Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
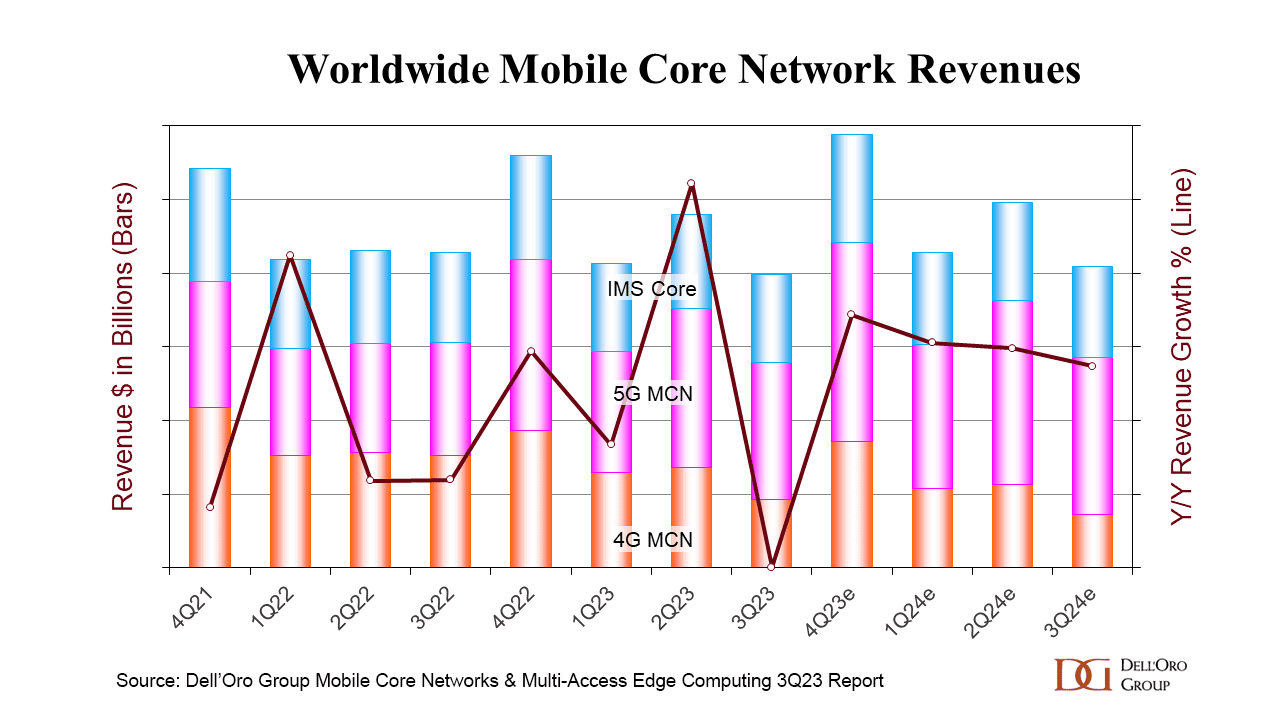
The global mobile core network (MCN) market has just turned in its lowest quarterly growth rate for almost six years, hit by a difficult political and economic climate, as well as by slow rollouts of 5G standalone core networks. Dell’Oro Group reports that the MCN market has become erratic, with the lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017. Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA), and China were the weakest performing regions in 3rdQ 2023.
“It has become quite obvious the MCN market has entered into a very unpredictable phase after breaking the highest growth rate in 2ndQ 2023 since 1stQ 2021, and now hitting the lowest performing growth rate in 3rdQ 2023 since 4thQ 2017. Last quarter, EMEA and China were the strongest performing regions and flipped this quarter, becoming the weakest performing regions,” stated Dave Bolan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group.
“Many vendors state that the market is volatile, attributing this phenomenon to macroeconomic conditions such as the fear of higher inflation rates, unfavorable currency foreign exchange rates, and the geopolitical climate.
