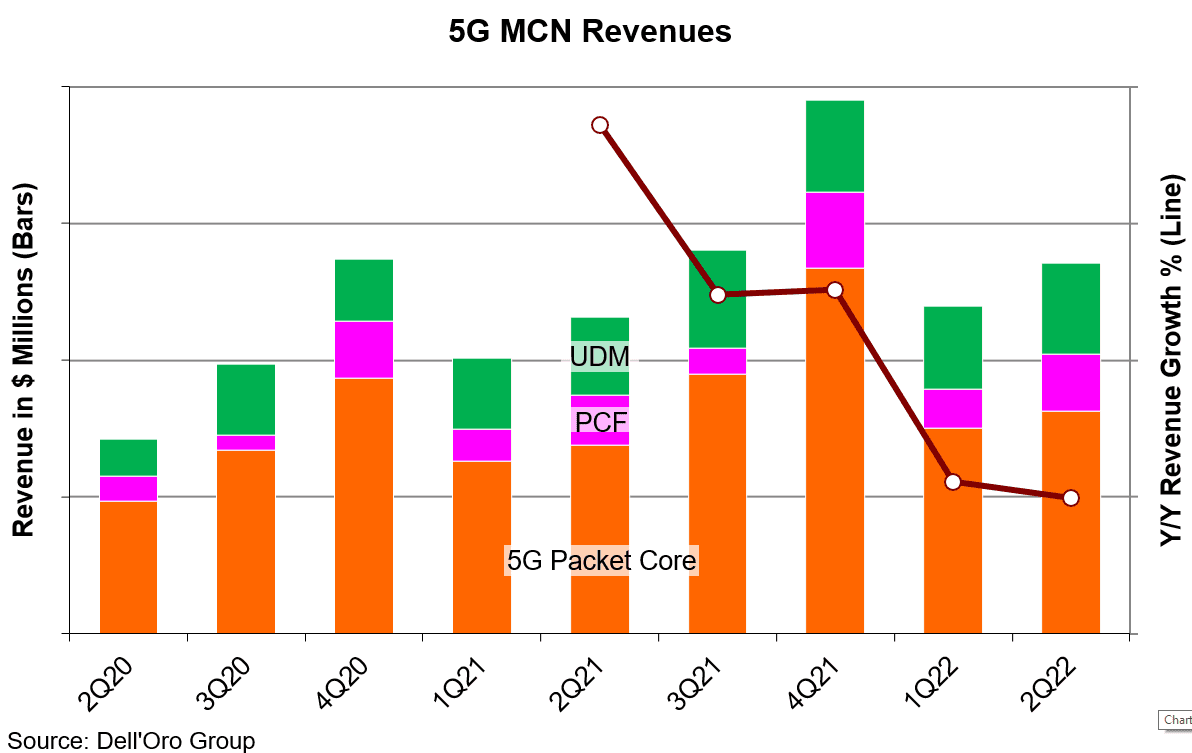
Revenues for the Mobile Core Network (MCN) [1.] market slowed to 6% year-over-year growth in 2Q 2021 after four quarters of double-digit growth, according to a new report by Dell’Oro Group.
Communication Service Providers (CSPs) indecisions about moving forward with 5G Standalone (5G SA/core network are slowing 5G Core market growth (except in China). It is now expected to decelerate over the next four quarters dropping to 17% year-over-year in 2Q 2022.
Note 1. The Mobile Core Network is in a transitional stage from 4G to 5G and a new type of core network called the 5G Core Service Based Architecture (SBA). The 5G Core SBA is designed to be a universal core that can be the core for mobile and fixed wireless networks, wireline networks, and Wi-Fi networks. This includes the ability to be the core for 2G/3G/4G, so only one core is necessary for the long term. In addition, the IMS Core will migrate into the 5G Core SBA.
With Network Function Virtualization (NFV) the 5G Core SBA is best served with Cloud-native Network Functions that disaggregates the hardware from the software and operates in a stateless function with the data separated from the control function among other things.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“We attribute the slowdown to the slow uptake of 5G Standalone (SA) networks. CSPs need to make decisions about which direction to take for 5G SA deployments. CSPs have several options to mull over, with new choices that were not available during the switch from 3G to 4G,” stated David Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “One decision CSPs need to make is about the selection of Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI). NFVI can be procured from a 5G core vendor, a third-party, the public cloud, or another platform like the Rakuten Communications Platform.”
Additional highlights from the 2Q 2021 Mobile Core Network Report:
• The Asia Pacific region accounted for 70% of the revenues for 5G Core as the Chinese SPs continue to build and Japanese SPs begin their buildouts.
