Year: 2023
Huawei reinvents itself via 5G-enabled digitalized services to modernize the backbone of China’s industrial sectors
In northern China sits Tianjin port’s “Smart Hub” – a fully digitalized and automated wharf where quay cranes, gantry cranes, stackers and forklifts are all controlled by a command center miles away. Powered by Huawei Technologies’ 5G telecommunications infrastructure, the smart port can move 36 20-foot equivalent units (TEU) per hour, much faster than humans.
“Digitalization is the industry trend, a direction not just for Chinese ports, but for all global ports,” Yang Jiemin, vice- president of Tianjin Port (Group), said during a recent visit by the South China Morning Post. “Our goal is to build a digital twin to Tianjin port in the next three to five years,” he added. The benefits of automation are clear. A staff of 200 operators and engineers can manage 1 million TEU in annual throughput at Tianjin port’s Terminal C, about 25 per cent of the employees needed in a typical year during its pre-digital age. The future has more in store: artificial intelligence (AI) for predicting congestion, big data analysis for parsing traffic trends and driverless trucks – all made possible by the ultra-fast exchange of data in 5G networks.
Shenzhen-based Huawei, with 195,000 employees in 2021 and one of the world’s largest research budgets, surpassing even that of Google and Microsoft, is now promoting the advantages of 5G-enabled digitalized services to modernize the backbone of China’s industrial production in coal mines, ports and even hospitals.
As U.S. sanctions tightened around Huawei’s access to critical technology, the firm’s smartphone business, which beat Apple to become the world’s second-biggest smartphone maker in 2018, came under tremendous pressure. Deprived of Google’s Android operating system and short of vital components, it sold its Honor budget smartphone business in 2020, the biggest driver behind its spectacular success. Huawei then pivoted back to its mainstay enterprise business, opening up new data-heavy products and services for customers to increase their usage and dependence on its 5G infrastructure.
The company established “legions” to spearhead the effort, a nod to the military parlance much liked by founder Ren Zhengfei, who served in the People’s Liberation Army. These cross-departmental business units were established to help clients digitally transform their products and services in mining, customs clearance and ports, energy savings at data centres, smart highways and the photovoltaic industry.
Last June, Huawei added five legions, bringing the total to 20. While it has not disclosed details about each legion, the chief executive of its airport and road legion, Li Junfeng, said the company was hopeful about the digitalization of transport.
“Airports and roads are also key infrastructure and it is difficult to expand in the overseas market. So we do not have plans for global expansion in the short term, but we will make some changes next year,” Li said in November, according to the state-owned Securities Times financial newspaper.
For Huawei, hopes are high that such industrial infrastructure can turn into a source of steady revenue – at least domestically – although the firm has declined to divulge the financial details of its showcase applications.
Huawei’s efforts to forge deeper ties with traditional industries build on its past work with the world’s private enterprises, leveraging its 5G connectivity and computing power to automate and upgrade various verticals, says Matthew Ball, chief analyst at research firm Canalys.
“Overall, this is an extension of what Huawei has done for years, even before the US sanctions, particularly its enterprise business, which had a strong vertical focus on delivering solutions across its portfolio,” Ball said.
“It’s just that its smartphone business has received more headlines.”
The jury is still out on whether Huawei can survive US sanctions, especially given Western reluctance to allow it future access to potentially sensitive data and network infrastructure contracts on national security grounds. The company has already undergone huge change since Trump added it to a trade blacklist in May 2019, barring it from doing businesses with US partners without special permits.
Huawei’s rotating chairman, Eric Xu, said in a new year’s message that the company had exited “crisis mode” and was ready to go “back to business as usual” in 2023. The bleeding has been staunched after it reported preliminary revenue of 636.9 billion yuan (HK$736.3 billion) for 2022, little changed from the previous year.
The pressure remained on Huawei even after Trump lost his re-election bid. Reports emerged last month that Joe Biden’s administration was considering cutting off Huawei from all its US suppliers, including Intel and Qualcomm, which produce the semiconductors critical to the company’s telecoms gear.
Huawei has been reporting its annual results since 2000 even if it is not subject to public disclosure regulations, a practice from bidding for tender contracts in public telecoms networks.
The share of China revenue in its overall business has increased from about half in 2018 to around two-thirds in 2021 due to a retreat from almost all overseas markets, including the Asia-Pacific, the Americas and Europe, the Middle East and Africa, according to its results.
Its consumer business, mainly smartphones and devices, has been hobbled by a lack of access to advanced chips.
At one point, Huawei briefly surpassed Apple and Samsung Electronics to become the world’s biggest handset vendor, but it is now out of the top five. By the third quarter of 2022, it finally ran out of less advanced in-house- designed semiconductors for its handsets.
Huawei’s carrier unit, once its bread-and-butter business of selling telecoms gear, has slipped as China’s telecoms operators gradually complete network upgrades. In 2021, its carrier business revenue was 40 per cent lower than in 2019 when China began 5G infrastructure installation.
That leaves enterprise as the only segment with growth, notching up a 2.1 per cent revenue increase in 2022, although its contribution was still less than one-sixth of total sales.
At the beginning of 2021, Huawei founder Ren told employees the company must make cloud computing its priority, and personally endorsed the firm’s partnership with coal mines.
The company is developing customized 5G mobile base stations for the mining industry that are resistant to dust, dampness and even shock waves from explosions. These devices are expected to support stable and fast upload of real-time data from unstaffed machinery, sensors and high-definition cameras, which would help China’s most dangerous industry cut back on the number of people working in the pits. The mining industry would be the first to use the model where scientists and experts from different corporate departments could come together to find solutions to specific industry problems, Ren said in 2021 in the Shanxi provincial capital of Taiyuan.
Enhancing end-to-end user experience, real-time processing of massive data and the operation, maintenance and management of complex networks would all become challenges for the financial industry in the future, according to a June speech by Cao Chong, the head of Huawei’s digital finance legion, the Securities Times reported.
Huawei has also made a foray into the electric-vehicle sector, with the high-profile launch of Aito cars, a brand launched jointly with Chinese electric-car maker Seres. However, competition is cutthroat in China, and Huawei ranked only sixth among the country’s electric-vehicle start-ups with a total of 76,180 units by the end of 2022. The company has also forged ties with a series of carmakers offering smart car components.