“Besides subscriber growth, the growth engine for the MCN market is the transition to 5G Standalone (5G SA), which employs the 5G Core. But after five years into the 5G era, we are still seeing more 5G Non-Standalone (5G NSA) networks being launched than 5G SA, and the pace of 5G SA networks has slowed from 17 launched in 2022 to only seven so far in 2023. However, we expect more 5G SA networks to be deployed in 2024 than in 2023, and we expect 2024’s market performance to be better than 2023,” continued Bolan.
Additional highlights from the 3Q 2023 Mobile Core Network and Multi-Access Edge Computing Report include:
- Two new MNOs launched commercial 5G SA networks in 3Q23: Telefónica O2 in Germany and Etisalat in the UAE.
- Ericsson is the vendor of record for the 5G packet core for all seven 5G SA networks launched in 2023.
- As of 3Q 2023, 45 MNOs have commercially deployed 5G SA eMBB networks.
- The top MCN vendors worldwide for 3Q 2023 [1.] were: Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and ZTE.
- The top 5G MCN vendors worldwide for 3Q 2023 were Huawei, Ericsson, ZTE, and Nokia.
Note 1. Dell’Oro did not supply any actual MCN market share percentages or numbers.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In August the Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) released Q2 figures that showed just 36 operators worldwide has launched public 5G SA networks, including two soft launches, by the end of June, an increase of just one on the previous quarter.
In total, the GSA said that 115 operators in 52 countries had invested in public 5G SA networks – that includes actual deployments as well as planned rollouts and trials – by the end of Q2, with no new names added during the quarter, and an increase of just three on the end of 2022.
About the Report:
The Dell’Oro Group Mobile Core Network & Multi-Access Edge Computing Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, shipments, and average selling prices for Evolved Packet Core, 5G Packet Core, Policy, Subscriber Data Management, and IMS Core including licenses by Non-NFV and NFV, and by geographic regions. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
About Dell’Oro Group:
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, and data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit https://www.delloro.com.
References:
Dell’Oro: RAN market declines at very fast pace while
Mobile Core Network returns to growth in Q2-2023
Dell’Oro: RAN Market to Decline 1% CAGR; Mobile Core Network growth reduced to 1% CAGR
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network & MEC revenues to be > $50 billion by 2027
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
Dell’Oro: Market Forecasts Decreased fo
r Mobile Core Network and Private Wireless RANs
One thought on “Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017”
Comments are closed.



5G Core deployments have been slow, few and far between because:
1] There is no 3GPP spec or ITU-T standard for IMPLEMENTATION of 5G SA core network- only 3GPP 5G Network Architecture (Specification # 23.501) spec. Reference: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3144
That has given rise to uncertainty and trepidation which resulted in many different 5G Core implementations-each requiring its own unique 5G Core download for 5G endpoint devices to realize 5G functions.
2] 5G Core network is more complex than the 4G-EPC core network (used in 5G NSA networks)) since it integrates new network functions (NFs). The integration and interoperability of these NFs becomes more complex, especially in the case of multi-vendor networks as there are NO STANDARDIZED interfaces.
3] Mapping the 3GPP architecture to a cloud native infrastructure.
4] All the new interfaces, protocols, network functions, signaling, subscriber databases, monitoring systems, routing technologies, etc that must be implemented.
5] Security: The 5GC network creates new challenges in securing IoT terminals and equipment for data protection. 5G Security requires 5G SA core network.
5] Network slicing: The management and maintenance of virtual networks (slices) with different levels of security and sensitivity of data and applications will represent a new challenge for operators.
6] Virtualization and software solutions: Managing virtualization and software solutions for 5GC networks requires new expertise and skills.
7] Cost: 5GC requires significant investment in new infrastructure and technology in an already competitive environment for operators.
8] Regulations: In some countries, regulations will require 5G networks to store and process data within the country or limit the ability of foreign companies to participate in 5G network deployments. These regulations may increase the cost and complexity of network operations.