• Top vendor ranking remains unchanged based on the four trailing quarters ending in 2Q 2021: Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Mavenir.
• 4G MCN (EPC) revenues are now in continual decline, but still represented 70% of the mix between 4G and 5G.
About the Report:
The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions.
To purchase this report, please contact at [email protected].
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Closing Comments:
The slowdown in 5G SA/core network growth should come as no surprise to IEEE Techblog readers. We’ve pounded the table for a very long time, stating that in the absence of an ITU standard or 3GPP IMPLEMENTATION spec, the 5G SA/core network growth would be slow with many different versions implemented by CSPs. That will inhibit interoperability and portability of 5G endpoints which have 5G SA software.
Equally important is that ALL 5G services and features (e.g. network slicing, automation, MEC, etc) require a 5G Core network while almost all 5G deployments today are 5G NSA which has a 4G core (EPC) network.
References:
CSPs’ Indecisions Slow 5G Core Growth Except for China, According to Dell’Oro Group
Why It’s Important: Rakuten Mobile, Intel and NEC collaborate on containerized 5G SA core network
RootMetrics touts 5G performance in Korea while users complain; No 5G SA in Korea!
AT&T 5G SA Core Network to run on Microsoft Azure cloud platform
Dell’Oro: MEC Investments to grow at 140% CAGR from 2020 to 2025
Telcos Loss: Private 5G & MEC/5G SA Core Network – Cloud Giants Take Market Share
T-Mobile Announces “World’s 1st Nationwide Standalone 5G Network” (without a standard)
Evaluating Gaps and Solutions to build Open 5G Core/SA networks
3 thoughts on “Dell’Oro: 5G SA indecisions slowing 5G Core network growth”
Comments are closed.



Plenty of trial activity and planned deployments of 5G SA/core network.
Nokia recently signed a single-vendor deal with A1 Telekom Group to deploy standalone 5G in Serbia and Slovenia.
Vodafone Spain has selected Ericsson for pre-commercial standalone 5G support, including cloud-native 5G core and future network applications.
In France, Orange is evaluating standalone 5G in tandem with related tech, including artificial intelligence and Open RAN. The long goal is “zero touch” operations and network slicing capabilities.
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20210825/5g/despite-trials-many-operators-hesitant-on-transition-to-standalone-5g
In the United States, T-Mobile US has taken the boldest public stand. In fact, it’s the only nationwide U.S. carrier with a Standalone 5G deployment. It launched its 5G SA network in 2020 on its 600 MHz spectrum.
In Europe, different companies are trialing 5G SA networks of their own. Deutsche Telekom and Samsung partnered earlier this year to create a 5G SA trial in Pilsen, Czech Republic, where they found 3x spectrum efficiency compared to LTE. On its home turf, Deutsche Telekom built a 5G SA radio site in Garching, near Munich, and said that it will soon be connected to a 5G SA core network. In nearby Austria, operator Drei has begun trials of a 5G SA core network operating on 700 MHz and 1500 MHz frequencies at its headquarters in Vienna’s Floridsodorf district.
In France, Orange is testing a 5G SA network with several partners including Mavenir, Casa Systems, Dell, and Xiaomi. The network has been deployed first in the town of Lannion, with the intent of providing a “zero-touch” network that automatically provisions services and auto repairs. In the United Kingdom, Vodafone UK has deployed a standalone 5G network at Coventry University aimed at VR training for healthcare professionals.
Other standalone networks are in the works – Nokia and A1 Telekom will deploy 5G SA in Serbia and Slovenia, while Ericsson and Vodafone Spain have partnered for standalone 5G support.
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20210831/5g/what-is-a-cloud-native-5g-network
5G NSA smartphones/tablets need a 5G SA/core network download to use ANY 5G SA features/functions. T-Mo has made that 5G SA download available for Samsung and OnePlus smart phones https://www.tmonews.com/2020/08/t-mobile-galaxy-s20-plus-ultra-oneplus-8-standalone-5g-update/
5G NSA is still supported because it uses 4G LTE signaling and EPC (4G Core network).
However, an analyst that tested T-Mo 5G SA: “The S20 Ultra would frequently fall back to non-standalone mode,” Thelander said. “The phone is not staying in standalone mode.”
Thus, any benefits might have derived from T-Mobile’s new standalone 5G offering “are hard to achieve,” he said dryly.
https://www.lightreading.com/test-and-measurement/t-mobiles-standalone-5g-proves-sporadic-in-initial-tests-/d/d-id/762990