The change in Huawei’s business is visible to consumers. On the ground floor of its Shenzhen flagship store, a three-storey building with a huge glass facade, customers approached a row of Aito cars during a recent visit, asking sales representatives about vehicle specifications and available discounts. At the other end of the showroom, Huawei’s latest smartphones and tablets were on display on long wooden tables. While analysts are generally sanguine on Huawei’s new enterprise business moves, the digitalization push is not expected to result in a short-term revolution.
“The enterprise business should be able to generate rapid growth in the next five to 10 years,” said Ivan Lam, a senior analyst at Counterpoint Research. But the threat of US sanctions remains the biggest obstacle for Huawei, according to Lam, especially for products that require advanced computing power such as smartphones, servers and car components.
“Huawei has never treated existing sanctions as the last, and it has been preparing for new restrictions in various ways, such as adoption of domestic technologies. We expect Huawei to reap the benefits of these efforts in coming years and close the gap in key technologies,” ” Lam said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, the South China Morning Post reported that Huawei Technologies Co chief financial officer Meng Wanzhou, daughter of company founder and chief executive Ren Zhengfei, is expected to take her turn as “rotating chairwoman” in the company from April, according to local media reports, signalling that a succession plan looks to be in place at the struggling Chinese telecommunications giant.
It would mark the first time that Meng, 50, has assumed the role since she was added as one of three rotating chairmen at Huawei in March last year, alongside Eric Xu Zhijun and Ken Hu Houkun. Xu’s current acting chairman term started on October 1 last year and will conclude on March 31.
During her six-month turn as the company’s top leader, Meng, who also serves as deputy chairwoman at Huawei, will head the company’s board of directors and its executive committee.
Meng was hailed as a national hero upon her return to China in a chartered flight in September 2021, following nearly three years under house arrest in Canada where she fought extradition to the US over a bank fraud case. Under a deal reached with US prosecutors, that case and other charges against Meng were dismissed last December.
References:
FCC grants Amazon’s Kuiper license for NGSO satellite constellation for internet services
On February 8th, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approved, subject to conditions, the application [1.] of Amazon’s Kuiper Systems LLC (Kuiper) for modification of its license for a non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite constellation providing Fixed-Satellite Service (FSS) and Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) using Ka-band radio frequencies.
Specifically, the FCC granted Kuiper’s request for approval of its updated orbital debris mitigation plan, thereby satisfying a condition of our action in 2020 conditionally granting Kuiper’s request to deploy and operate its NGSO system. This FCC action will allow Kuiper to begin deployment of its satellite constellation in order to bring high-speed broadband connectivity to customers around the world.
Note 1. See Kuiper Systems Request for Modification of the Authorization for the Kuiper NGSO Satellite System, IBFS File No. SAT-MOD-20211207-00186 (filed Dec. 7, 2021). Kuiper is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Amazon.com Services (Amazon).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

In 2020, the FCC had granted Amazon’s Project Kuiper permission to deploy 3,236 satellites aimed at closing the digital divide. But the project has been delayed due to concerns about its orbital debris. This week the FCC said it is requiring Kuiper to comply with a series of orbital debris conditions.
The FCC announcement also contained reference to an apparent objection to the order by satellite rival Space X and others that seemed to want to limit an expansion of Kuiper’s constellation, but the regulator apparently wasn’t having nay of it: “When the Commission applied the 100 object-years condition in the SpaceX’s Gen2 Starlink Order, SpaceX had already launched thousands of satellites and had data reflecting its actual satellite failures, which was used to inform the Commission’s approach to satellite reliability monitoring for the Gen2 Starlink system.”
“The Commission noted that the 100 object-years metric was new and untested, but reasoned that an incremental approach based on a clear benchmark was appropriate in the context of a planned deployment that is at a scale not previously undertaken and also untested. As Kuiper has not started deploying or operating its constellation, we find it is not be necessary to impose such a condition at this time.”
Last October, Amazon switched the launch of its first Kuiper satellites – Kuipersat-1 and Kuipersat-2 -from the RS1 rocket in development by ABL Space to the debut flight of the Vulcan rocket from United Launch Alliance, the joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin. That delayed the launch till 2023 (it still hasn’t happened), but with this legal hurdle now overcome it looks set to launch satellites unabated using any rocket it choses, including from Jeff Bezos owned Blue Origin.
References:
DA-23-114A1.docx – Federal Communications Commission
https://www.fcc.gov/document/international-bureau-grants-kuiper-satellite-modification
https://telecoms.com/519860/fcc-gives-nod-to-amazon-kuiper-broadband-satellite-deployment/
OpenVault: U.S. broadband users on 1-Gig tiers climbed to 26% in Q4 2022
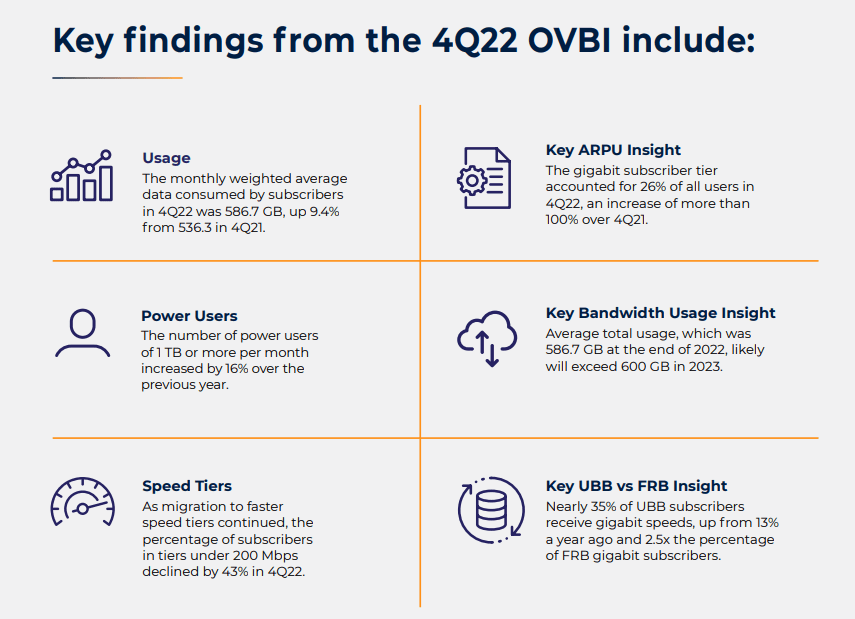
The 4Q22 edition of the OpenVault Broadband Insights (OVBI) report indicates that average household broadband consumption neared 600 GB per month, the percentage of subscribers on gigabit tiers more than doubled, and usage by participants in the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) continued to outpace that of the general population. OpenVault expects household data usage to surpass 600GB by Q4 2023 and possibly reach 1 terabyte by the end of 2028.
Editor’s Note: OpenVault bases its findings on data from “millions” of individual broadband subscribers that are collected and aggregated from a software-as-a-service broadband service management tool in use by a wide range of ISPs. The data is used to pinpoint usage patterns, including the differences between two key categories: subscribers on flat-rate billing (FRB) plans that offer unlimited data usage and those on usage-based billing (UBB) plans, on which subscribers are billed based on their bandwidth consumption. OpenVault data is used for benchmarking purposes by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in specific comparative analyses.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
With broadband consumption on the rise, there’s been an increase in “power users” – households that use more than 1TB of data per month. The percentage of users at that level rose 18.7% year-over-year. “Super power users” – those consuming 2TB or more per month – climbed 25%, from 2.7% to 3.4%. That’s a nearly 30x increase within the past five years, OpenVault said.
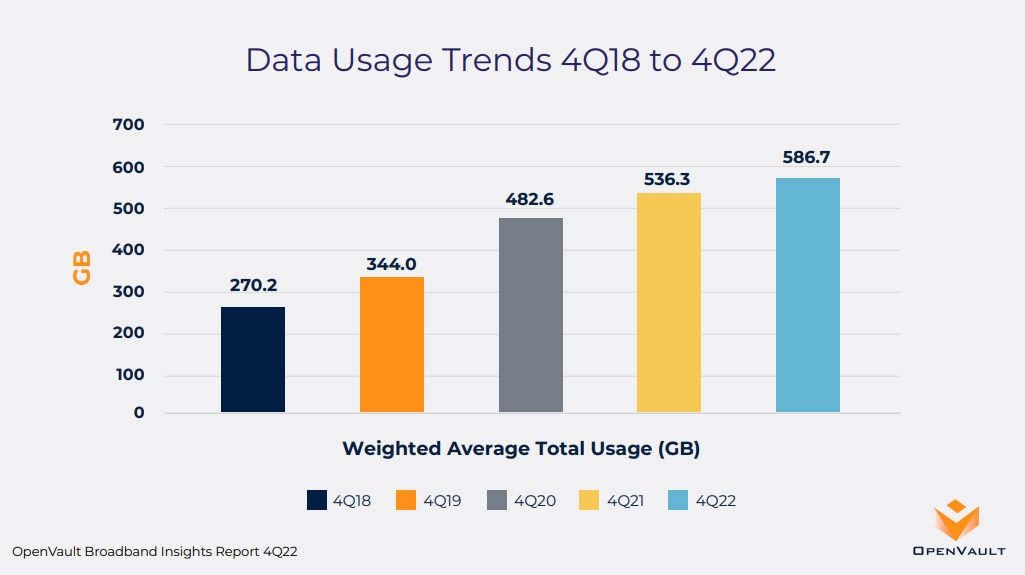
- European average data usage (268.1 GB) grew 12.5% from a year ago, a faster pace than the North American annual growth rate of 9.4%.
- North American median data usage (396.6 GB) was more than 2.5x that of European median data usage (148.2 GB) in 4Q22, a slightly smaller difference than observed in 4Q21.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The percentage of U.S. broadband subs on 1-Gig (or higher speed) tiers climbed to 26% in Q4 2022, more than double the 12.2% observed in the year-ago period, OpenVault. As broadband speeds increase, the percentage of broadband customers provisioned for speeds of 200 Mbit/s or less is on the decline – 31% at the end of 2022, down 43% year-over-year, OpenVault found. Adoption of gigabit speeds has jumped significantly among Usage Based Billing (UBB) subscribers, increasing to almost 35% in 4Q22 from 13.4% in 4Q21.
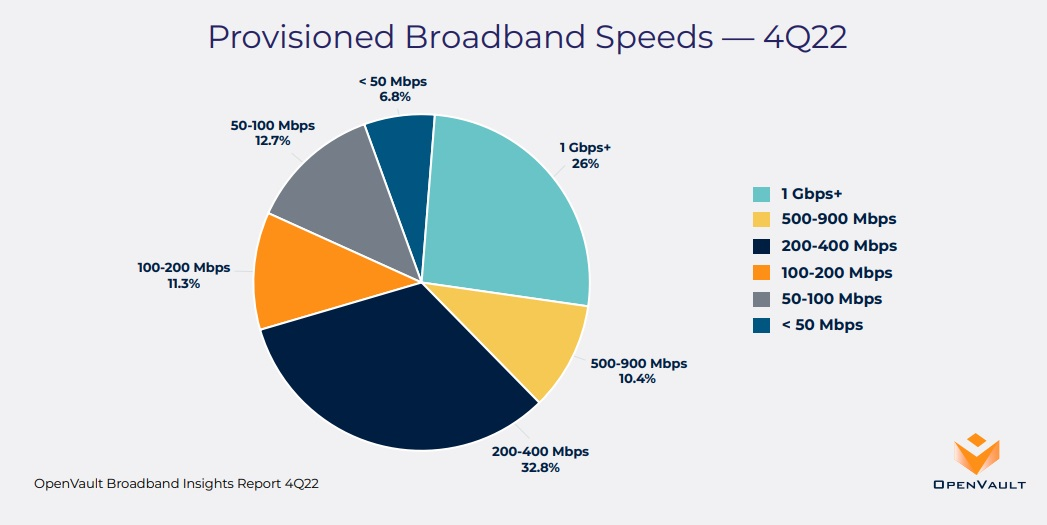
OpenVault found that average data usage in households on the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Plan (ACP) continues to outpace the field. In Q4, average usage in ACP households was 688.7GB, 17% higher than the broader average of 586.7GB. OpenVault has observed that some households in the ACP program use the funds to upgrade to faster speed packages.
References:
https://openvault.com/resources/ovbi/ (register to download the report)
OpenVault: Broadband data usage surges as 1-Gig adoption climbs to 15.4% of wireline subscribers
Ookla: Fixed Broadband Speeds Increasing Faster than Mobile: 28.4% vs 16.8%
MoffettNathanson: 87.4% of available U.S. homes have broadband; Leichtman Research: 90% of U.S. homes have internet
ITU-R M.2150-1 (5G RAN standard) will include 3GPP Release 17 enhancements; future revisions by 2025
ITU-R Recommendation M.2150 (previously known as IMT 2020) is being updated with new features for the 3GPP and ETSI-DECT 5G radio interface specifications in Annex 1, 2 and 4. This updated recommendation has been given the temporary name “M.2150-1.”
The main changes include the addition of enhanced capabilities for 3GPP 5G-SRIT (Set of Radio Interface Technologies), 3GPP 5G-RIT (Radio Interface Technology), DECT 5G-SRIT, and some consequential changes to the overview sections of the text, as well as to the Global Core Specifications.
This M.2150-1 revision is expected to be completed at ITU-R WP 5D meeting #44 which is June 13-22, 2023 in Geneva.
Annex 1: 3GPP 5G SRIT
The main purpose of this update is to align Rec. ITU-R M.2150 to the Release 17 December 2022 version of the 3GPP Specifications of 3GPP 5G-SRIT. The main features introduced in this update are:
– Addition of new modulation schemes for NB-IoT and LTE-M (LPWANs for IoT connectivity)
– The addition of new numerologies for NR;
– New logical channels and their mapping to physical channels;
– Reduced Capability (RedCap) NR devices.
Annex 2: 3GPP 5G RIT- aka “5G-NR”
The main purpose of this update is to align Rec. ITU-R M.2150 to the Release 17 December 2022 version of the 3GPP Specifications of 3GPP 5G-RIT. The main features introduced in this update are:
– The addition of new numerologies for NR
– New logical channels and their mapping to physical channels
– Reduced Capability (RedCap) NR devices.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Since 3GPP Release 16 5G-NR URRLC in the RAN spec has not been completed yet, it was not submitted to 5D for inclusion in M.2150-1. Therefore, ITU M.2150-1 still does not meet the URLLC Minimum Performance Requirements specified in ITU-R M.2410. In particular, 3GPP Rel 16 URRLC in the RAN:
| 1335 | 830074 | Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) | NR_L1enh_URLLC | 1 | Rel-16 | R1 | 6/15/2018 | 12/22/2022 | 96% | RP-191584 |
Annex 4: DECT 5G – SRIT
The DECT 5G – SRIT consists of two components: 1.] DECT-2020 NR and 2.] 3GPP 5G-NR. The followings contain the information for each of the component RITs.
– DECT-2020 NR component RIT The original submission contained the layers up to the ‘Medium Access Control’ layer. In this update the ‘Data Link Control’ (DLC) and ‘Convergence’ (CVG) layers have been added.
– 3GPP 5G- NR component RIT. The changes are identical to those in Annex 2. The main purpose of this update is to align Rec. ITU-R M.2150 to the Release 17 December 2022 version of the 3GPP Specifications of 3GPP 5G-RIT.
• The addition of new numerologies for NR
• New logical channels and their mapping to physical channels
• Reduced Capability (RedCap) NR devices.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
ITU-R WP5D meeting #43 considered future revisions of Recommendations ITU-R M.2150 (and ITU-R M.2012) after year 2023 and prepared initial and preliminary revision schedules in which revisions of both Recommendations would be completed by the end of 2025. That may or may not include what pundits label “5G-Advanced,” which is coming from 3GPP Release 18.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Objectives for WP5D – WG Technology Aspects at the 44th WP 5D meeting (June 12-23, 2023 in Geneva):
i) finalize preliminary draft revision “after year 2021” of Recommendation ITU-R M.2150;
ii) finalize preliminary draft revision of Recommendation ITU-R M.2012-5;
iii) finalize the Report ITU-R M.[IMT.ABOVE 100GHz];
iv) finalize preliminary draft revisions of Recommendations ITU-R M.2070-1 and ITU‑R M.2071-1 “Generic unwanted emission IMT‑Advanced”;
v) continue working on OOBE BS/MS for IMT-2020 “Generic unwanted emissions IMT‑2020.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
IMT 2020.SPECS approved by ITU-R but may not meet 5G performance requirements; no 5G frequencies (revision of M.1036); 5G non-radio aspects not included
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
Executive Summary: IMT-2020.SPECS defined, submission status, and 3GPP’s RIT submissions
https://www.itu.int/pub/R-REP-M.2410-2017
ETSI DECT-2020 approved by ITU-R WP5D for next revision of ITU-R M.2150 (IMT 2020)
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR-2022-02-24-5G-Standards.aspx
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-17
Alaska Communications uses XGS-PON, FWA, DSL in ~5K homes including Fairbanks and North Pole
That build was funded, in part, through the Connect America Fund II (CAF II) program.
“While we consider fiber to be the gold standard, Alaska’s vast geography, weather conditions and existing middle mile network infrastructure make it hard to deploy a one-size-fits all technology,” the spokesperson said in the email.
Fixed wireless also underlies a project completed in 2022 that made gigabit service available to more than 1,200 homes at Fort Wainwright.
“Our network upgrades on Fort Wainwright use fiber-fed mesh wireless as the last mile delivery,” the spokesperson explained. “Our mesh networks use fiber and radios to create a redundant mesh of connectivity around the customer. We selected mesh because it’s fast to deploy, gives the customer a fiber-like experience and allows rapid deployment on military installations.”
The backhaul infrastructure underlying the Alaska Communications network expansion also used a wide spectrum of technologies.
On one end of the spectrum, the XGS-PON deployment is supported by the company’s core packet switched and optical transport networks. At the other end of the spectrum for lower-speed deployments, the company in “minimal cases” uses bonded copper for backhaul, the spokesperson said. For some of those lower-speed deployments, the company also relies on a combination of fixed wireless and fiber.
Interestingly, Alaska Communications fiber installations use a combination of aerial and buried cable. The use of buried cable is a bit of a surprise, recognizing that the ground in Alaska is frozen solid for a considerable portion of the year.
The company plans further expansion into the Interior in 2023 and beyond, according to a press release about the broadband expansion.

Fort Wainwright family housing equipped with an Alaska Communications receiver. Mesh networks use fiber and radios to create a redundant mesh of connectivity around the customer. (Photo: Business Wire)
Contact:
Heather Marron, Manager, Corporate Communications
[email protected]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Qualcomm Introduces the World’s First “5G NR-Light” Modem-RF System for new 5G use cases and apps
Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. today announced Snapdragon® X35 5G Modem-RF System, the world’s first “5G NR-Light” [1.] modem-RF system. NR-Light, a new class of 5G, fills the gap in between high-speed mobile broadband devices and extremely low-bandwidth NB-IoT devices. NR-Light devices, powered by Snapdragon X35, can be smaller, more cost-efficient, and provide longer battery life than traditional mobile broadband devices.
Note 1. 5G NR-Light is not an ITU-R recommendation, but rather a subset of 5G-NR in 3GPP Release 17, which was “frozen” on June 10, 2022. In 5G NR Release 17, 3GPP introduced a new tier of reduced capability (RedCap) devices, also known as NR-Light. It is a new device platform that bridges the capability and complexity gap between the extremes in 5G today with an optimized design for mid-tier use cases. When compared to 5G enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) devices that can support gigabits per second of throughput in the downlink and uplink, NR-Light devices can efficiently support 150 Mbps and 50 Mbps in the downlink and uplink, respectively, due to the designed optimizations:
- narrower bandwidths, i.e., 20 MHz in sub-7 GHz or 100 MHz in millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency bands,
- a single transmit antenna,
- a single receive antenna, with 2 antennas being optional,
- optional support for half-duplex FDD,
- lower-order modulation, with 256-QAM being optional, and
- support for lower transmit power
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In a briefing provided in advance to journalists, Gautam Sheoran, Qualcomm’s vice president of product management, defined the X35’s target market as “entry-level devices that may not necessarily need multi-gigabit speeds.” The X35 doesn’t support millimeter wave (mmWave) connections, even though Qualcomm continues to praise mmWave. But the X35 can support theoretical peak download speeds of 220 Mbit/s, with best-case uploads of 100 Mbit/s. “We should look at it as bringing all of the benefits of 5G at a much smaller data rate,” Sheoran said.
“The chipset is not only NR-Light, it also supports 4G fallback,” Sheoran added. “It’s really a future proof product that will last a number of years.” Sheoran emphasized that IoT gear built on its new systems was not that far off. “We expect devices to come out in the market around the first half of next year,” he said. “Sampling is actually happening as we speak.”
Snapdragon X35 offers a device platform that bridges the complexity and capability gap between the extremes in 5G today and addresses the need for mid-tier use cases. This lower cost option provides device makers with a long-term migration path to replace LTE CAT4+ devices, ultimately increasing 5G adoption and allowing for faster transition to a unified 5G network. In addition to Snapdragon X35, Qualcomm Technologies also announced Snapdragon® X32 5G Modem-RF System, a modem-to-antenna solution built to lower complexity and fuel cost-efficient NR-Light devices.
“Snapdragon X35 brings together key 5G breakthroughs expected from the world’s leading wireless innovator,” said Durga Malladi, senior vice president and general manager, cellular modems and infrastructure, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. “The world’s first 5G NR-Light modem features a cost-effective, streamlined design with leading power efficiency, optimized thermal, and reduced footprint. Snapdragon X35 is poised to power the next wave of connected intelligent edge devices and empower a wide spectrum of uses. We look forward to working with industry leaders to unleash what’s possible with a unified 5G platform.”

World’s first 5G NR-Light modem-RF with a new streamlined architecture:
Snapdragon X35, a 3GPP Release 17 RedCap modem with optimized RFIC and PMIC modules, offers OEMs new 5G capabilities to create next-generation devices for a new era of use cases. The flexible, streamlined architecture and high-level modem-RF integration deliver superior power and thermal efficiency while enabling a small form factor design tailored to fit in compact devices.
Expansion of 5G ecosystem to new wave of use cases:
Snapdragon X35 brings a unique mix of capabilities in data rates, power consumption, complexity, and reduced footprint needed to cost-effectively enable new use cases such as entry-level industrial IoT devices, mass tier fixed wireless access consumer premise equipment, mass tier connected PCs, and first generation 5G consumer IoT devices like direct-to-cloud glasses and premium wearables.
With support for both LTE and 5G NR-Light, Snapdragon X35 is backwards compatible and future-proof enabling OEMs to develop devices which coexist with a wide range of 4G and 5G device classes helping scale 5G NR-Light services.
Breakthrough performance with advanced Modem-RF feature set:
Snapdragon X35 is equipped with advanced modem-RF technologies aimed to significantly reduce power consumption, enhance 5G coverage, lower latency, increase battery life, and improve uplink speeds:
– Qualcomm® QET5100 Envelope Tracking
– Qualcomm® Smart Transmit™ Technology
– Qualcomm® 5G Ultra-Low Latency Suite
– Qualcomm® 5G PowerSave Gen 4
In addition, Snapdragon X35 supports dual-frequency GNSS (L1+L5) to offer precise positioning suited to enable new industrial use cases and applications. With its global RF-band support, Snapdragon X35 supports all spectrum bands within Sub-6GHz, FDD, and TDD, to satisfy the needs of various markets.
These innovations and other improvements in Snapdragon X35 are designed to power a new generation of use cases and applications. Qualcomm suggested the company’s new chipset could be used in such gadgets as fixed-wireless consumer premise equipment as well as mobile hotspots, smartwatches and other upmarket wearables, connected cameras, industrial sensors, and augmented-reality glasses running what Sheoran called “glass-to-cloud” apps.
Customer sampling of Snapdragon X35 and X32 are expected to begin in the first half of 2023 and commercial mobile devices are expected to be launched by the first half of 2024. For additional details, please visit the Snapdragon X35 webpage.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/iot/qualcomm-starts-connecting-dots-on-5g-nr-light-/d/d-id/783124?
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-17
https://portal.3gpp.org/Home.aspx?tbid=373&SubTB=373#/55934-releases
Juniper Research: 5G to Account for 80% of Operator Revenue by 2027; 6G Requires Innovative Technologies
5G to Account for 80% of Operator Revenue by 2027:
Juniper Research has forecast that communications operators are likely to generate $625B from 5G services globally by 2027, a substantial rise from the $310bn predicted for the end of 2023. The new report, Operator revenue strategies: Business models, emerging technologies & market forecasts 2023-2027, forecasts that 80% of global operator-billed service revenue will be attributable to 5G by 2027; allowing operators to secure a return on investment into their 5G networks. However, the increasing implementation of eSIMs into new devices will drive global cellular data traffic to grow by over 180% between 2023 and 2027, as data traffic is offloaded from fixed and Wi-Fi networks to 5G.
Juniper Research noted that the increasing implementation of embedded subscriber identity modules (eSIMs) into new devices would drive global cellular data traffic to grow by over 180% between 2023 and 2027, as data traffic is offloaded from fixed and Wi-Fi networks to 5G. Previous Juniper studies have observed that after spending more than a decade offering a potential breakthrough in mobile communications, embedded eSIM technology has enjoyed noticeable growth in the past 12 months, making its way from smartphones to smart devices. The report also calculated that, driven by Apple’s innovation disrupting the smartphone sector, the value of the global eSIM market was expected increase from $4.7bn in 2023 to $16.3bn by 2027.
Juniper Research author Frederick Savage commented: “eSIM-capable devices will drive significant growth in cellular data, as consumers leverage cellular networks for use cases that have historically used fixed networks. Operators must ensure that networks, including 5G and upcoming 6G networks, are future‑proofed by implementing new technologies across the entirety of networks.”
6G Development Necessitates Innovative Technologies:
To prepare for this increasing demand in cellular data, the report predicts that 6G standards must adopt innovative technologies that are not currently used in 5G standards. It identified NTNs (Non‑terrestrial Networks) and sub-1THz frequency bands as key technologies that must be at the center of initial trials and tests of 6G networks, to provide increased data capabilities over existing 5G networks.
However, the research cautions that the increased cost generated by the use of satellites for NTNs and the acquisition costs of high-frequency spectrum will create longer timelines for securing return on 6G investment for operators. As a result, it urges the telecommunications industry to form partnerships with specialists in non-terrestrial connectivity; thus benefitting from lower investment costs into 6G networks.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.juniperresearch.com/pressreleases/operator-5g-revenue-to-reach-$625bn-by-2027
Juniper Research: CPaaS Gobal Market to Reach $29 Billion by 2025
Juniper Research: 5G connectivity opportunity for the connected car market
Juniper Research: 5G Fixed Wireless Access to Generate $2.5 Billion in Operator Revenue by 2023
ITU-R report in progress: Capabilities of the terrestrial component of IMT-2020 (5G) for multimedia communications
Introduction:
ITU-R WP5D is working on a preliminary draft of a report that addresses the capabilities of IMT-2020 to distribute multimedia content such as video, audio, text and graphics, including support for real-time multimedia interactive applications. The new report also addresses the capabilities of IMT-2020 user devices and base stations to support such multimedia communications with low latency and wider transmission bandwidth. It complements Report ITU-R M.2373 on “Audio-visual capabilities and applications supported by terrestrial IMT systems,” which addresses the capabilities of IMT systems for delivering audio-visual services to the consumers and also covers some aspects of production of audio-visual content.
Multimedia applications include network video, digital magazine, digital newspaper, digital radio, social media, mobile TV, digital TV, touch media, etc., that are enabled by IMT-2020 technologies. Beyond the traditional media service, the new media application not only supports accurate delivery of content, but also supports real-time interaction and real-time uploading of user-generated content. The users can be both consumers and producers of new media content.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Note:
Ultra low latency is needed to support almost any type of multimedia applications. In particular, the URLLC performance requirements must meet those specified in ITU-R M.2410 –Key requirements related to the minimum technical performance of IMT-2020 candidate radio interface technologies. The current version of IMT 2020 (ITU-R M.2150) doesn’t meet the M.2410 ultra low latency requirement of <1ms in the data plane and <10msec in the control plane. Until 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN spec is completed and performance tested, we don’t expect any serious use of 5G for multimedia applications.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Applications for multimedia content include but are not limited to:
– audio-visual applications,
– network video applications,
– digital online magazine applications,
– digital online newspaper applications,
– internet radio applications,
– social media applications,
– mobile internet TV applications,
– touch media applications,
– online information distribution applications,
– on-demand video applications
– imaging and audio distribution applications
– content dissemination applications
– file delivery application
_ Real time uploading of multimedia content
_ Electronic classroom presentation technology
_ Full motion video conferencing
This report covers the application of IMT technology to the specific applications mentioned above. For details of applications of the Broadcasting service for multimedia, please refer to the list of ITU‑R Recommendations and ITU-R Reports below.
Relevant ITU-R Recommendations and Reports:
- Recommendation ITU-R BT.1833 – Broadcasting of multimedia and data applications for mobile reception by handheld receivers
- Recommendation ITU-R BT.2016 – Error-correction, data framing, modulation and emission methods for terrestrial multimedia broadcasting for mobile reception using handheld receivers in VHF/UHF bands
- Recommendation ITU-R M.2083 – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond
- Recommendation ITU-R M.2150 – Detailed specifications of the terrestrial radio interfaces of International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020)
- Report ITU-R BT.2049 – Broadcasting of multimedia and data applications for mobile reception
- Report ITU-R BT.2295 – Digital terrestrial broadcasting systems
- Report ITU-R M.2373 – Audio-visual capabilities and applications supported by terrestrial IMT systems
Multimedia Use cases:
- Ultra-high-definition multimedia content
- Virtual reality (VR) panoramic video
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Entertainment live streaming
- Live eCommerce (use of live webcast technology to carry out new sales methods)
- Smart venue (new viewing experiences at live events or activities)
- Live streaming production and distribution of events
IMT-2020 capabilities for real-time multimedia interaction and media content uploading:
Interactive multimedia allows the user to control, combine and manipulate a variety of media types, such as text, computer graphics audio and video materials, animation and virtual reality.
To enable interactive task completion during voice conversation, IMT-2020 is capable of supporting low-delay speech coding for interactive conversational services (refer 3GPP TS22.261, 100 ms, one-way mouth-to-ear).
Table 1. below (from 3GPP TS 22.261 Table 7.1-1.) gives a capability example of IMT-2020 to support high data rate and traffic density scenario for an interactive audio and video application in indoor hotspot.
Table 1. High data rate and traffic density scenario of IMT-2020 for an interactive audio and video application
| Scenario | Experienced data rate (DL) | Experienced data rate (UL) | Area traffic capacity (DL) | Area traffic capacity (UL) | Overall user density | Activity factor | UE speed | Coverage |
| Indoor hotspot | 1 Gbit/s | 500 Mbit/s | 15 Tbit/s/km2 | 2 Tbit/s/km2 | 250 000/km2 | Note 2 | Pedestrians | Office and residential (Note 1) |
| NOTE 1: A certain traffic mix is assumed; only some users use services that require the highest data rates. | ||||||||
Conclusions:
This report (in progress) summarizes various capabilities of terrestrial component of IMT-2020 for Multimedia communications. Multimedia is an immersive technological way of presenting information that combines audio, video, images, and animations with textual data. Multimedia applications include network video, digital magazine, digital newspaper, digital radio, social media, touch media, etc., and can be easily enabled using IMT-2020. New emerging technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are becoming key technologies to upgrade the traditional multimedia industries.
The IMT-2020 capabilities can support the evolving interactive multimedia communication with the capabilities not only broader bandwidth, higher data rate, but also lower latency and higher reliability.
The typical technologies are flexible and dynamic resources allocation, uplink enhancement e.g. UL MIMO, UL Carrier Aggregation and Dual connectivity, and related architecture improvement, which can connect the user to a high-definition video, real-time multimedia interaction virtual world on their mobile device.
Live events with high definition and ultra-high definition content can be streamed via IMT-2020 radio network with higher throughput. HD and UHD content (e.g. news, sport event) can be real-time produced and on demand distributed to mobile devices without any interruptions through IMT-2020 higher user experienced data rate and low latency. The entertainment industry will hugely benefit from IMT-2020 wireless networks, which are expected to enable HD virtual reality games with a better real-time interactive gaming experience, and high dynamic range video streaming without interruption. Cloud AR and Cloud VR with HD or UHD video can be supported with higher user experienced data rate and low latency supported by IMT-2020. It is foreseeable that with the support of IMT-2020 technology, it will gradually bring consumers more amazing virtual experiences.
References:
Evaluating Multimedia Protocols on 5G Edge for Mobile Augmented Reality
https://www.routledge.com/5G-Multimedia-Communication-Technology-Multiservices-and-Deployment/Bojkovic-Milovanovic-Fowdur/p/book/9780367561154
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20220413/5g/what-is-the-5g-multimedia-priority-service-mps
IMT 2020.SPECS approved by ITU-R but may not meet 5G performance requirements; no 5G frequencies (revision of M.1036); 5G non-radio aspects not included
Ericsson Mobility Report: 5G monetization depends on network performance
A special Ericsson Mobility Report – called the Business Review edition – addresses monetization opportunities as they relate to 5G. Flattening revenues have been a challenge for service providers in all parts of the world, often impacting network investment decisions as part of their business growth strategies, known as ‘monetization’ in the industry.
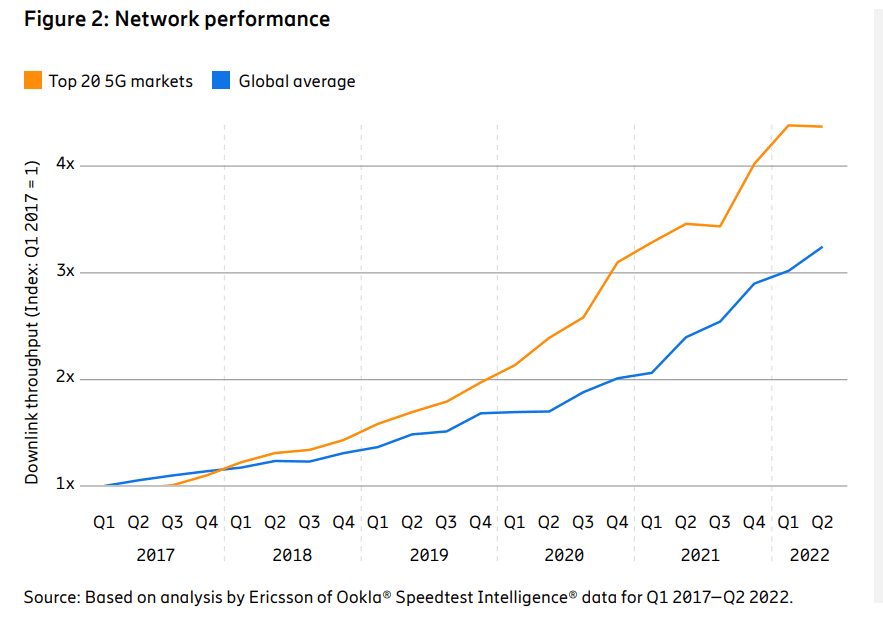
The report highlights a positive revenue growth trend since the beginning of 2020 in the top 20* 5G markets – accounting for about 85 percent of all 5G subscriptions globally – that correlates with increasing 5G subscription penetration in these markets.
The report finds:
- Tiered pricing models are key for service providers, both for effectively addressing the individual needs of each customer and for continuing to drive long-term revenue growth.
- The top 20 5G markets have seen a significant network performance boost following the introduction of 5G services.
- After a period of slow or no growth, wireless service revenue curves are again pointing upwards in these leading markets. This correlate with 5G subscription penetration growth.
- In the top 20 5G markets, the average downlink throughput has increased by 4.3 times over the past 5 years. This is 32 percent more than other markets on a global level, showing the positive impact 5G has had on network performance and user experience. The most significant network performance improvement in the top 20 5G markets was in 2020, following the introduction of 5G NSA network services.
- In the top 20 5G markets, the median downlink throughput of 5G is 5.8 times higher than the throughput of 4G (187 Mbps vs. 32 Mbps) in Q3 2022. This performance boost is what service providers could offer to consumers as an immediate benefit of upgrading to 5G.
Fredrik Jejdling, Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, Ericsson, says: “Meeting our customers’ challenges is at the heart of our R&D efforts and every resulting product we develop. The link between 5G uptake and revenue growth in the top 20 5G markets underlines that not only is 5G a game changer, but that early adopters benefit. What is particularly encouraging about this is that while 5G is still at a relatively early phase, it is growing fast with proven early use cases and a clear path to medium and long-term use cases.”
As expected, Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) is the main early use case for 5G, driven by increasing geographical coverage and differentiated offerings. More than one billion 5G subscriptions are currently active across some 230 live commercial networks globally. 5G eMBB offers the fastest revenue opportunities for 5G, as it is an extension of service providers’ existing business, relying on the same business models and processes. Even in the top 20 5G markets, about 80 percent of consumers have yet to move to 5G subscriptions – one pointer to the potential for revenue growth.
As highlighted in the November 2022 Ericsson Mobility Report, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) is the second biggest early 5G use case, particularly in regions with unserved or underserved broadband markets. FWA offers attractive revenue growth potential for CSPs as it largely utilizes mobile broadband assets. FWA connections are forecast to top 300 million within six years.
Beyond consumer subscribers, there are growing opportunities in enterprise and public sector applications across the world. Ericsson sas that 5G enables significant value for enterprises, with private 5G networks and wireless wide area networks being deployed for enterprise and industrial use.
Upgrading existing 4G sites to 5G has the potential to realize increases of 10 times in capacity and reduce energy consumption by more than 30 percent, offering the possibility of growing revenue and lowering costs, while addressing sustainability.
Jejdling adds: “Revenue growth and sustainability are recurring themes in my discussions with customers. In this special Ericsson Mobility Report edition, we have explored how service providers are tapping 5G opportunities. We see initial signs of revenue growth in advanced 5G markets with extensive coverage build-out and differentiated service offerings. An equally crucial aspect of 5G is that it brings cost advantages and helps service providers handle the data growth needed to drive future revenue. This can make 5G the growth catalyst that the market has been waiting for.”
Read the full Ericsson Mobility Report Business Review Edition report here.
*Note: The markets categorized as the Top 20 5G markets in the report are: Australia, Bahrain, China, Denmark, Finland, Hong Kong, Ireland, Japan, Kuwait, Monaco, Norway, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan, the UAE, the UK and the US.
They were selected on the basis of 5G subscription penetration. These markets represent 85 percent of all 5G subscriptions globally – with each market having 5G penetration above 15 percent.
Related links:
Ericsson Mobility Report site
Ericsson 5G
Ericsson 4G and 5G Fixed Wireless Access
Breaking the energy curve
5G the next wave – what does consumers want
Nokia introduces new Wavence microwave solutions to extend 5G reach in both urban and rural environments
Nokia today announced the availability of the UBT-m XP, the latest addition to its Wavence product family designed to support mobile operators and enterprises with premium coverage in both dense urban and rural environments. Nokia’s newest E-Band radio is a high-capacity outdoor unit with a small, light form factor and the highest transmit power available on the market; ideal for urban microwave transport applications.
Nokia SteadEband, a stabilized three-foot antenna that combats common E-Band issues [1.], was also announced to complement UBT-m XP. It includes tower vibrations and movements due to thermal effects. Combined with the UBT-m XP, it can increase the typical E-Band link distance by up to 50 percent, helping mobile operators deliver multi-gigabit 5G connectivity to their customers. These new products address all use cases for improving link distance as well as the energy efficiency of the Wavence portfolio.
Note 1. The E-Band is 71-76 and 81-86 GHz, standardized worldwide, commonly referred to as “80 GHz,” but it’s always that range, said Nokia Microwave Radio Links VP Giuseppe Targia, noting that the E-Band is suitable for both urban and suburban environments.
Urban Coverage Boost:
The UBT-m XP is a single ultra-broadband transceiver with an integrated modem and diplexer, offering best-in-class energy efficiency with twice the transmit power compared to the industry average. In recent tests, Nokia demonstrated a 12-kilometer-long link using the Nokia UBT-m XP and the SteadEband antenna.
Rural Broadband Extension:
Nokia also announced the launch of the Outdoor Channel Aggregator (OCA) to support mobile operators looking to expand the reach and capacity of their networks for rural broadband applications. The OCA aggregates multiple UBT-T XP radios, Nokia’s high-capacity, high-power, outdoor dual-band radio, for N+0 operations and allows for increased throughput with improved system gain of up to 10 dB compared with traditional aggregation methods. This is important in increasing the link distance or to optimize OPEX/CAPEX by removing the requirement for larger antenna or repeater systems.
Nokia is also introducing the Carrier Aggregation High Density (CAHD) card, which adds ‘single pipe’ capacity to the backhaul to support the link distance. The innovative CAHD module enables 10 Gbps backhaul capacity over multiple channels and supports seamless migration from existing low-capacity backhaul to high capacity hence preserving an operator’s investment.
Nokia’s ‘Simplified RAN Transport’ solution optimizes radio access base station and microwave radio transport hardware to the minimum. This provides enhanced serviceability and operations without the need for dedicated indoor microwave equipment. Nokia’s solution saves 30 percent more energy versus a traditional microwave site solution, due to a reduced number of units and less air conditioning requirements. Additionally, it also enables lower TCO and reduced site footprint.
Nokia’s comprehensive Wavence portfolio provides a complete microwave solution for all use cases covering short-haul, long-haul, E-Band, and SDN-based management both for mobile operators and Enterprises. Its zero-footprint implementation for full-outdoor architectures can be integrated directly with RAN and IP devices with common management. This contributes to an overall reduction in network energy consumption and its software features and automation help to achieve further energy-saving targets.
“It’s no secret that capacity and radio efficiency are driving the market, said Emmy Johnson, Chief Analyst, Sky Light Research. “According to Sky Light Research’s latest forecast, the high-capacity E-band market is expected to grow north of 60 percent in 2023. Nokia’s newest products answer this call but with the added benefit of high power and energy efficiency. The sustainability and power metrics are impressive, as they not only lower TCO but also help meet climate change guidelines.”
Giuseppe Targia, Vice President, Microwave Radio Links at Nokia, said: “We are further strengthening our industry-leading Wavence portfolio with the addition of these next-generation products. The winning combination of the UBX-m XP and the SteadEband offers our customers a high-performance transport solution with leading capacity and coverage for both urban and rural environments. Microwave links are cost-efficient and fast to deploy, representing a robust alternative to fiber backhaul.”

Nokia’s Wavence UBT-mX
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Wavence – Microwave transmission
https://www.nokia.com/networks/mobile-networks/wavence-microwave-transmission/e-band-portfolio/



?$QC_Responsive$&fmt=png-alpha&wid=640)